Lecture 5: Block 2- Glutamate + Article
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Glutamate is an
excitatory amino acid transporter
Two sources of glutamate synthesis
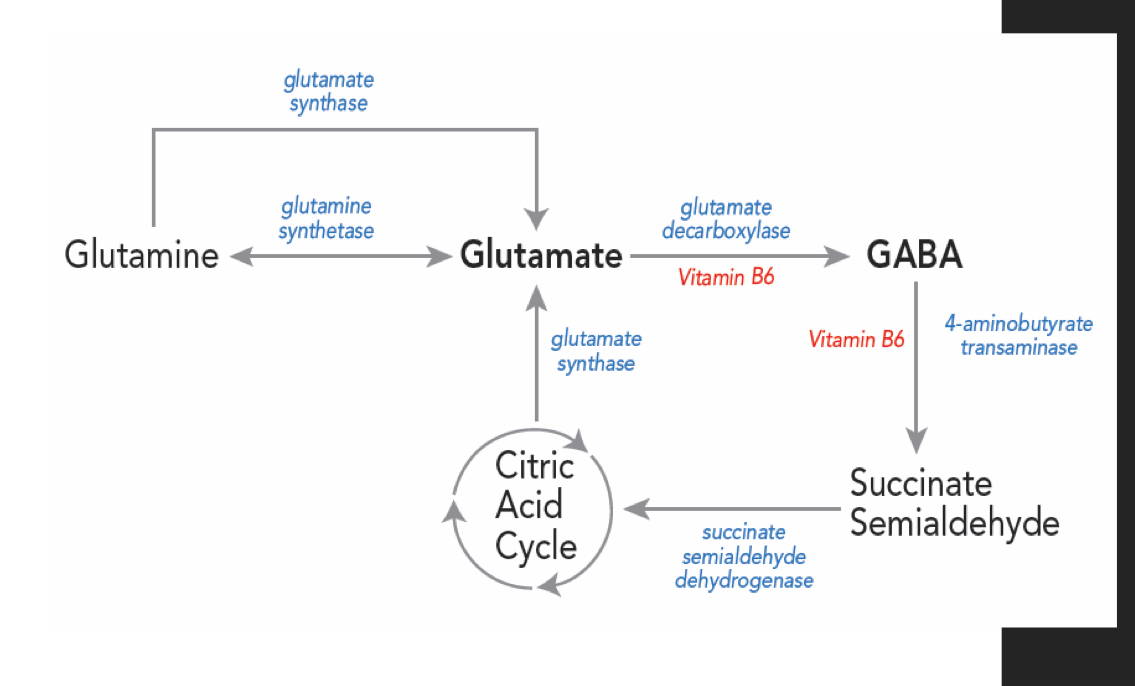
1- Glucose via the Krebs cycle: alpha- Ketoglutarate is converted to glutamate via transaminase.
2- Glutamine: converted to glutamate by glutaminase
Krebs Cycle
Glucose enters glycolysis and becomes pyruvate.
Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA → enters the Krebs cycle.
One of the intermediates, α-ketoglutarate, is converted into glutamate by transaminase enzymes.
Glutamate Receptors
Neurotransmitter:
Agonists:
Receptors:
Glutamate
AMPA, NMDA, Kainate
AMPA Receptor, NMDA Receptor, Kainate Receptor
AMPA
Permeable to both Na+ and K+
Not permeable to Ca2+
Depolarizes 1st
NMDA
Permeable to both NA+ and K+
Permeable to Ca2+
Voltage dependent: Inward ionic current needed. When GLU binds → pore opens but.. Mg2+ prevented ions from passing freely (Magnesium block) Mg2+ pops out only when neuron is depolarized.
NMDA GLU Receptors: Ligand gated needs ____
Glutamate
NMDA GLU Receptors: Voltage Gated membrane must ..
be depolarized
NMDA Sub Units
NR1 (Glycine binds) NR2A, NR2B, NR2C, NR2D (GLU binds to NR2), NR3A, NR3B.
NMDA Receptor location
high conc. in the cortex (cortext plays large role in relapse), hippocampus, basal ganglia, hypothalamus
Important for:
LTP and Excitotoxicity
NMDA Receptors→ _____ has to be present for binding
Glycine (Obligatory co-agonist)
NMDA : Need at least one ____ and ____ subunit.
NR1, NR2
AMPA Subunits:
GluR1-GluR4
AMPA Subunits: Need ___ ___ ___ subunit
More than one
AMPA Receptor Location
High Conc. in cortex; hippocampus; basal ganglia; cerebellum NAc and Amygdala.
AMPA Receptors: Important for
increasing NMDA receptors → LTP
KA (Kainate) Subunits:
GluR5, GluR6, GluR7, KA1, KA2
KA Subunits: Need ___ ___ ___ subunit.
More than one
KA: AMPA Receptor location:
High conc. in cortex, hippocampus; cerebellum; amygdala.
KA: Important for
LTP, Excitotoxicity
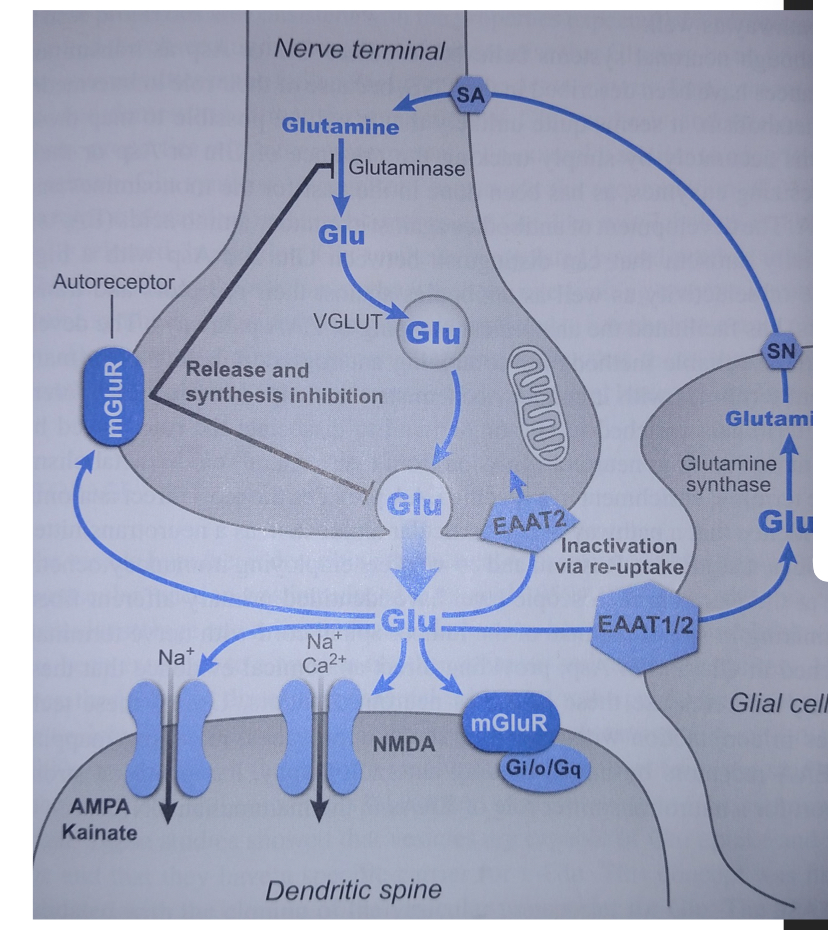
What enzyme converts glutamine into glutamate in presynaptic terminals?
Glutaminase converts glutamine into glutamate.
What vesicular transporter loads glutamate into synaptic vesicles?
Glutamate is loaded by VGLUT
What triggers glu release at the presynaptic terminal?
Depolarization opens voltage gated Ca2+ channels. Ca@+ enters the terminal and triggers Ca2+ dependent exocytosis of Glutamate filled vesicles.
Why is Mg2+ important for NMDA receptor function?
At resting membrane potential, Mg²⁺ blocks the NMDA channel, preventing ion flow.
Depolarization ejects Mg²⁺, allowing Na⁺, K⁺, and Ca²⁺ to pass.
This makes NMDA receptors coincidence detectors for synaptic plasticity.
Which ion is NMDA-specific that AMPA cannot pass, and why does it matter?
NMDA receptors allow Ca²⁺ influx, which activates intracellular signaling pathways important for synaptic plasticity and learning.
AMPA receptors do not pass Ca²⁺.
What is the difference between ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors?
Ionotropic (AMPA, NMDA) are ligand-gated ion channels producing fast excitation.
• Metabotropic (mGluRs) are GPCRs that produce slower, modulatory effects on synaptic activity.
How does ketamine affect glutamate signaling?
Ketamine is a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist.
It reduces NMDA-mediated excitation and can influence reward behaviors and drug effects.
What clinical applications involve altering glutamate co-agonists?
Glycine, an NMDA co-agonist, can be manipulated to change NMDA receptor activity.
Studies show glycine-related interventions can modify conditioned place preference for drugs such as nicotine.
How can blocking AMPA receptors affect drug reward?
Blocking AMPA receptors decreases ionotropic glutamate signaling.
This can enhance or reduce drug-induced conditioned place preference depending on the drug and experimental design.
The lecture specifically notes heroin CPP is facilitated when AMPA responses are blocked.
What happens to glutamate transporter function during drug exposure?
Some drugs lead to changes in glutamate transporter expression or function, shifting glutamate levels and potentially altering reward pathways as compensation for drug effects.
What do voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels do during glutamate neurotransmission?
Answer:
VGCCs stay closed at resting potential.
When the terminal depolarizes, they open, letting Ca²⁺ flow in and trigger neurotransmitter release.
What are the major roles of glutamate in drug-related behaviors based on the lecture examples?
Glutamate receptors contribute to reward learning.
• Modulating AMPA/NMDA signaling can change conditioned place preference for drugs like heroin, nicotine, and alcohol.
• Drugs that block or enhance glutamate transmission can either attenuate or increase drug effects.
What are the different types of glutamatergic receptors? How do they vary? Which one is associated with drug abuse?
Ionotropic- (AMPA, NMDA, Kainate)- Fast, open ion channels. AMPA: Fast Na^+ currents. NMDA: slower, needs depolarization, lets Ca²+ in.
Metabotropic- (mGluRs)- slow, uses G-proteins.
Ionotropic- Specifically NMDA is related to drug abuse because its Ca²+ entry drives the plasticity that drugs activate.
What are the NMDA and AMPA subunits? What binds to each? What is the NMDA co-agonist?
NMDA:
NR1 (Glycine binds) NR2A, NR2B, NR2C, NR2D (GLU binds to NR2), NR3A, NR3B. NMDA Co-agonist is GLYCINE
AMPA: GluR1-GluR4, - Bins to glutamate
What are the glutamate transporters? Which handles re-uptake? Where is it located?
a. Vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) - Located on synaptic vesicles, packages glutamate into vesicles.
b. Plasma membrane glutamate transporter (EAAT2)- Responsible for removing glutamate from the synapse. Performs glutamate reuptake, located on neuronal membranes and glial cells.
EAAT performs glutamate reuptake.
What is the main overall finding of the D’Souza paper?
Glutamate is essential for drug reward, and blocking glutamate transmission generally reduces drug-seeking for cocaine, nicotine, and alcohol.
How do most drugs of abuse affect glutamate?
They indirectly increase glutamate signaling in reward circuits like the VTA and nucleus accumbens.
Which drug directly acts on glutamate receptors?
Alcohol
What happens when NMDA receptors are blocked?
Reward for cocaine, nicotine, and alcohol decreases.
What is unusual about NMDA antagonists and heroin?
They can increase heroin self-administration, possibly because the reward feels weaker
What is the role of AMPA receptors in drug reward?
Blocking AMPA receptors reduces cocaine and alcohol reward.
What is the basic role of mGlu2/3 receptors?
Activating them decreases drug-seeking behavior
What clinical medications target glutamate and reduce drug reward?
Acamprosate (alcohol), memantine, and NAC (restores glutamate balance).
Which brain regions are key for glutamate’s role in reward?
The VTA and nucleus accumbens.
What is a key takeaway for treatment development?
Glutamate receptors and transporters are promising targets for addiction medications.