Regulation of Temperature (Thermoregulation)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Define Thermoregulation
the process of regulating body temperature within its tolerance limits. It is the maintenance of balance between heat production and heat loss. Both of these values should be equal.
Why is thermoregulation important?
Cells in our body perform chemical reactions (metabolism), which have an optimum temperature of 37 degrees Celsius. These reactions occur more efficiently when the temperature is maintained
Results of increased body temp
Nerve malfunction
Change in the structure of proteins (denature enzymes)
Death
Why is our internal body temperature usually warmer than our surroundings?
Metabolic activity of the cells in our body produces heat (heat input) → increases body temp
What is referred to as heat loss (output)
when body increases in metabolic activity (due to strenous activity - exercise), it needs to remove the resulting heat from our internal environment
How does heat exchange occur in the skin?
Conduction - transfer via direct contact
Convection - transfer by the movement of a liquid or gas
Radiation - transfer by infrared radiation being emitted by objects
Evaporation - liquid forming a gas, which absorbs heat energy
what is metabolic rate?
Metabolic rate is the rate at which energy is released by the breakdown of food.
define sweating
the active secretion of fluid by the sweat glands and the periodic contraction of cells surrounding the ducts to pump the sweat to the skin surface
define shivering
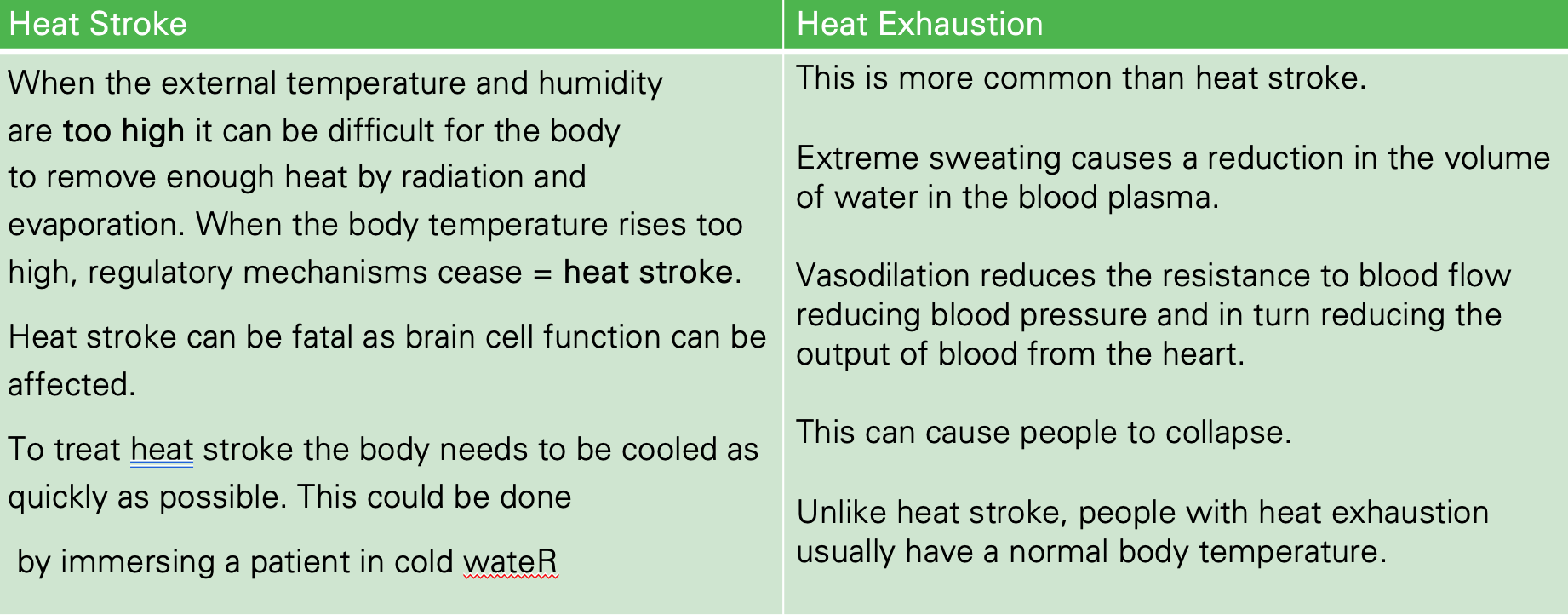
compare heat stroke and heat exhaustion