Lab 12 - Spinal cord, PNS & special senses
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
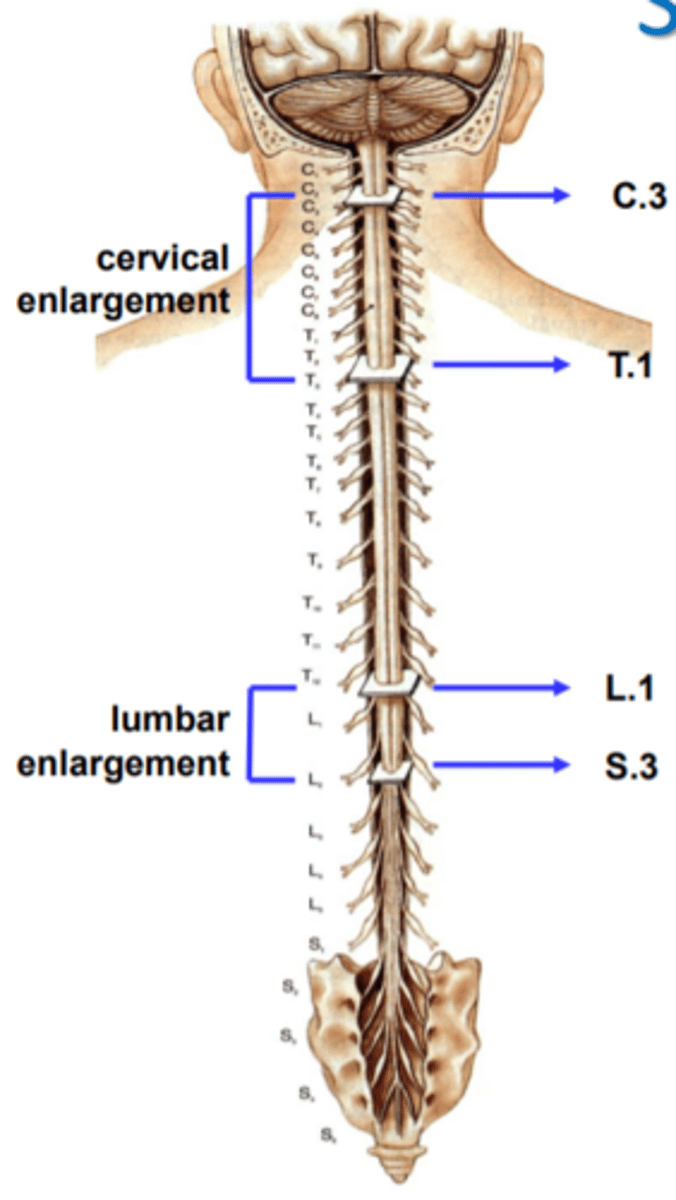
cervical enlargement (1)
in cervical region
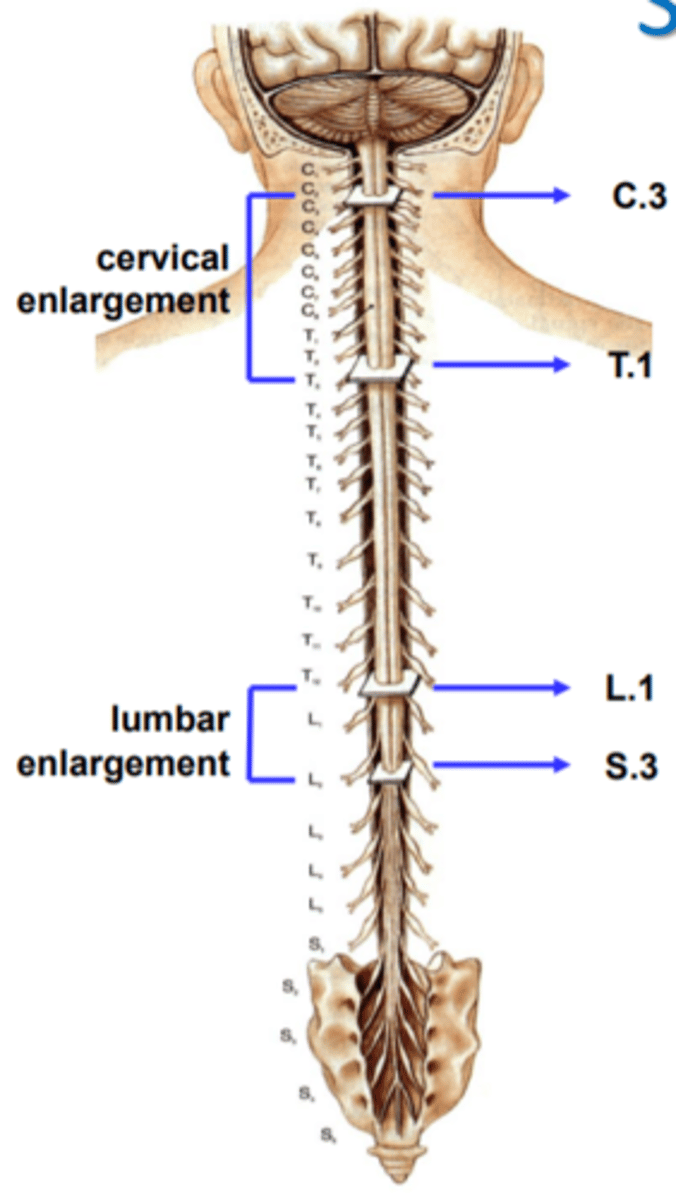
Lumbar enlargement (2)
in lumbar region
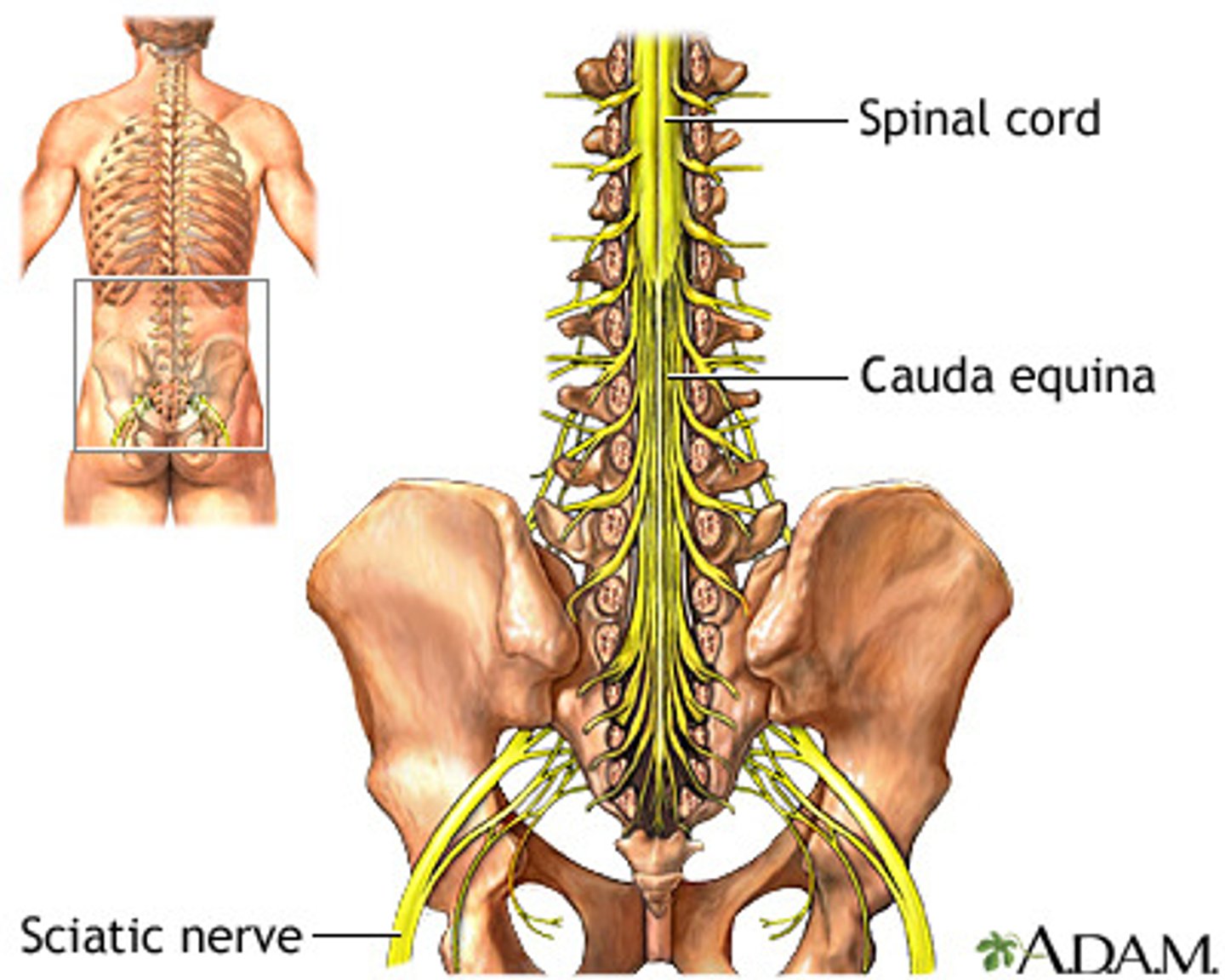
conus medullaris (3)
cone shaped end of spinal cord between L1 & L2
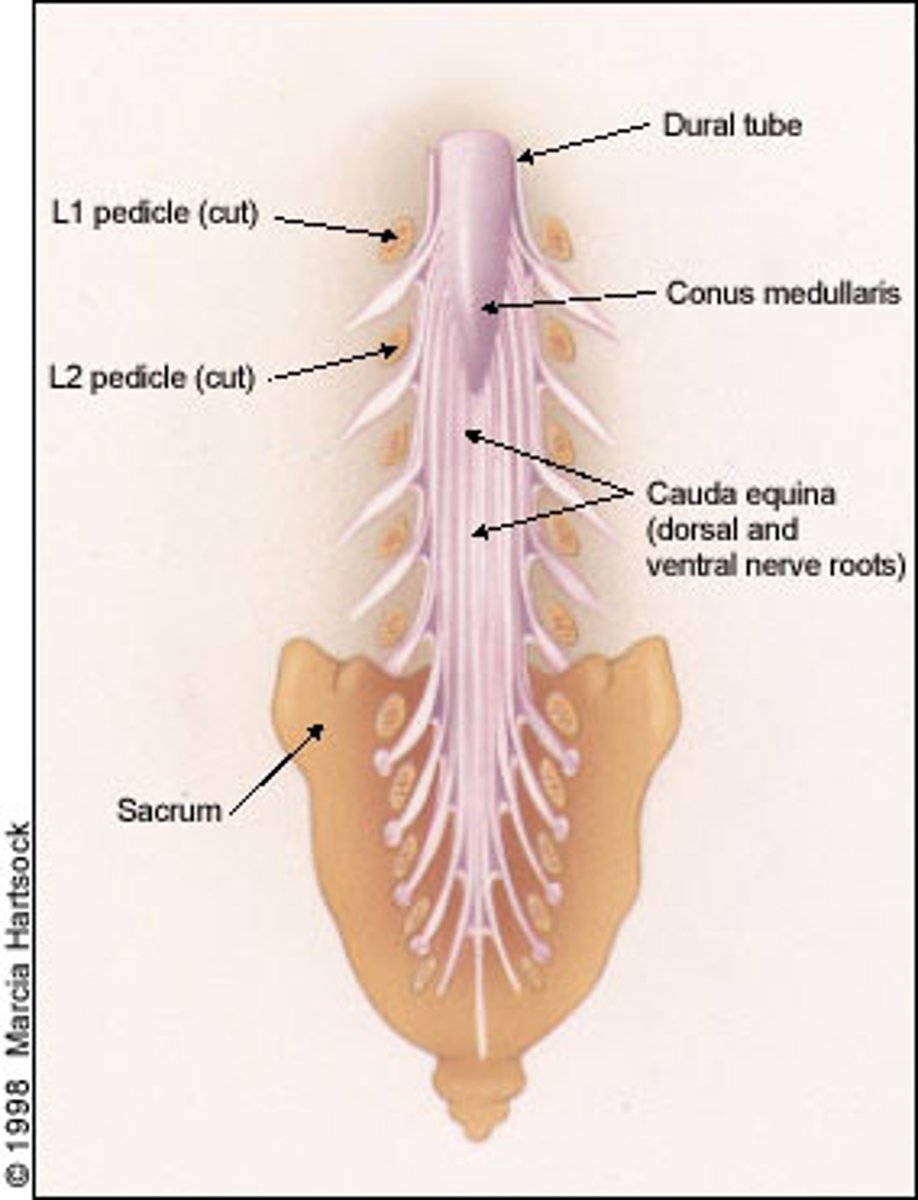
Cauda equina (4)
bottom of spine
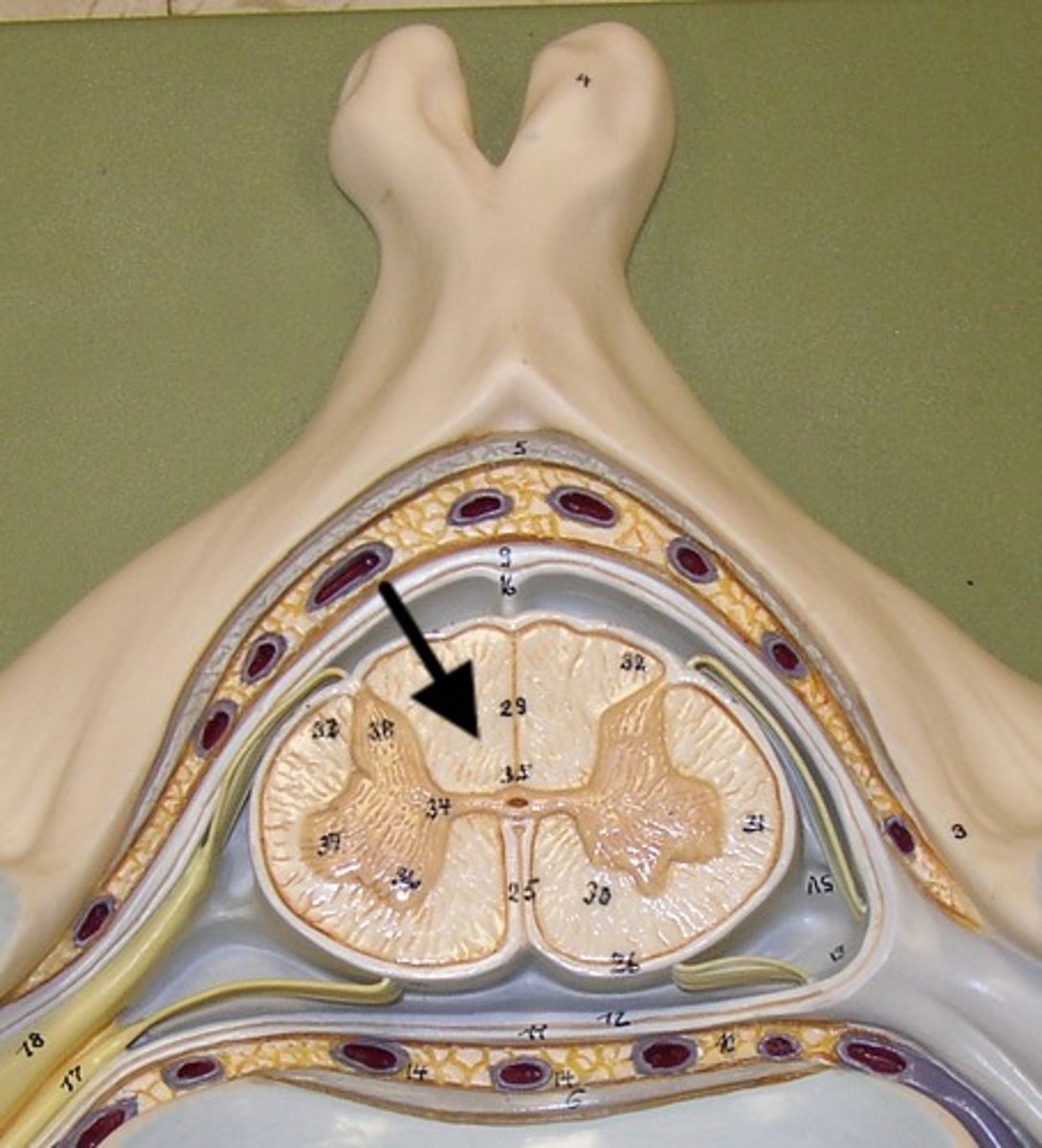
Central canal
In the middle of spinal cord
White matter
contains myelinated axons; relays messages
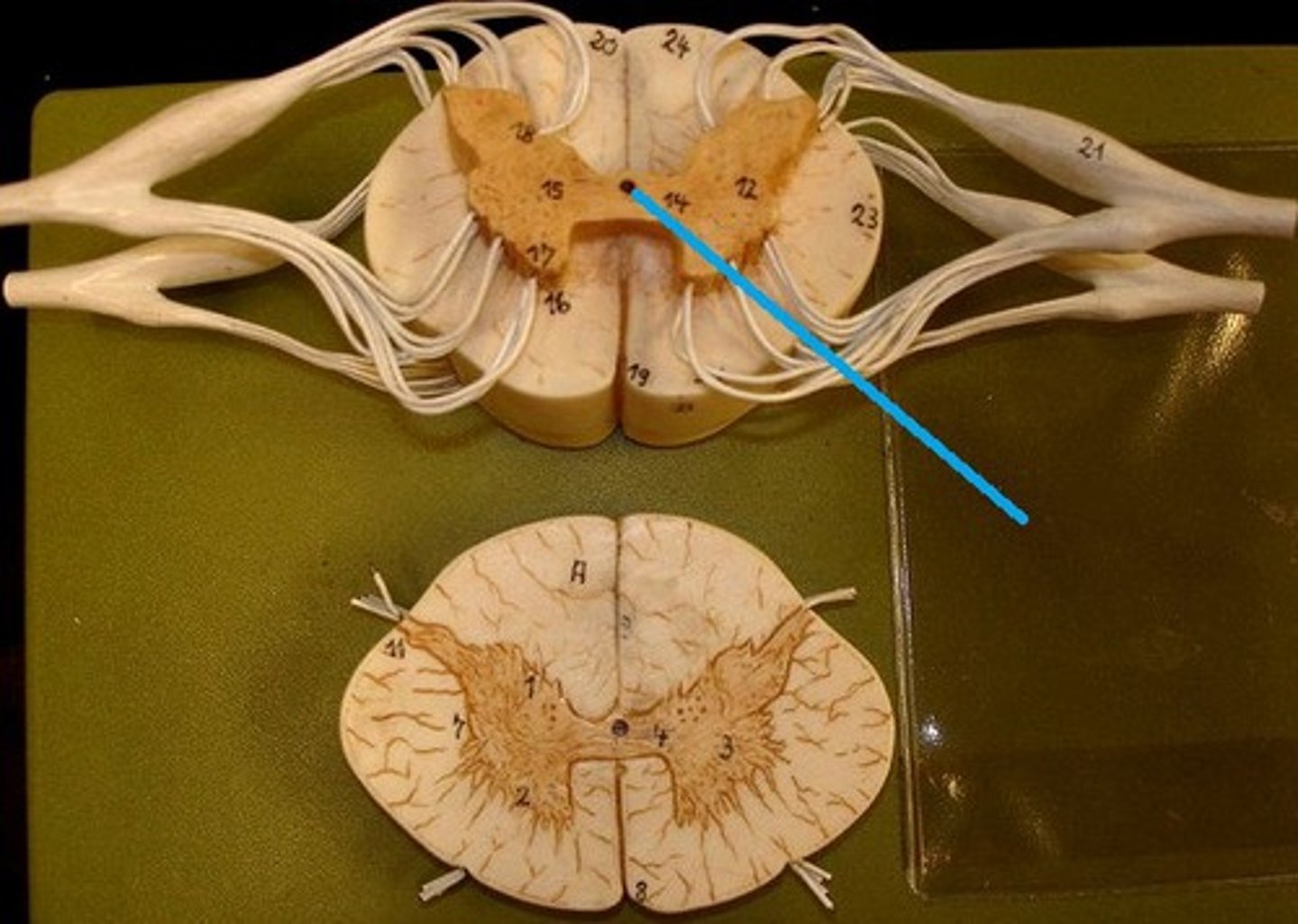
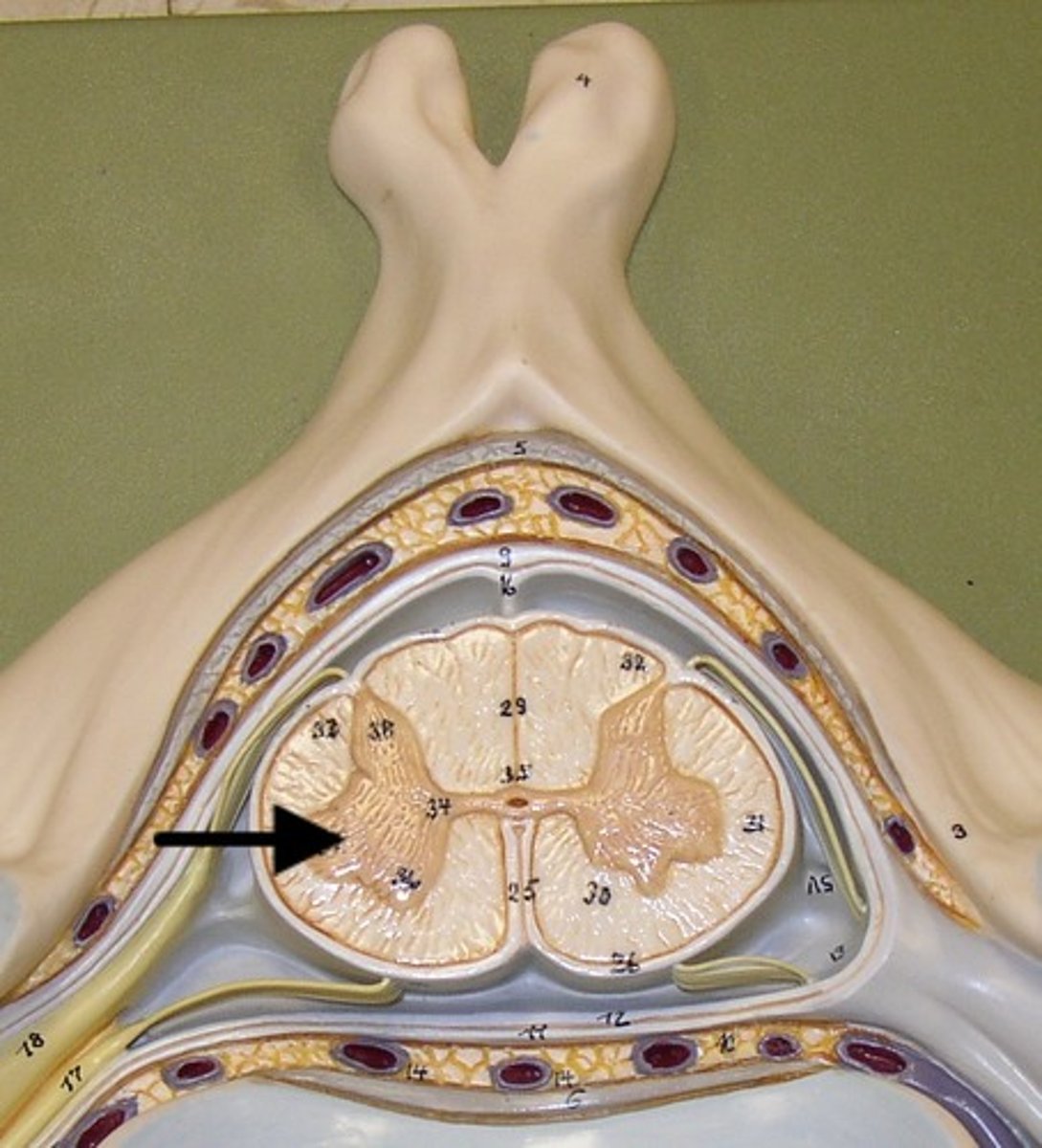
grey matter
contains cell bodies
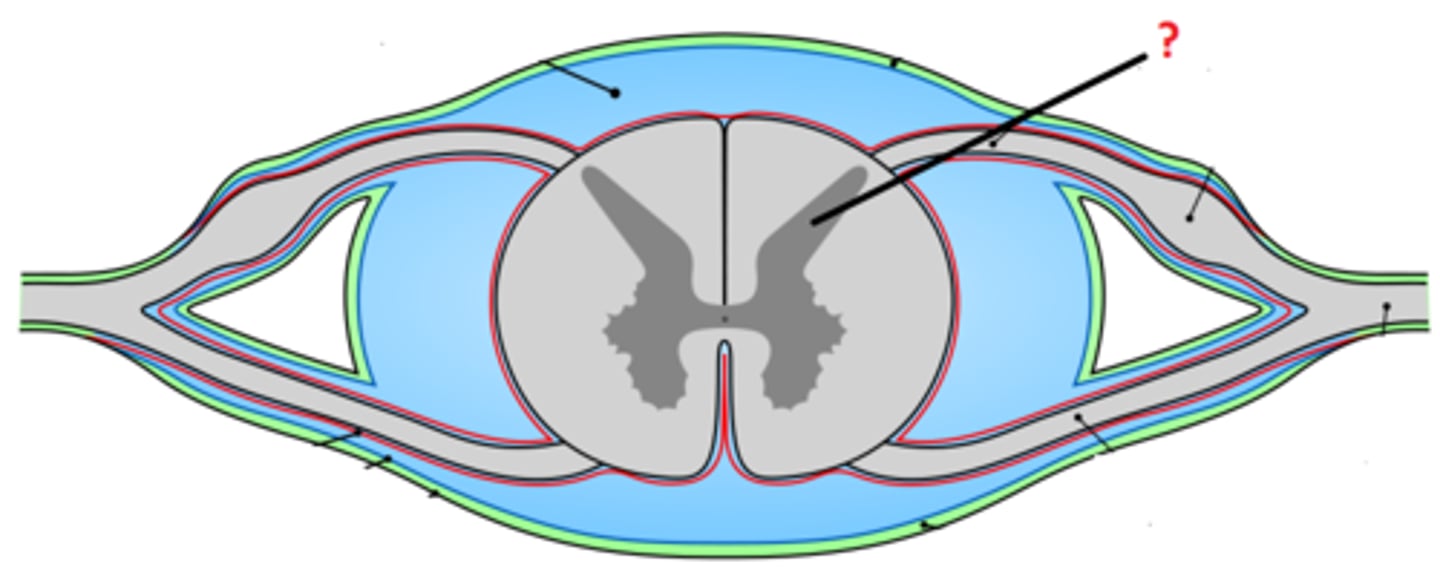
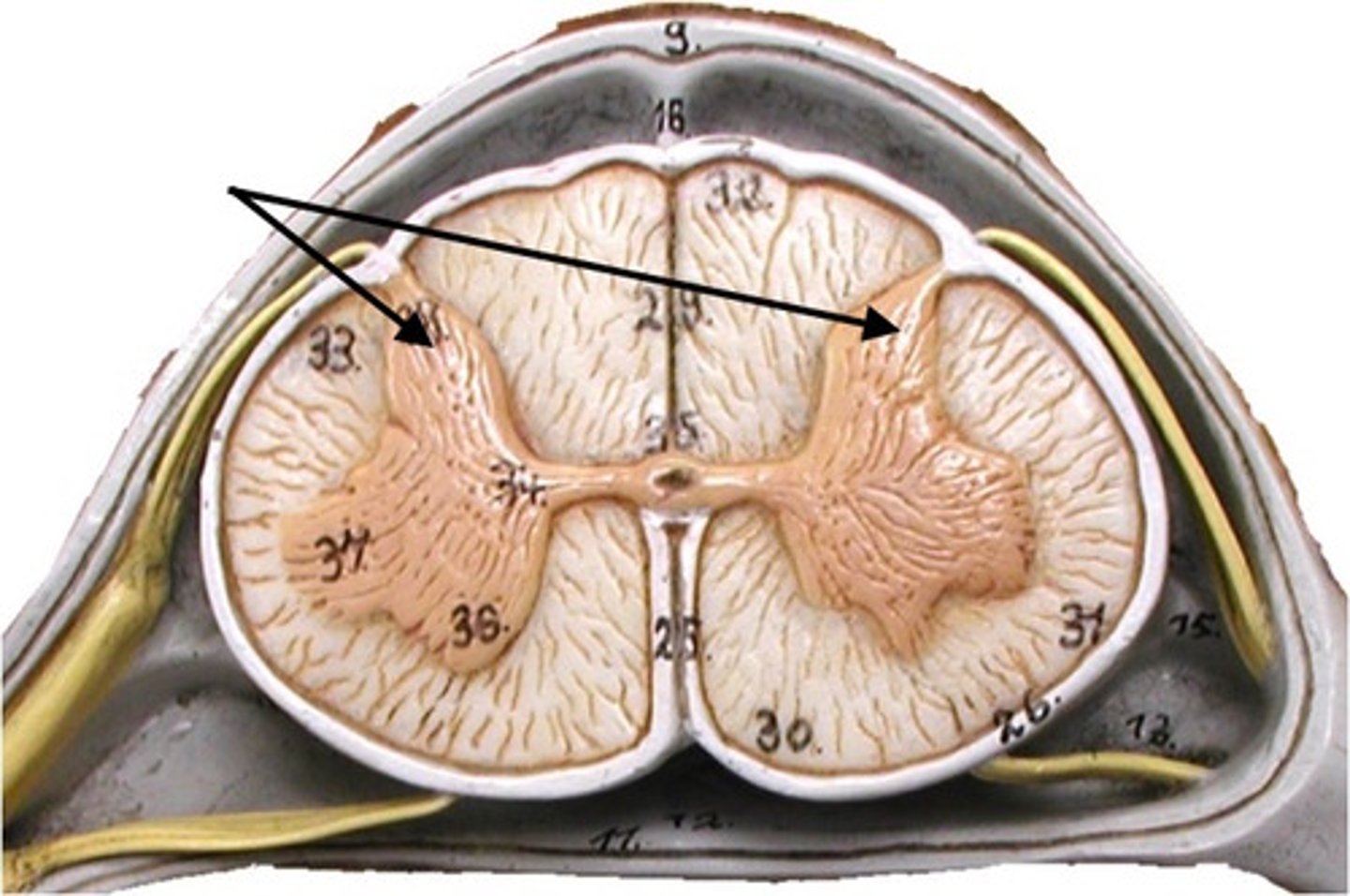
dorsal (posterior) horns
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
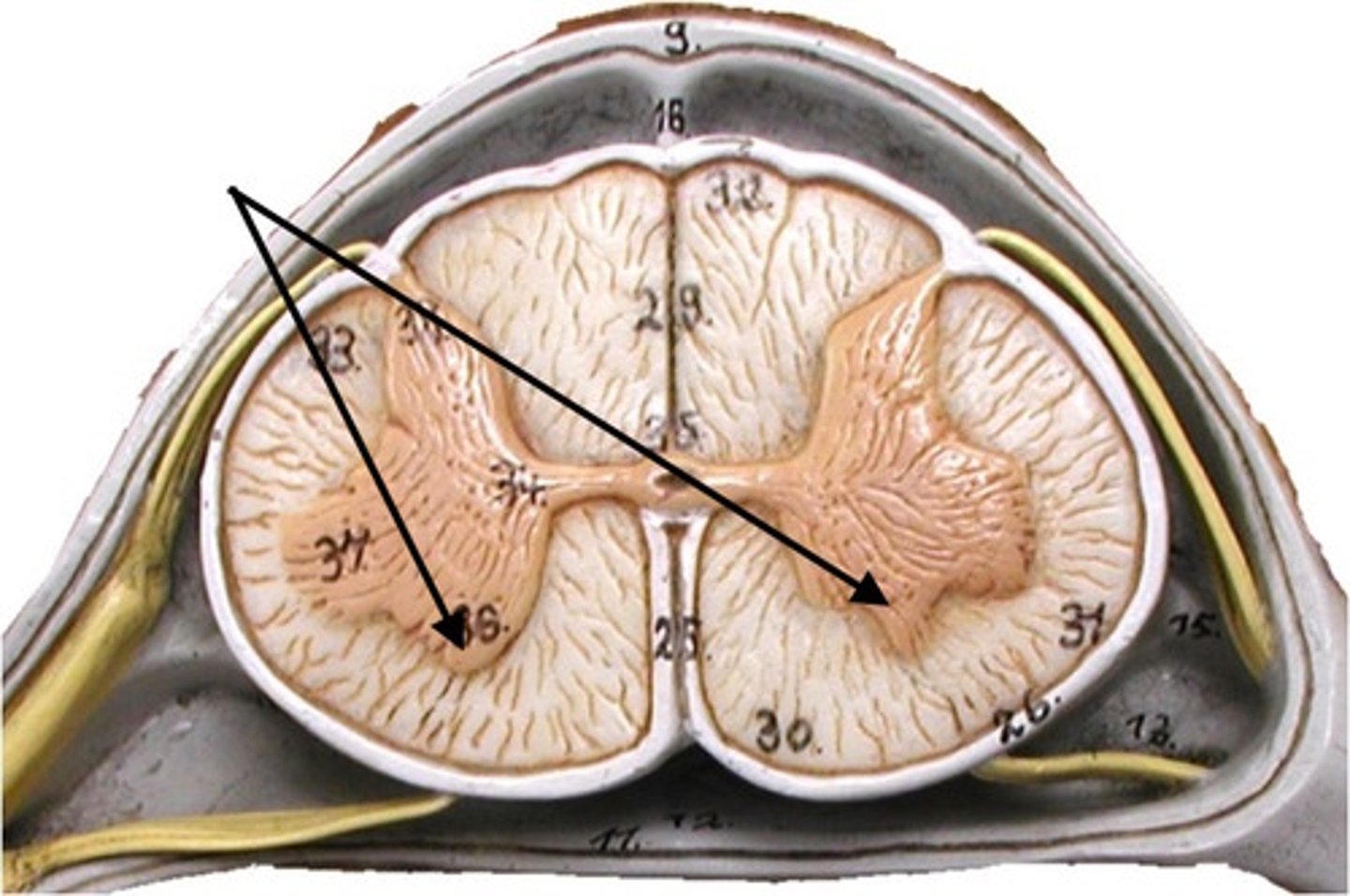
Ventral ( anterior ) horns
contains cell bodies of somatic motor neurons
Lateral horns
contians cell bodies of visceral motor( autonomic) neurons
spinal nerve
begins at junction of a dorsal and a ventral root
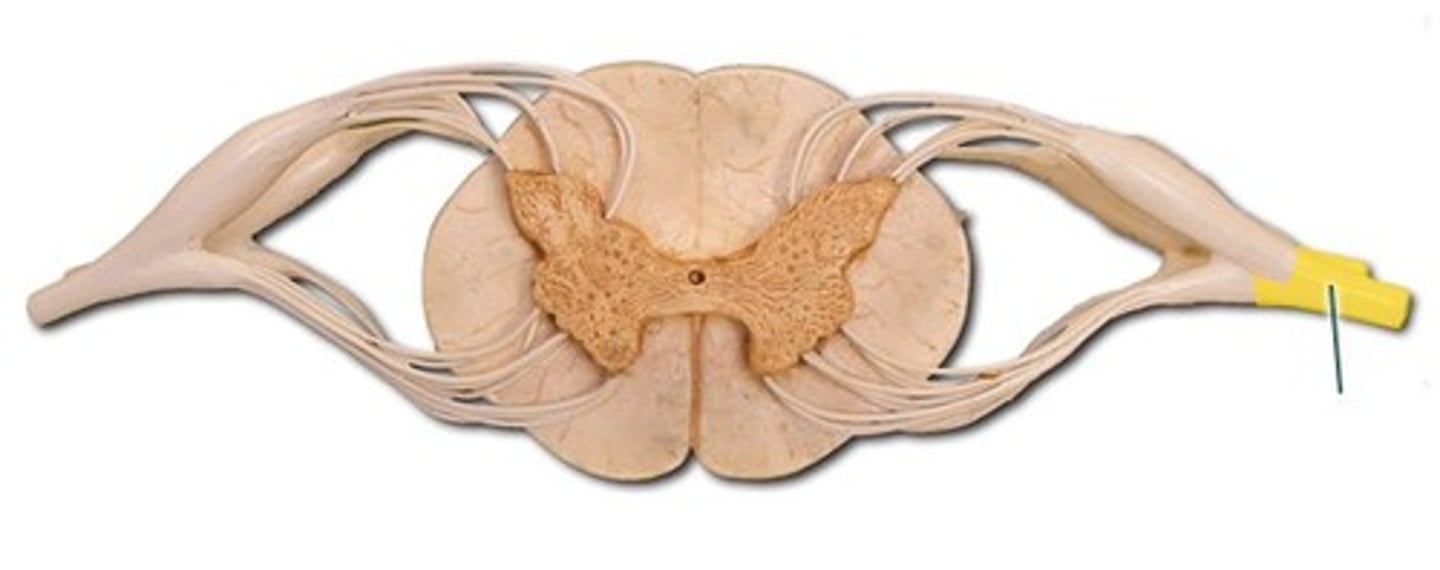
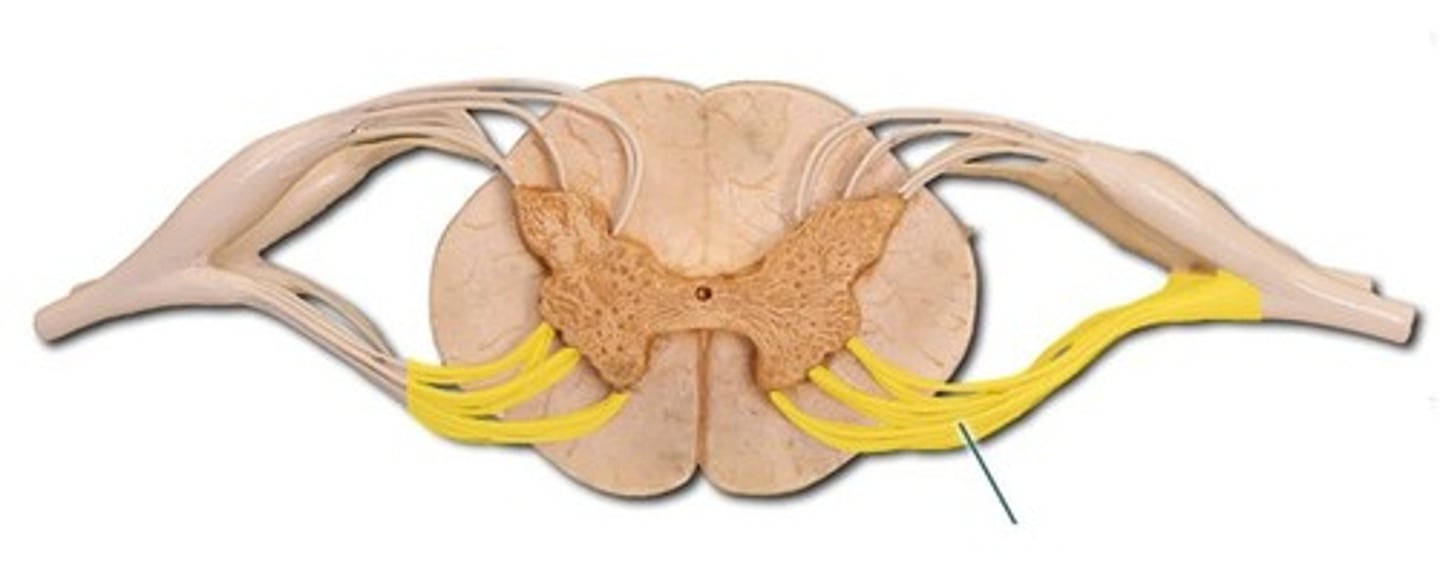
dorsal( posterior) root of spinal nerve
Contains sensory neuron axons.
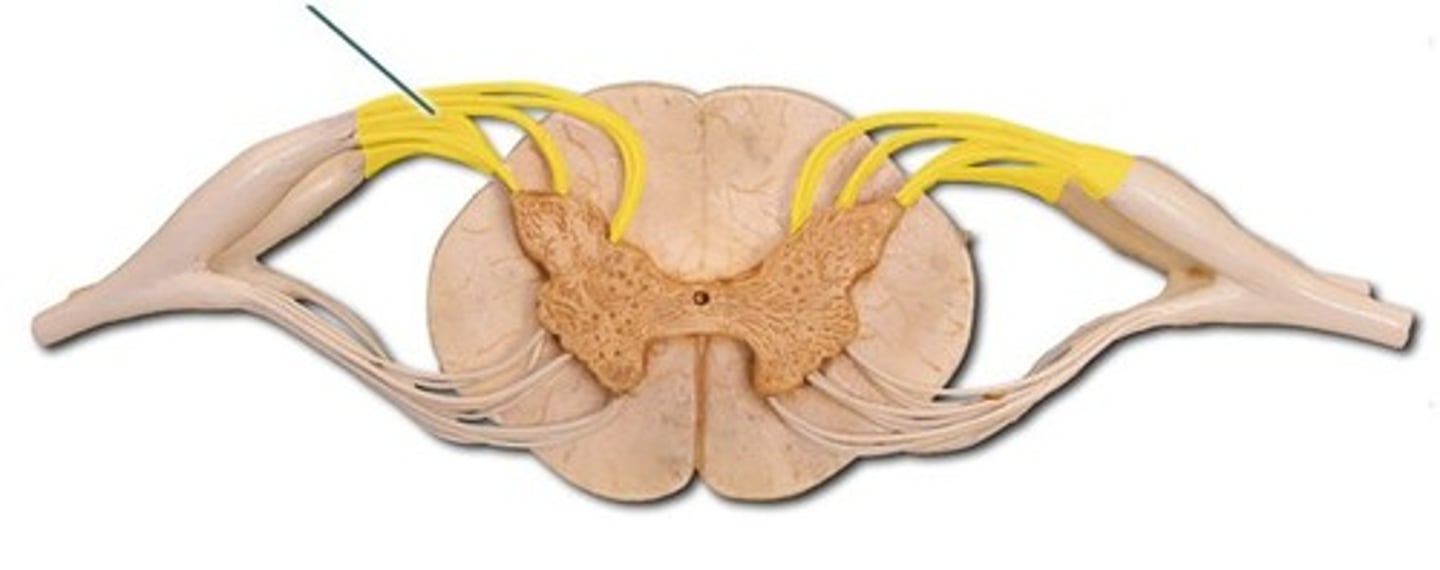
dorsal ( posterior) root ganglion
Enlarged area connects to dorsal root; sensory
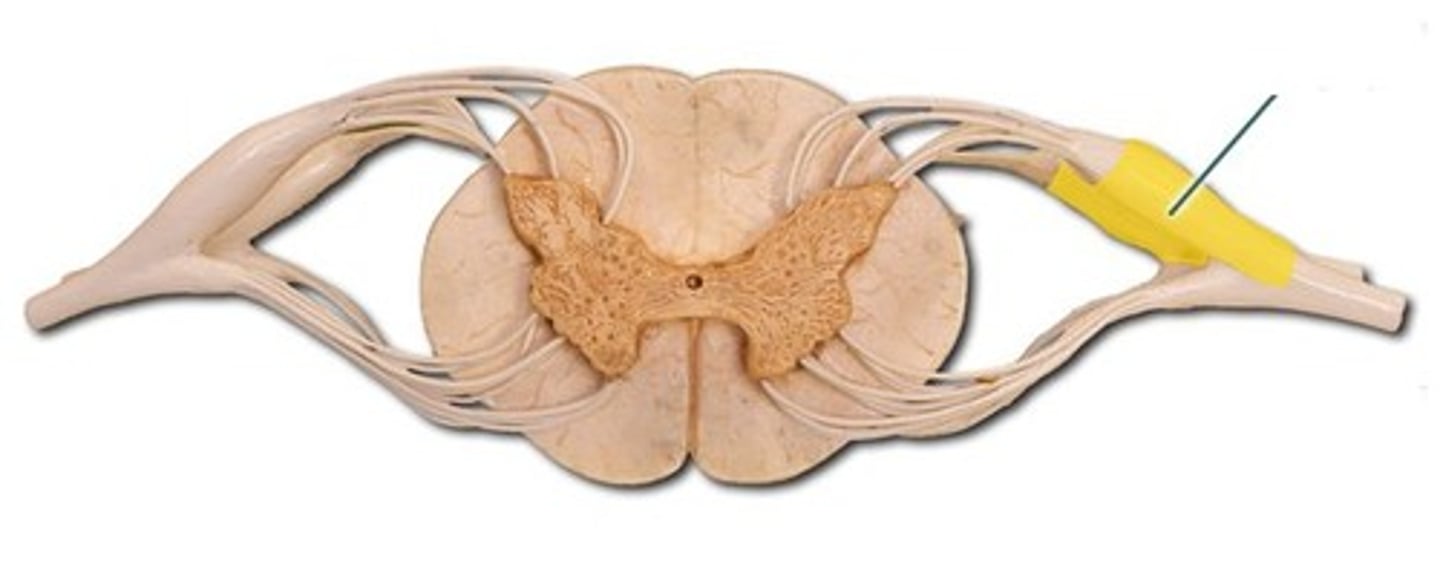
Ventral ( anterior) root of spinal nerve
continas motor neuron axons
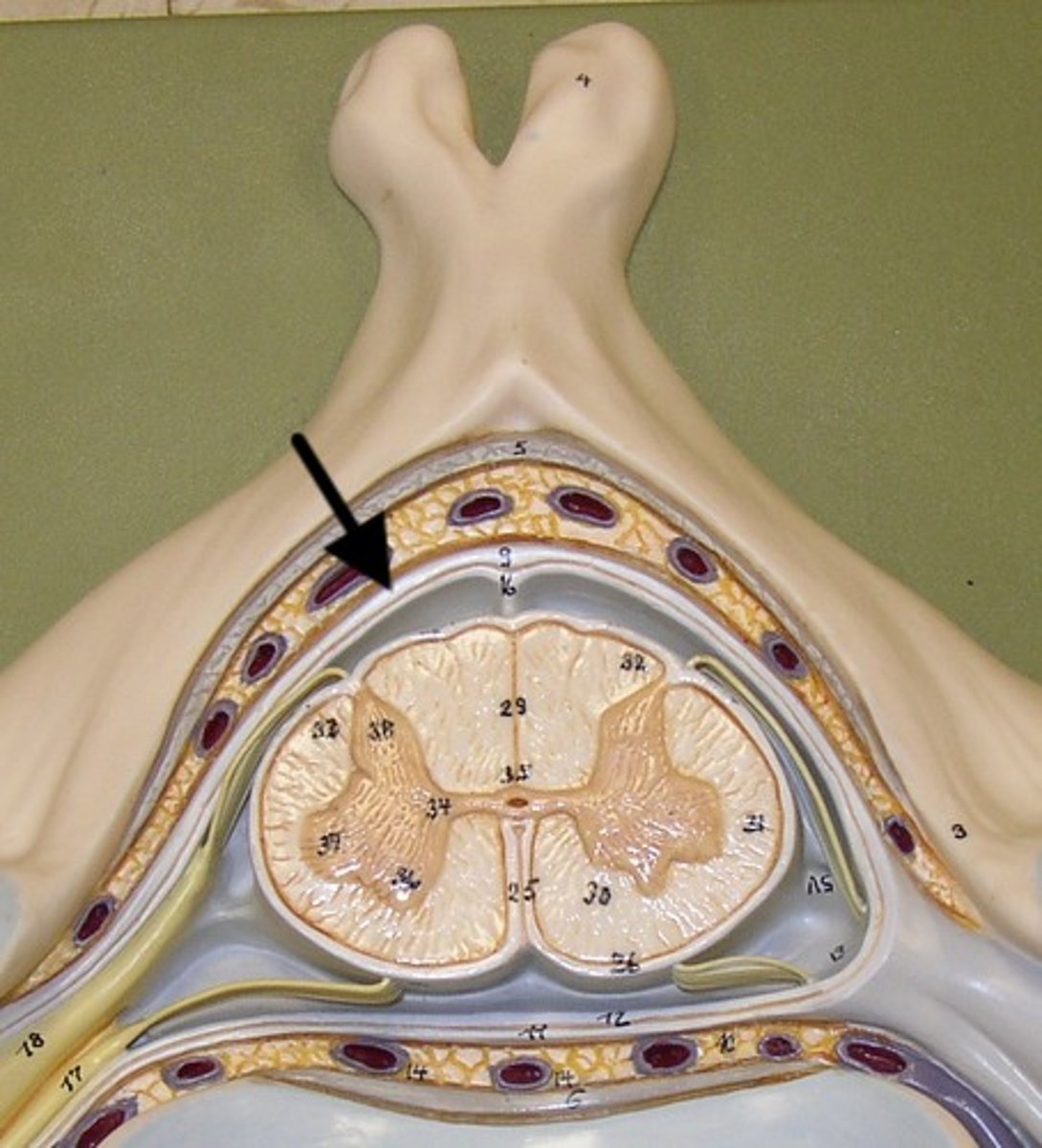
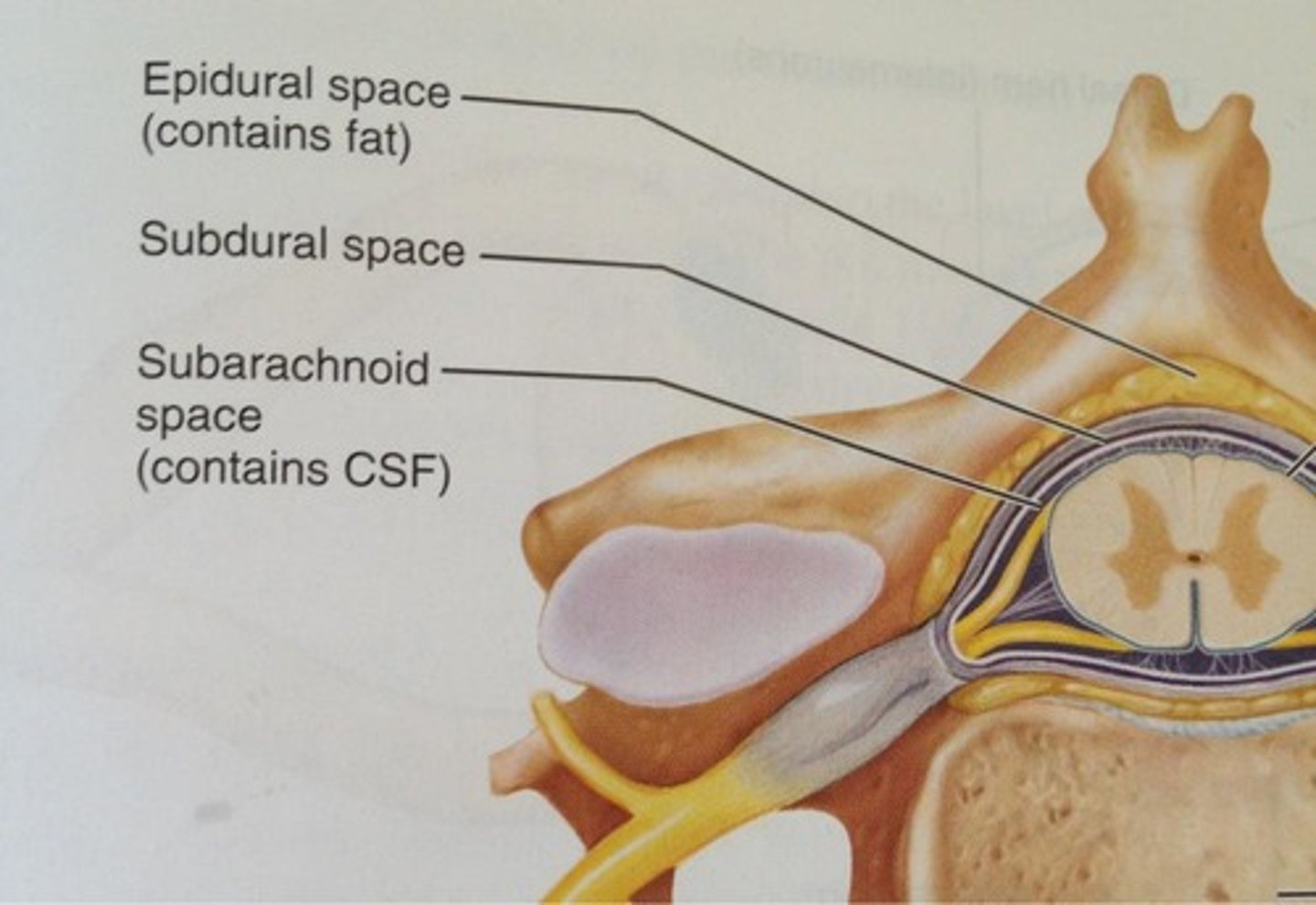
epidural spcae
space between intervertebral foramen and dura mater, contains fat
dura mater
Outermost layer of the meninges
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
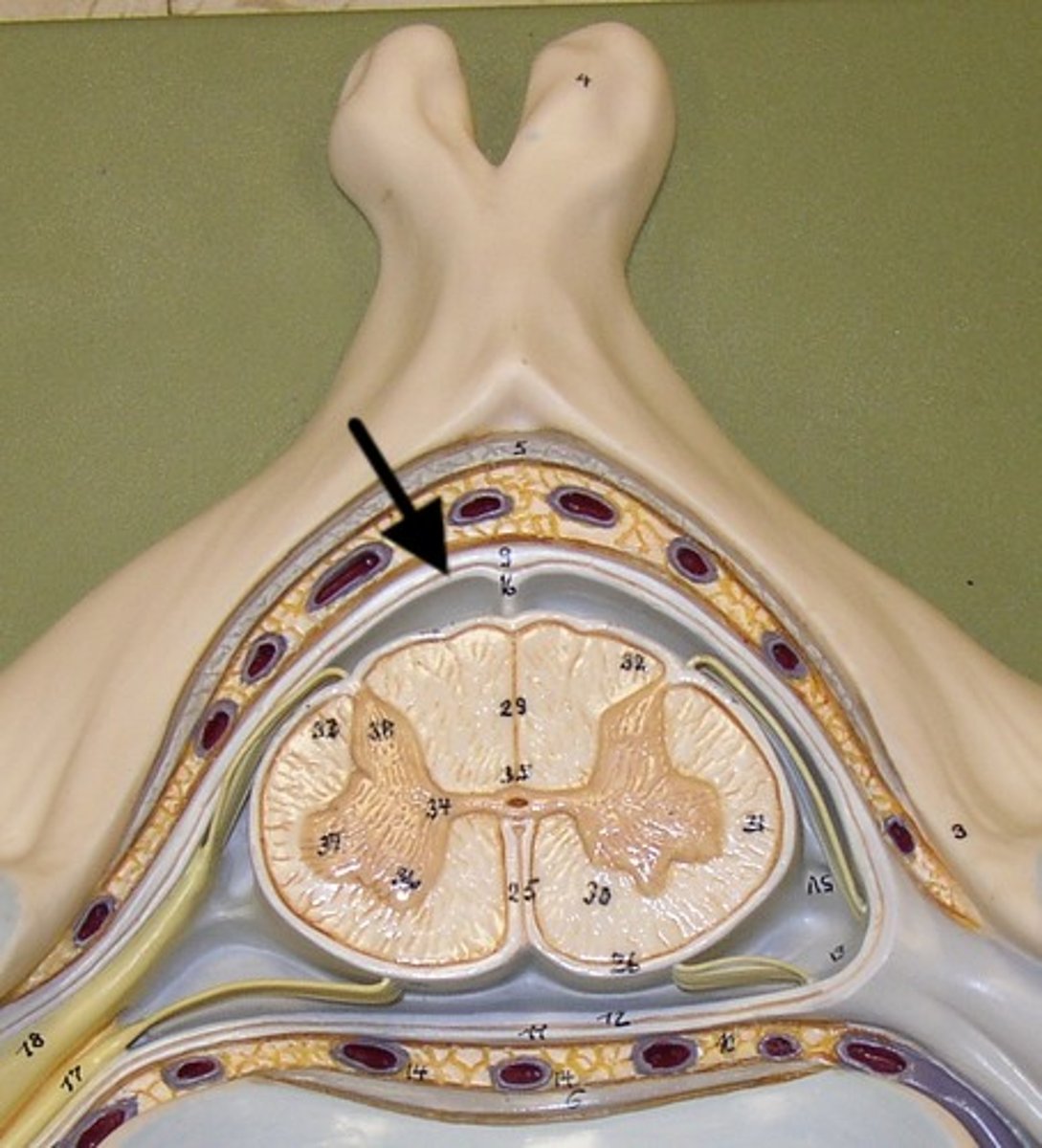
arachnoid mater
middle meningeal layer
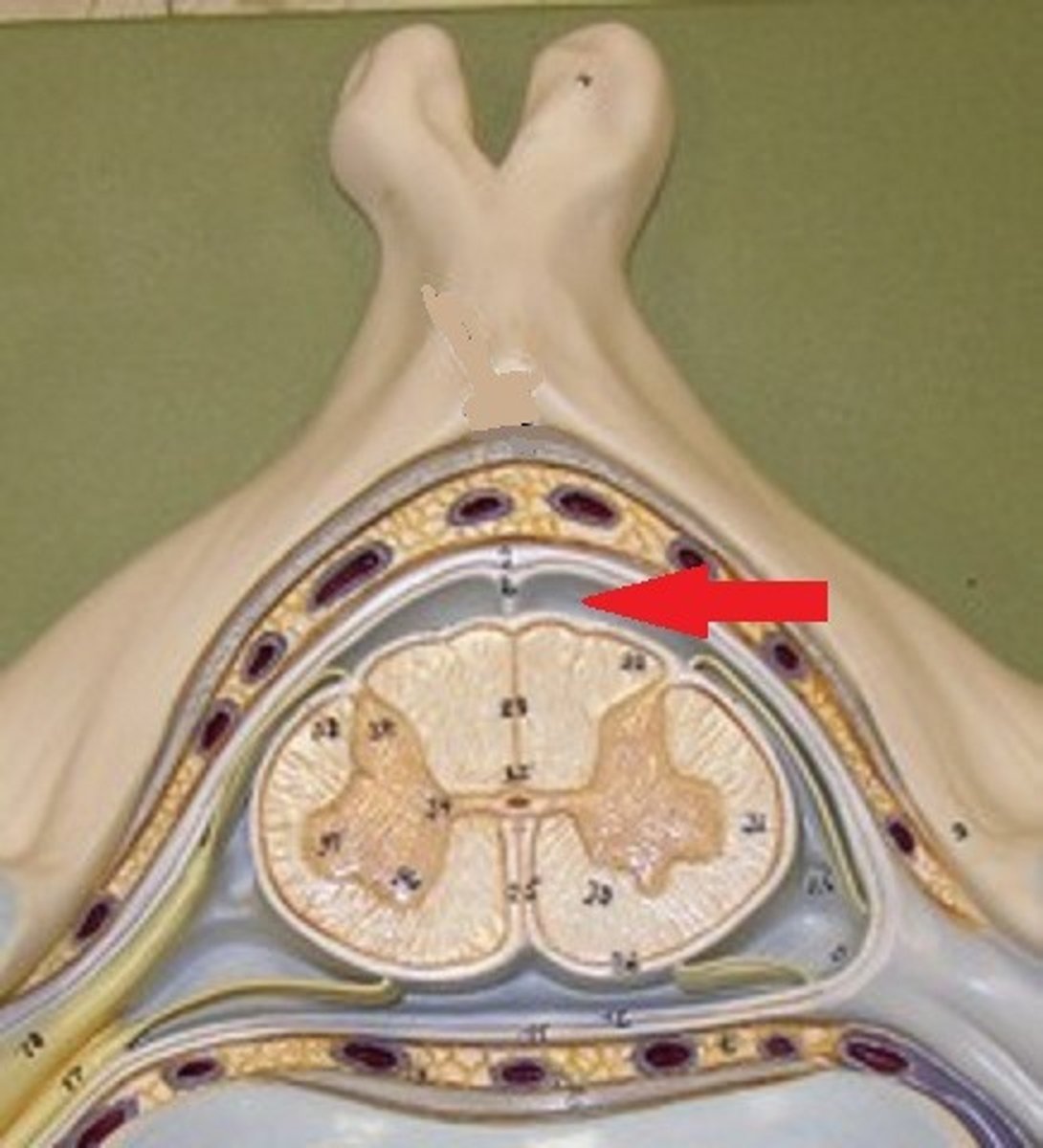
subarachnoid space
Space between arachnoid and pia mater, contains CSF.
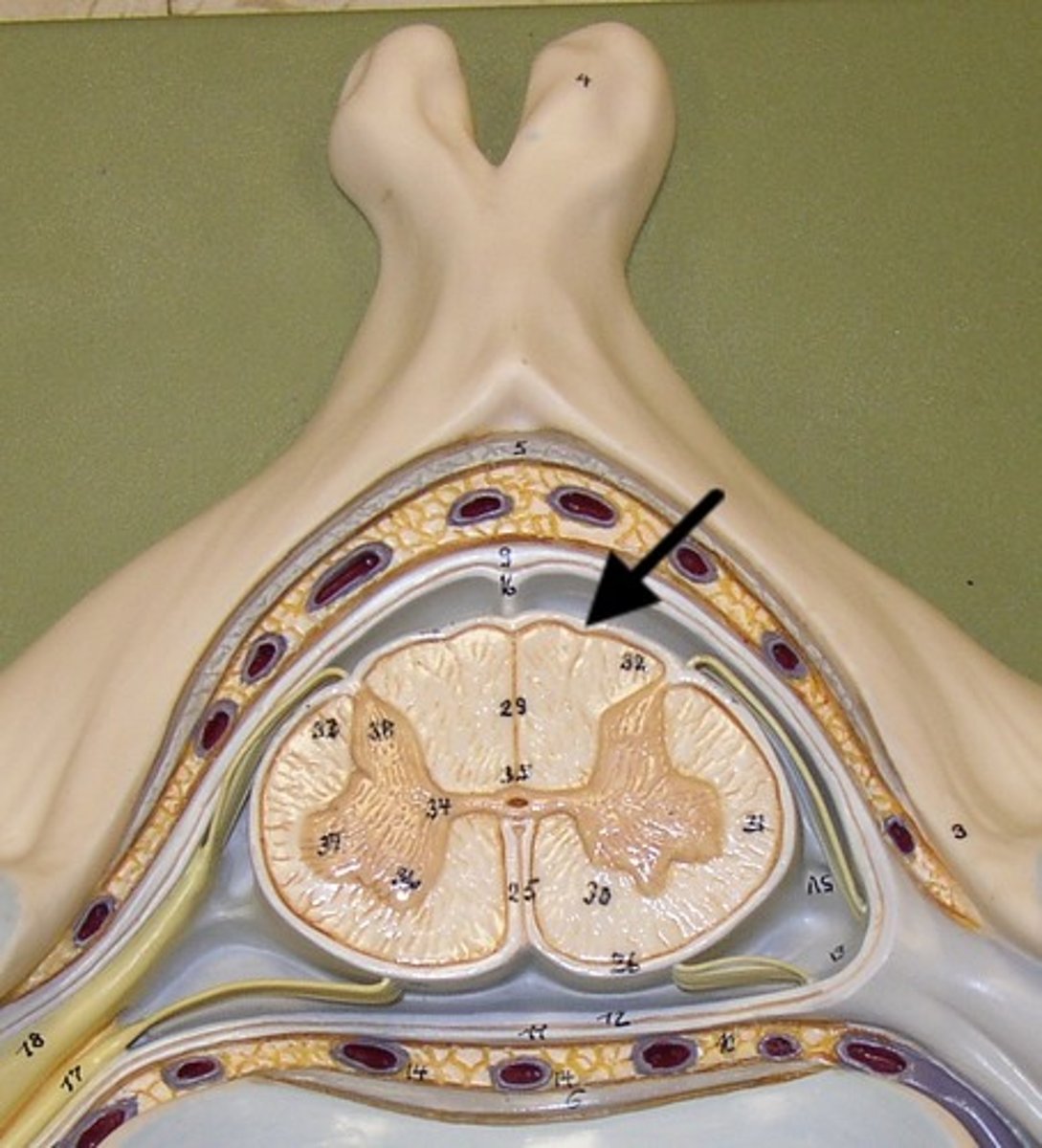
Pia mater
Innermost layer of the meninges
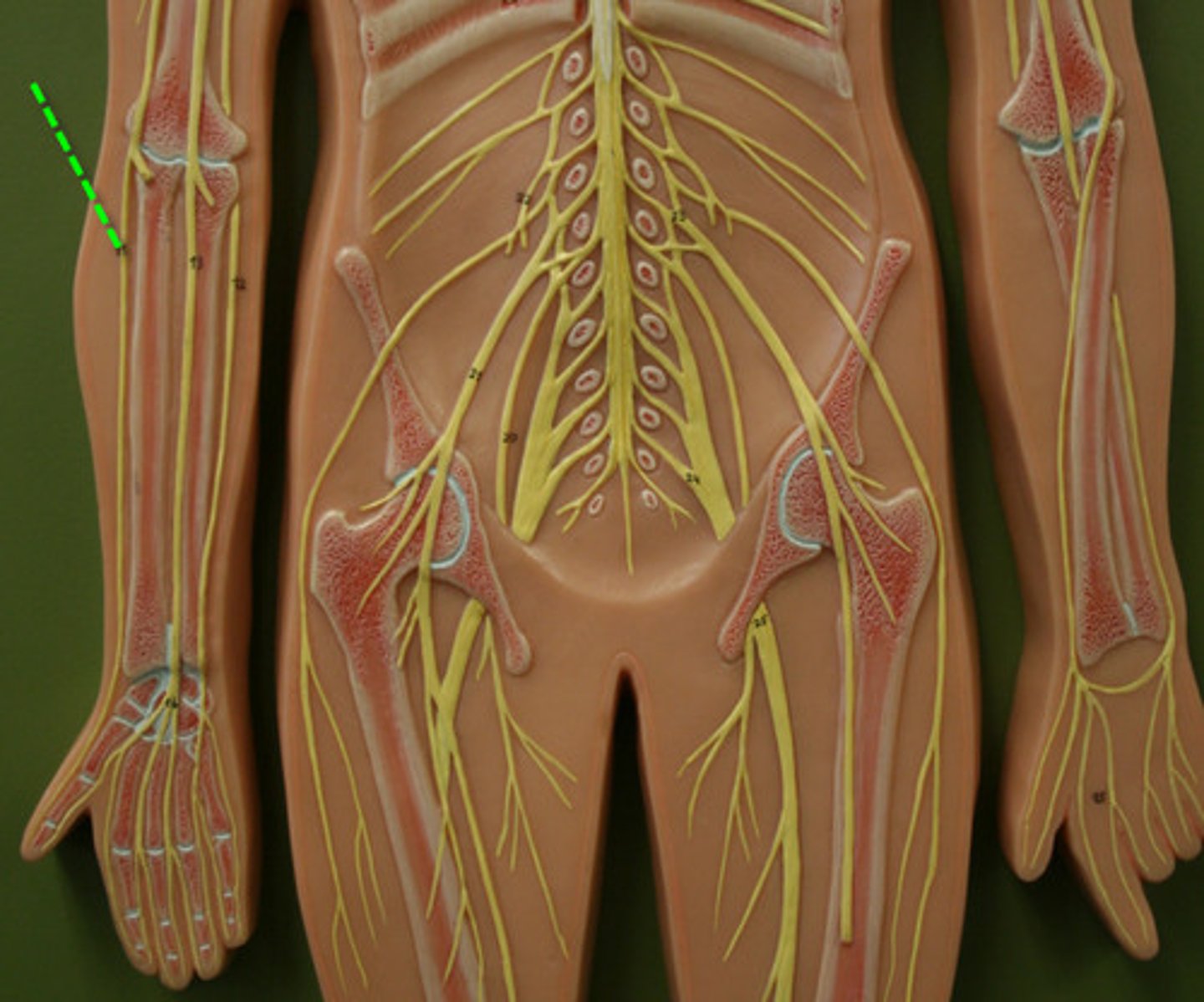
Cervical Nerves
C1-C8
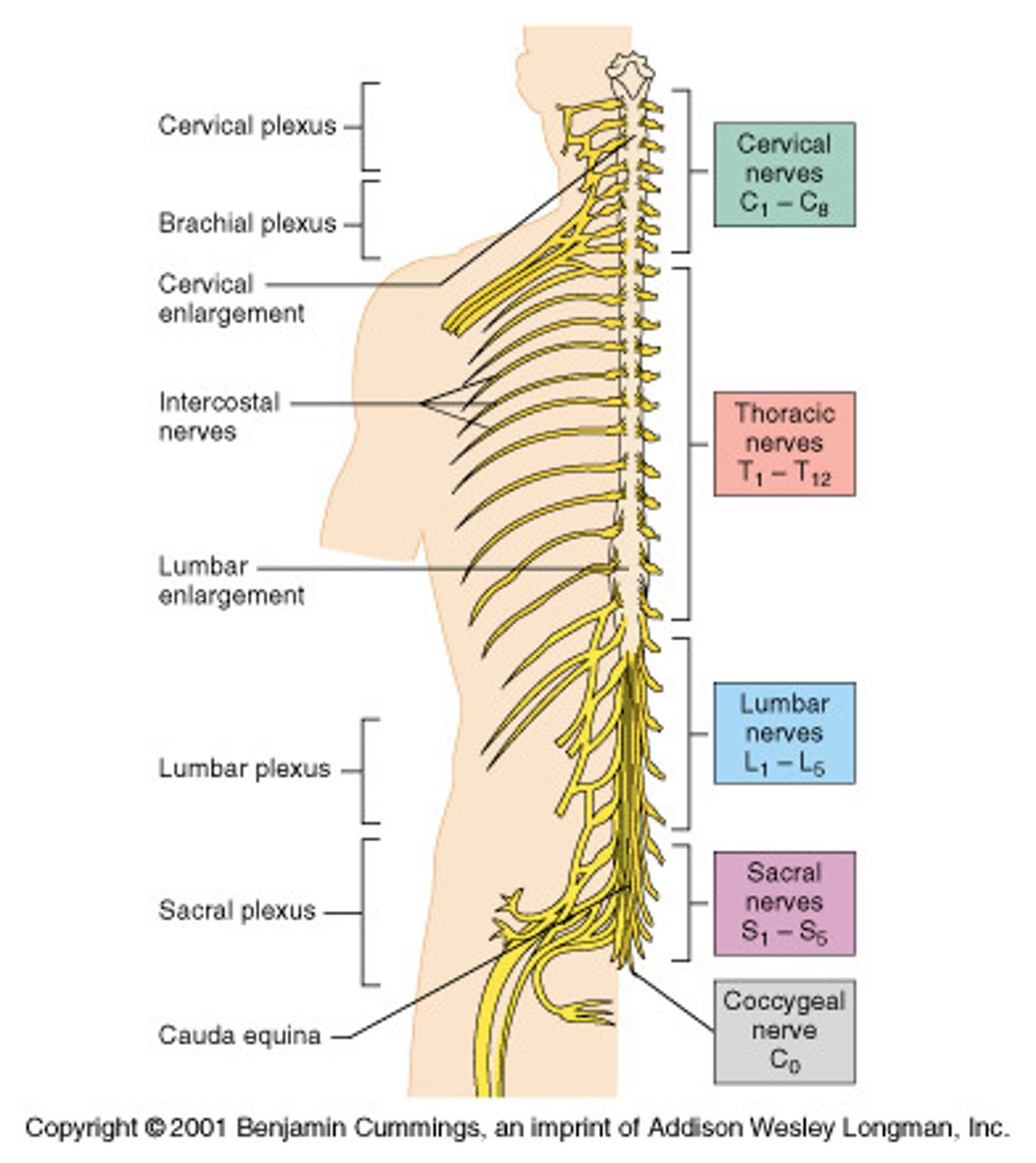
Thoracic nerves
T1-T12
Lumbar Nerves
L1-L5
scaral nerves
S1-S5
coccygal nerve
CO1
cervical plexus
C1-C5
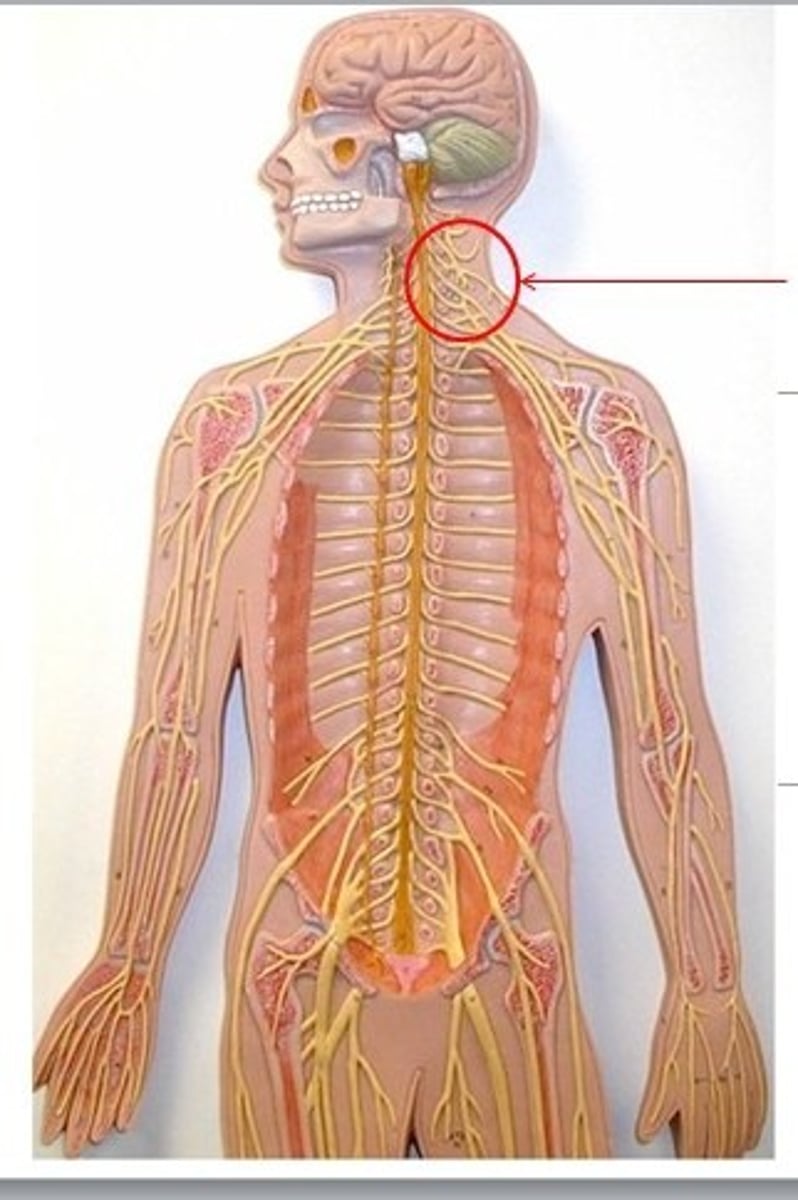
brachial plexus
C5-T1
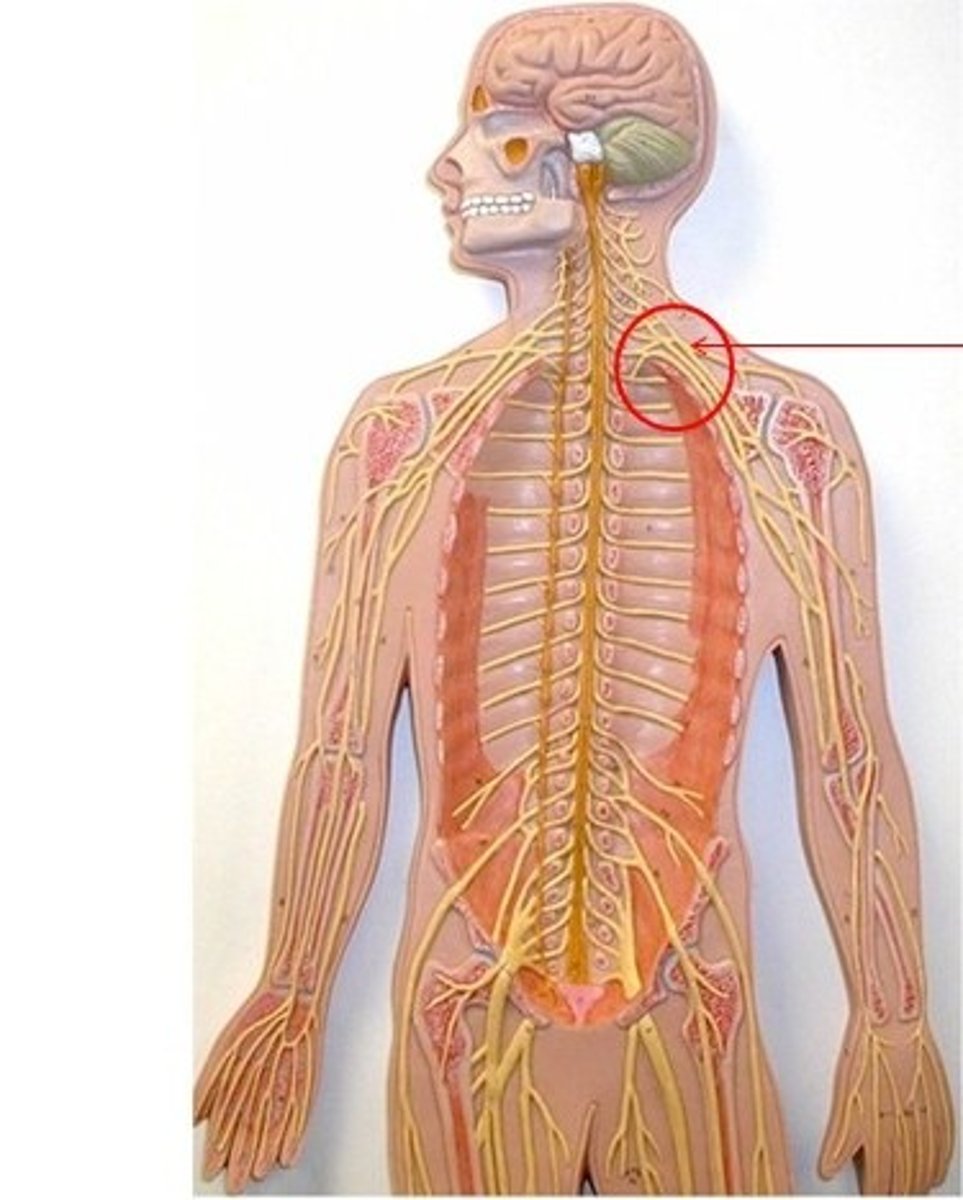
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
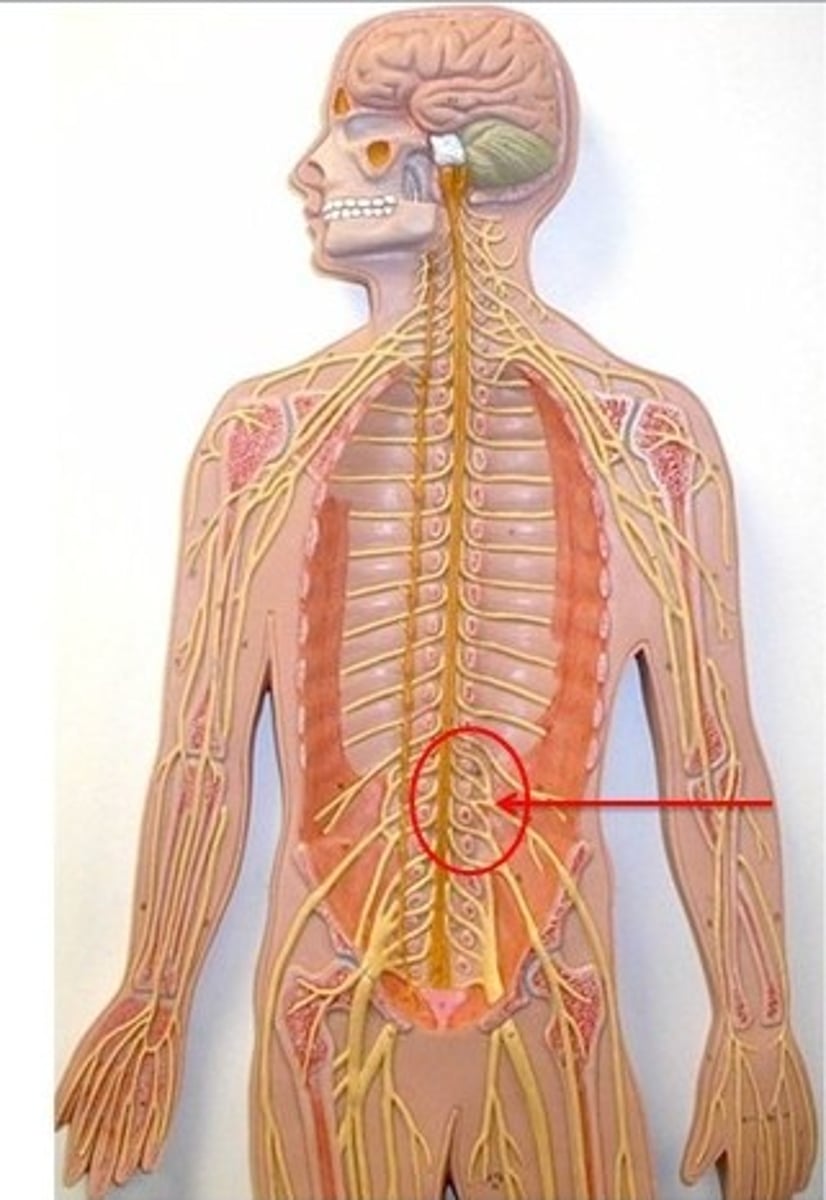
sccral plexus
L4-S4
phernic nerve
Motor: diaphragm
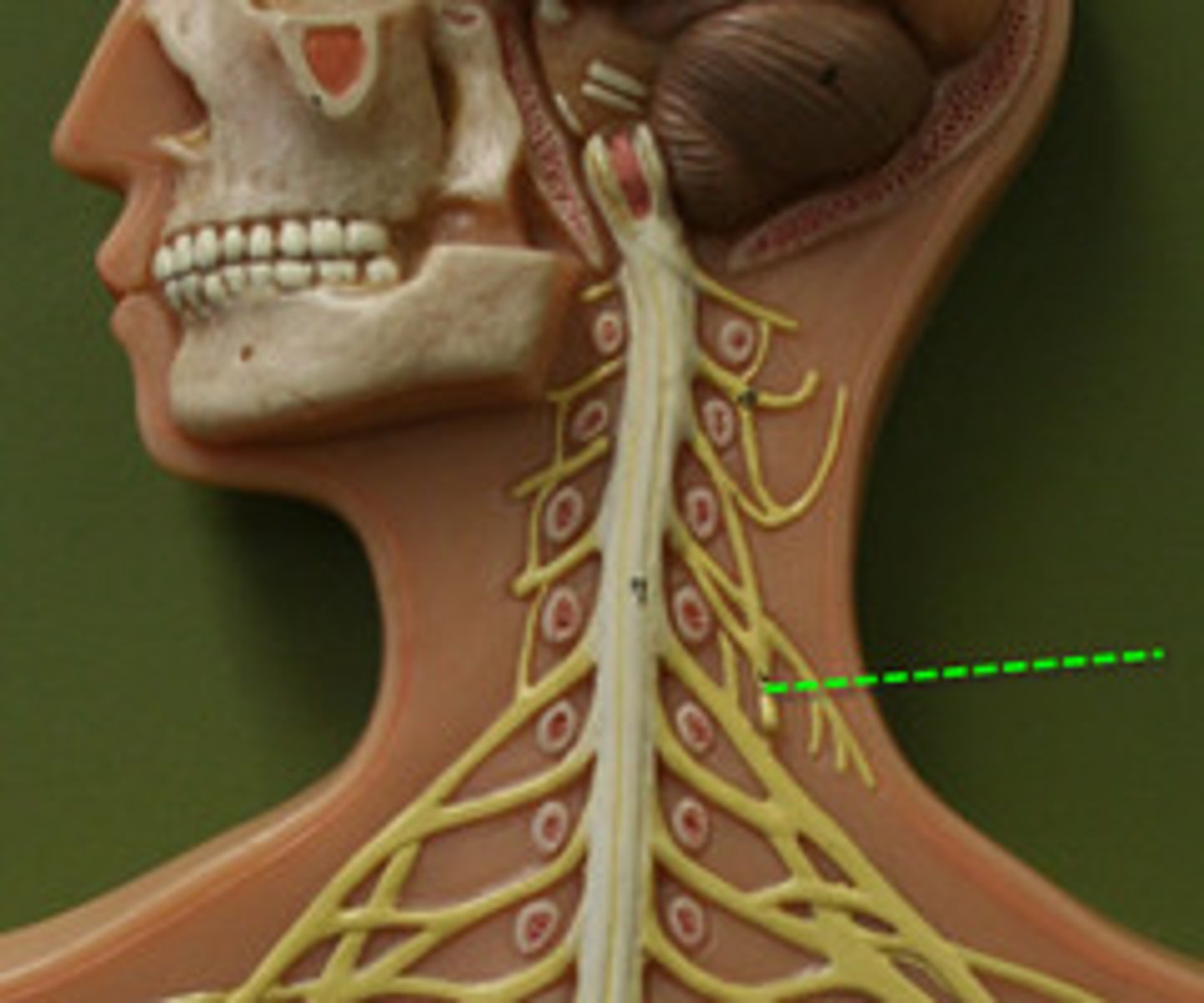
Axillary nerve
motor: shoulder
sensory: shoulder
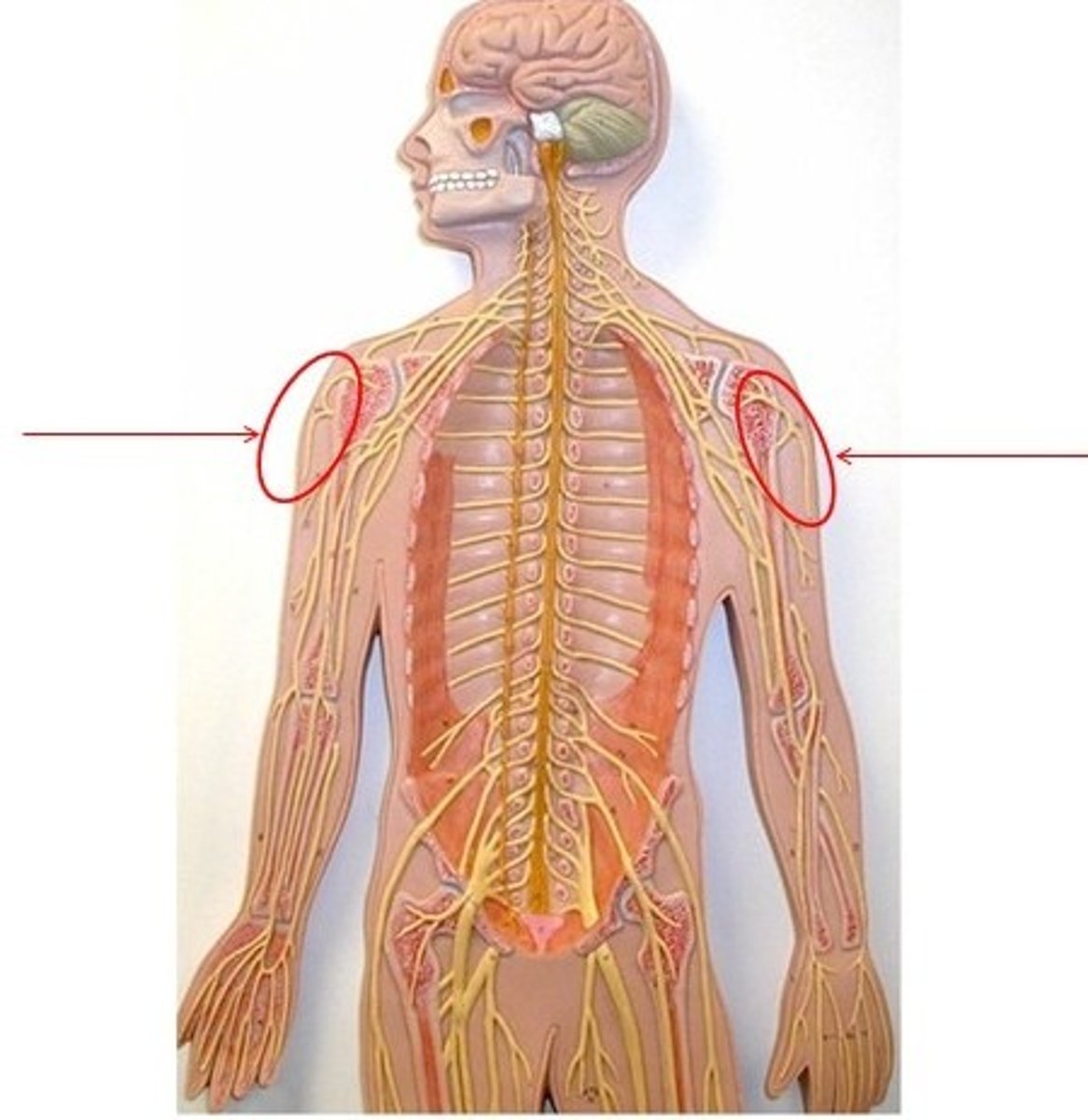
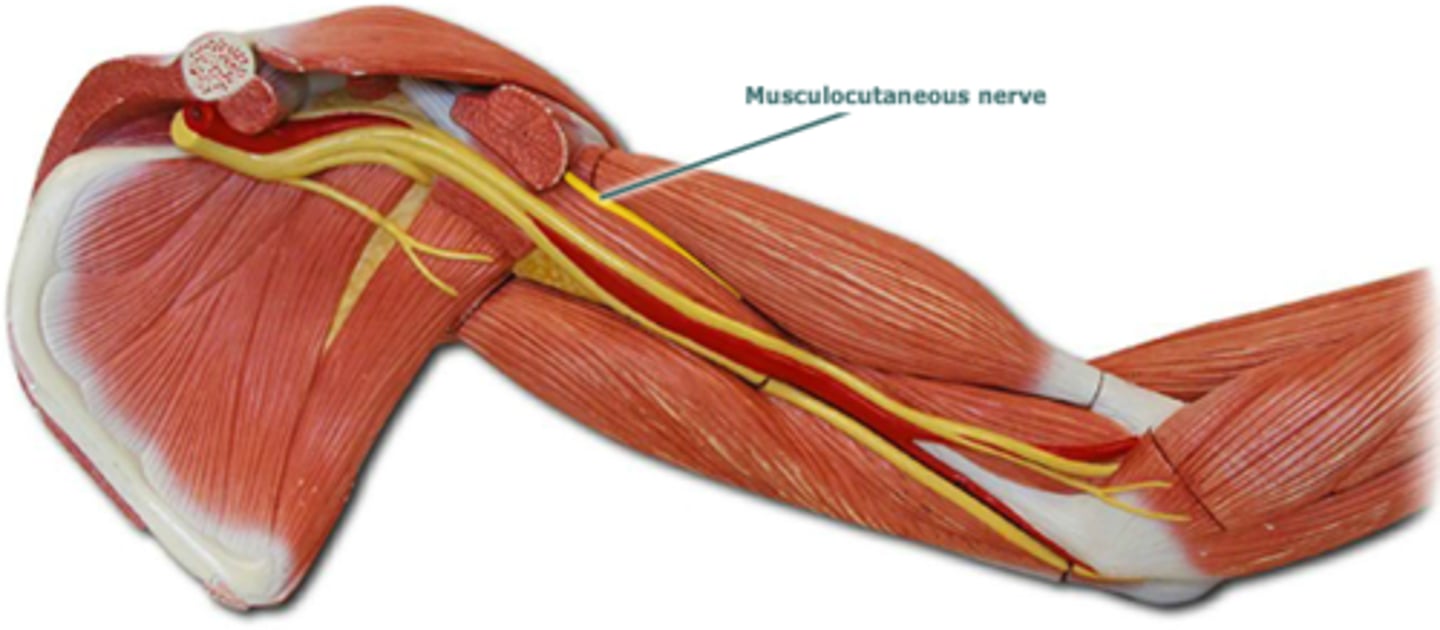
musculocutaneous nerve
motor: anterior arm
sensory: lateral forearm
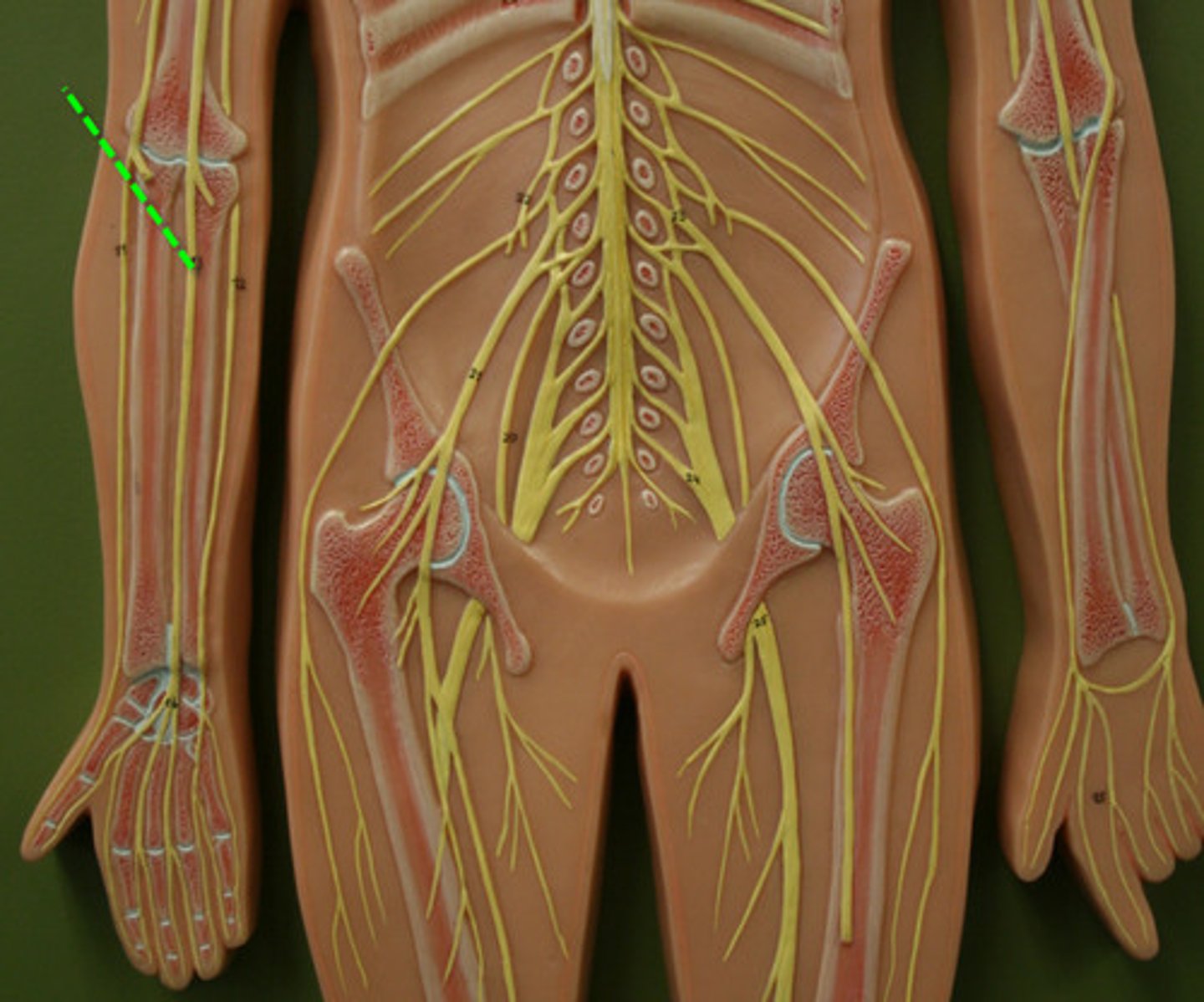
Median nerve
motor: anterior forearm and hand
sensory: lateral hand
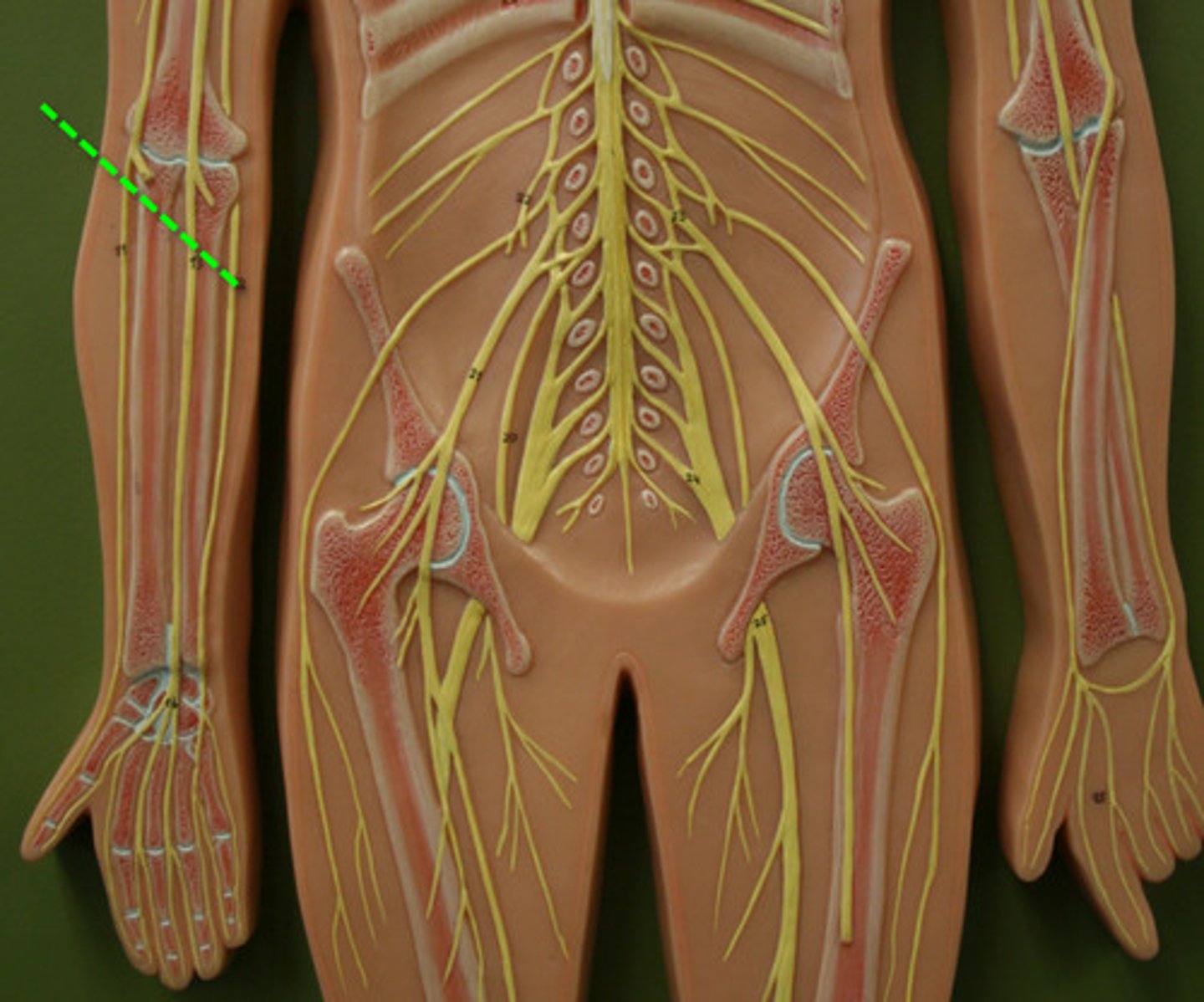
Ulnar Nerve
motor: anterior forearm and hand
sensory: medial hand
Radial nerve
Motor: posterior arm and forearm
sensory: posterior arm, forearm hand
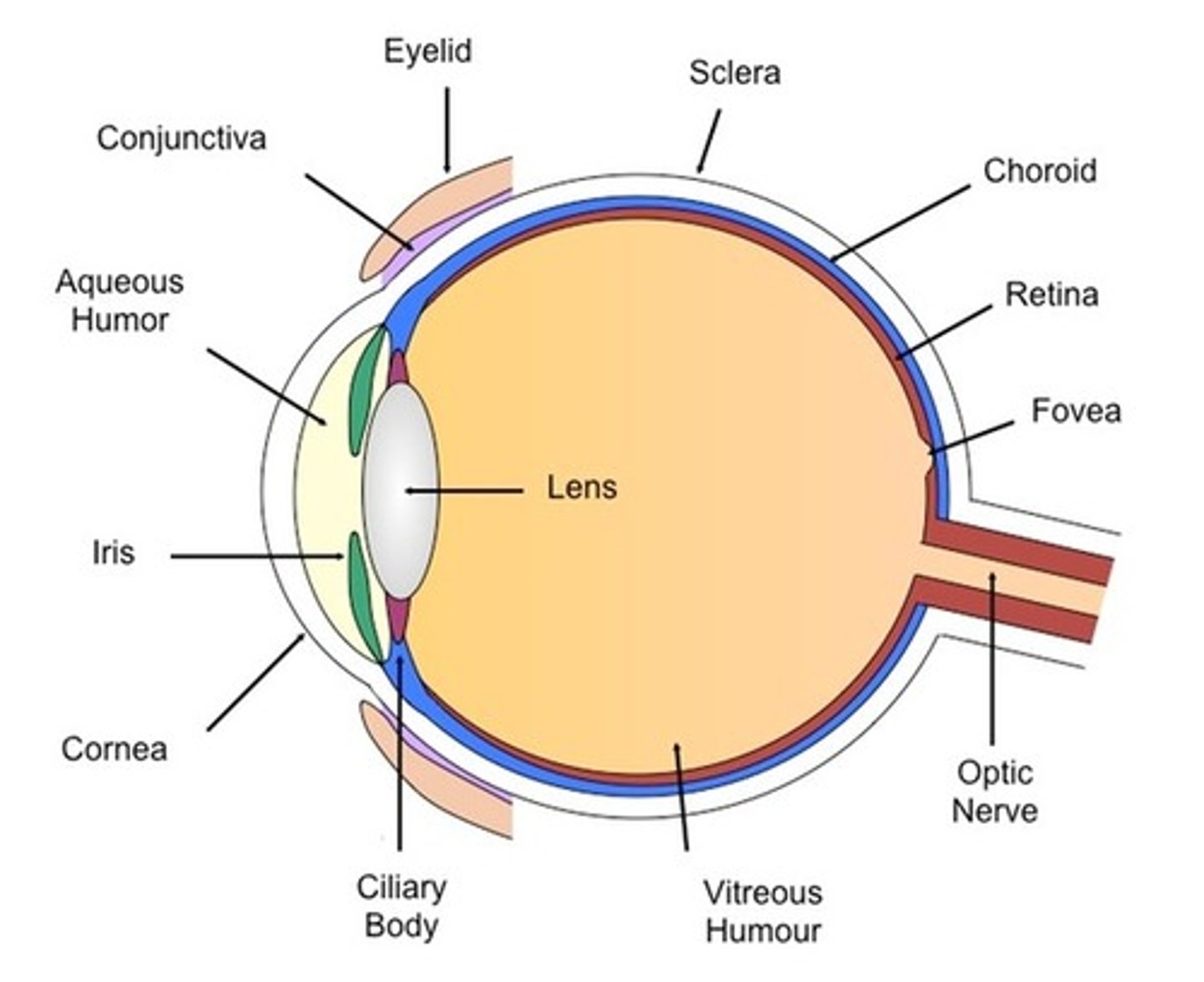
sclera
white of the eye
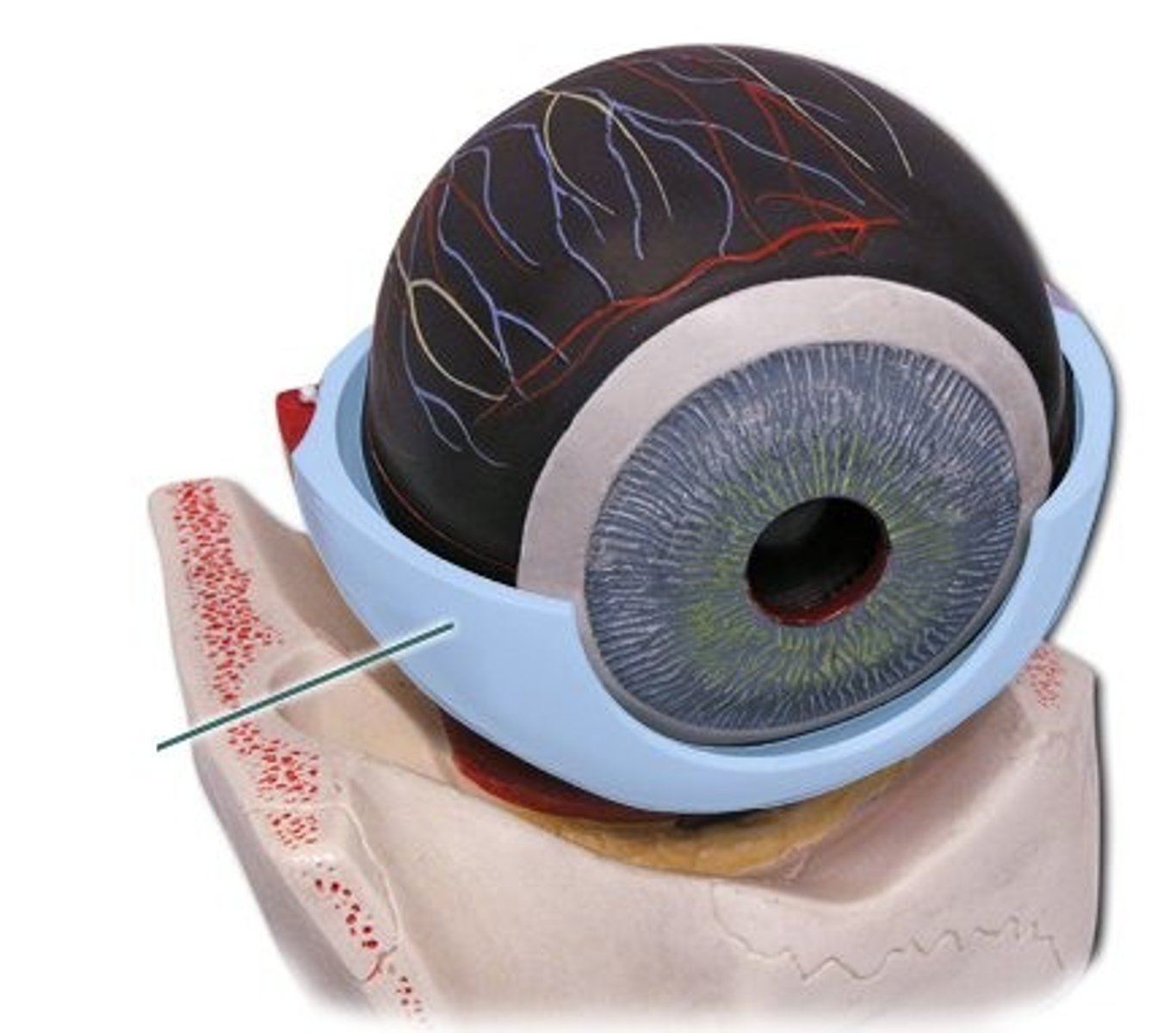
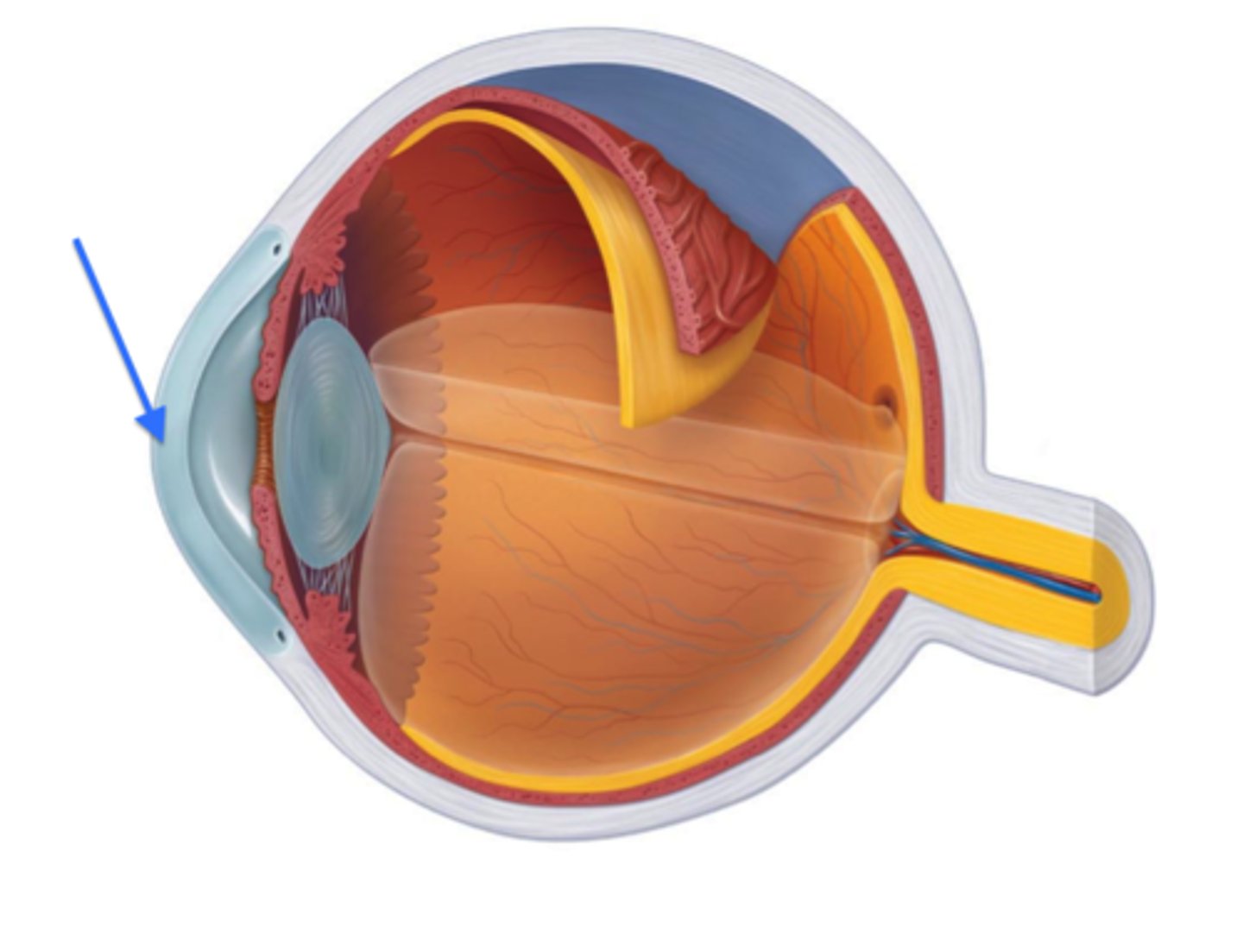
cornea
transparent layer, bulges: refracts light
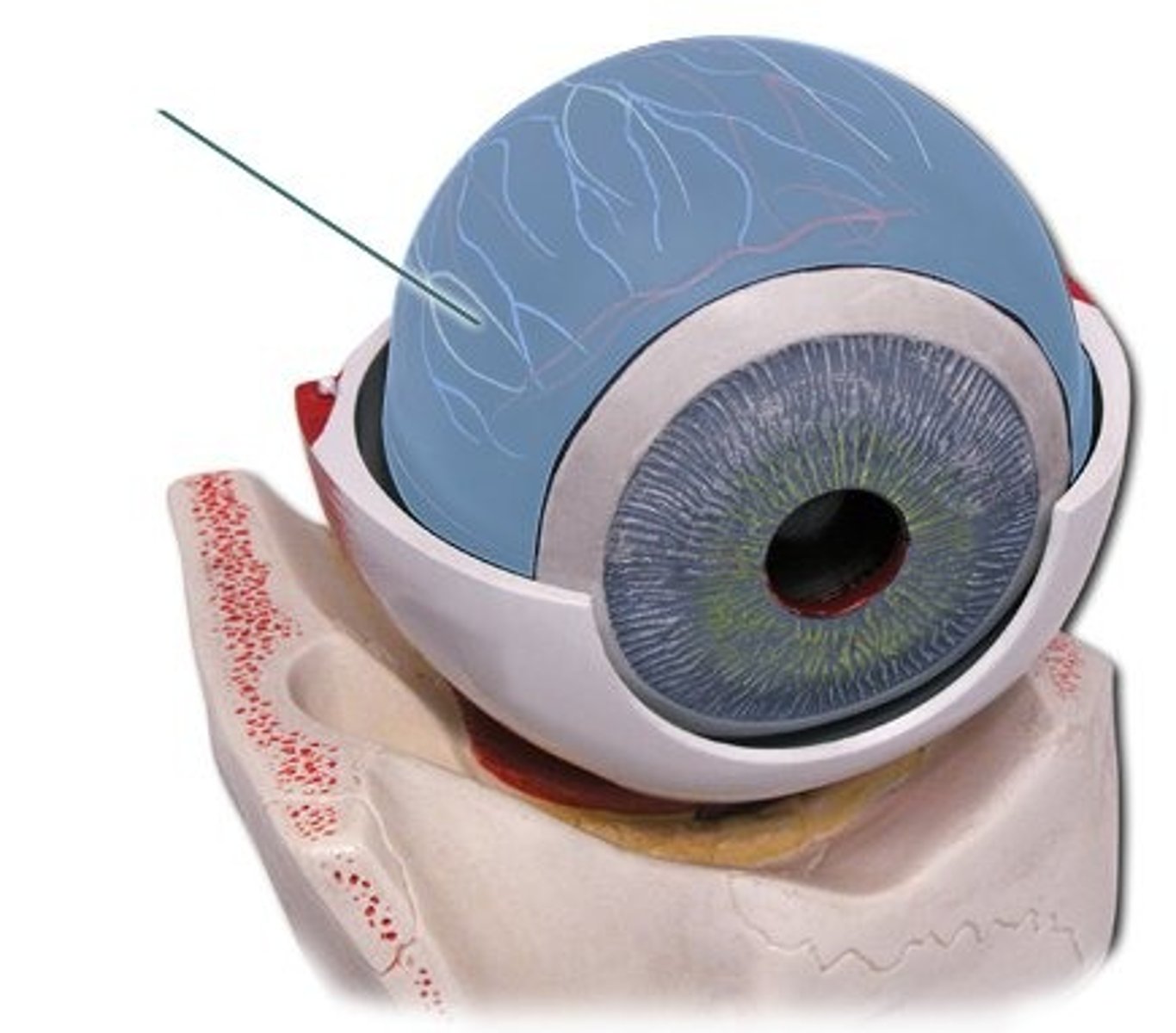
Choroid
dark membrane with blood vessels; nourishes eye, absorbs excess light
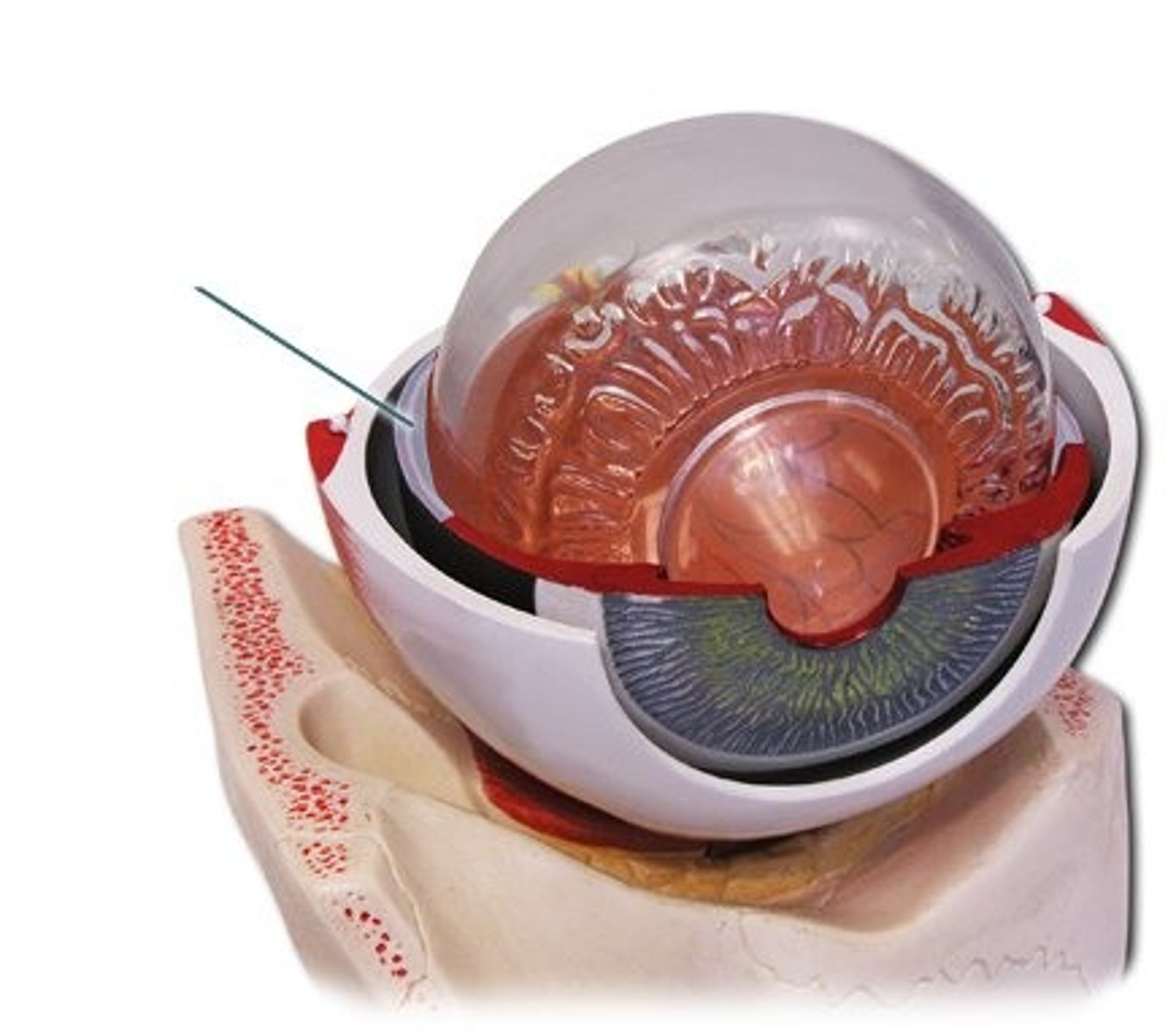
ciliary body
Contains ciliary muscle and process

suspensory ligament
attaches lens to the ciliary process
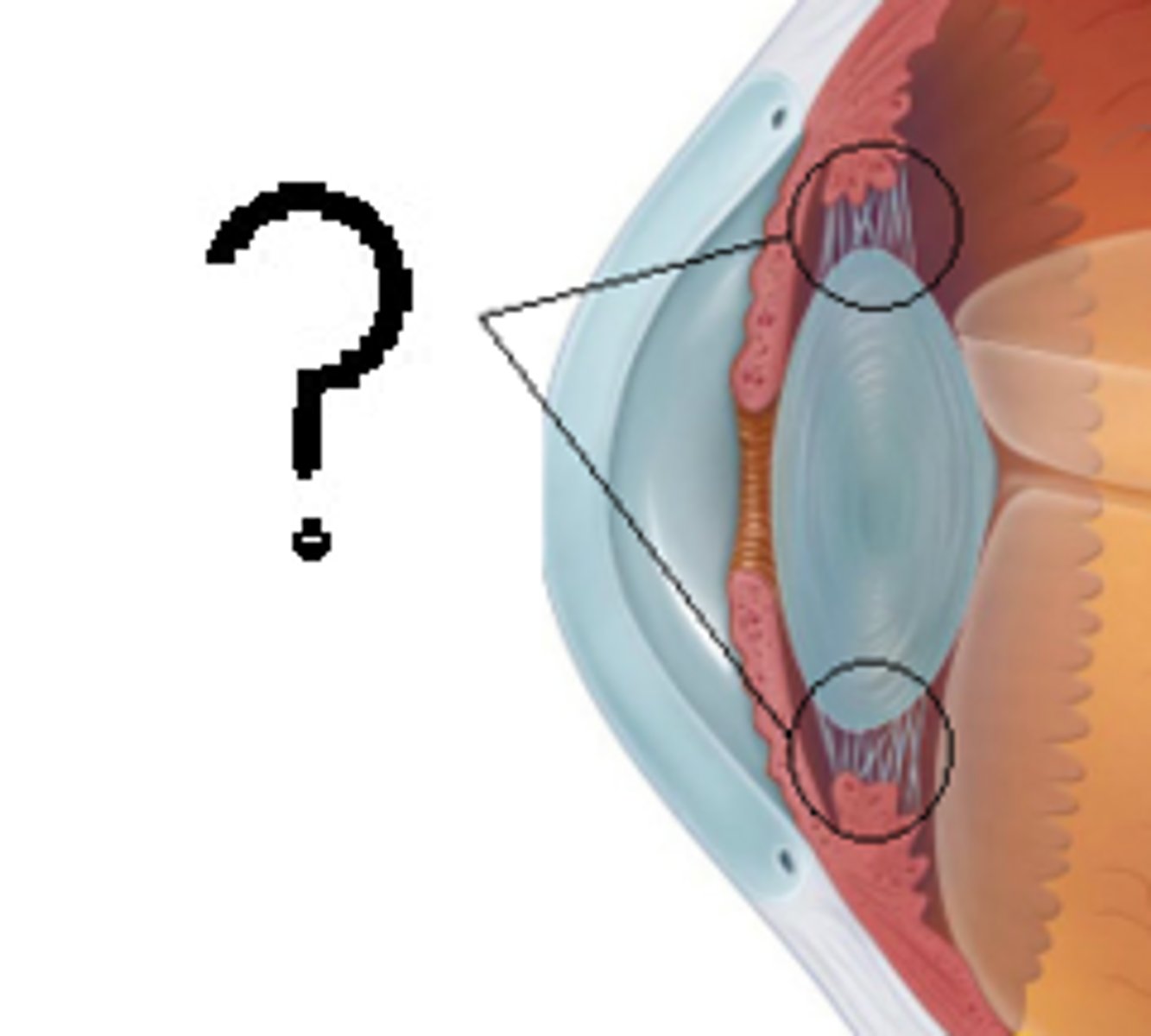
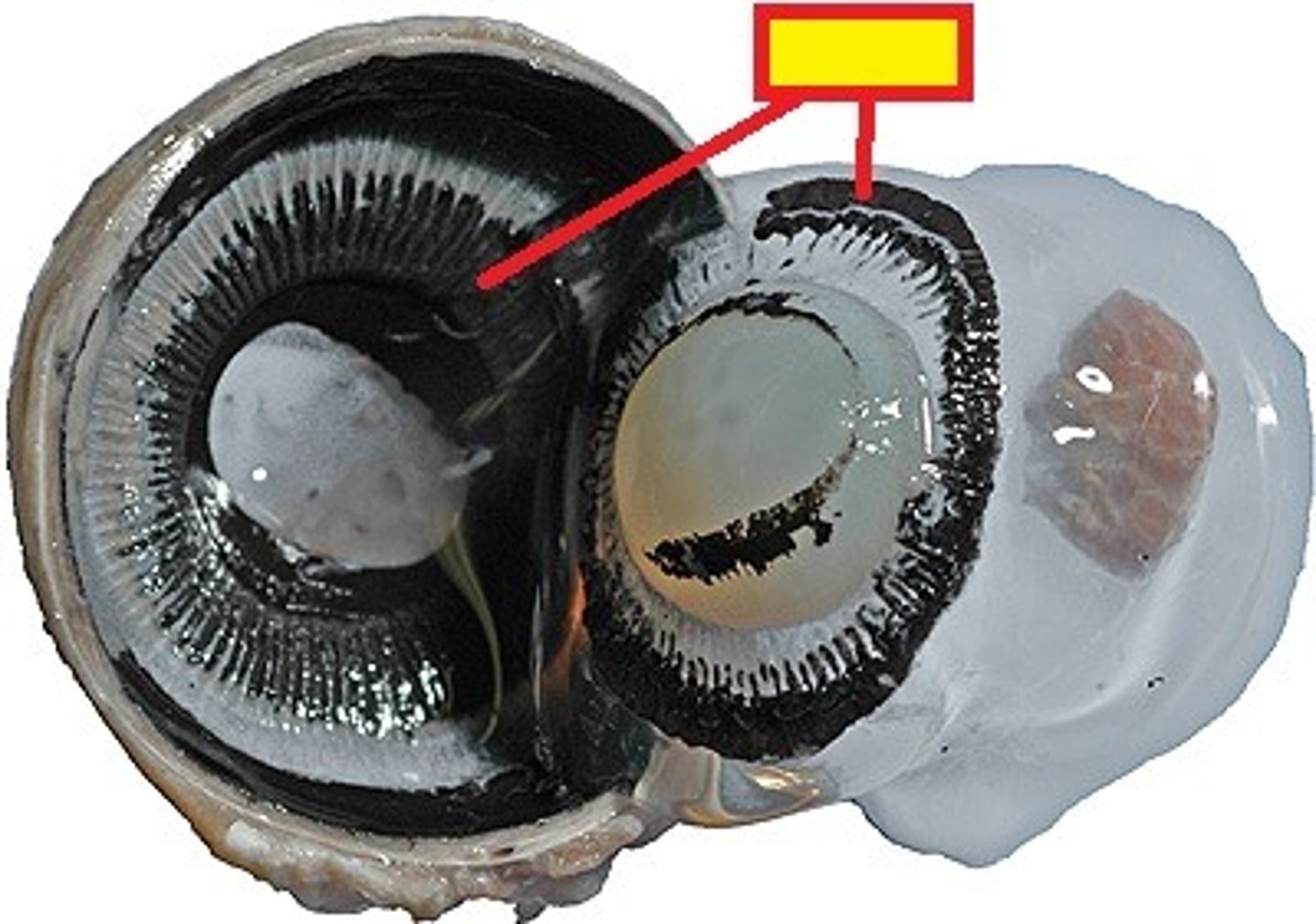
iris
pigmented; contians muscles that control the amount of light entering the eye by changing pupil diameter
pupil
opening of iris; allows light to enter eye
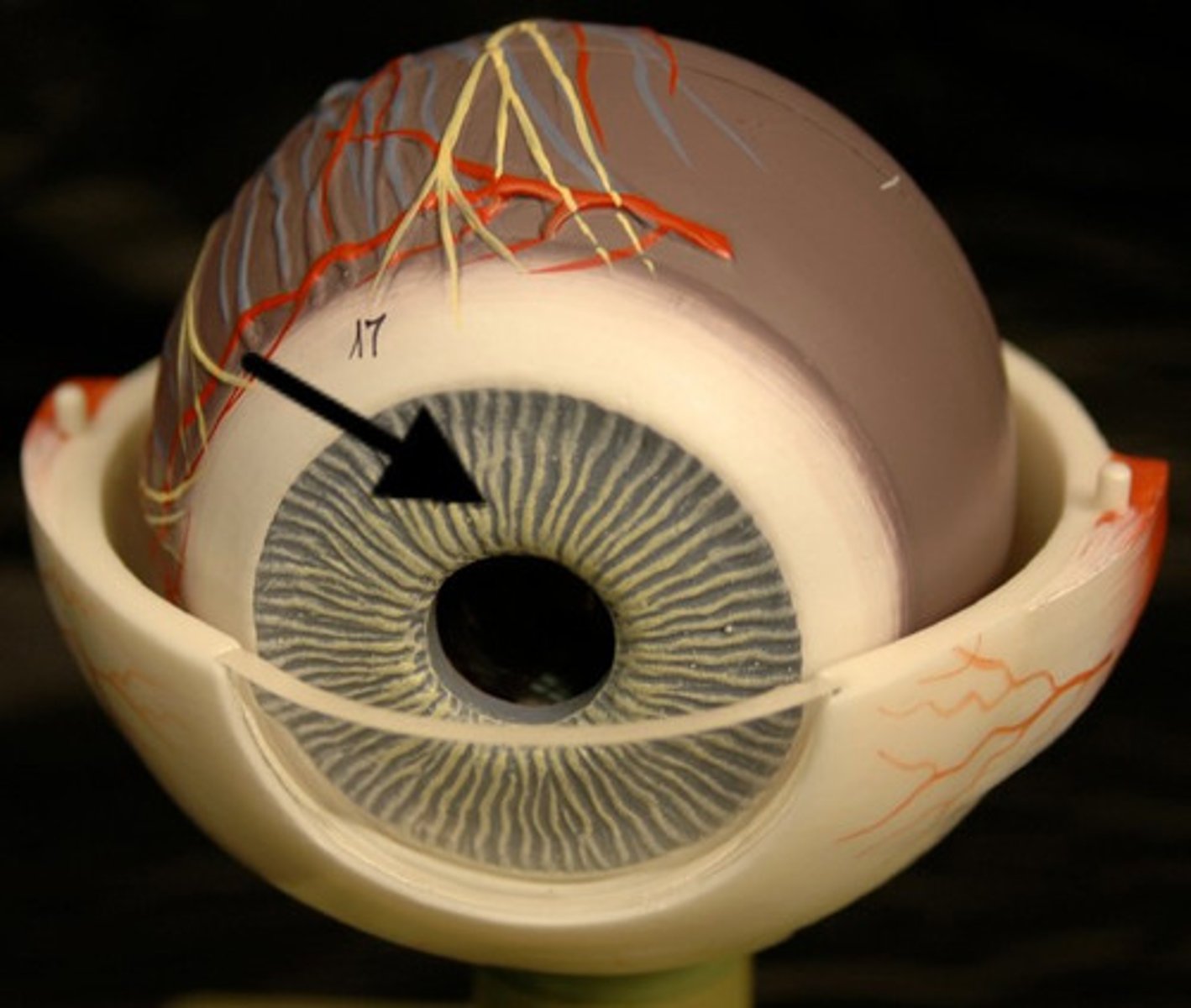
retina
contains photoreceptors
rods
respond to low light, night vision
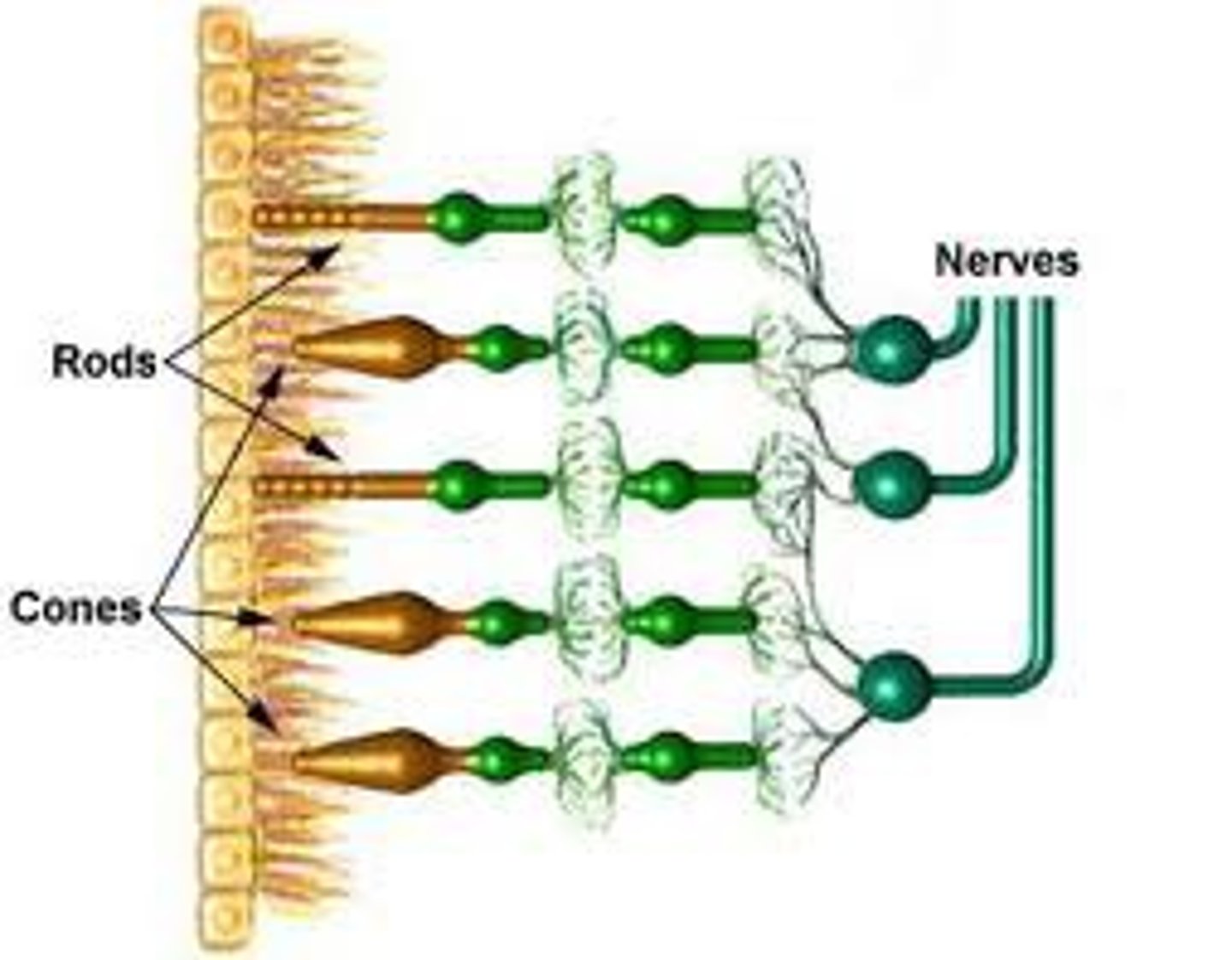
cones
function best in bright light, perceive colors
macula lutea
area of high photorecptor density
fovea centrails
center of macula lutea; produces highest visual acuity
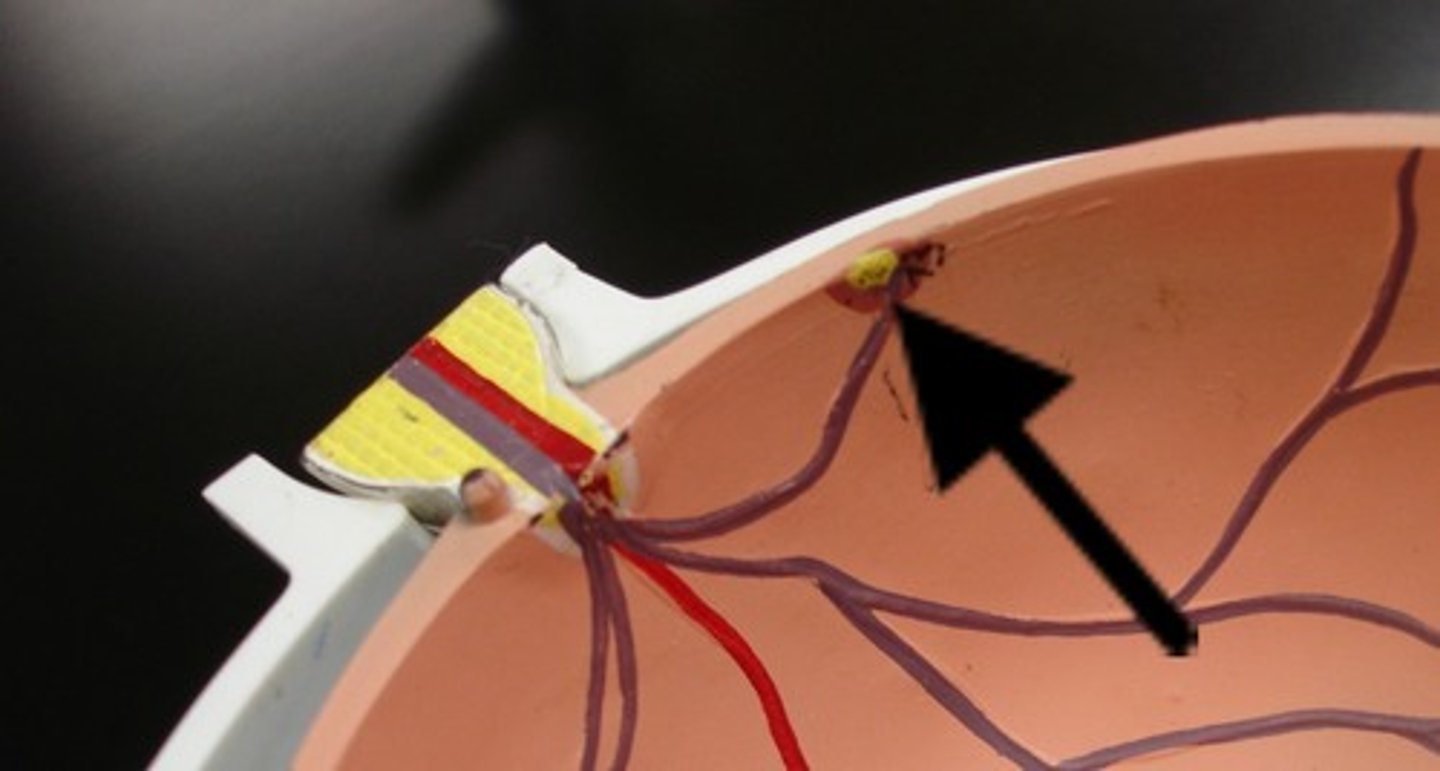
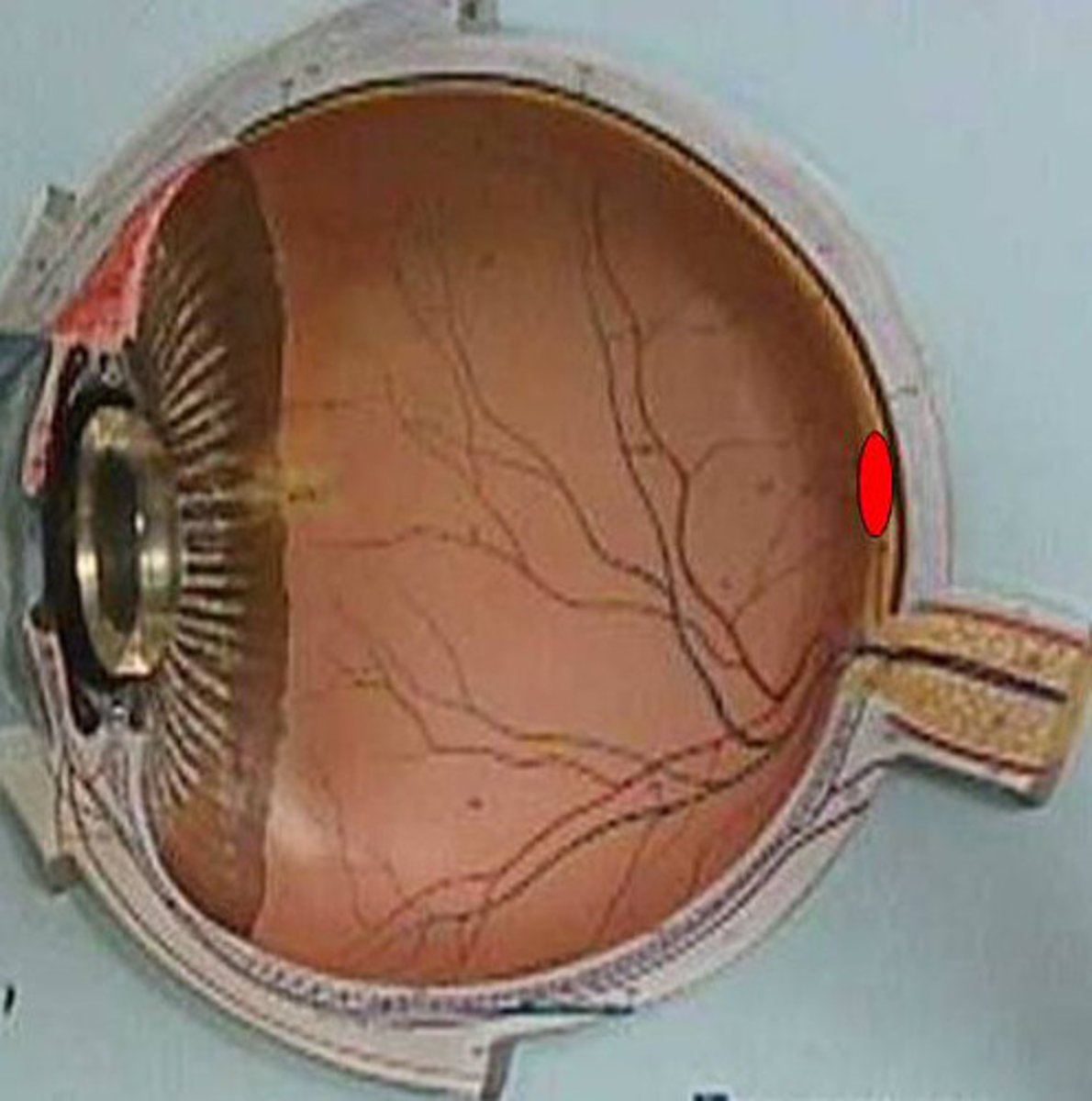
optic disc
region with no photoreceptors
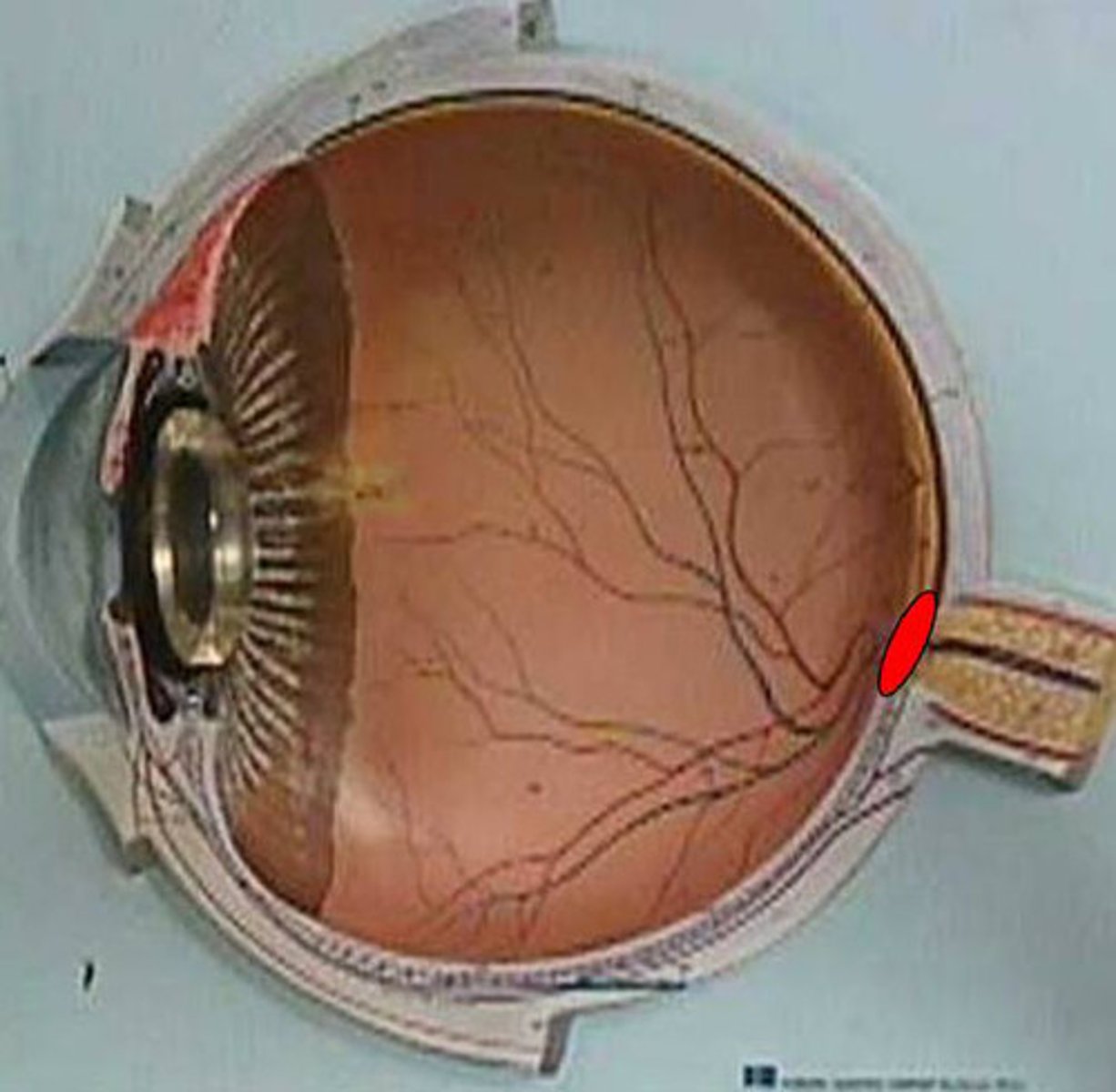
arteriole/venule
blood supplying oxygen and nutrients to eye
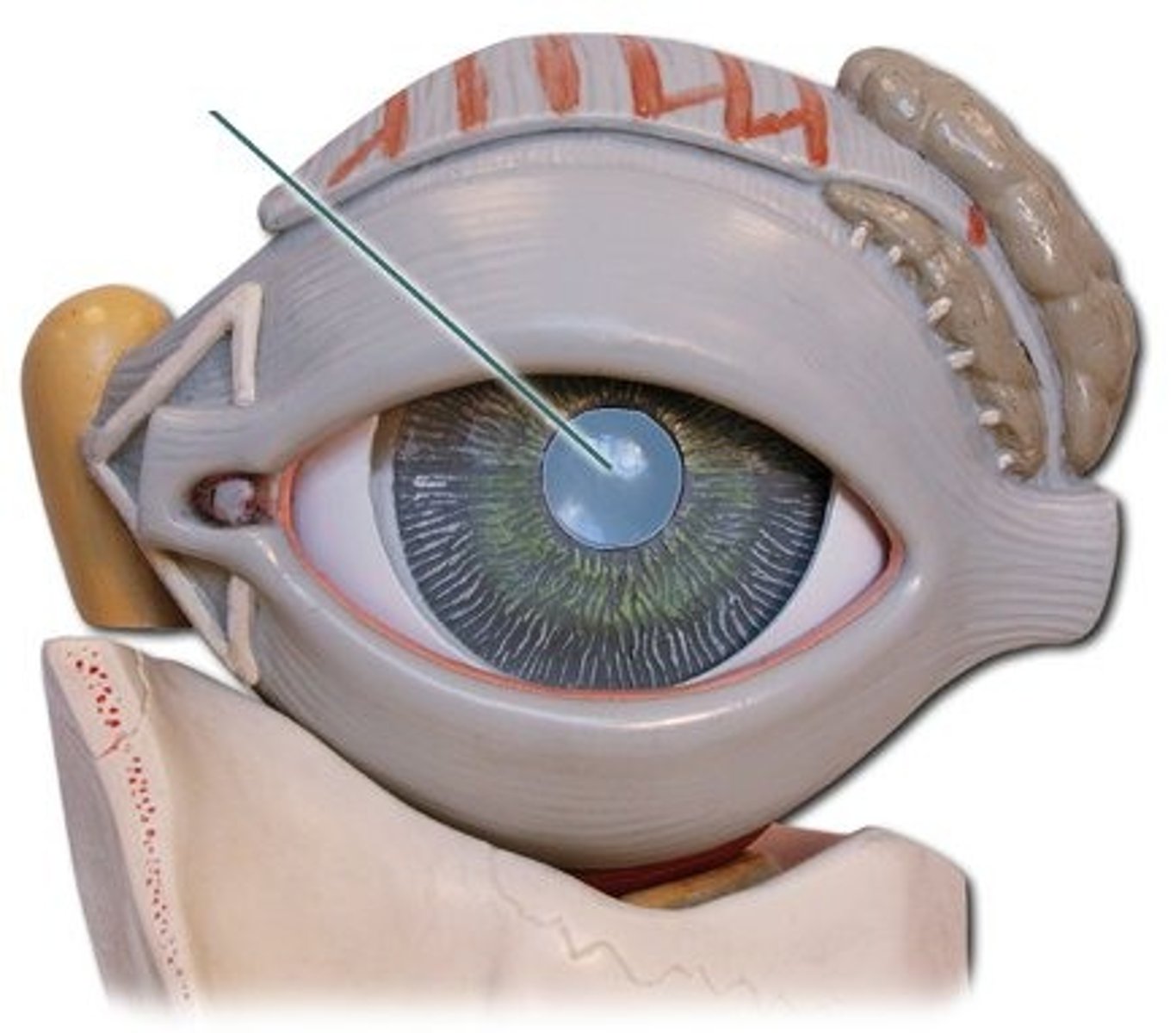
lens
Focuses light onto retina
optic nerve
carries input form eye to brain
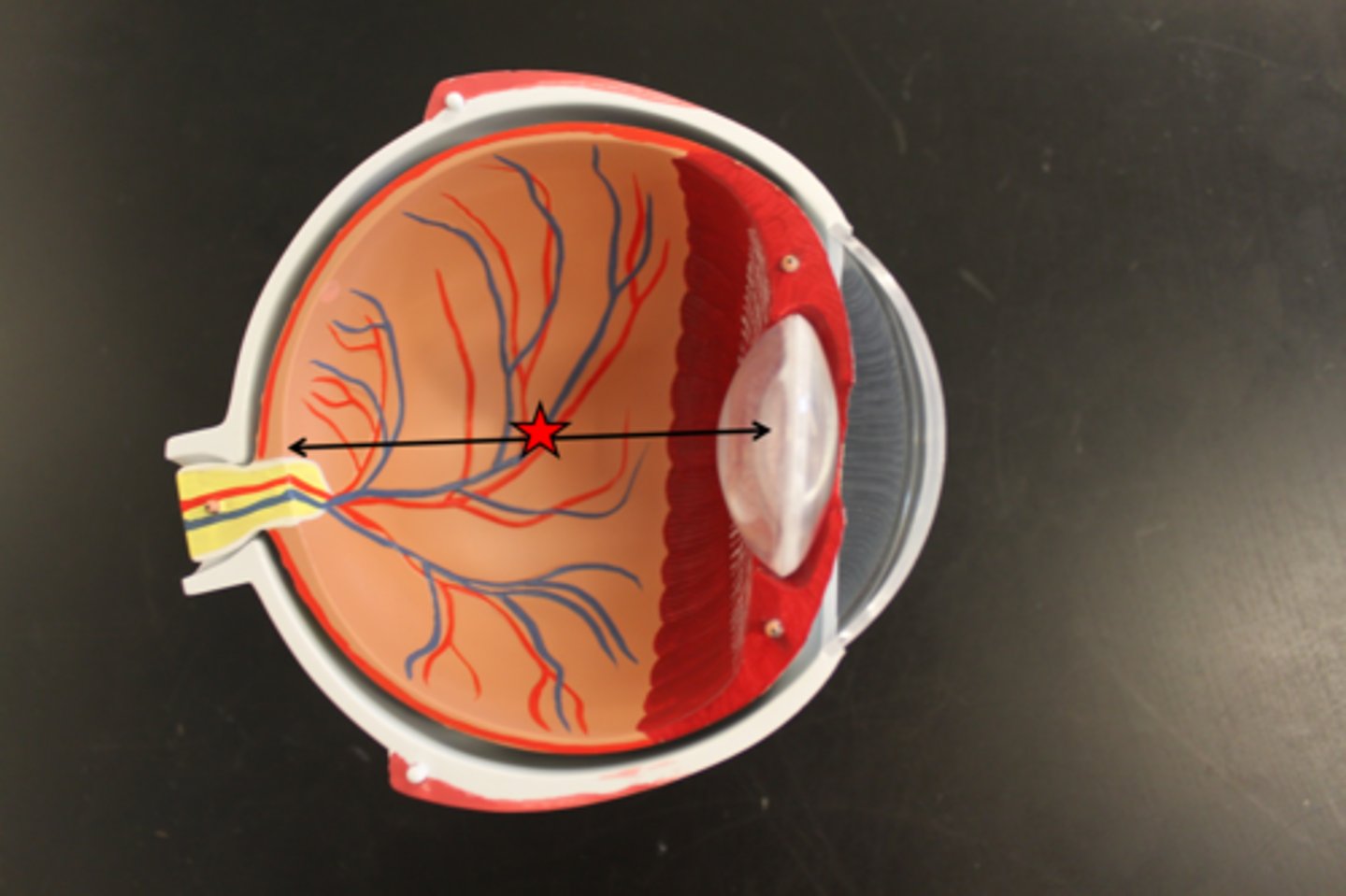
anterior cavity
cavity anterior lens
posterior cavity
cavity posterior to lens
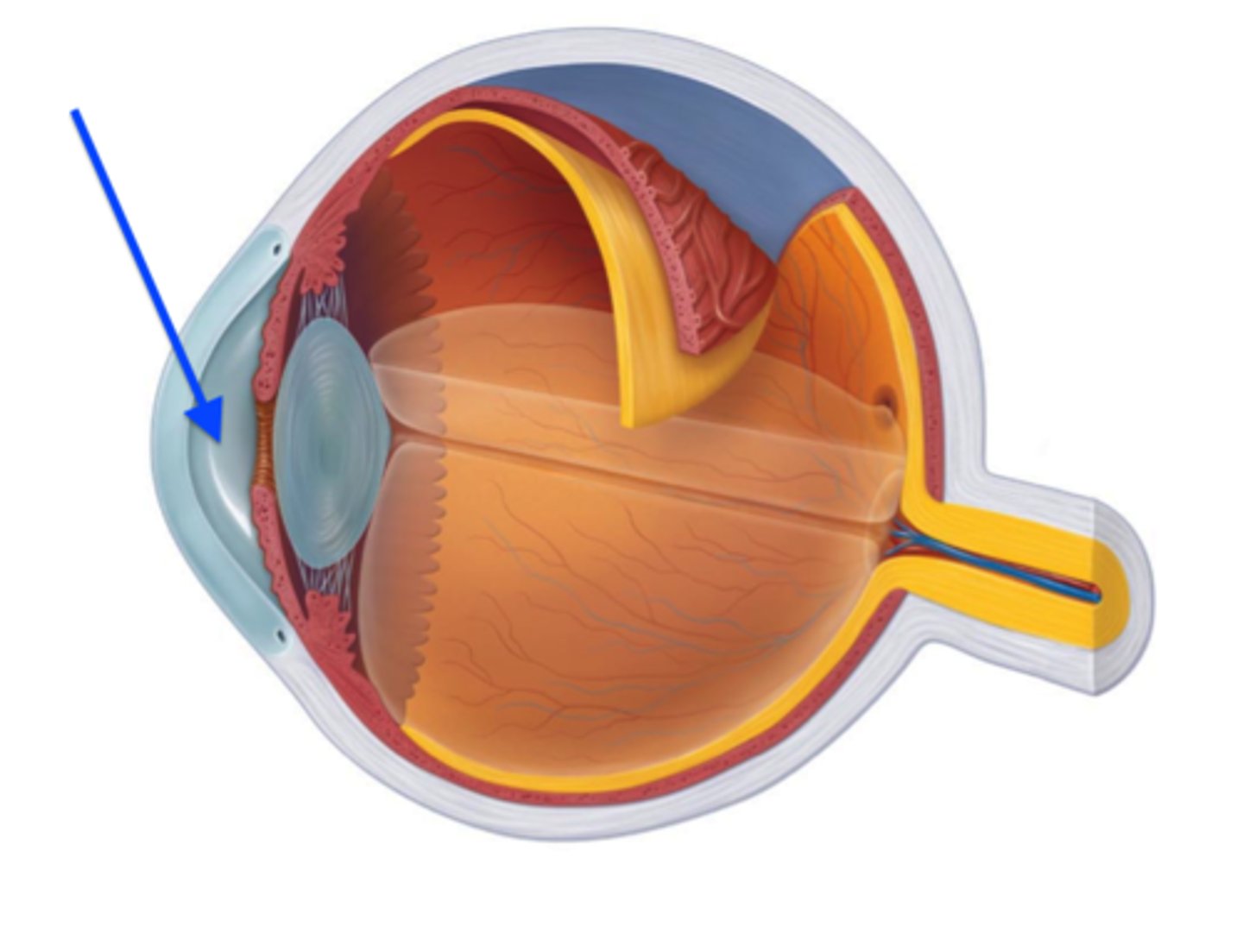
aqueous humor
fluid in the eye, found between the cornea and the lens
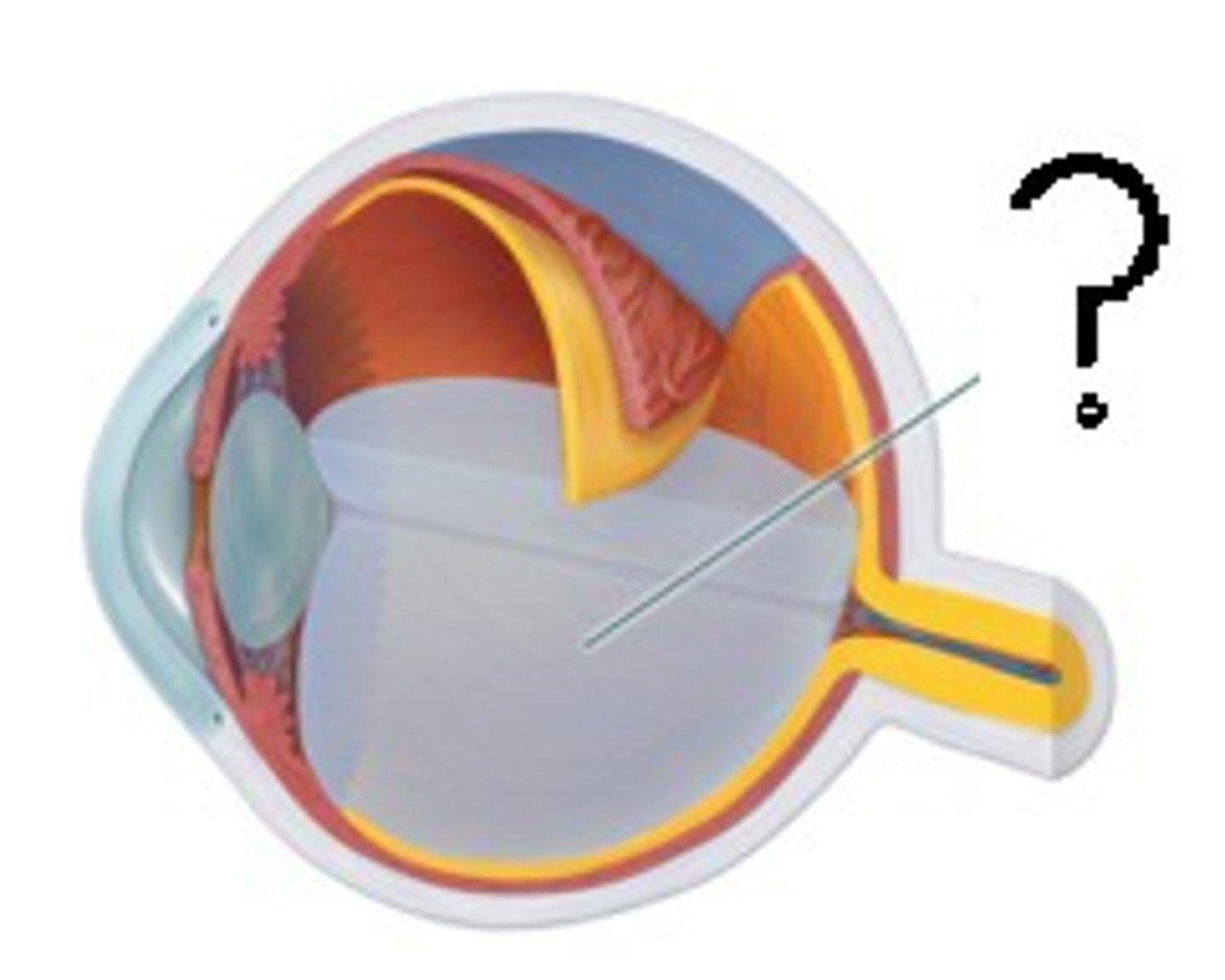
vitreous body
a transparent jellylike substance filling the interior of the eyeball
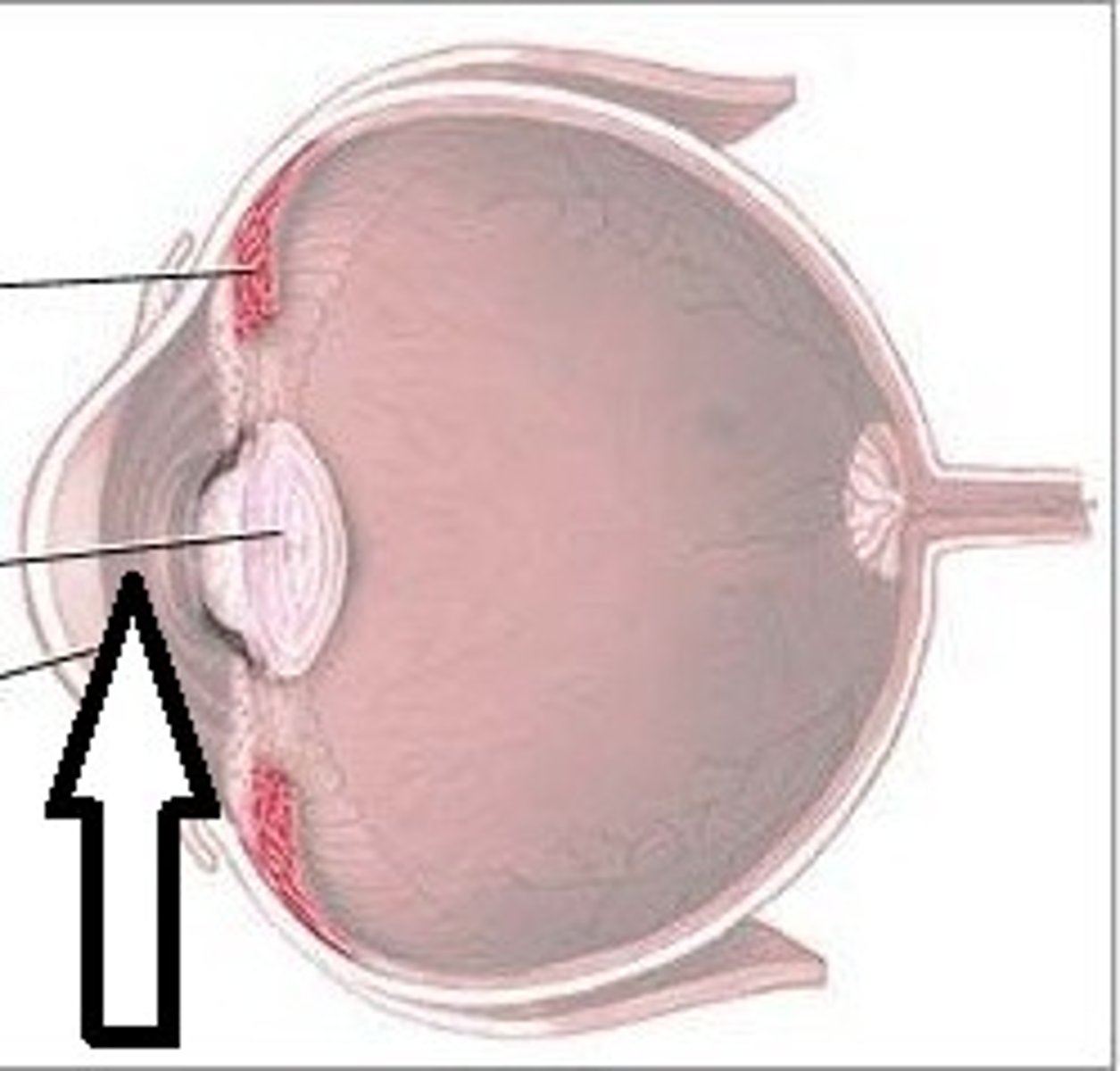
lacrimal gland with ducts
Secretes lacrimal fluid containing mucus, antibodies, and lysozyme
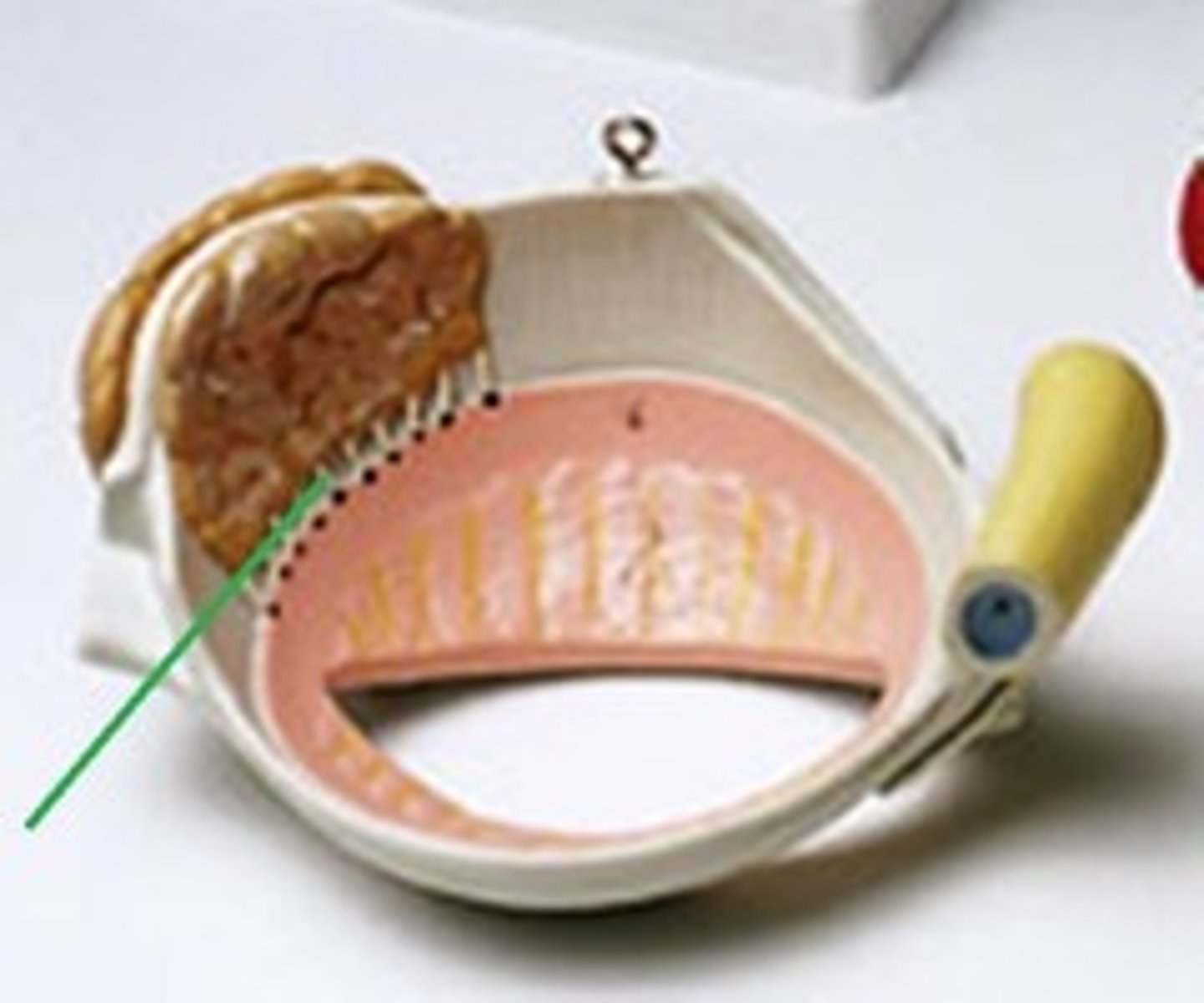
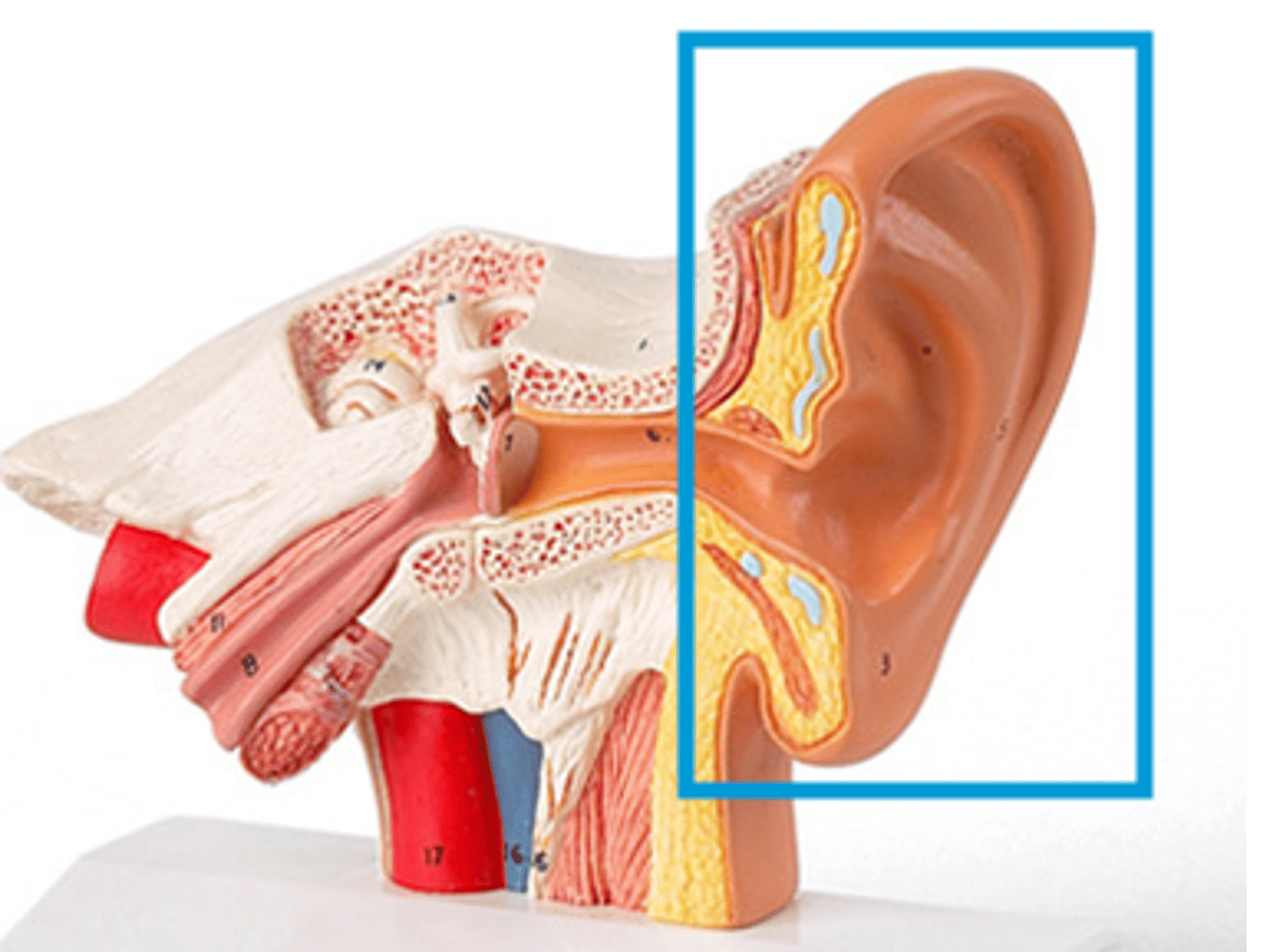
auricle
external ear
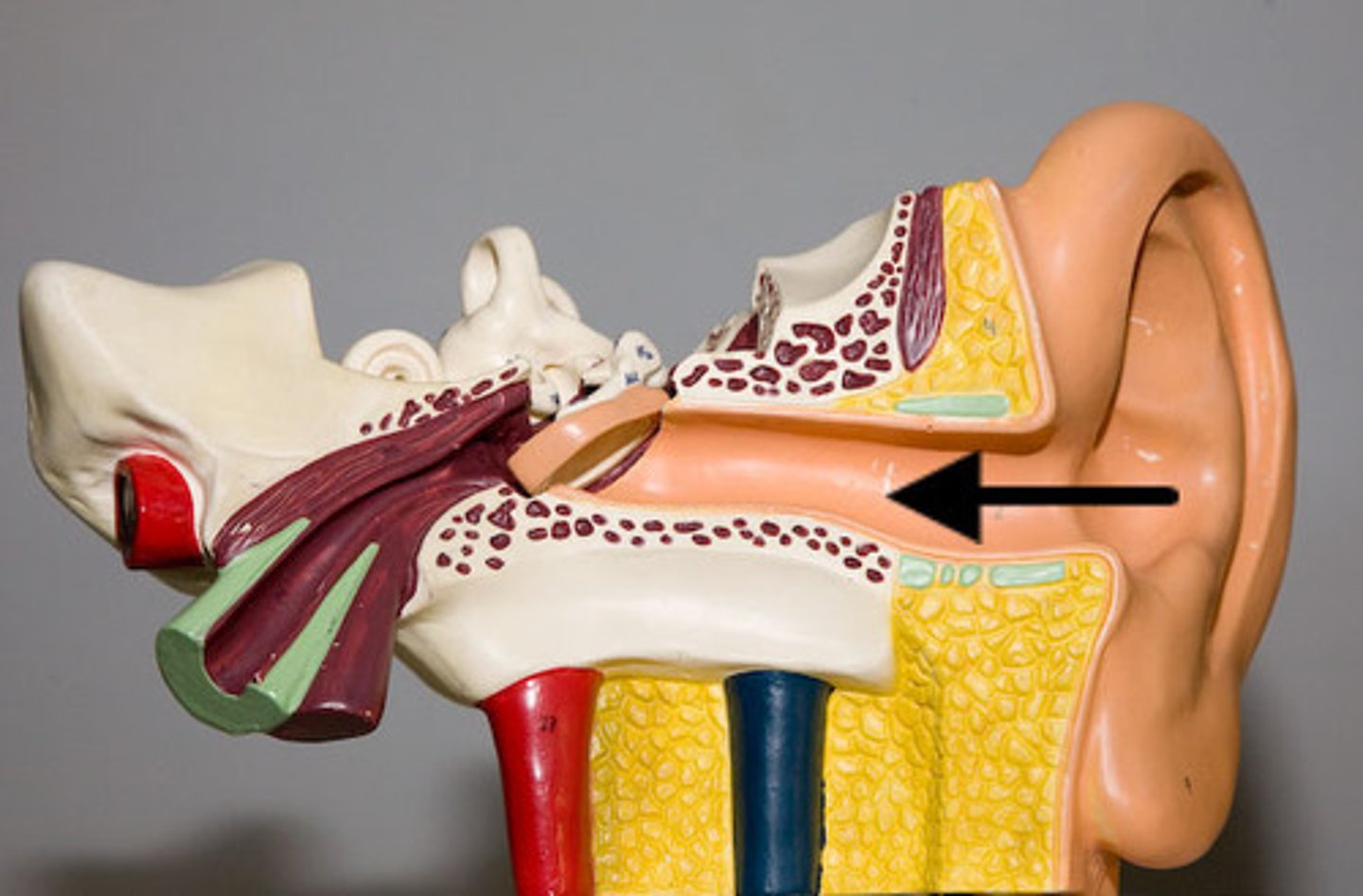
external auditory canal
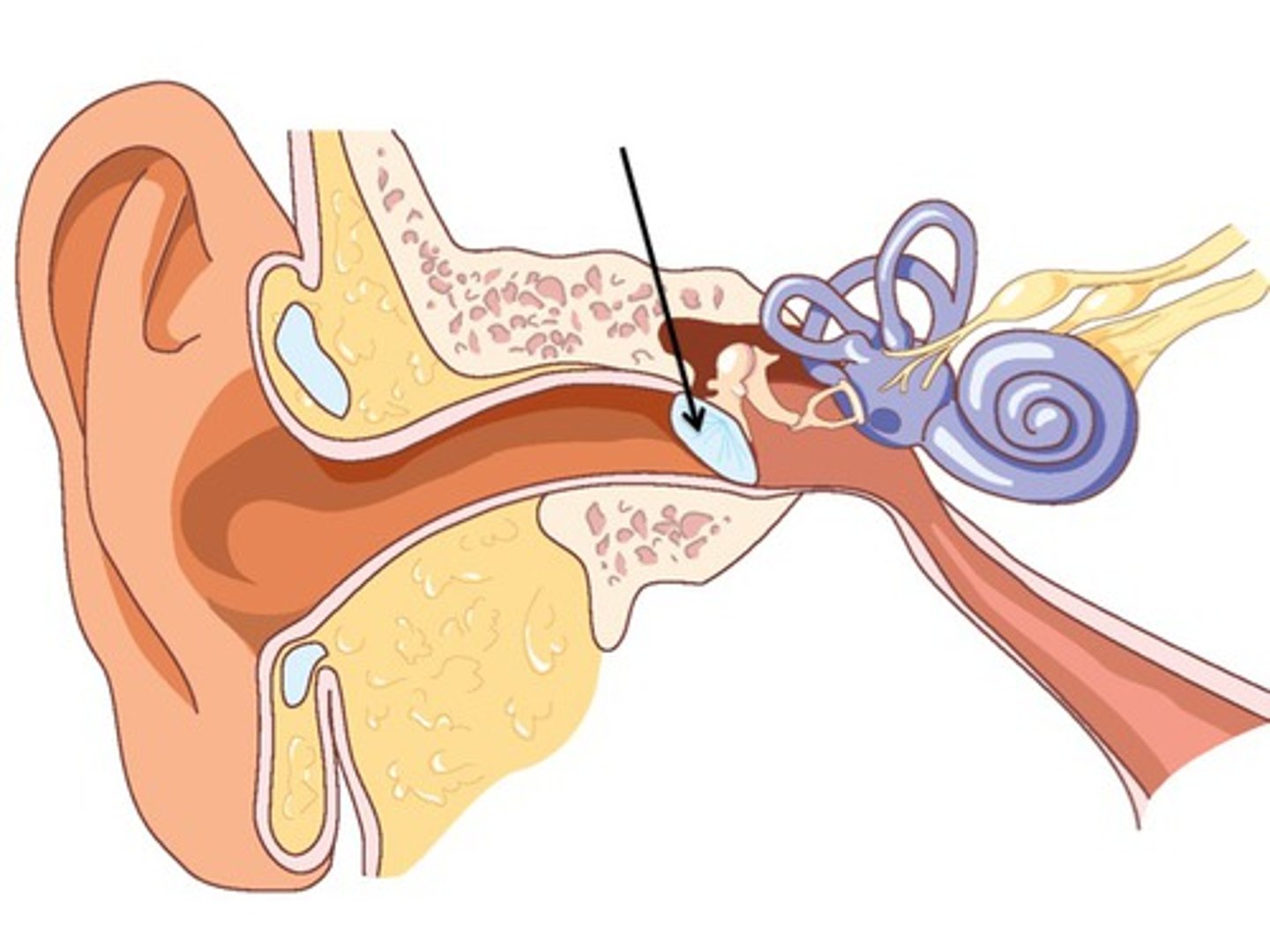
tympanic membrane
vibrates at same frequency as sound waves; transmit vibrations to ossicles
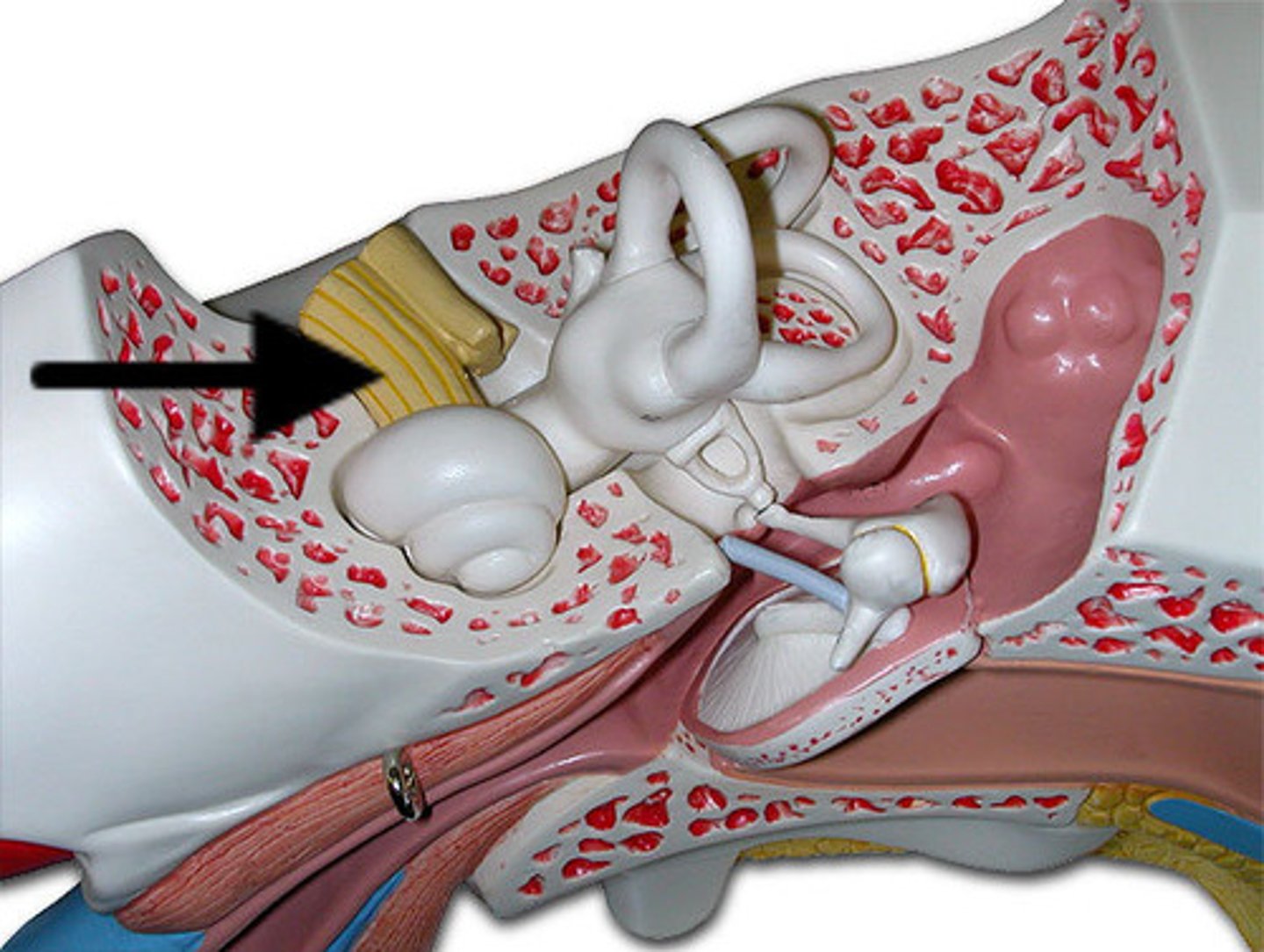
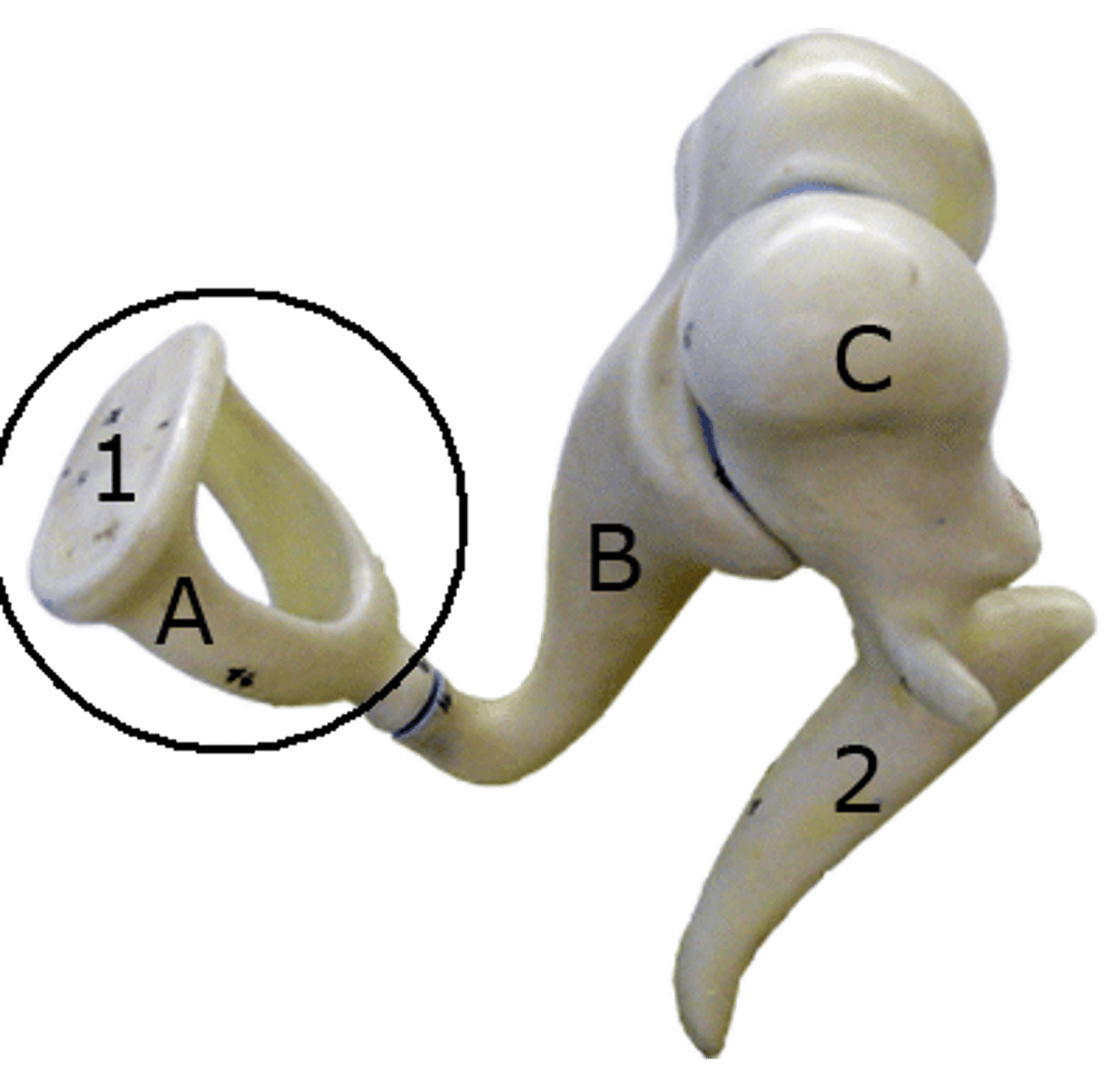
malleus
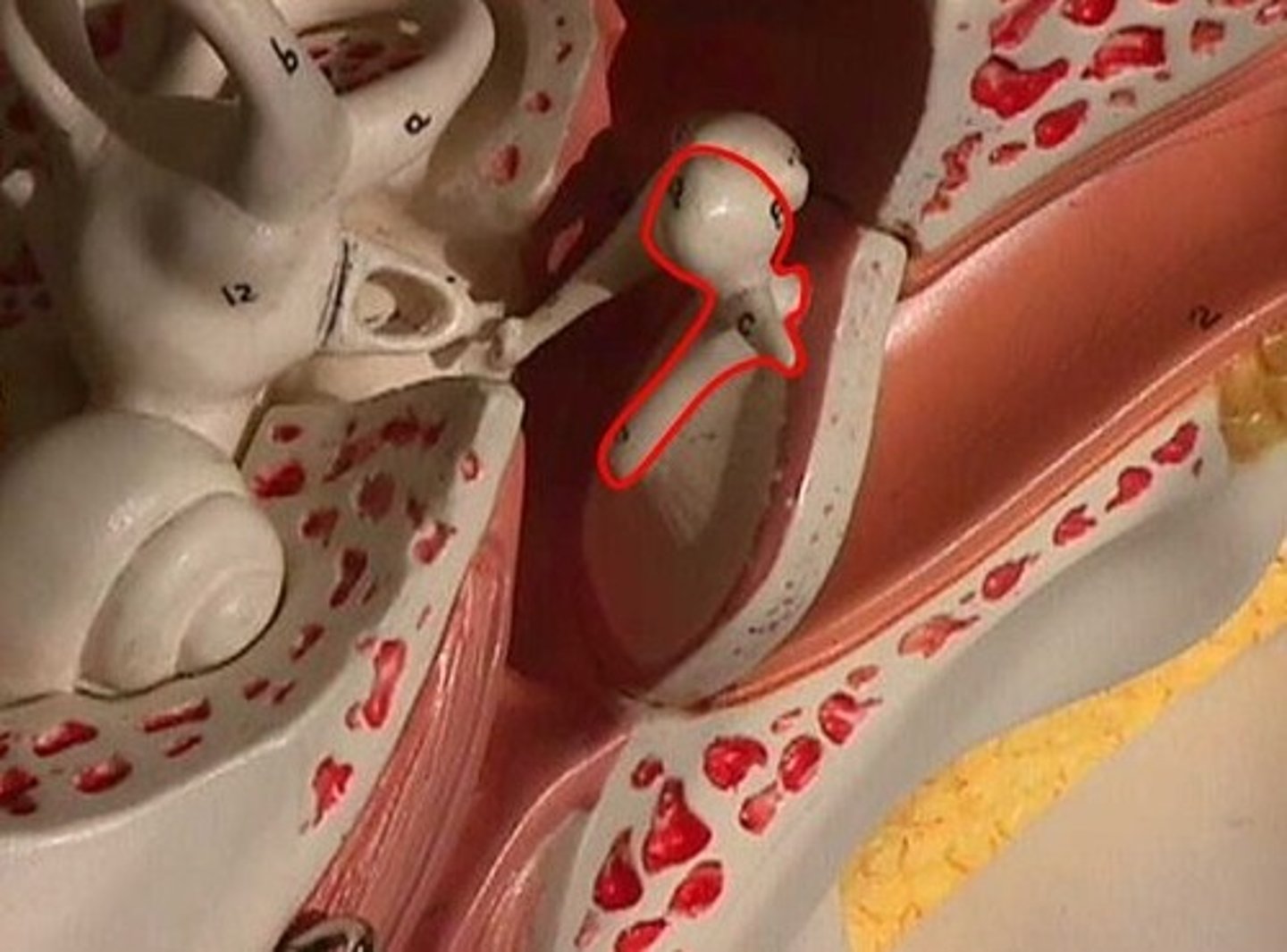
inucs
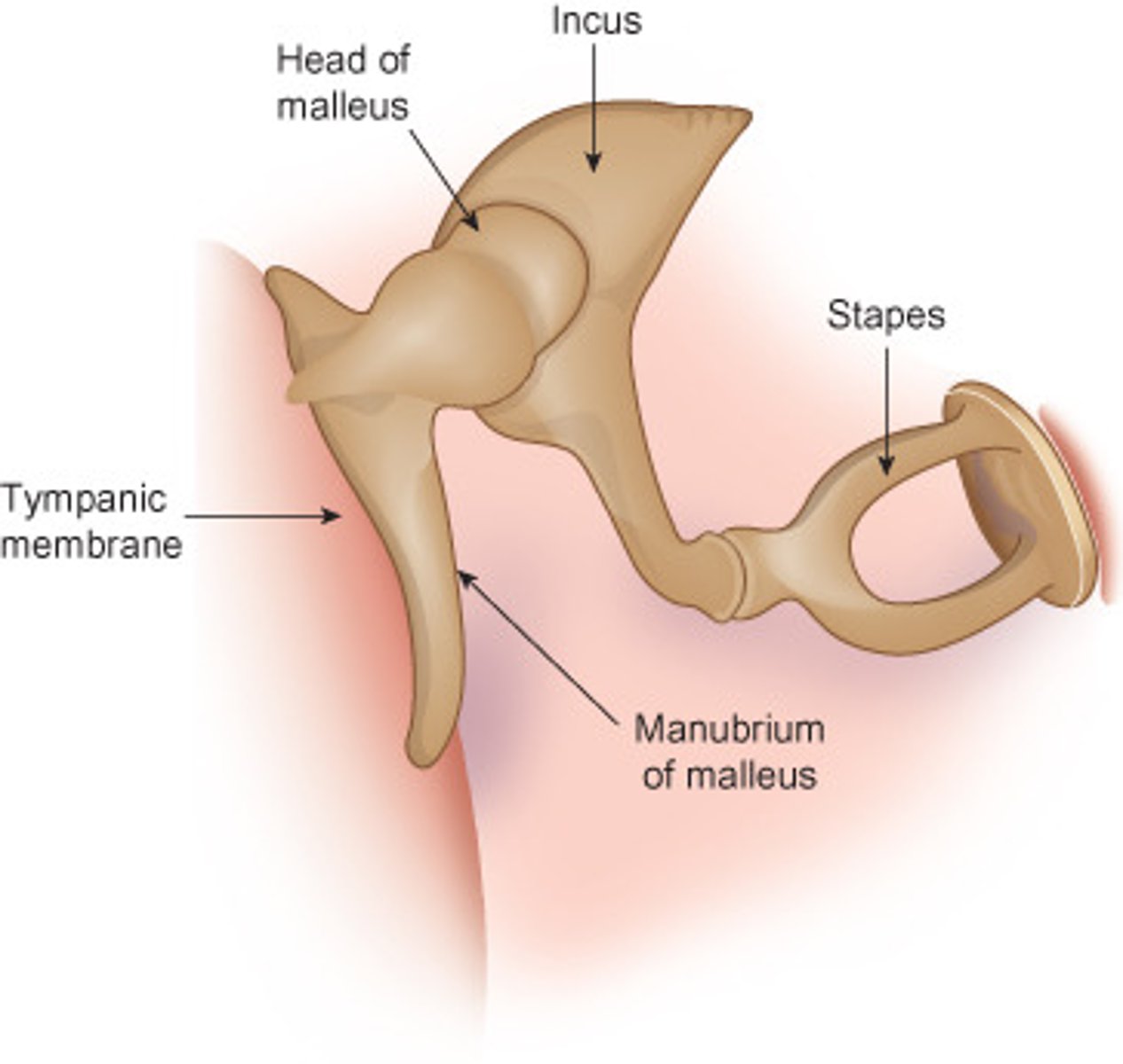
stapes
pharyngotympanic tune
cochlea
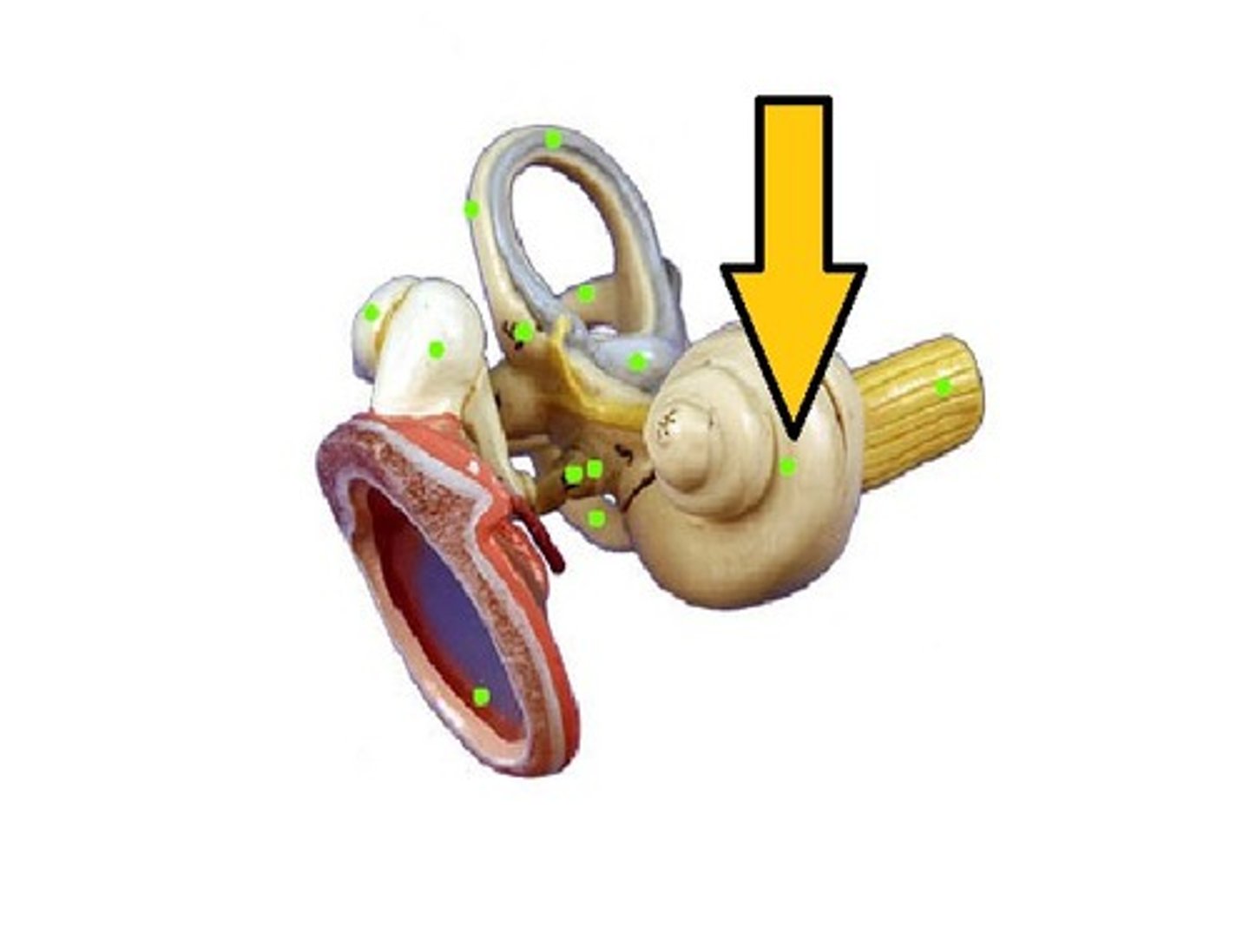
spiral organ
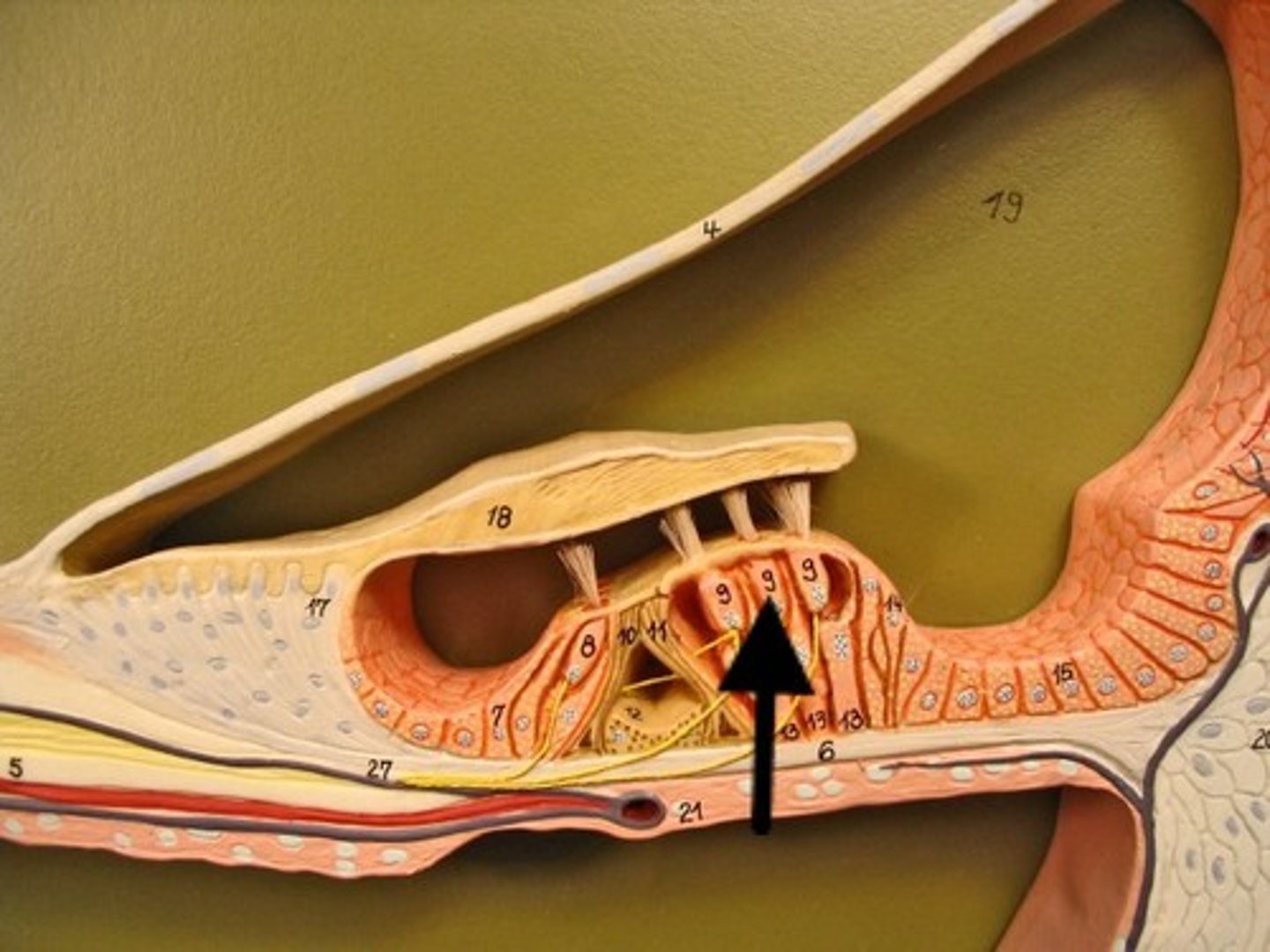
Contains hair cells for sound detection.
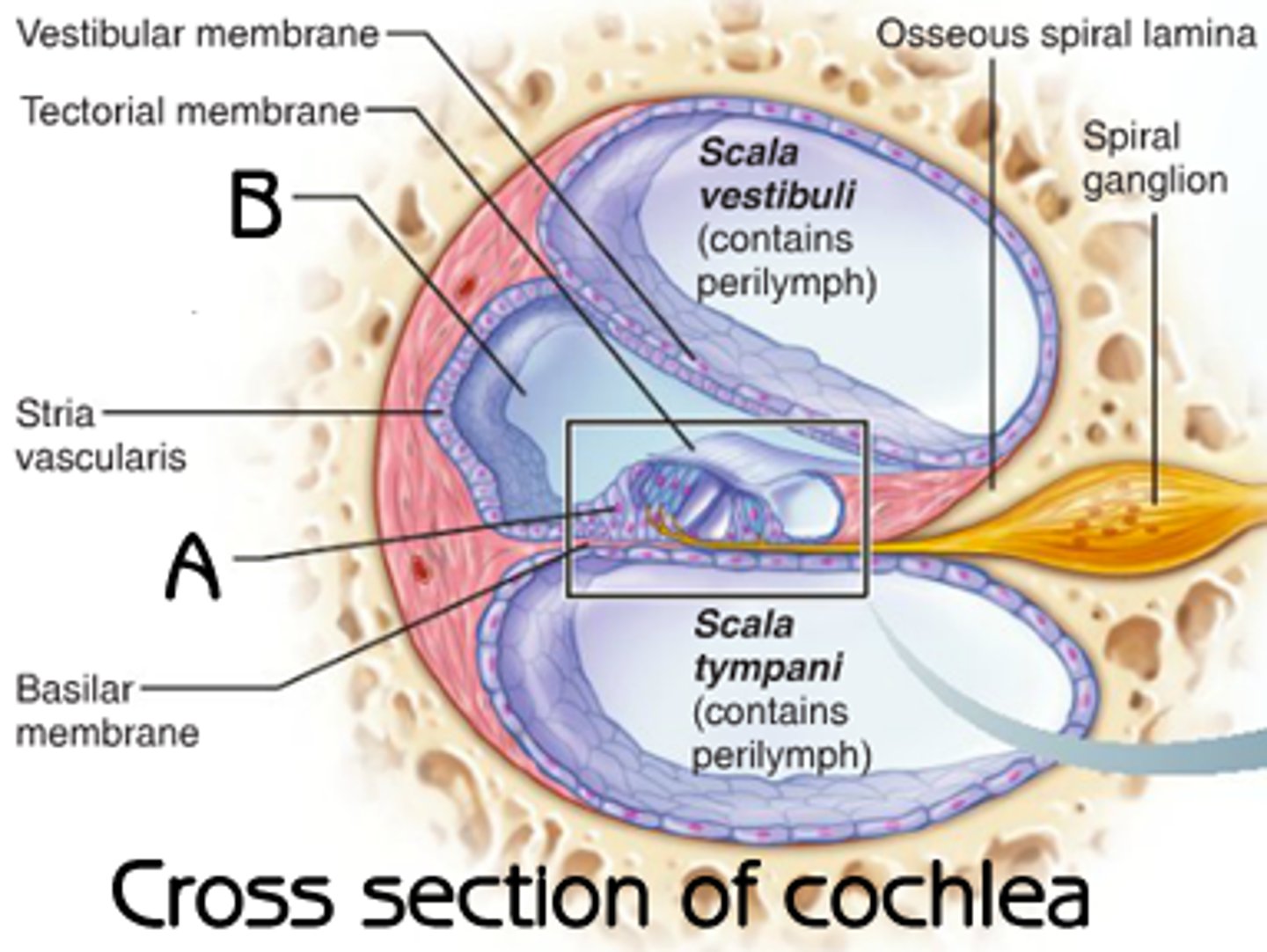
tectorial membrane
hair cells push tectorial membrane, bending hair cells
hair cells
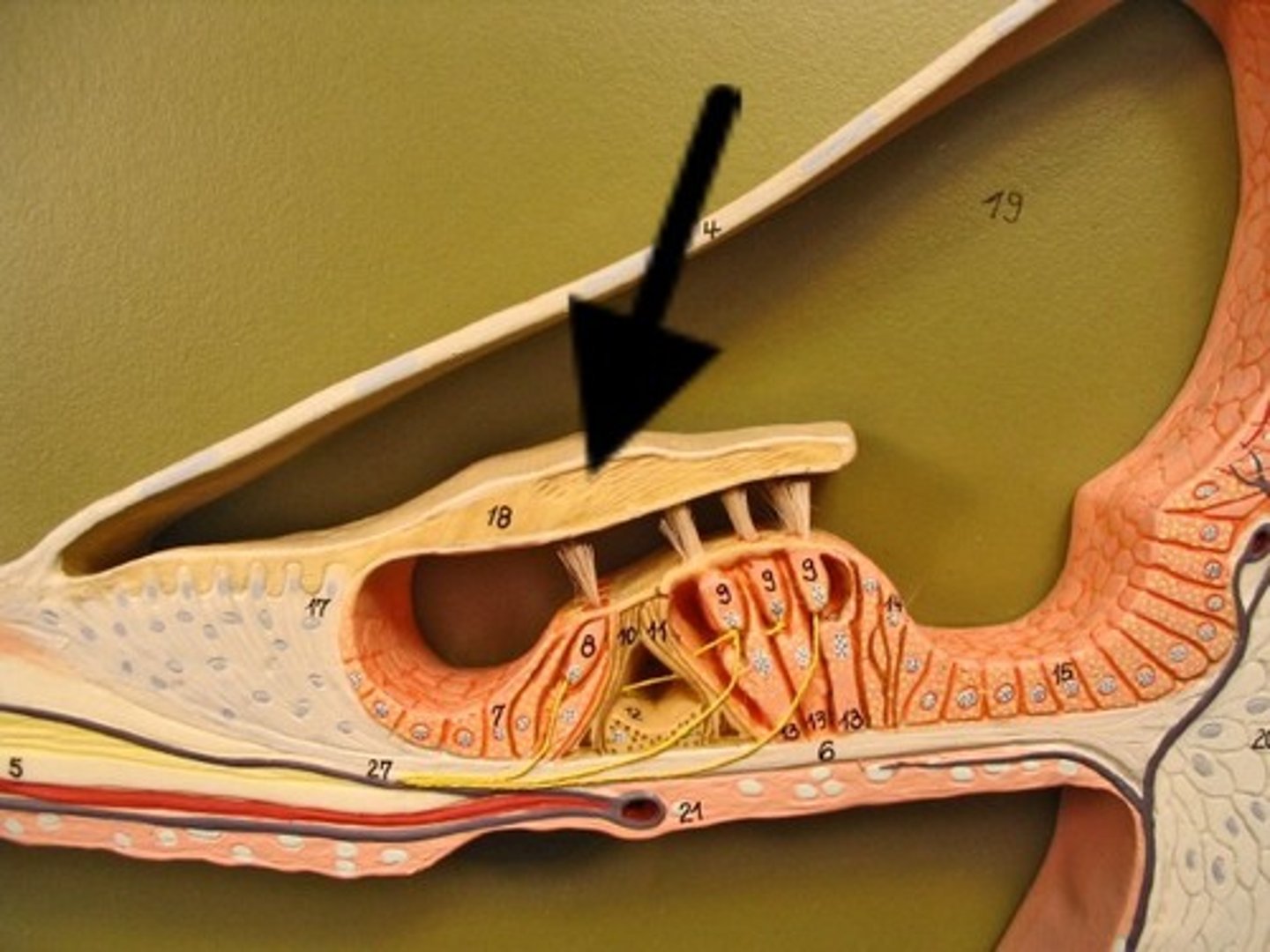
basilar membrane pushes on hair cells; when bent, create action potentials in cochlear nerve
basialar membrane
fluid of cochlea
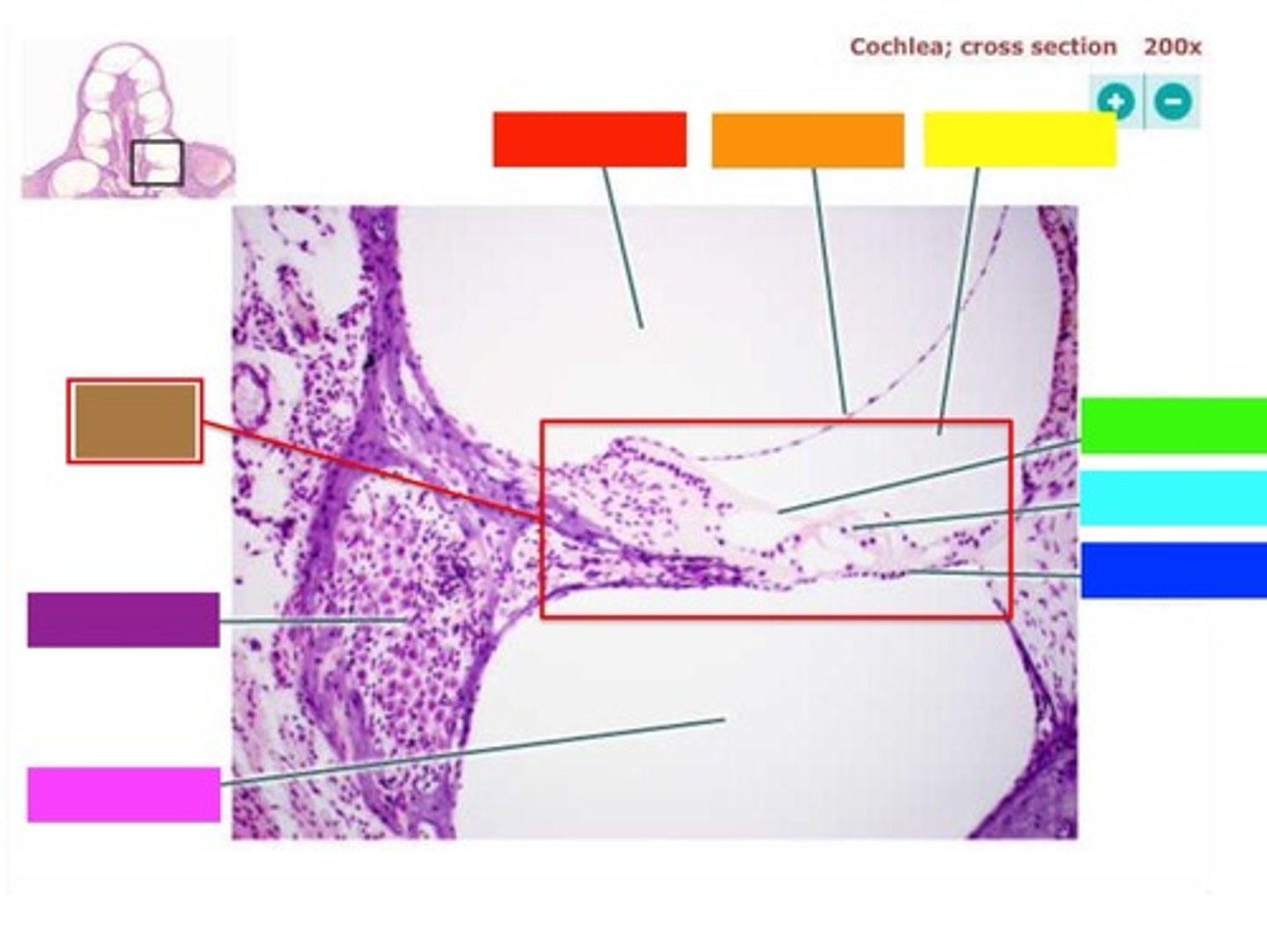
cochlear nerve
carries auditory information to the brain
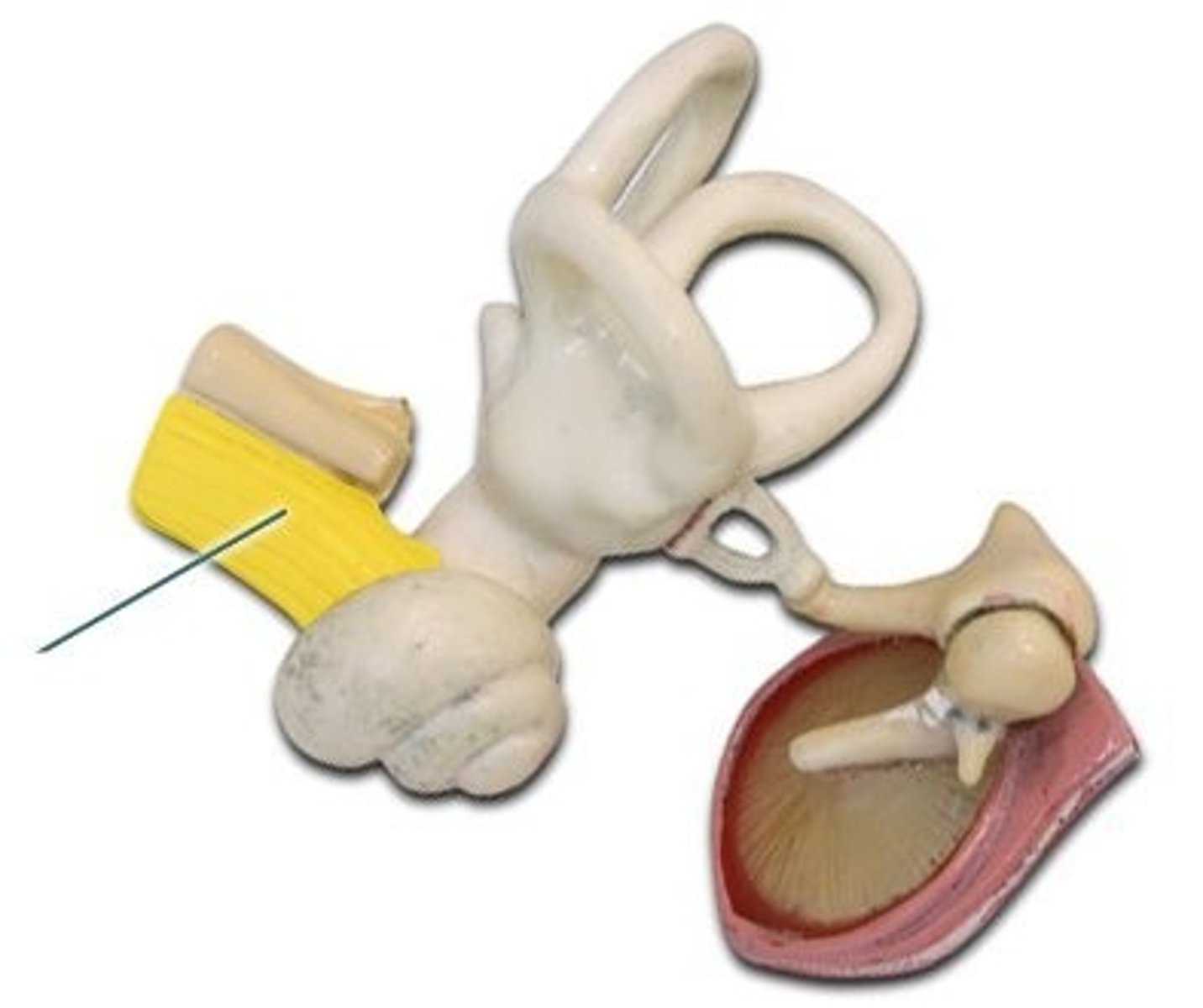
Semircular canals
equilibrium/balance - rotational acceleration of head
vestibule
equilibrium/balance- linear acceleration of head
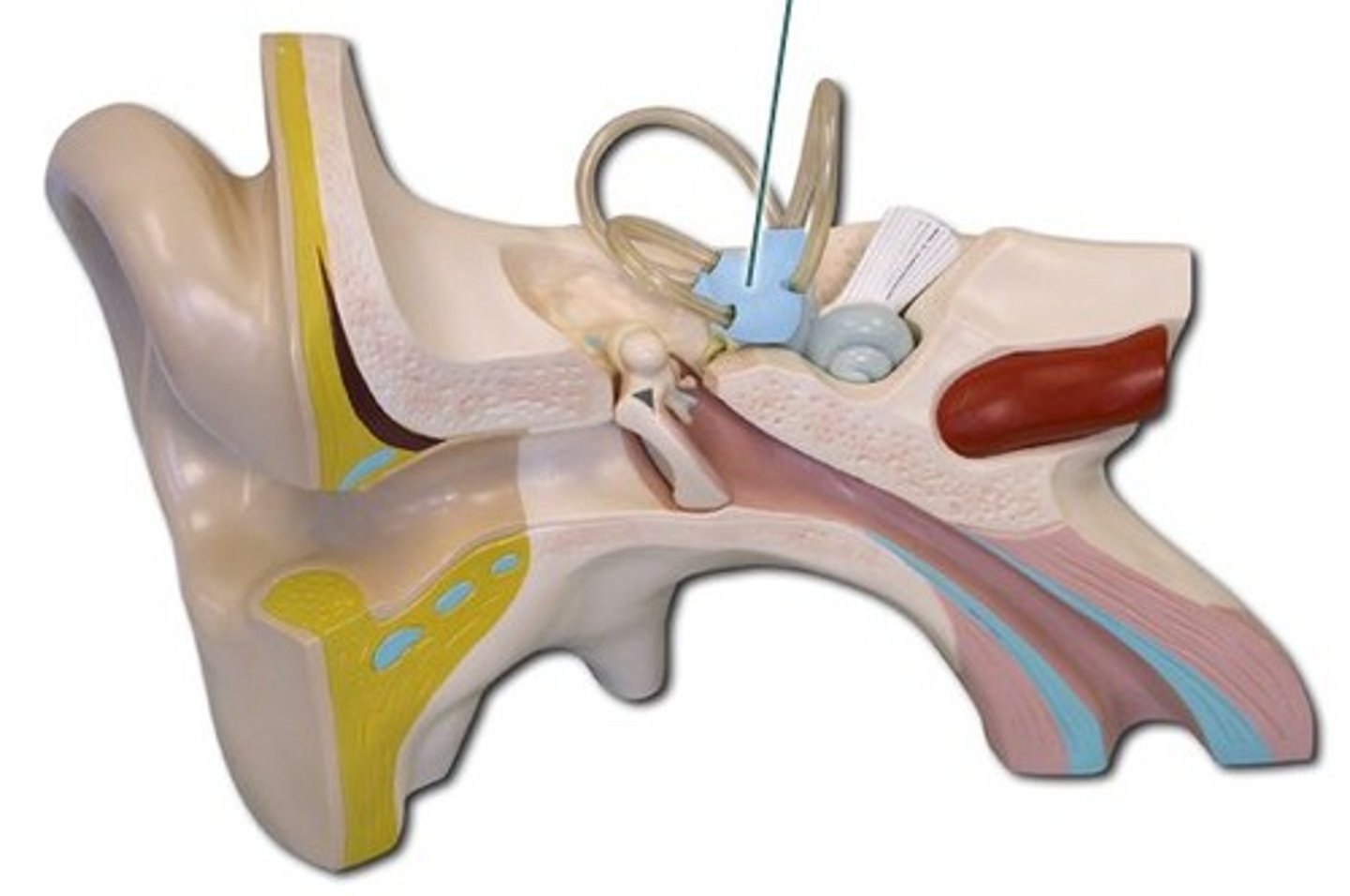
vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance