Human Anatomy Exam 1
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
purposes of the skin
-shield against heat, light, injury, infection
-regulates temperature
-stores water and fat (protection from cold)
-provides sensation (pain, temperature, touch)
layers of the epidermis
- stratum (mature keratinocytes, protective layer, layer of dead keratinocytes at very top)
- squamous cell layer (immature keratinocytes)
- basal layer (where cell division and replication occurs, keratinocytes start here and move upwards over ~1 month)
contents of the dermis
blood vessels, lymphatic structures, hair follicles, sweat glands, nerves, fibroblasts, pressure sensors
keratinocyte replication v. fibroblast replication
keratinocytes make up the epidermis, produced in the basal layer, move up through the squamous layer, end in the stratum before dying and flaking off the skin
fibroblasts make up the dermis, after one cell is produced, the original mother cell undergoes apoptosis and is reabsorbed into the bloodstream
subcutaneous layer
deepest skin layer - connection to fascial plane, network of collagen, fat layer aids in warmth and shock absorption
functions of the spine
- provides a point of attachment for muscles (produce movement) and ligaments (check movement)
- protect spinal cord and nerves (CNS cannot regenerate)
- support head and viscera (maintain even horizon for vestibular function and vision)
- act as linkage for upper and lower segments in functional activity (locomotion, posture)
primary curves (of the spine)
thoracic and sacral kyphosis - follows natural concavity of the fetal position in utero
secondary curves (of the spine)
cervical and lumbar lordosis - "acquired" convexity based on movement (baby looks up to feed, baby learns to roll and crawl)
segments of the spinal column
33 total - 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 4 coccygeal
degrees of movement at the spine
extension/hyperextension - 25 degrees
flexion - 80 degrees
lateral flexion - 25 degrees
transverse foramina
found on cervical vertebrae only, vertebral artery exits through C2-C6
bifurcated spinous processes
landmark of only C2-C6, allows for attachment of nuchal ligament and increased blood flow
uncovertebral joint
space between the uncinate process and adjacent vertebral body, found between the lower 5 cervical vertebrae
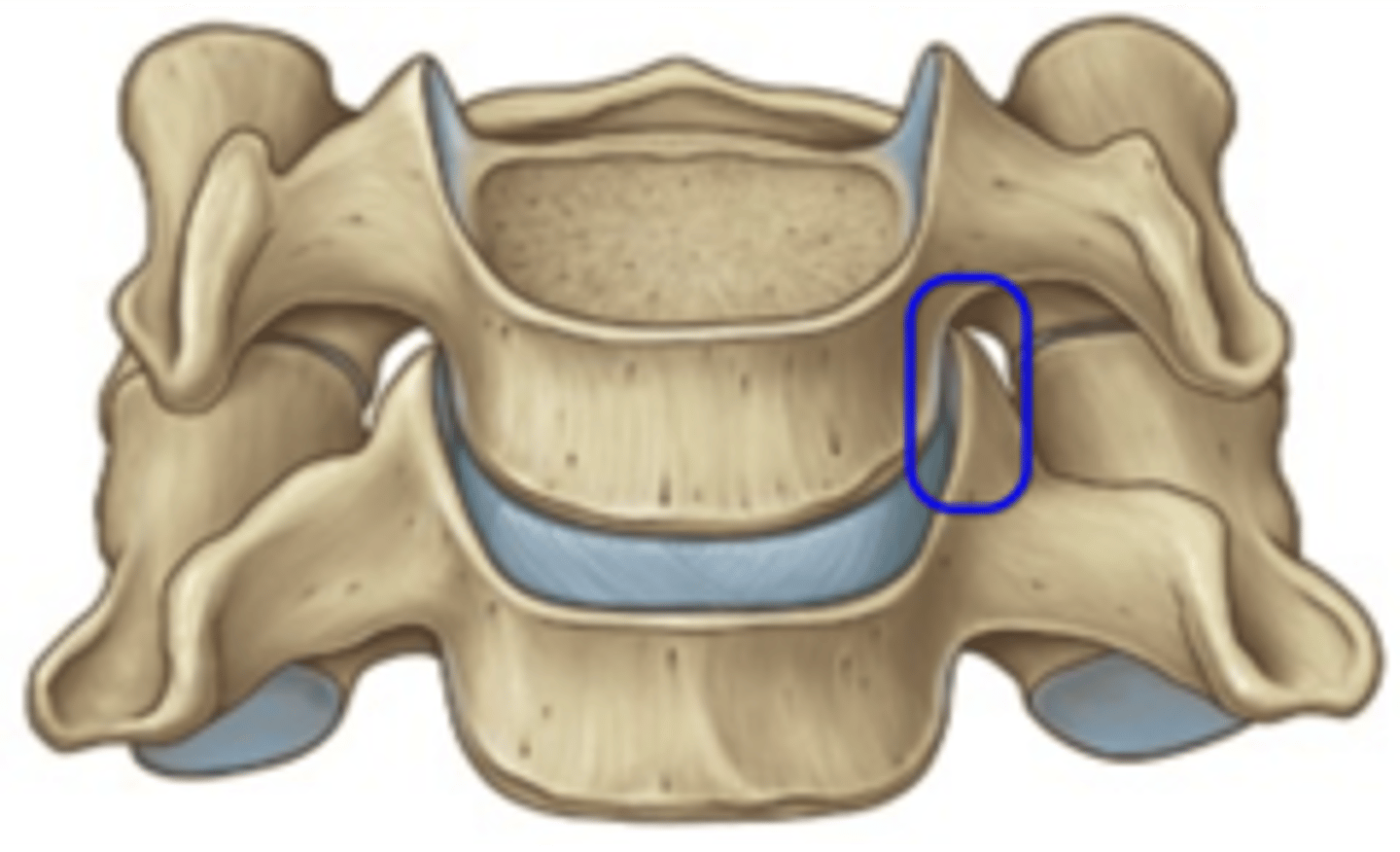
uncus (uncinate process)
process on cervical vertebrae only - lip on either side of the vertebral body
functions of uncovertebral joints
- guides cervical flexion and extension
- reduce cervical lateral rotation
- prevent posterior translation of neighboring vertebra
- reinforce posterolateral aspect of IV disc (as they are small in this region)
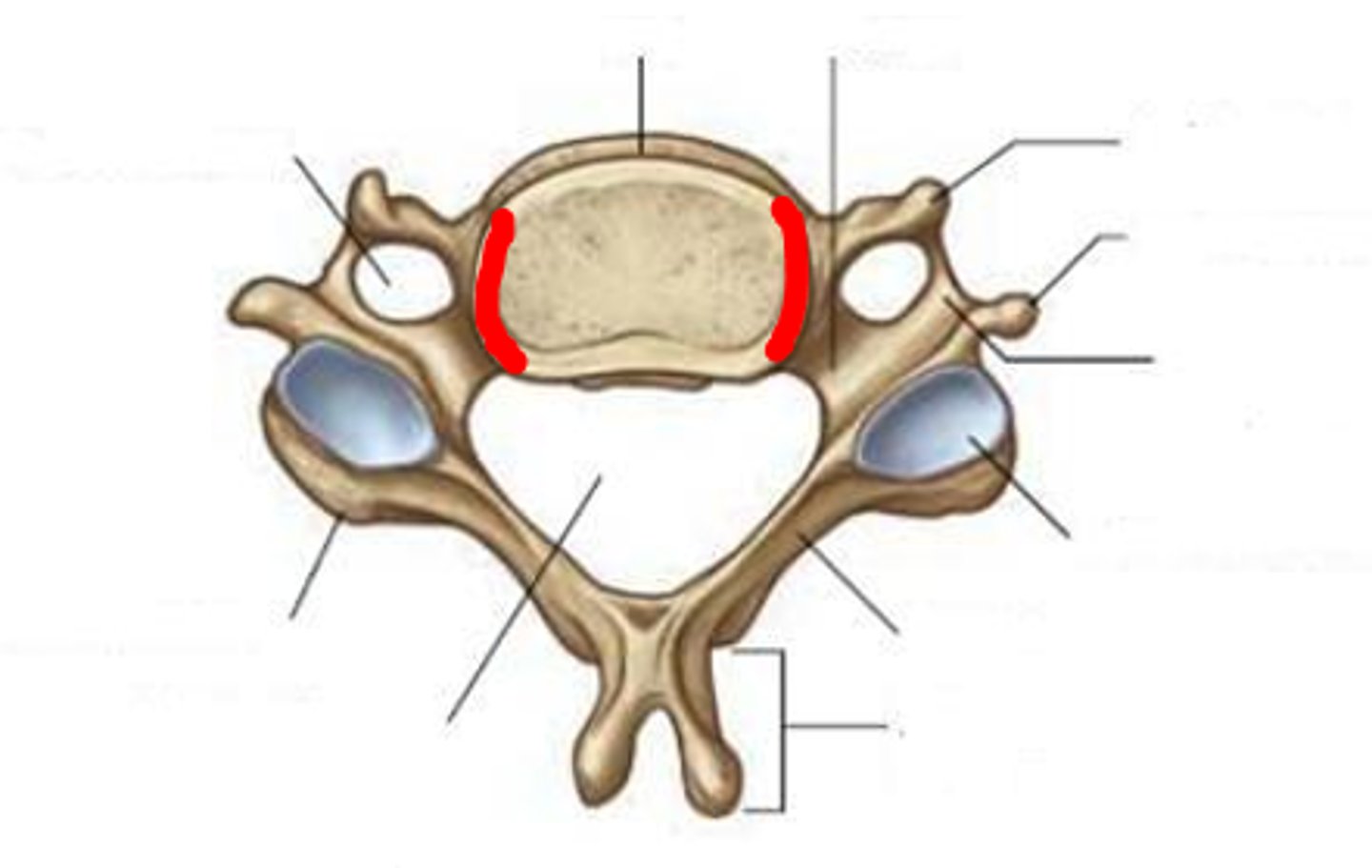
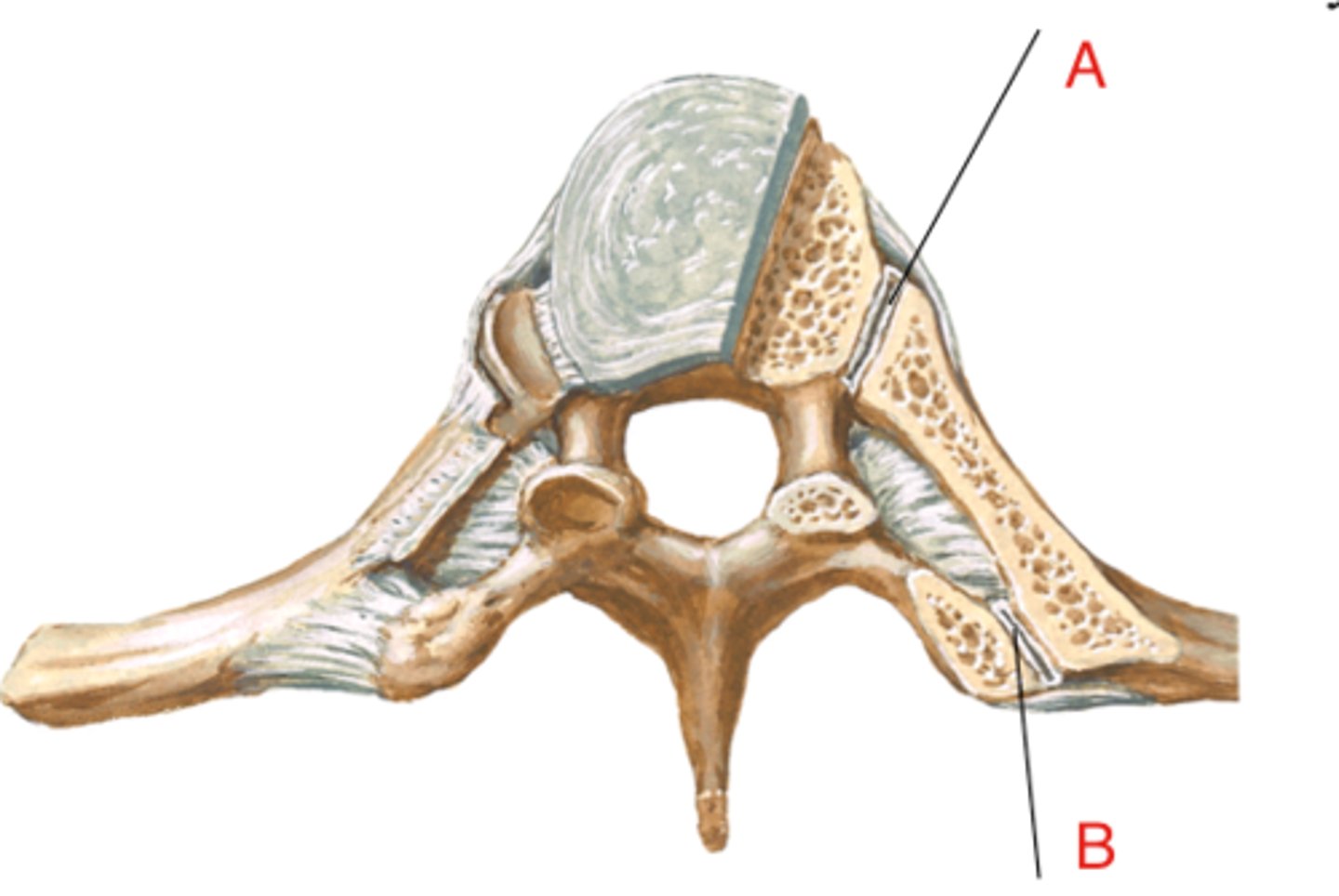
costovertebral joint
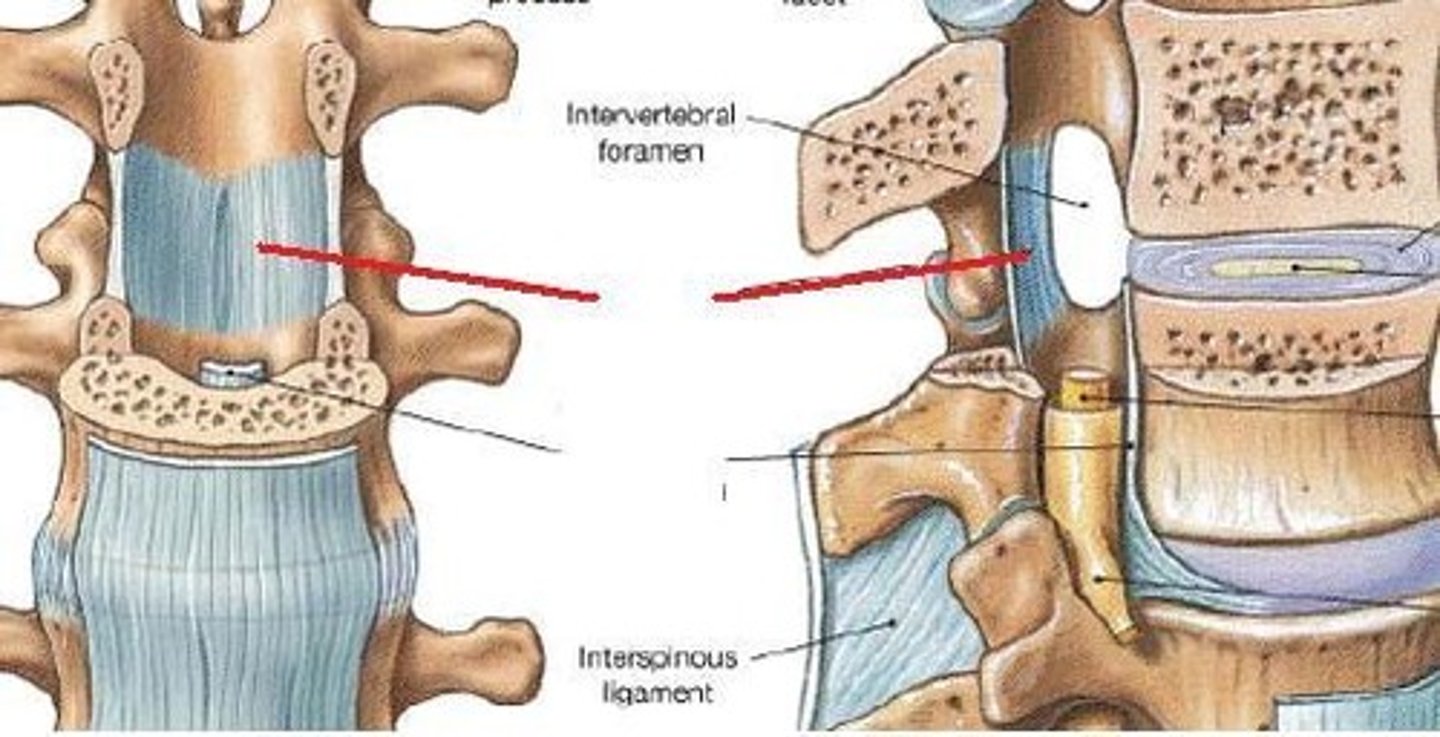
superior and inferior costal facets of the body of thoracic vertebrae articulation with the head of the rib (A on image)
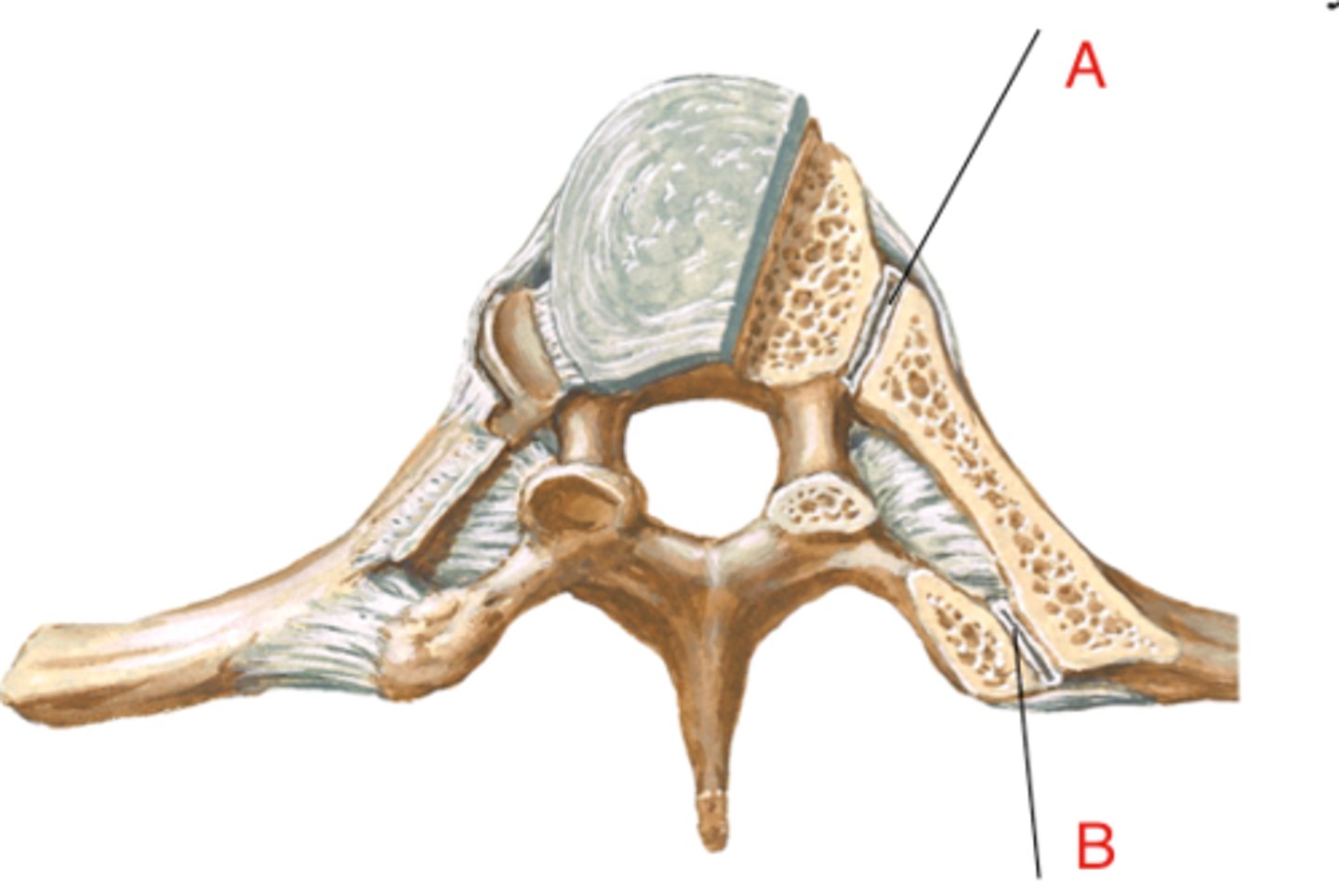
costotransverse joint
costal facet on transverse process of thoracic vertebrae articulation with the tubercle of the rib (B on image)
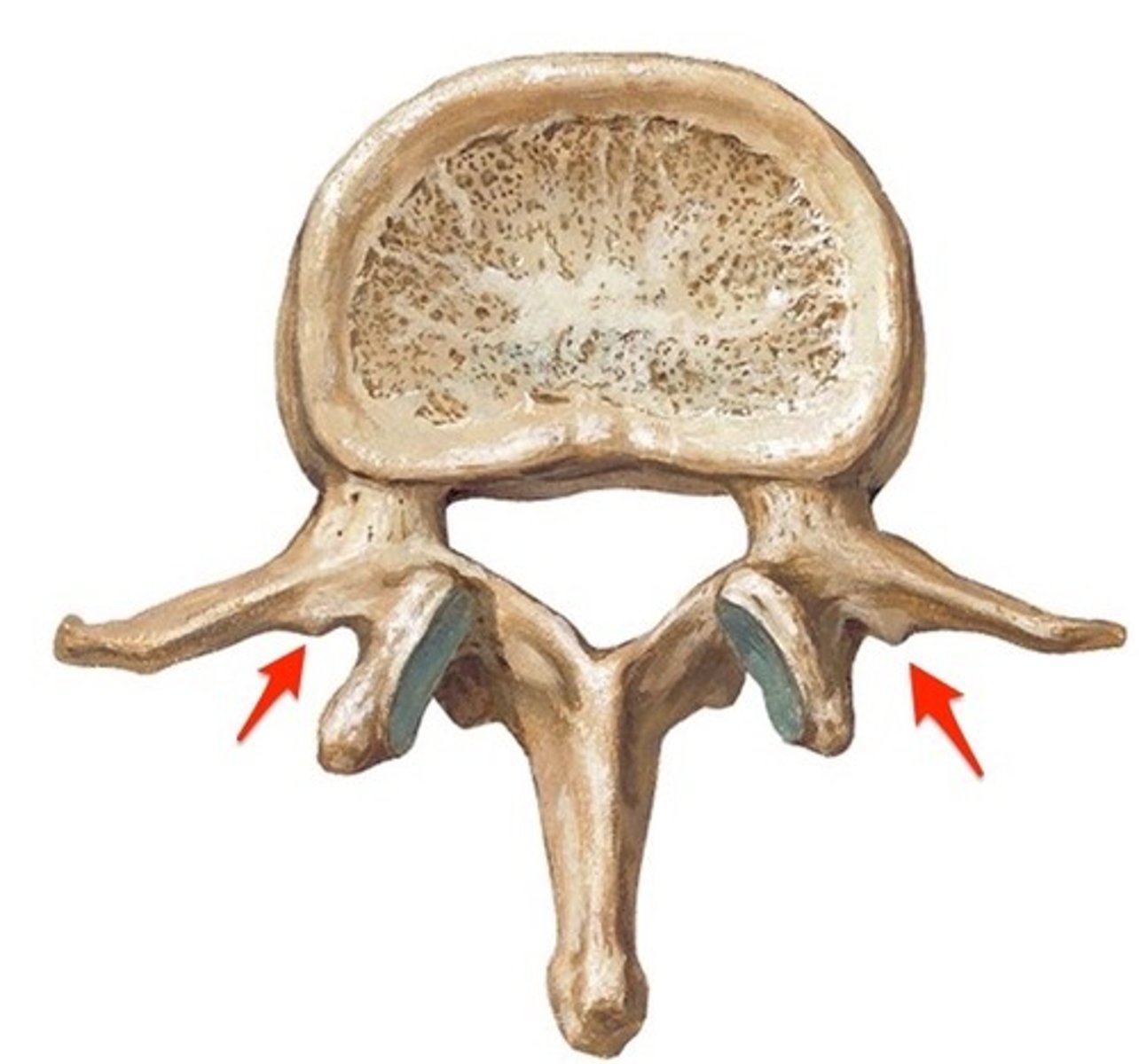
mamillary processes
processes specific to lumbar vertebrae, found on the posterior aspect of the superior articular process
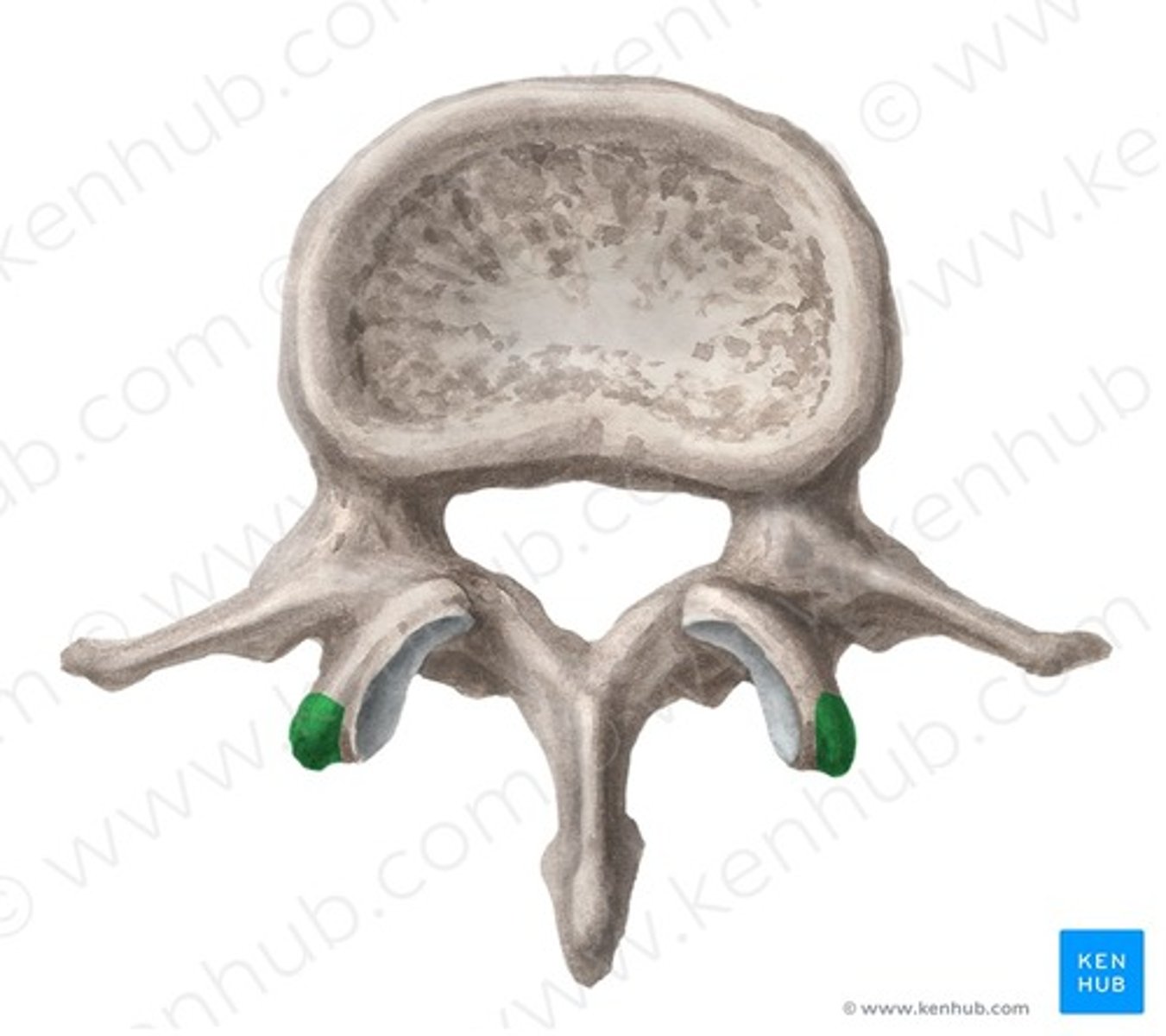
accessory processes
processes specific to lumbar vertebrae, found in between transverse and spinous processes on the lamina
cervical superior facet orientation
Back, Up, Medial (45 degree angle)
small masses allow gliding between vertebrae - works with uncinate process to limit rotation and guide lateral flexion without injury
thoracic superior facet orientation
Back, Up, Lateral (60 degree angle)
allows significant rotation between vertebrae because ribs create a bony stop that limits rotation
lumbar superior facet orientation
Back, Medial (90 degree angle)
limited rotation between vertebrae - receives pressure from head/arms/trunk etc, maintain linkage to lower body (rotation while walking)
intervertebral joints
articulations between vertebral bodies - cartilaginous symphyses with a fibrocartilage intervertebral disc in between
zygapophyseal joints
articulations between superior and inferior articular facets - gliding type synovial joints, very small movement at each joint has cumulative effect
approximation
facets move closer together during extension/hyperextension (IV foramen decreases in size)
distraction
facets move farther apart during flexion (IV foramen increases in size)
spinal tropisms
57% of people have flat/normal facets, 31% have asymmetric (restricts movement on one side), 12% have half-moon shape (restricts some movement)
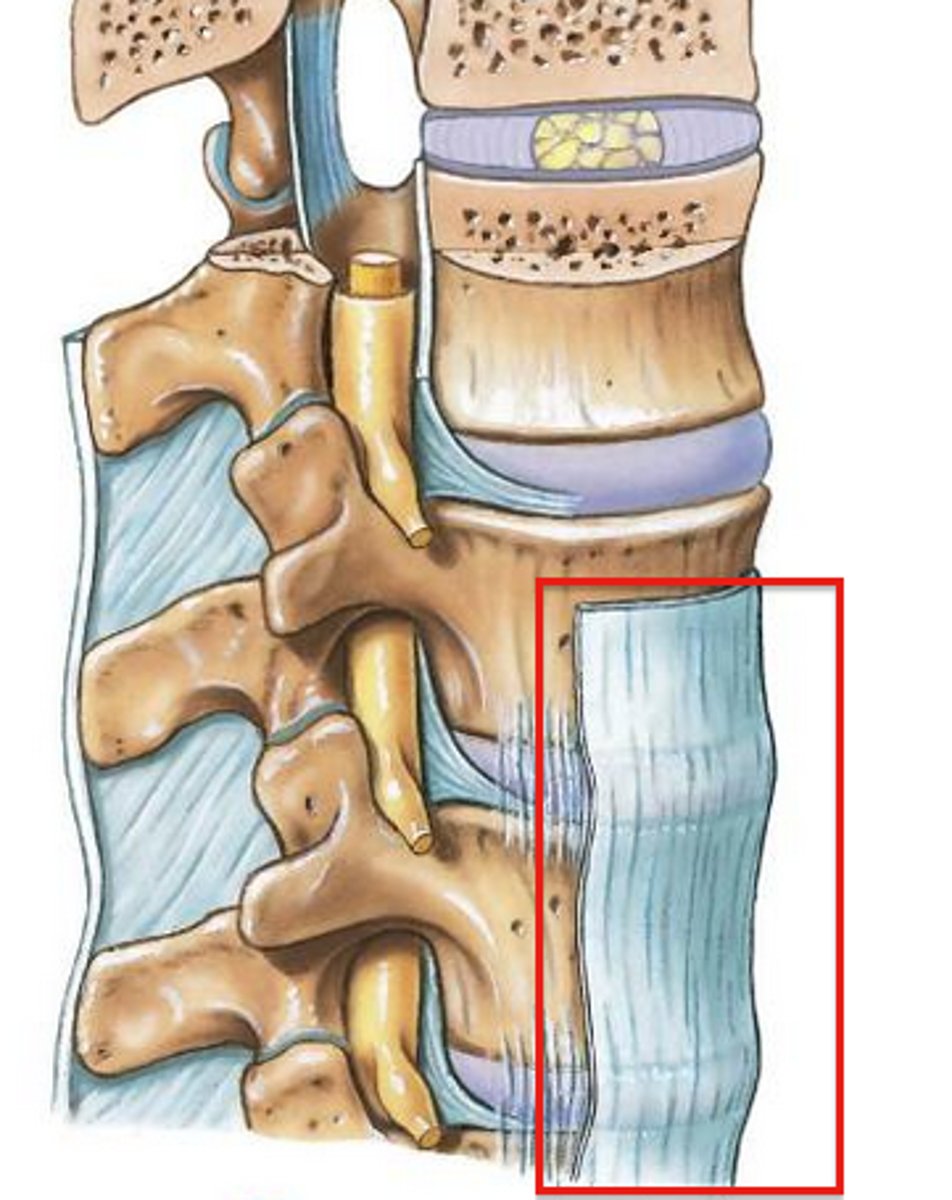
anterior longitudinal ligament
runs down anterior vertebral bodies, checks extension/hyperextension
posterior longitudinal ligament
runs down posterior vertebral bodies/anterior vertebral canal, checks flexion, becomes tectorial membrane superiorly
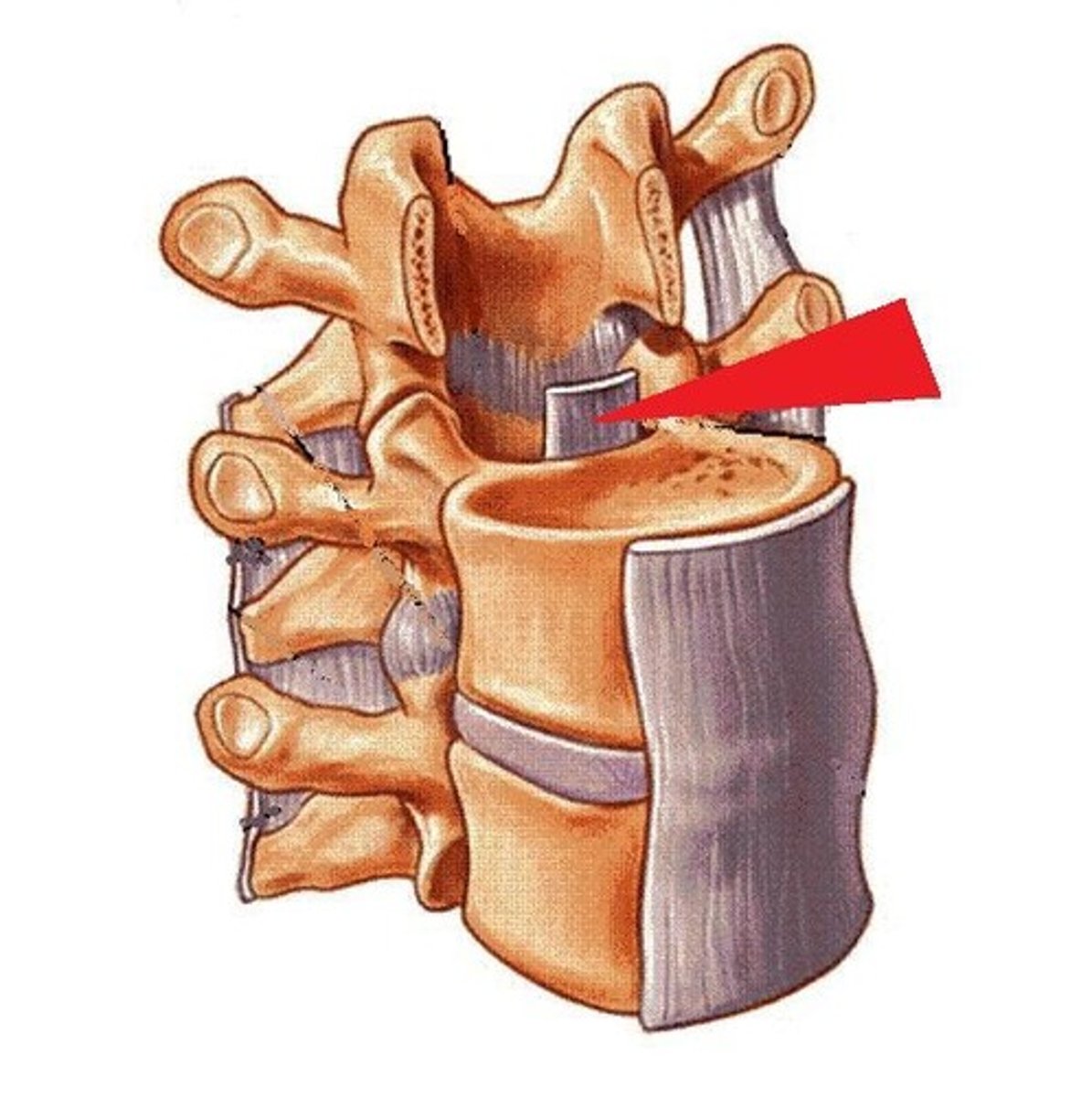
ligamentum flavum
connects lamina of adjacent vertebrae, protects spinal cord (primary action), also checks flexion and rotation (accessory)
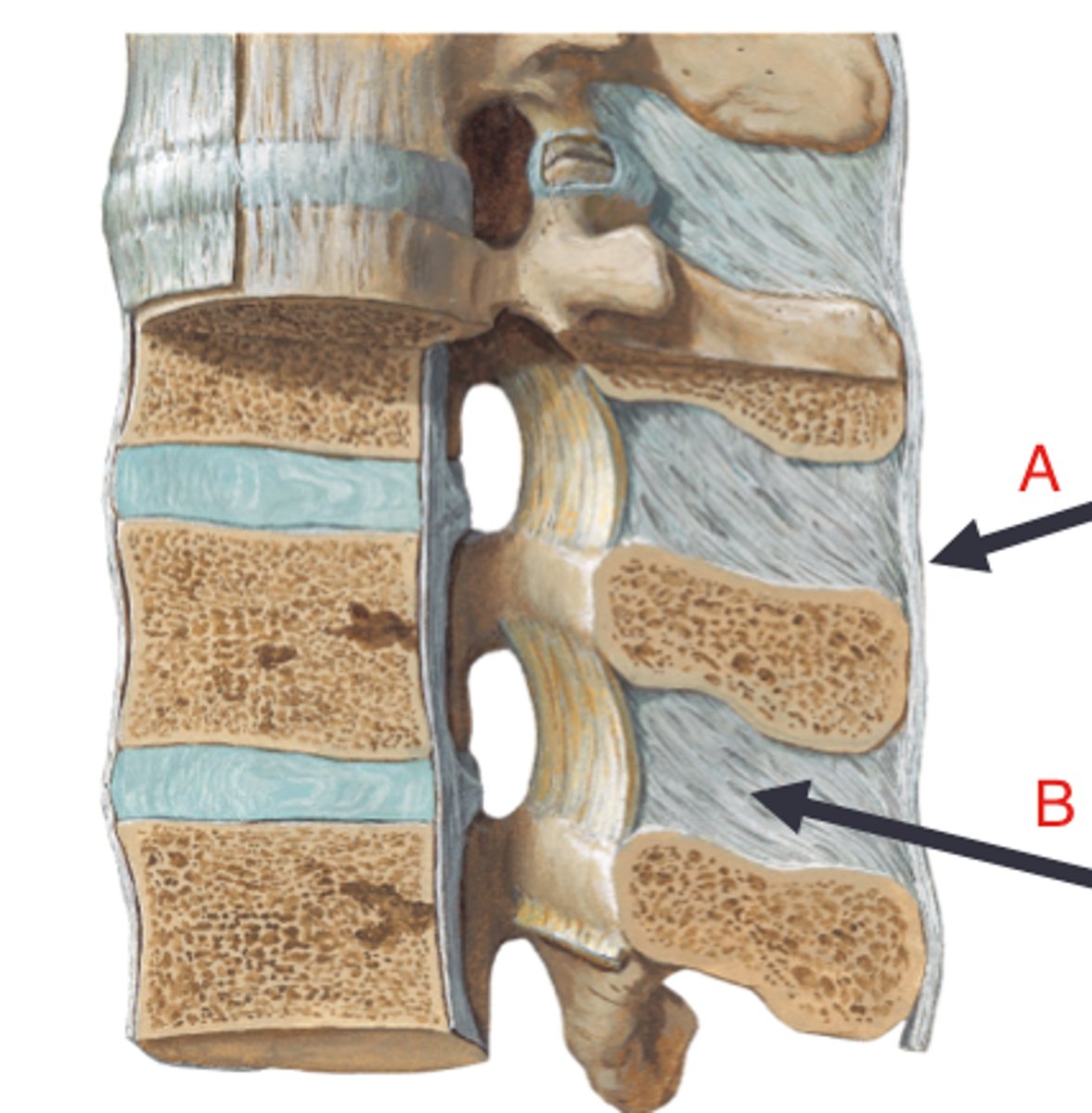
interspinous ligaments
connects spinous processes, checks rotation (primary) and flexion (accessory)
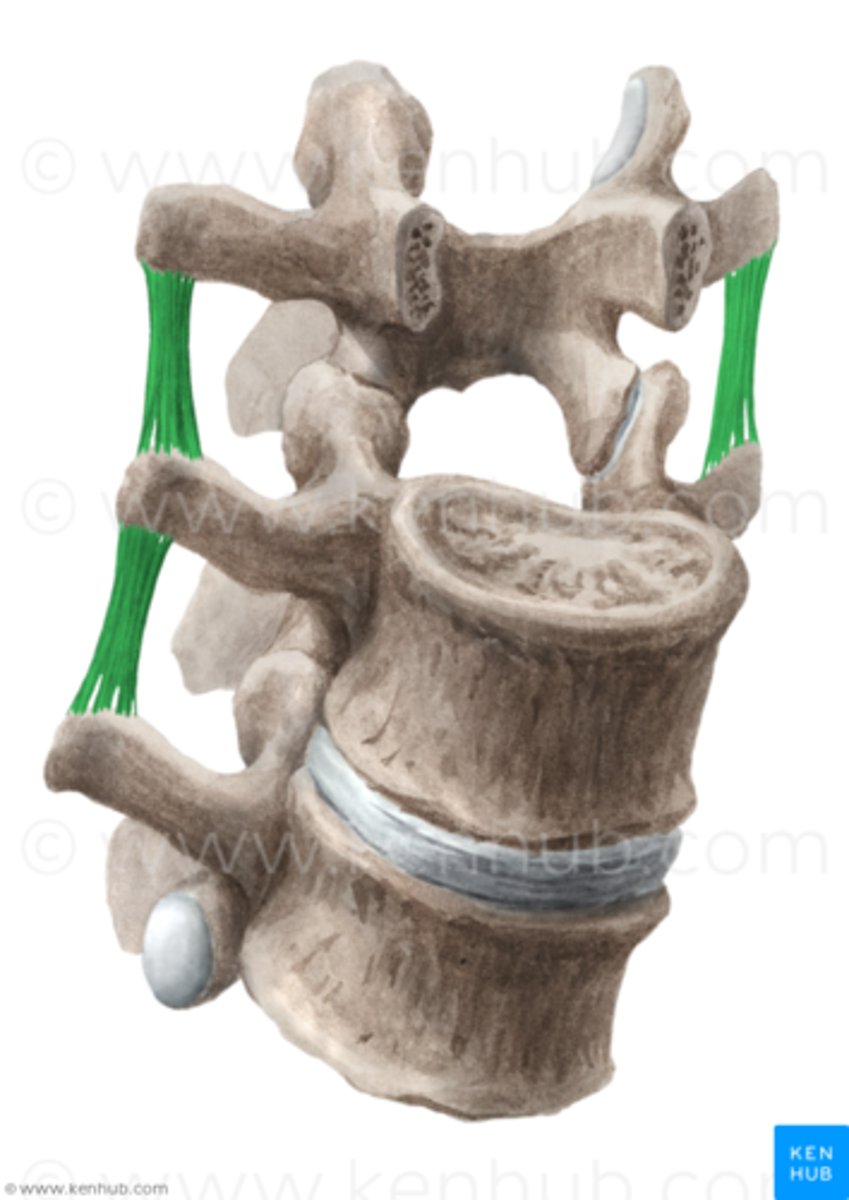
intertransverse ligaments
connects transverse processes, checks rotation (primary) and flexion (accessory)
supraspinous ligaments
connects tips of spinous processes, checks flexion (primary ligament for this check), becomes nuchal ligament superiorly (A in image)
tectorial membrane
continuation of PLL, anchors to anterior rim of foramen magnum (A on image)
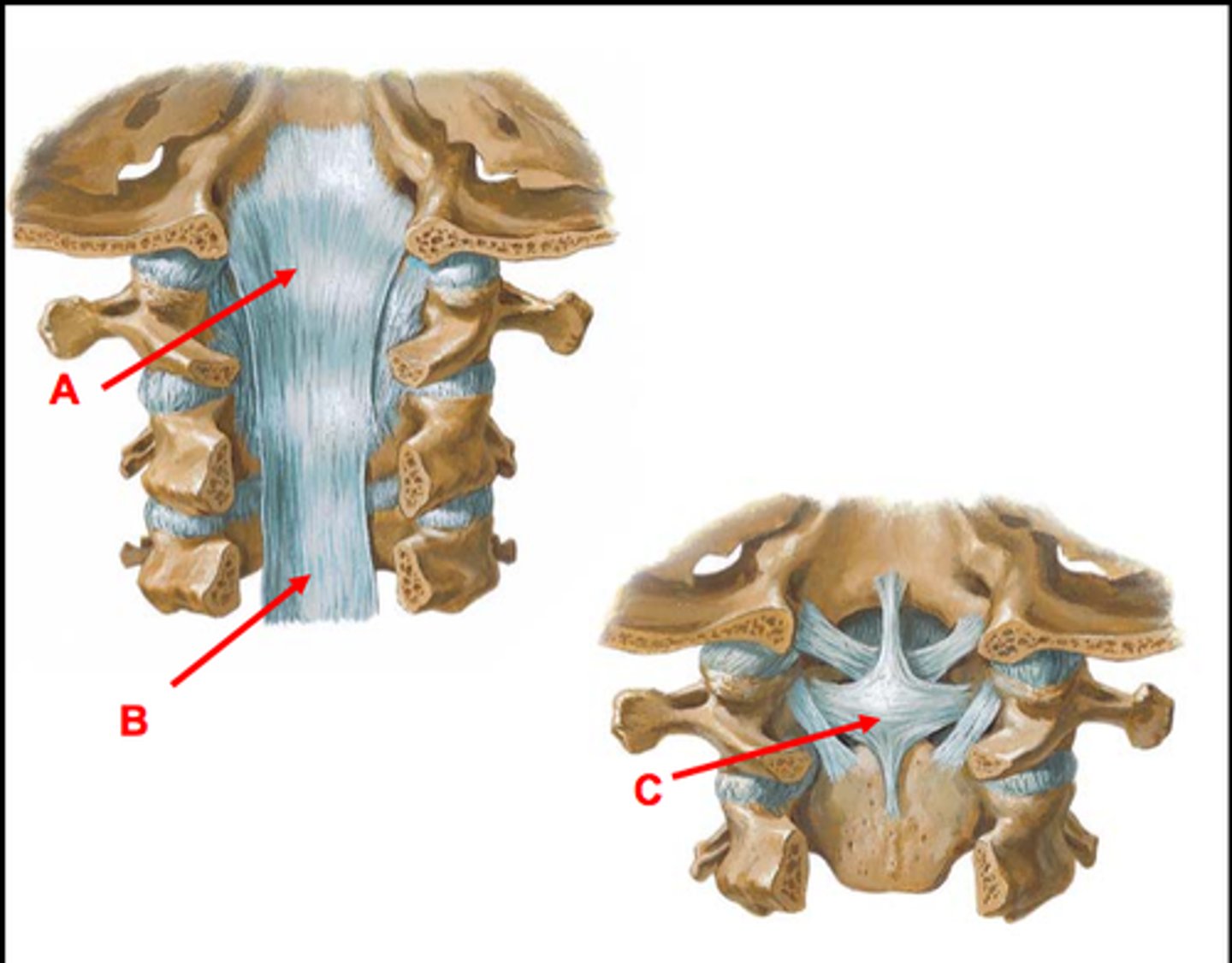
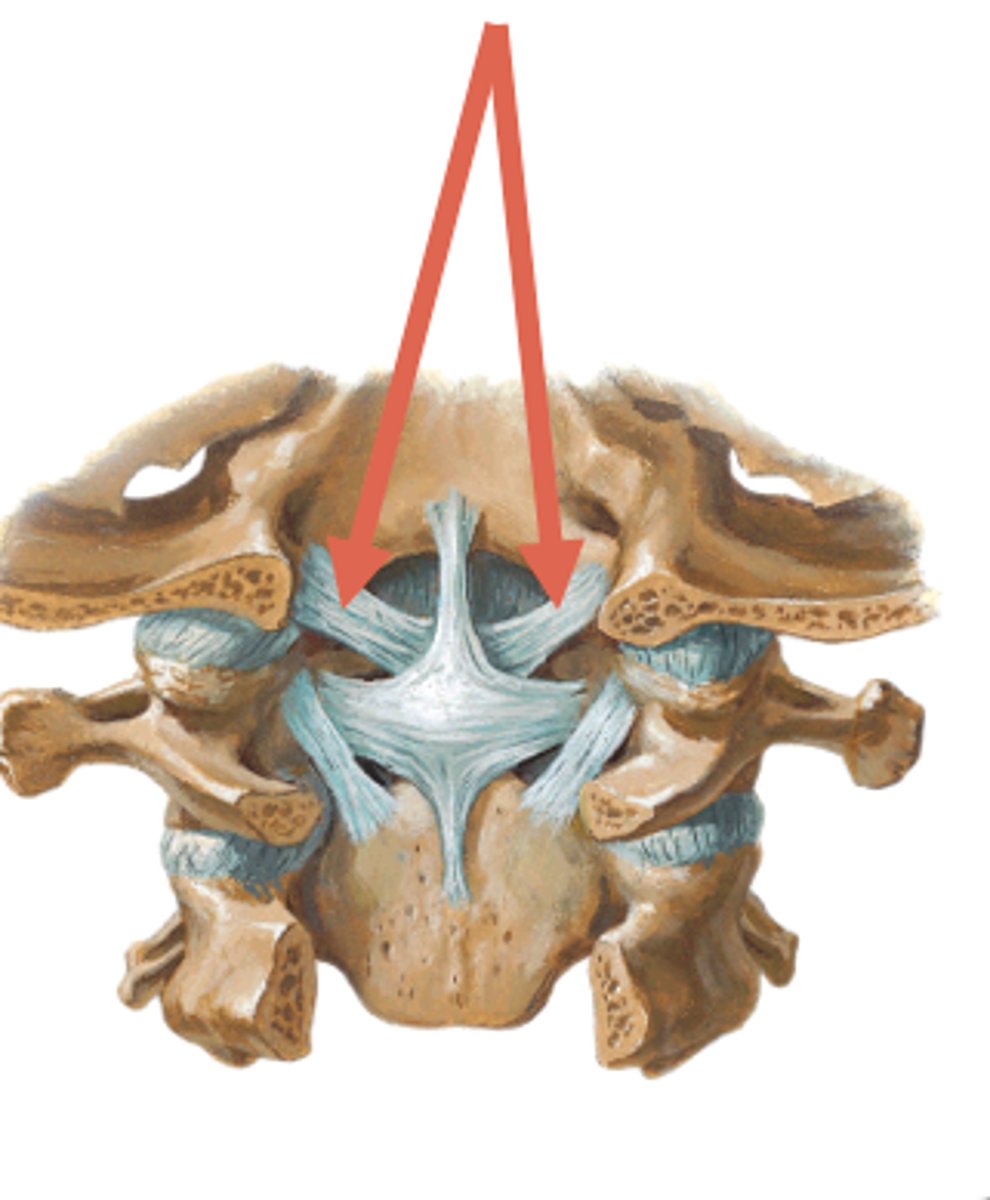
cruciform ligament
transverse portion anchors to lateral margins of the vertebral canal of C1, touching posterior dens of C2, superior and inferior portions anchor to the anterior rim of the foramen magnum and posterior rim of the dens of C2 - important in counteracting anterior translation of C1 relative to C2
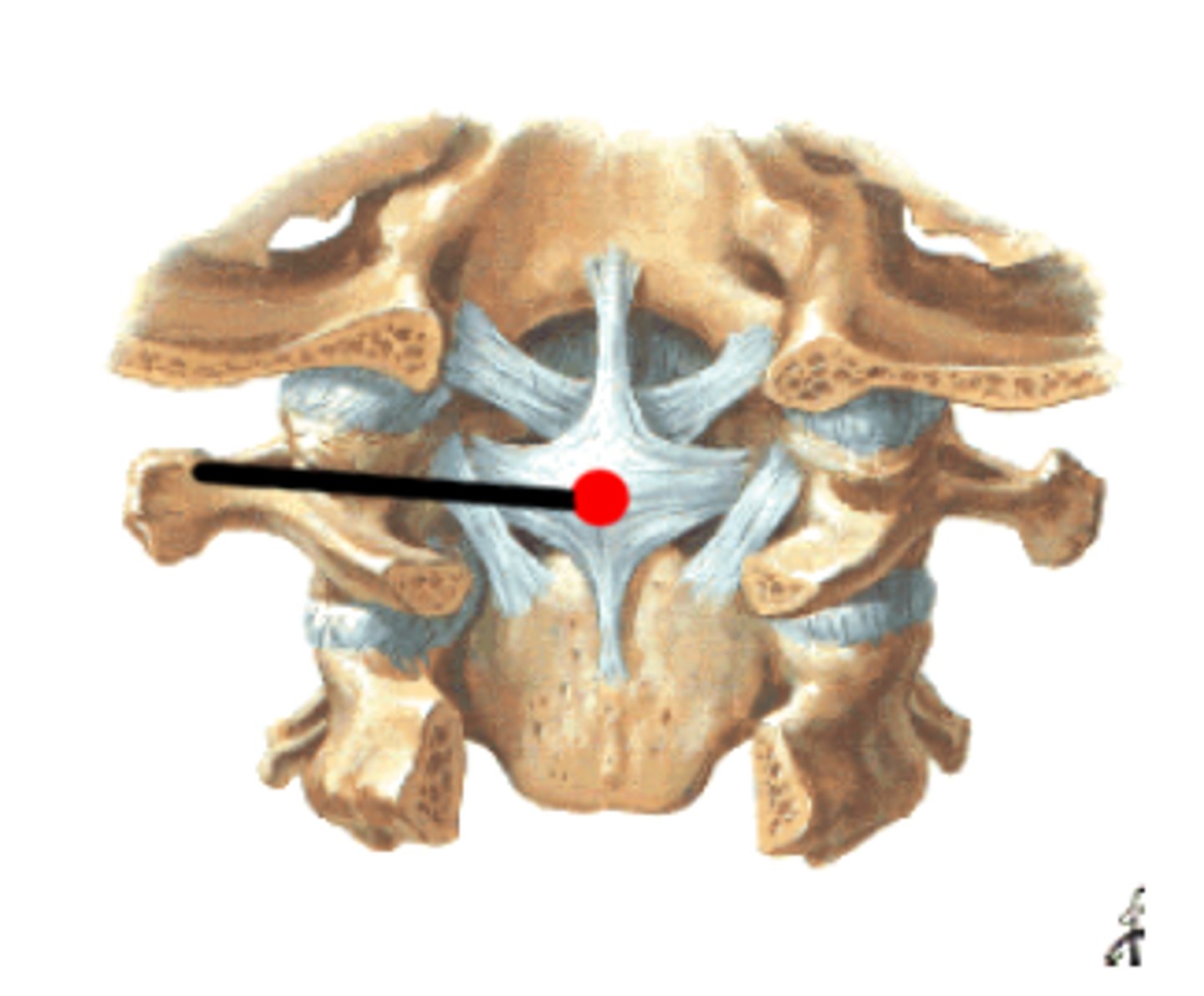
apical ligament
ligament deep to tectorial membrane and superior portion of the cruciform ligament - anchors to the foramen magnum and dens of C2
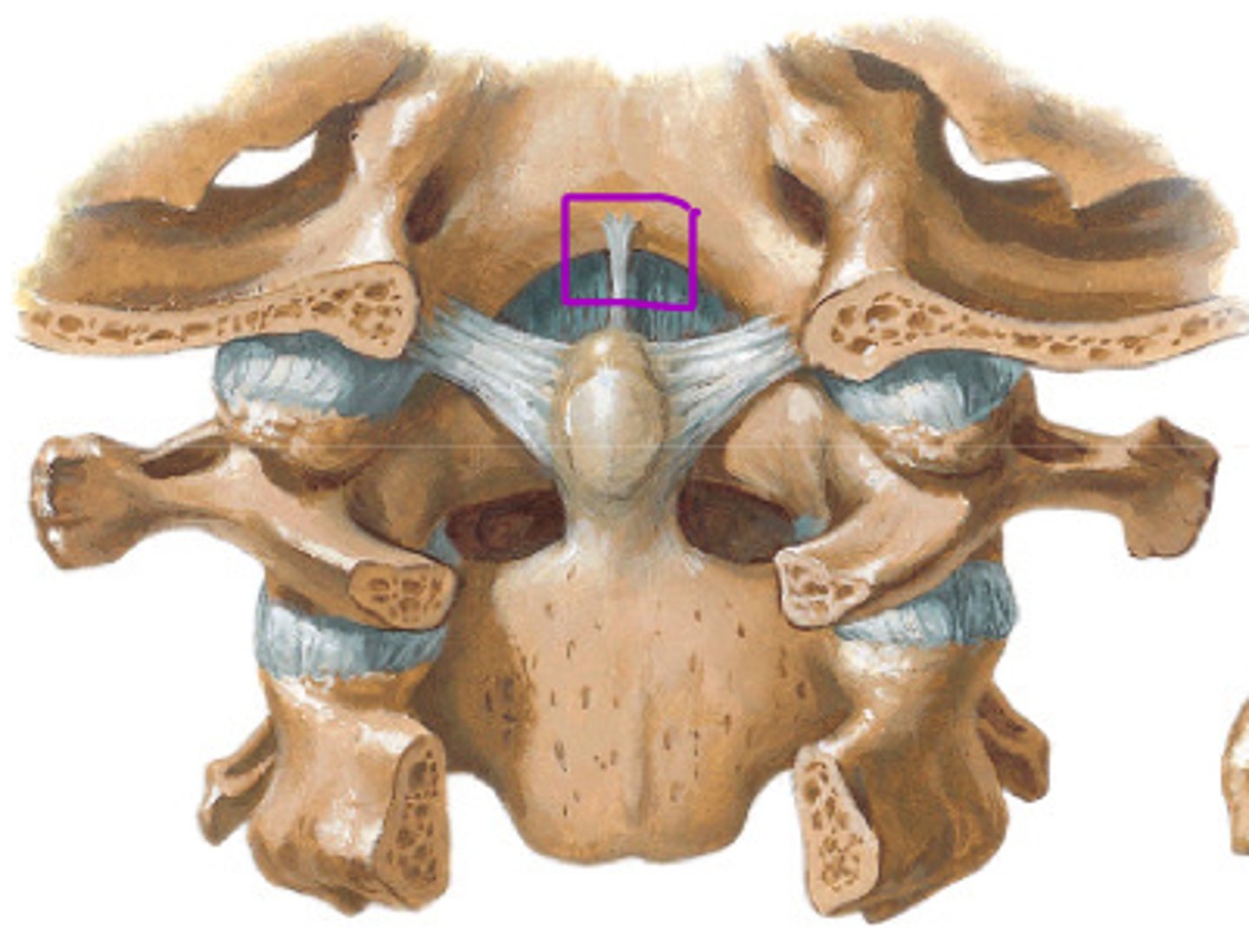
alar ligament
ligament deep to tectorial membrane and cruciform ligament - anchors from the lateral margins of the dens to the foramen magnum - helps to guide cervical rotation
annulus fibrosis
outer layer of the intervertebral disc, composed of lamellae (thin fibrocartilage rings), has blood supply and is slightly neural
main functions: cushion shearing and torsional forces, will resist distraction of adjacent vertebral sections, keeps nucleus pulposus in place
nucleus pulposus
inner gelatinous part of the intervertebral disc, avascular and aneural
main functions: resist compressive forces, gives disc its height
(if decrease in fluid --> loss of column height --> facet approximation --> decrease in IV disc foramen size --> pathology (ex. osteoarthritis/pinched nerves) --> pain and limited function
if it leaks, it leaks in the posterolateral direction (least ligamentous support)
vertebral endplates
connecting mechanism of intervertebral disc to bone, interwoven into disc (part of disc, not subchondral bone) - contains hyaline and fibrocartilage covering the top and bottom aspects of the disc, central portion of the plate has a permeable membrane
functions: maintain connections of intervertebral joints, prevent nucleus pulposus from bulging, absorb pressure
cervical and lumbar enlargements
2 sites on the spinal cord where nerves serving the upper and lower limbs emerge
conus medullaris
tapering/end of the spinal cord at the level of L1
cauda equina
long roots through the vertebral canal starting at the level of L2 - develops throughout the lumbar and sacral spine, exits out their foramina to the pelvis, perineum, and LE (stays within the meninges)
meninges
three protective membranes (dura, arachnoid, pia) that surround the brain and spinal cord - protection of neural fluid, CSF flows within
dorsal root ganglion (DRG)
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons - where CNS starts and PNS ends, meninges stop there
denticulate ligaments
anchors within the spinal cord that connect pia/arachnoid mater - centers the spinal cord (side-to-side stability) om the vertebral canal and helps CSF flow
anchors of the spinal cord
brain (superior), filum terminale (inferior), denticulate ligaments (lateral)
filum terminale
fibrous, blue-white colored, extension of the conus medullaris that adheres to the 1st coccygeal segment - needed for orientation of the cauda equina (connective in nature, not neural)
L4
level of the iliac crest, useful for spinal tap (extracting CSF) or lumbar puncture (injection of local anesthetic to do a nerve block)
medial branch of posterior rami
innervates multifidus, zygapophyseal joints, and the periosteum of the vertebral arch
recurrent meningeal/sinuvertebral nerve
nerve with 2-4 filaments on each side of vertebra at all levels and ascending/descending branches - arises from ventral rami and sympathetic trunk (grey communicantes), starts right after meninges end - recurs and goes back into the vertebral column, collects data from the annulus fibrosus before going back in, important in referred pain and occipital headaches
ascending and descending branches of the recurrent meningeal nerve
innervates the posterior longitudinal ligament, posterior aspect of superior disk, anterior aspect of dura, spinal canal vessels
branches of posterior rami
lateral branch, intermediate branch, medial branch
branches of anterior ramus
recurrent meningeal/sinuvertebral nerve, skeletal branch, muscular branch
sensory information
travels through the dorsal root to the posterior spinal cord
motor information
travels from the anterior spinal cord through the ventral root
white matter v. grey matter
white matter "travels" (myelinated) and grey matter "thinks" (unmyelinated)
path of vertebral artery
paired arteries that arise from the subclavian artery, ascend through the transverse processes of C2-C6 (not C7 - transverse foramen not big enough), pass behind lateral mass of C1 and enters the dura behind the occipital condyle, ascend through the foramen magnum and join to form the basilar artery
portions of vertebral artery
proximal (initial branch off subclavian - prone to compression due to longus colli and scalene muscles), transverse (C2-C6 levels - prone to compression from osteophytes and subluxed facet joints), suboccipital (groove for vertebral artery of C1 - prone to compression from cervical rotation), intracranial (join to basilar artery - prone to plaque and stenosis)
arteries of the spinal cord
2 posterior spinal arteries, 1 anterior spinal artery, radicular artery, arterial vasocorona
arterial vasocorona
artery functioning as an anastomosis (interconnection of vessels), surrounding the whole spinal cord - fed by radicular artery, connects to anterior and posterior spinal arteries - allows for collateral circulation
radicular artery
spinal cord arteries that go interior - fed by various arteries in each region (cervical, thoracic, abdomen, pelvis)
batson venous complex
spinal veins - internal connects from cord and canal, also has an external segment
occipital triangle
boundaries: rectus capitis posterior major, obliquus capitis inferior, obliquus capitis superior
contents: vertebral artery (laying down in C1), suboccipital nerve
stages of development in utero
pre-embryonic (conception-week 2), embryonic (week 2-8), fetal (week 8-birth)
pre-embryonic stage
conception-week 2 - zygote (30 hours) --> moves from uterine tube to cavity, continued cell division to form blastomere --> morula phase (3 days) --> blastocyst (4 days) --> inner layer of blastocyst turns into bilaminar embryonic disk (day 6-14) --> embryonic disk forms ectoderm, endoderm, yolk sac, and amnion
bilaminar embryonic disk
stage at day 6-14, the blastocyst embeds into the uterine wall, ectoderm and endoderm form, yolk sac (that will provide nourishment) and amnion (where growth will occur) form, the disk is located between these two spaces
zygote
fertilized egg, forms 30 hours after fertilization
blastomere
a cell formed by cleavage of a fertilized ovum, made of 4 cells
morula
A solid ball of cells that makes up an embryo, made up of 12+ cells - forms 3 days after fertilization
blastocyst
stage 4 days after fertilization, outer layer will develop into the placenta, inner layer will develop into bilaminar embryonic disk
embryonic stage
week 2-8 - gastrulation (days 14-21), somite formation (day 18), neurulation (begins day 19), neural tube development, differentiation into mantle and marginal layer (day 26), neuropores close (day 28-30), mantle layer divides into association plate and motor place, neural crest divides into sensory and motor nerves, intervertebral disc development (around 4th week), formation of limb buds (high level of development weeks 5-8)
gastrulation
days 14-21 - blastocyst-->gastrula - mesoderm is formed
endoderm
innermost germ layer, develops day 6-14 - develops into liver, pancreas, respiratory system cells - much of the viscera
ectoderm
outermost germ layer - develops day 6-14 - develops into sensory organs, epidermis, nervous system
develops into the neural plate around day 16 --> neural groove around day 18
mesoderm
middle germ layer - develops day 14-21 - develops into dermis, muscle, skeleton, excretory organs, and eventually the circulatory system (including the heart)
neurulation
begins on day 19, formation of the CNS begins - neural groove--> neural tube
neural tube
forms when the folds of the neural groove touch, starts cervical and closes rostro-caudal to eventually become the spinal cord - adjacent somites on either side will eventually turn into vertebra and spinal segments
neural crest
remaining ectoderm cells adjacent to the neural tube --> divides and develops into the dorsal root ganglion + forms peripheral sensory nerves/forms motor connections
neuropores
spots where the neural tube does not close right away - superior closes on day 27 (or 28) and becomes the forebrain, inferior closes on day 30 and becomes the conus medullaris
neural tube differentiation
day 26 - two rings of cells form the mantle layer and marginal layer --> the mantle layer further divides into the association plate and motor plate
association plate
dorsal portion of the mantle layer of the neural tube - when neural crest divides, it projects cells through, they stretch out and become DRG/peripheral sensory nerves in the adult system
motor plate
ventral portion of the mantle layer of the neural tube - when neural crest divides, it projects cells through, they stretch and form motor connections
mantle layer
inner portion of the developing neural tube (day 26) --> develops into gray matter
marginal layer
outer portion of the developing neural tube (day 26) --> develops into white matter
somites
specialized portions of mesoderm that begin to form on day 18, line up against the neural tube, rostro-caudal development - include the sclerotome, myotome, and dermatome
sclerotome
anteromedial portion of the somite --> develops into skull and bones of the vertebral column
myotome
posteromedial portion of the somite --> develops into skeletal muscle
dermatome
lateral portion of the somite --> develops into the dermis
limb buds
Bumps of tissues developed from the mesoderm layer that will form into limbs - embryo resembles human form by week 8
intervertebral disc development
4th week (pre-cartilaginous or mesenchymal stage) - start seeing development of spinal segments - neural tube squeezed to form disc, neural tube surrounded by embryonic cartilage, collagen fibers form the annulus fibrosus (by 10th week - totally developed by 5-6 months)
spinal cord growth
during fetal stage (weeks 8-12) - vertebra and spinal cord grow together at first, but then the column begins to grow faster than the cord - at week 12, the cauda equina forms because the cord cannot keep up but nerves continue to grow
formation of the brain
begins on day 28 with the closure of the superior neuropore - three main vesicles become the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
failure of rostral closure
when the superior neuropore does not close by day 28 - anencephaly can occur (skull not fully formed, no forebrain, no cortex --> stillborn)
failure of caudal closure
when the inferior neuropore does not close by day 30 - spina bifida
spina bifida
most common congenital spinal defect (1:2,500 live births), lack of development of neural arch/axis (severity ranges from occulta --> cystica (meningocele) --> cystica (menigomyelocele)
spina bifida occulta
most common and least severe form of spina bifida, usually at L5-S1, may be asymptomatic, tuft of hair, no functional issues
spina bifida cystica
severe spina bifida
meningocele - meningeal cyst, may be covered by skin or thin membrane, sac contains only meninges, normal physical life possible with treatment
meningomyelocele - contains meninges and spinal cord, spinal nerves in cyst, much more severe - loss of sensory and motor function, cannot maintain CSF pressure causing hydrocephalus, pt typically wheelchair bound
clinical significance of the multifidus
critical for long term stability of the spine - this muscle has highest % of type 1 fibers out of all back muscles (high aerobic capacity) - immobility --> atrophy --> inability to do long bouts of standing/walking/working --> low back pain
congenital malformations (of the back)
5% of the population has some sort of lumbar tropism/abnormality, can be an occult condition - examples include lumbarization and sacralization, where L5 or S1 migrates up or down (can be asymptomatic or cause pain, depending on the situation)