Economics - Microeconomics
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is Economics?
study of how humans use limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
study of the production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services
Economics: Key Concepts
Scarcity
Choice
Efficiency
Equity
Economic Well-Being
Sustainability
Change
Interdependence
Factors of Production (FoPs)
Land: anything taken from the planet, grown or mined
Labor: workers
Capital: physical or financial resources used to produce value in an economy, any man-made tool, tangible and intangible
Entrepreneurship: people who invest time and effort and take on financial risks in the hope of profit
Ex: Disneyland Parks
Land: oil, cleared land, metal, food resources
Labor: cast, technicians, board members, ride conductors, security
Capital: electricity, employee training programmes
Entrepreneurship: expanding parks, production managers, advertisers, designers
Demand: Definition
the quantity of a product a consumer is willing and able to purchase at various prices
Law of Demand
when the price of a product increases, the quantity demanded decreases and vice versa, ceteris paribus
The Income Effect
change in consumer purchasing power from a change in price
when price increases, purchasing power decreases
The Substitution Effect
consumers will substitute goods/services that become relatively more expensive
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
utility gained from the next unit is lower the utility gained from the previous unit
Ceteris paribus
all other factors held constant
Determinants of Demand
number of buyers
taste and preference
income (normal goods and inferior goods)
price of related goods (substitute goods or complementary goods)
Normal Goods
as income increases, the demand for a product increases
Inferior Goods
as income increases, the demand for a product decreases
Substitute Goods
two alternative goods that could be used for the same purpose
Ex: Coca-Cola vs Pepsi
Complementary Goods
goods that are purchased separately but are used together
Economic Assumptions
Ceteris Paribus: “all things being equal” to isolate the impact of one variable
Rational Consumers: assume that consumers make decisions based on logic and reason, aiming to maximize utility given available information
Utility Maximization: assumed to make choices that will give them the highest level of satisfaction or happiness
Perfect Knowledge: assume all consumers and producers have perfect knowledge
Dependence on Primary Sector: Impact
dependence on primary sector:
diversification of goods is limited, less focus on secondary and tertiary sector, which helps economic development more
labor force not proportional to GDP contribution
primary sector = low elasticity of demand
risk of droughts, agricultural input and output may be unequal → seasonal unemployment
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): Equation
(% change in Quantity Demanded) / (% change in Price)
%∆Qd / %∆P
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES): Equation
(% change in Quantity Supplied) / (% change in Price)
%∆QS / %∆P
PED & PES: Indicators
PED or PES > 1 [Elastic]
PED or PES = 1 [Unit Elastic]
PED or PES < 1 [Inelastic]
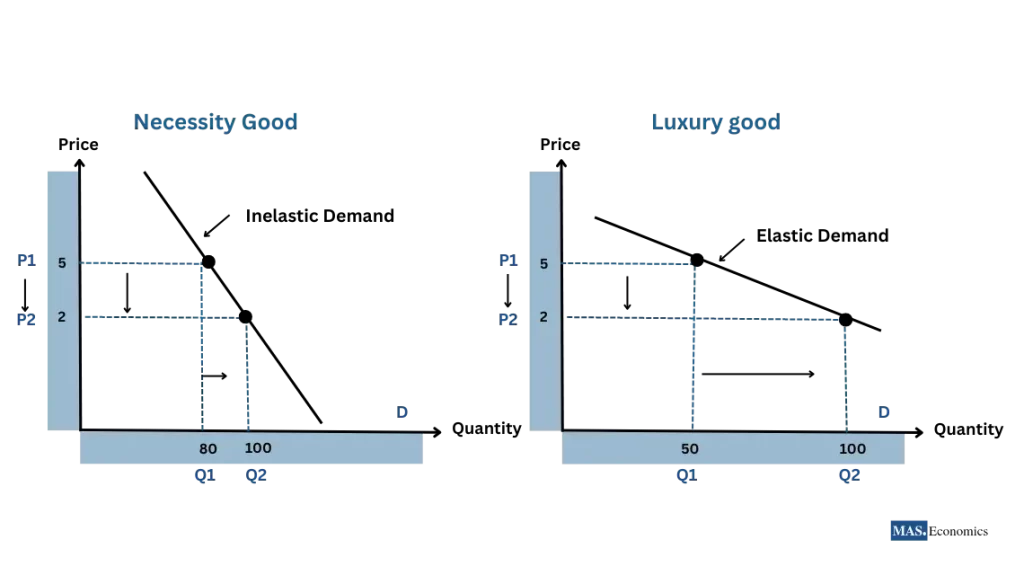
Price Inelastic vs Elastic Graph
Inelastic: necessities; medicine and prescriptions; addictive substances
Elastic: luxury goods; consumer discretionary (non-essential but desirable if affordable)