W6 - Monopolistic Competition
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
how do models of monopolistic competiton differ from classical models
classical models argue trade occurs between different countries
this model predicts intra-industry trade
internal EOS
large firms have advantage over small firms
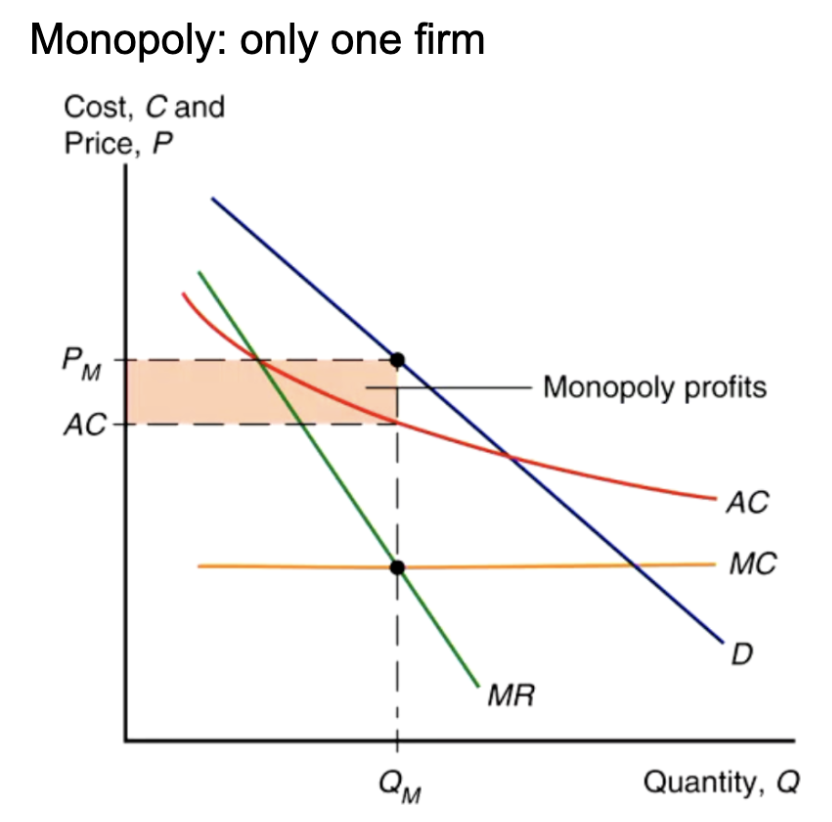
firns maximise proft where
MR = MC
formula for marginal costs
MC = change in TC / change in Q
AC FORMULA
C/Q
formula for price in monopolistic competition
P = c + 1/(b x n)
does MC increase or decrease with price or Q
it is constant
quantity produced depends on (5)
sales
number of firms
demand curve
firm price
competitor pricr
using demand curve how do firms choose P and Q combination?
Choose Q where MR > MC
Choose Price where this Q meets the demand curve
Difference between AC and price = profit
How does trade affect market size (S) and firm costs?
Trade increases S, allowing firms to produce more, lowering AC due to external EOS
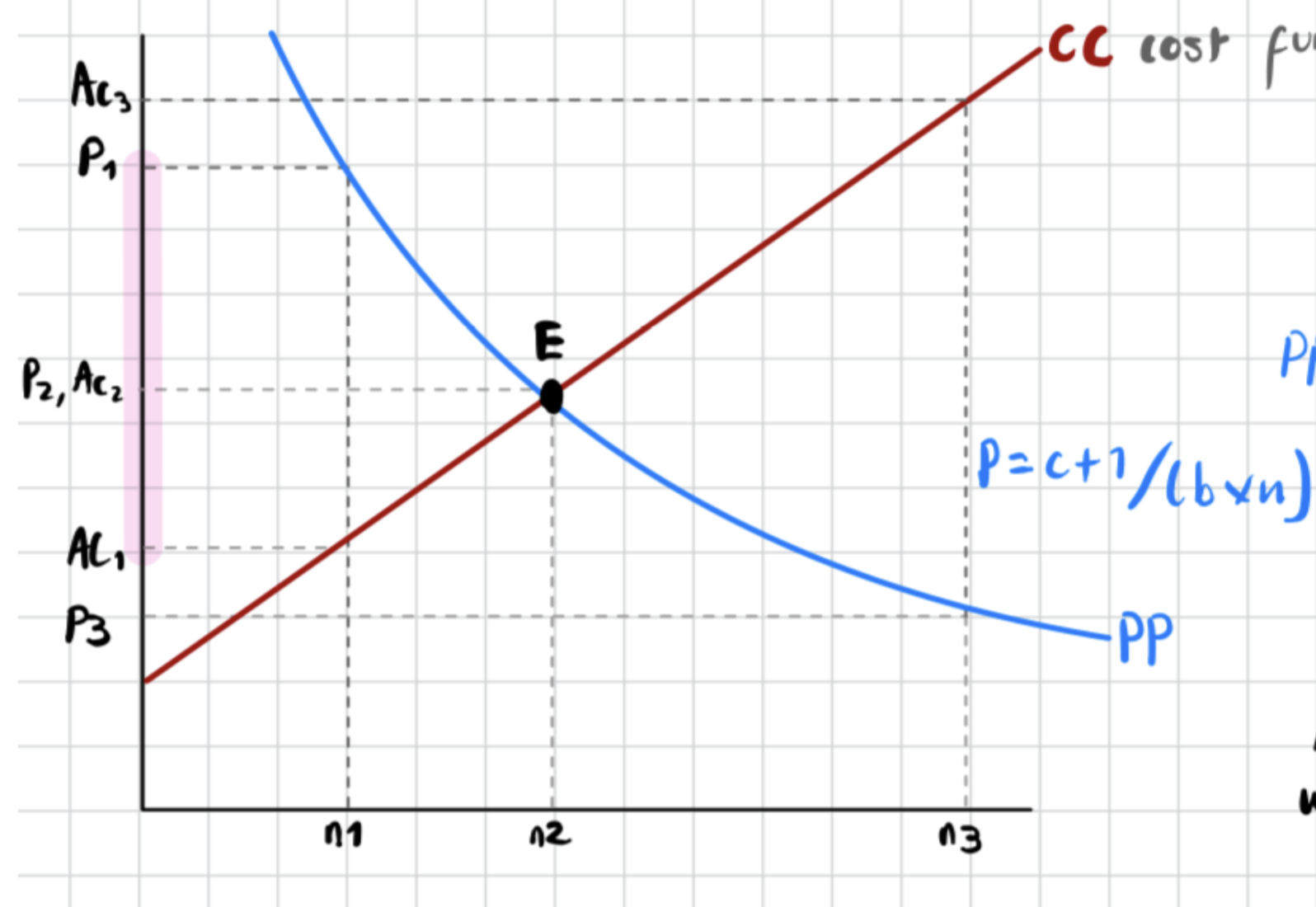
What is the “zero-profit condition” (CC curve)?
Long-run equilibrium where Price = Average Cost, so no incentive to enter or exit the market
what happens to prices when number of firms in industry increases
gap between average costs and prices shrinks
show equilibrium and zero profit condition in monopolistic markets on graph
mechanism between trade and monopolistic markets
increases market size so Prices go down due to price convergence, while no. of firms increases - customers benefit
why is trade between industries
a large share of world trade is between similar but differentiated products - economists assume consumers favour variety - depends on degree of substitution
can benefit from internal EOS