GEO2440 Spatial Data Analysis 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Measurement
Measuring on screen.
This includes working out a measurement. E.g. distance, area.
And also adding geometry attributed to work out lengths of already established segments.
Types of measurement
Cartesian
Ellipsoid
Cartesian
Treating the Earth as flat.
E.g. British National Grid.
Ellipsoid
Treating the Earth as an ellipsoid.
Map projection
The way a spherical Earth is transformed into a flat one.
Bigger the distance, the worse the difference is.
Queries
A request to select features or records from a database.
Often written as a statement or logical expression.
Combining queries
AND
OR
NOT
OR AND
AND NOT
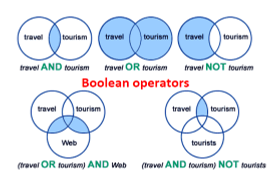
What do queries produce?
A map.
A binary answer where true = 1 and false = 0.
Types of queries
Aspatial
Spatial
Aspatial queries
Questions about attributes.
In a table, e.g. pulling out road types and querying the attributes.
Aspatial query example 1
Select areas where mortality rate is more than 58.0 per 1000.
Spatial queries
A statement or logical expression that selects geographic features based on a location or spatial relationship.
Do they touch? Intersect? Cross? Overlap? re they within a certain distance of one another?
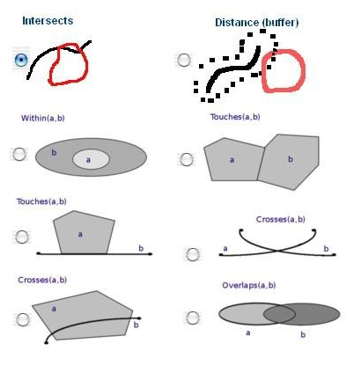
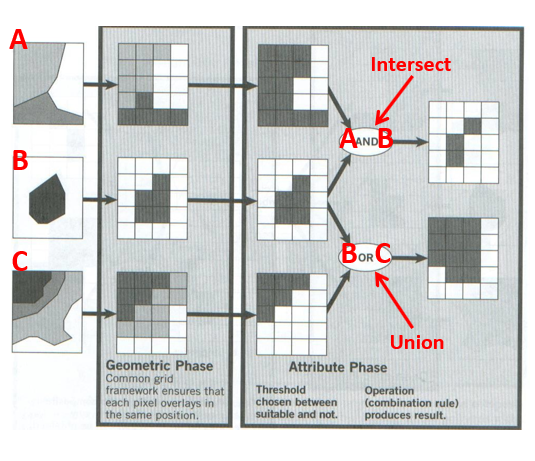
Map overlay (spatial query)
The geometric intersection of two or more datasets to combine, erase, modify or update features in a new output dataset.
Can be both raster and vector
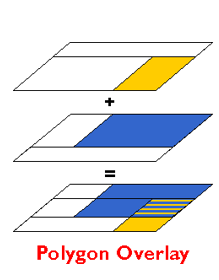
Vector map overlay
Overlays points, lines OR polygons in one layer over polygons in another layer.
Operations: erase, identity, intersect, spatial join, symmetrical difference, union, update, split, clip, select.
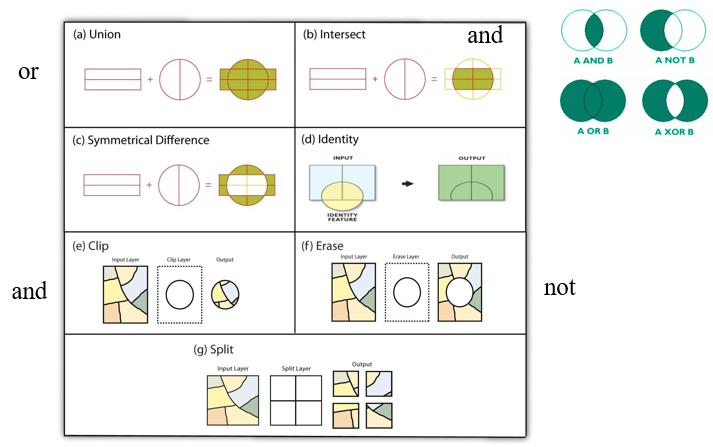
Vector map overlay: union
Combines two layers.
Vector map overlay: symmetrical difference
Removes overlap.
Vector map overlay: identity
Crossover between spatial and aspatial - uses an attribute table.
Vector map overlay: erase
Erases a section.
Opposite of clip.
Vector map overlay: split
Splits an original into sections based on the other layer.
Vector map overlay: intersect
Computes a geometric intersection of the input features. Features or portions of features which overlap in all layers and/or feature classes will be written to the output feature class.
Returns only where both are true.
E.g.: where a 200m road buffer and agricultural land intersect.
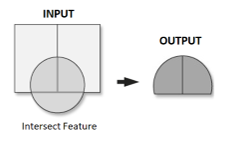
Vector map overlay: clip
A command that extracts features from one feature class that reside entirely within a boundary defined by features in another feature class.
Used to cut out a piece of one feature class using one (or more) features in another feature class as a cookie cutter to create a geographic subset of the features.
E.g. clip the coastal paths in England to just a nature reserve boundary.
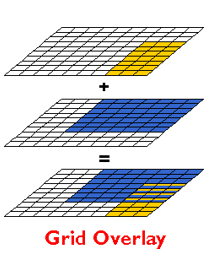
Raster map overlay
Overlays the pixel or grid cell values in each data layer using Boolean, arithmetic or relational operators to produce a new value in the composite data layer.
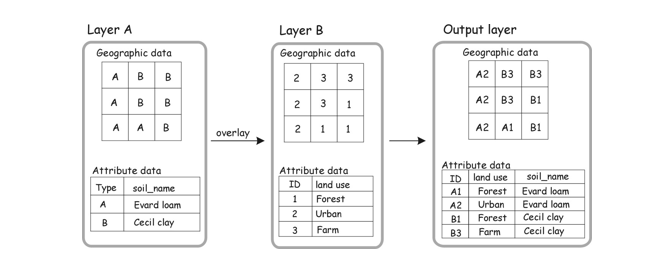
Map algebra
A language for combining data layers by applying a combination of operators (mathematical, Boolean. relational) to create new data layers.
Mathematical functions
Here are examples of operations that you can use in map algebra:
Arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division)
Statistical operations (minimum, maximum, average, median)
Relational operations (greater than, smaller than, equal to)
Trigonometric operations (sine, cosine, tangent, arcsine)
Exponential and logarithmic operations (exponent, logarithm).
Mathematical map algebra
Local operations
Global operations
Focal operations
Zonal operations
Local operations
Map algebra on a cell-by-cell basis.
E.g. two rasters stacked on top of one another, you add each cell one by one.
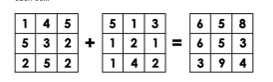
Global operations
Apply a bulk change to all cells in a raster.
E.g. add a value of 1 to all grid cells.
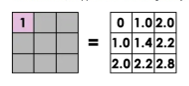
Focal operations
Spatial functions that compute an output value of each cell using neighborhood values.
Can be used to smooth an image.
Zonal operations
Apply a math function to a group of cells within a specified zone.
E.g. to find out how much rain is in a watershed.
Boolean map algebra
Cells that meet criteria are coded in the output raster with a 1, while those that are false receive a 0.
Can be raster or vector.
Relational map algebra
Evaluates specific conditions such as where the slope is less than 10 degrees.
Will output a true (1) and a false (0).
Raster calculator
Treats a layer like a variable in an equation.