capillaries arteries veins
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms

anatomy of blood vessels
3 layers of BVs (tunics) → what they look like varies between BVs
In contact with CT → outside of an organ
Tunica externa
Tunica media
Tunica intima
tunica externa
Areolar connective tissue that merges it to the organ
Becomes more dense the closer you get to the tunica media
Vasa vasorum: network of small arteries located in larger arteries
tunica media
Elastin and collagen fibers
Mainly smooth muscle
Vasoconstriction: reduces diameter during contraction
Vasodilation: increases diameter during relaxation
Thin in veins, thick in arteries
tunica intima
Inner lining of the endothelium facing the lumen
Simple squamous epithelial cells → then basement membrane → then thin CT (lamina propria) → then a fenestrated layer of elastic fibers
blood vessel histology
Aorta → largest BV
Arteries → rounder because they have higher blood pressure
Veins → irregularly shaped
Largest tunic in arteries → tunica media
Largest tunic in veins → tunica external
has elastic, muscular, or arterioles
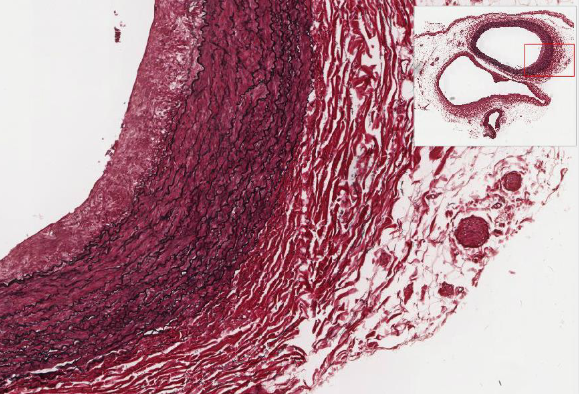
elastic arteries
largest diameters
Withstand blood pressure values between diastolic to systolic values
Internal elastic lamina provides elastic properties
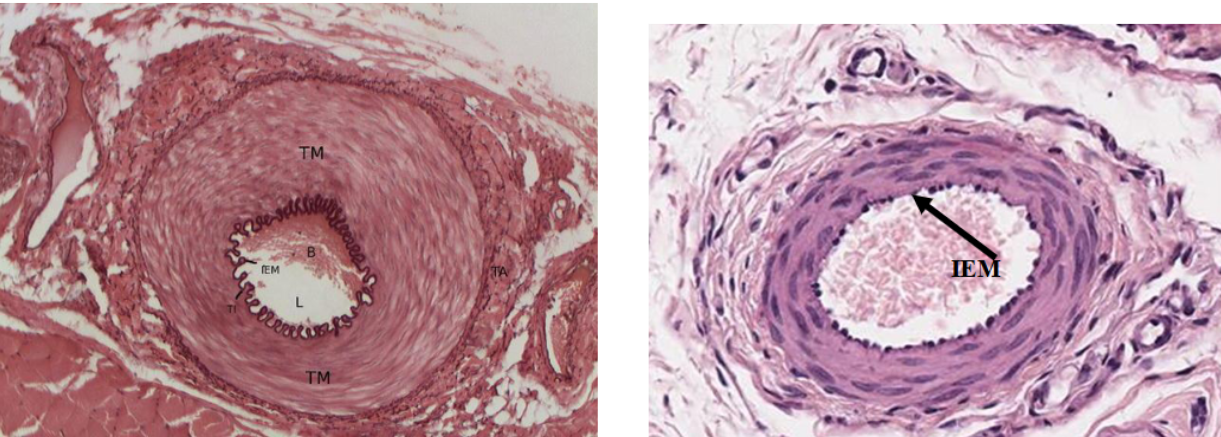
muscular arteries
more smooth muscle in the tunica media (thicker)
Distributing arteries: muscle cells can regulate blood flow to various regions of the body
Responsible for the profusion (pushing) of blood to organs
IEM = internal elastic membrane
arterioles
smallest type of artery
Nearest the capillaries
know aorta
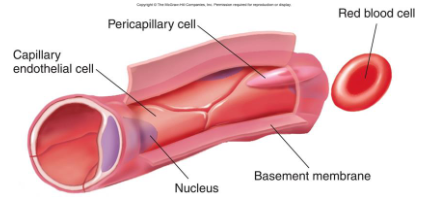
capillaries
Capillaries: vary in size
Internal lining of endothelium
Fenestrations: small openings through which substances move by diffusion
Fenestrated, continuous, or sinusoidal capillaries
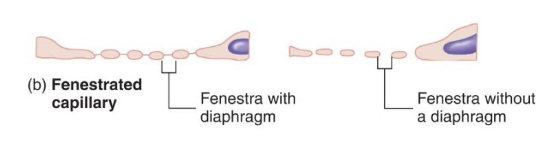
fenestrated capillaries
contain areas of small openings → allow for fluid transport between blood and interstitial fluid

continuous capillaries
no openings → continuous
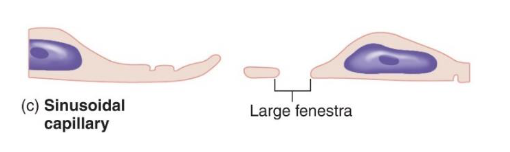
sinusoidal capillaries
have the largest windows in the endothelial lining
Allows large formed elements (proteins) to pass
Located in liver, spleen, bone marrow
distribution of blood in different parts of the circulatory system
adult males: 5-6 liters
adult females: 4-5 liters

capillary blood flow
Capillary Blood Flow
Blood flows from arterioles through the metarterioles → then through the capillary network
Thoroughfare channel: distal part of the metarterioles → connects with the venous capillaries → then to the venule draining the capillary bed
Smooth muscle sphincters: control blood flow through the true capillary capillaries → bc there is not enough blood to fill all the capillaries at a given time
Not all capillaries have blood in them
Can close off a capillary → control where blood will flow through the capillary bed
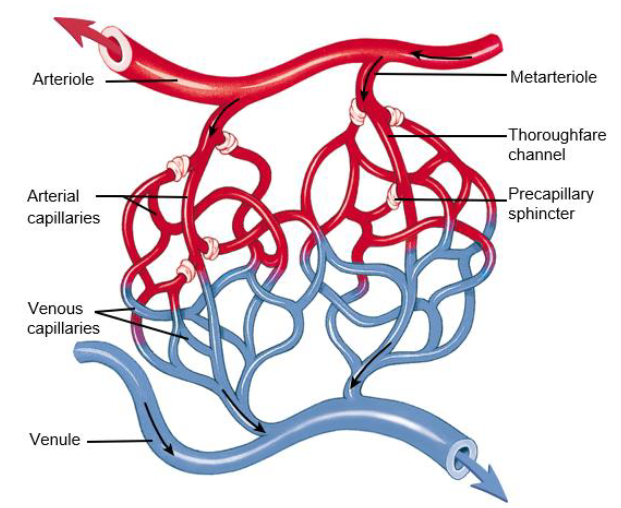
capillary blood flow
laminar, turbulent, and perfusion
laminar flow
velocity of blood flow in the center of the BV is greater than that towards the outer edges
turbulent flow
blood travels so fast and becomes disordered when it passes by an obstruction in a vessel/rough surface
perfusion
volume of blood flowing through arteries, veins, and capillary
increasing elasticity has a large effect on perfusion
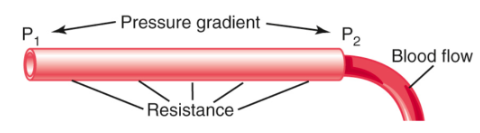
blood flow equation
P = F/A mmHg → Ohm’s Law
Increase the diameter (the area in which it is distributed): decrease pressure
Inversely proportional
Increase the numerator (the force of blood): increases pressure
Directly proportional
Blood flow (F) = (P1 - P2)/R
Determined by:
Pressure gradient: the pressure difference of blood between the two ends of the vessel
Vascular resistance: the impediment of blood flow through the vessel
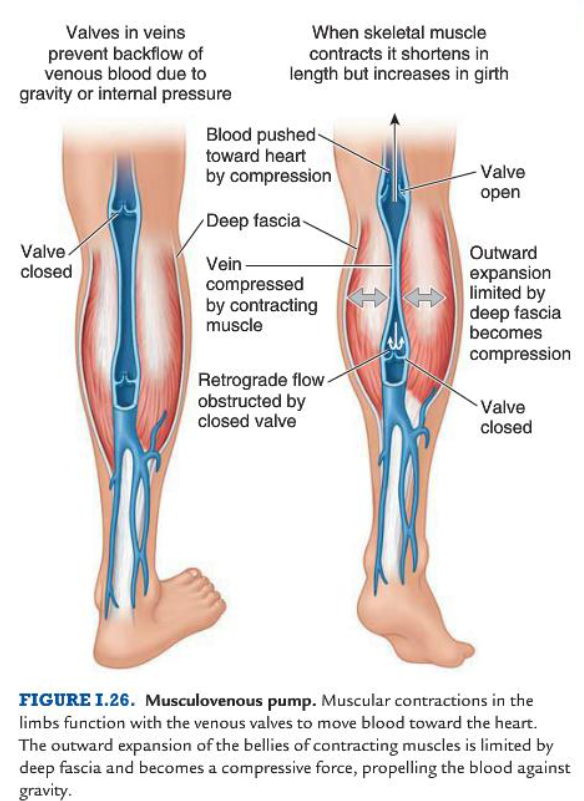
venous return
Musculovenous pump: where muscular contractions become a compressive force propelling venous blood against gravity
Any retrograde flow from this action is obstructed by closing valves