Introduction to Chemotherapy -- Pharm II Exam 2
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
NCCN evidence blocks categories and definitions
E -- efficacy and regiment agent
S -- safety of regiment/agent
Q -- quality of evidence
C -- consistency of evidence
A -- affordability of regiment/agent
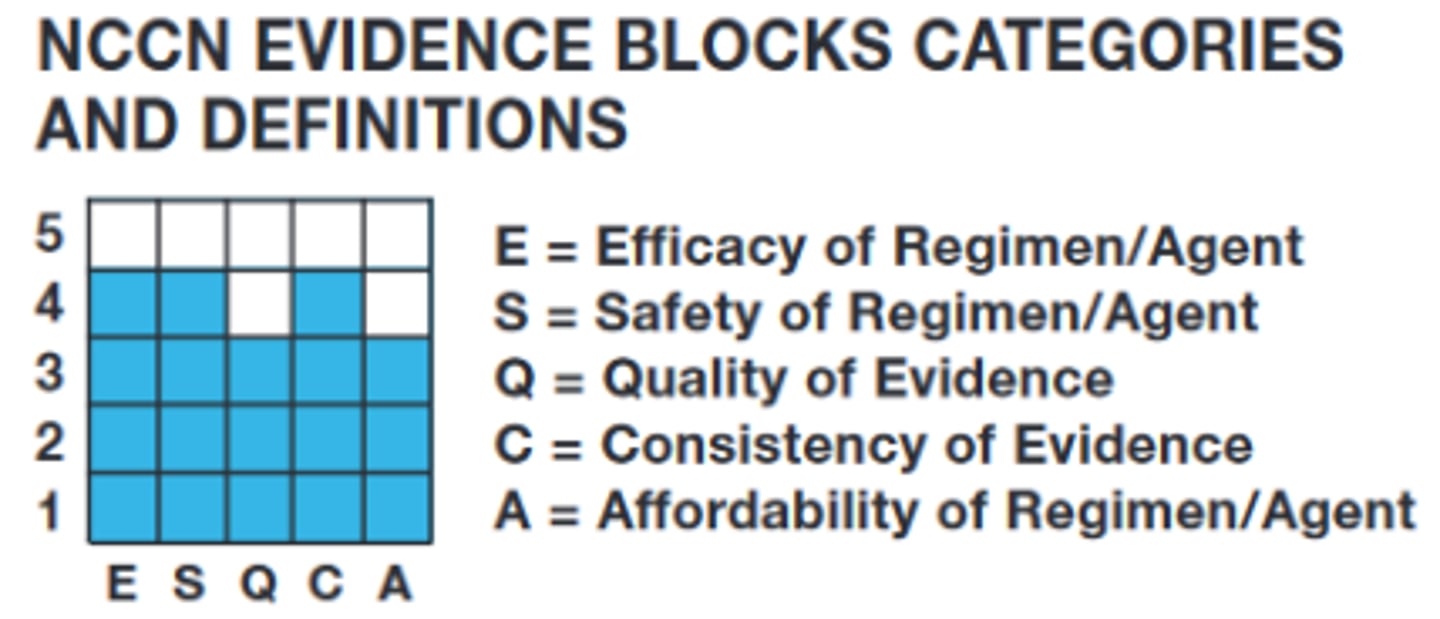
NCCN evidence blocks categories -- more or less blue blocks are better overall?
MORE
cancer: simple definition
uncontrollable cell growth
- malignant cell rapidly proliferate compared to healthy cells
Factors of cancer
Multifactorial
- sex
- age
- race
- genetic predisposition
- environmental carcingogen exposure
most important factor of cancer
environmental exposure
viruses implicated in cancer?
yes
HPV --> cervical cancer
Cancer treatment
25% pts can be cured by surgery and/or radiation alone
the remainder must receive systemic chemo
overall 5-year survival rate of cancer treatment
68%
in general, cancer treatment should be:
1. surgery -- removal of tumor
2. radiation -- shrink tumor
3. chemotherapy -- kill cancer cells or slow growth
goal of treatment (ideal)
achieve a cure (long term, disease-free survival)
- requires eradication of every neoplastic cell... very hard
when a cure is not attainable:
- control the disease to prevent enlargement and spread
- extend survival and maintain quality of life
- treat cancer as a chronic disease for "near normal" existence
Principles of chemotherapy -- objective
- induce apoptosis or a lethal cytotoxic even in cancer cells
- stop tumor growth progression
prinicples of chemo -- general mechanism of action
- target DNA or essential metabolic pathways of cell replication
ideal anticancer drug:
- interferes with process unique to malignant cells
traditional anticancer drugs
lack specificity, affecting all cells (healthy and cancerous) --> many adverse effects
chemotherapy is often dosed by:
Body surface area
Principles of chemotherapy
- surgery and radiation are always preferred to chemo
- primary chemotherapy
- neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- adjuvant chemotherapy (A = after)
primary chemotherapy
- chemotherapy is the primary treatment in pts with advanced cancer for which no alternative treatment exists
ex: hodgkin and non-hodgkin lymphoma
neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- chemotherapy in patients with localized cancer for which alternative localized therapies, such as surgery, exist but which have been shown to be less than completely effective
adjuvant chemotherapy
A = after
- chemotherapy is administered after surgical resection
- goal of chemo is to reduce the incidence of recurrence and to improve overall survival of pts
Combination chemotherapy
- for each cancer, multiple chemotherapy agents are used simultaneously for best results
- cell cycle specific agents: good for rapidly proliferating cancers (e.g. leukemia)
- non-cell cycle agents: better for slower growing cancers but more toxicity
benefits of combo therapy:
- maximal cell killing within a tolerated range of toxicity
- effective against a broader range of cell lines
- may delay and/or prevent development of resistant cancer cell lines
agents with similar toxicities require...
dose reductions when combined
ex: myelosuppression, nephrotoxicity, cardiotoxicity
Cell Cycle
M phase (Mitosis)
- prophase
- metaphase
- anaphase
- telophase
Interphase
- G1 phase: growth/gap phase
- S phase: DNA synthesis phase
- G2 phase: growth/gap phase
G1 phase
gap/growth phase
- generation of enzymes needed for DNA synthesis
G2 phase
gap/growth phase
- DNA double check
- generation of cellular components for mitosis
prophase
- centrosomes begin to form mitotic spindle
metaphase
- chromosomes align in middle of cell
- microtubules attach to centromeres in preparation of separation
anaphase
chromosomes are separated
telophase
- chromosome cluster to opposite sides
- new nuclear membrane forms
there are _____ checkpoints in the cell cycle to assess cells for abnormalities (like mutations in DNA)
3
- G1 checkpoint
- G2 checkpoint
- M phase checkpoint
cell cycle specific proteins
monitor integrity of DNA
- can initiate DNA repair or apoptosis in severe damage
- e.g. p53, chk-1, chk-2
if the p53 gene or other checkpoint proteins become mutated...
damaged cells enter the S phase and mitosis --> mutated cancer cells form with potential drug resistance
alkylating agents/Adducting agents
cell cycle non specific
damage DNA by forming adducts with it
- may be referred to as "cross-linking" agents by formation of cross links with DNA
- form an electrophile intermediate which is then attacked by a nucleophile
types of aklylating cross links
- inter DNA strand cross link
- intra DNA strand cross link
- DNA/protein cross link
- DNA/RNA cross link
cross linnked dna is ....
recognized as damaged during cell-cycle checkpoints --> apoptosis
alkylating agents -- drugs
- cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide
- carmustine
- temozolomide
- platinum coordination complexes (cisplatin, carboplatin)
Cyclophosphanmide and ifosfamide -- MOA
alkylating agents
Cyclophosphanmide and ifosfamide -- metabolism
must be metabolized in the liver to active compounds
- this produces a toxic byproduct = acrolein
Cyclophosphanmide and ifosfamide n-- acrolein elimination
eliminated by the kidneys
- can lead to hemorrhagic cystitis = bladder becomes inflamed, starts bleeding --> hematuria
what medication is given with Cyclophosphanmide and ifosfamide as ppx for hemorrhagic cystitis?
mesna (mesnex)
carmustine (gliadel) -- MOA
alkylating agent (nitrosoureas)
nitrosoureas
- highly lipophilic
- cross blood-brain barrier (MUST cross BBB)
carmustine (gliadel) -- exists as...
a wafer formulation for brain tumors called gliadel wafer
Temozolomide (temodar) -- MOA
- DNA methylating agent (MTIC active metabolite)
Temozolomide (temodar) -- metabolism
prodrug
- spontaneously hydrolyzed to active metabolite MTIC at physiological pH --> MTIC methylates DNA fragments --> apoptosis
Temozolomide (temodar) -- can it cross BBB?
yes: lipophilic and crosses BBB
- used in glioblastoma multiforme
Platinum coordination complexes
- cisplatin
- carboplatin
- oxaliplatin
Platinum coordination complexes -- MOA
covalently binds DNA bases (guanine) and forms DNA cross links --> denatures double helix --> apoptosis
platinum coordination complexes -- ade
- nephrotoxicity --> dose-limiting toxicity is cisplatin
- ototoxicity --> high potential for hearing loss
ppx to reduce risk of nephrotoxicity in platinum coordination complex use
- amifosine (ethyol)
microtubule inhibitors cell cycle specific?
yes: M phase
microtubule inhibitors : MOA
disrupt mitosis (in metaphase; M phase) by interfering with microtubule formation or degradation
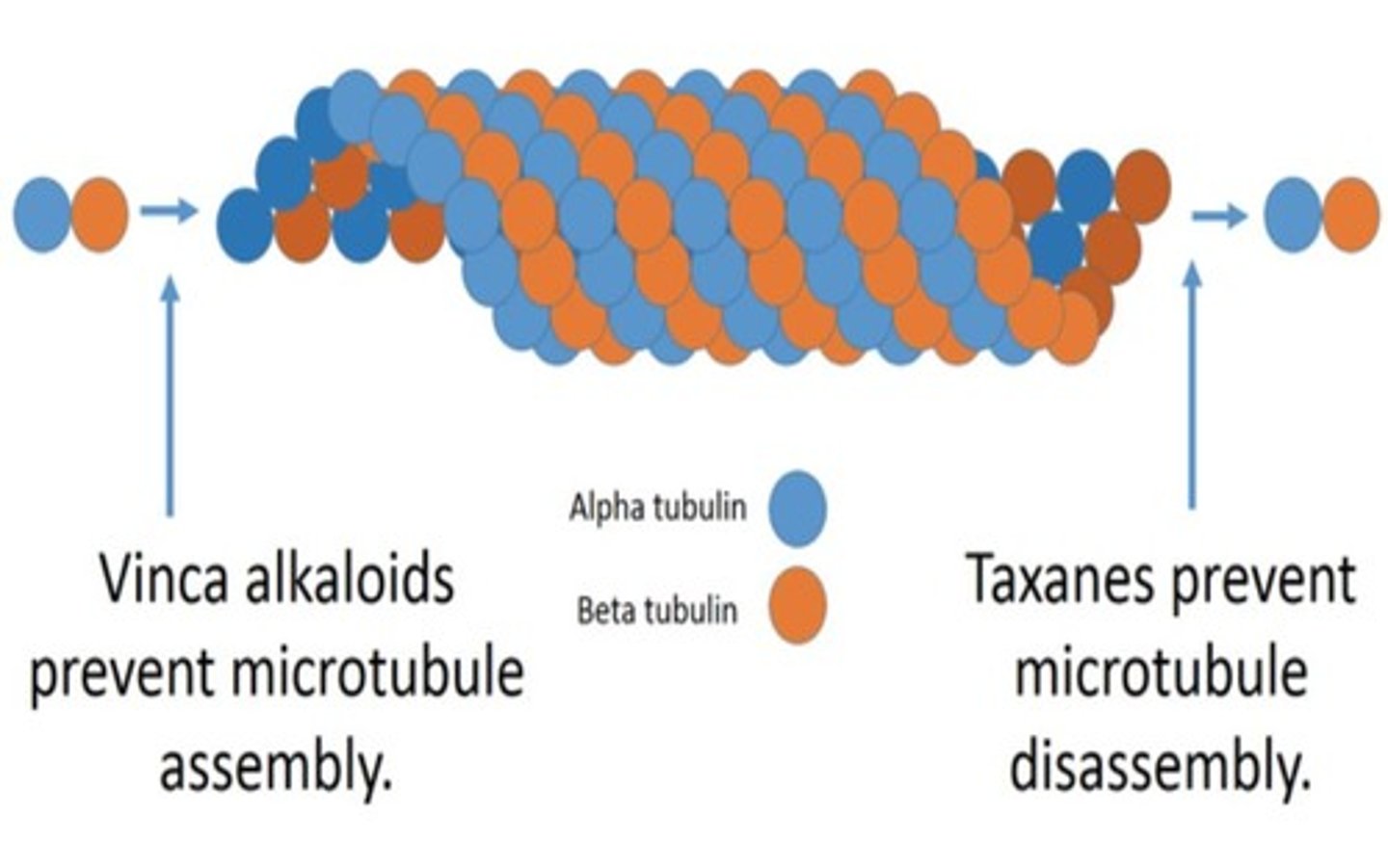
2 main classes of microtubule inhibitors
- Vinca alkaloids
- Taxanes
Vinca alkaloid agents:
vincristine (oncovin)
vinblastine (velban)
vinca alkoloids -- MOA
Cell Cycle specific (M phase)
- bind to tubulin (microtubular subunit) --> block ability for tubulin to polymerize and form microtubules --> dysfunctional mitotic spindle --> chromosomes never separate = apoptosis
taxanes -- agents
paclitaxel (abraxane)
taxanes -- MOA
cell cycle specific (M phase).
taxanes hyperstabilize microtubules --> prevents breakdown of mitotic spindle --> cell remains frozen in metaphase = apoptosis
peripheral sensory neuropathy is a toxicity highly associated with:
- vinca alkaloids (vincristine, vinblastine)
- taxans (paclitaxel)
anti-metabolites: cell specific?
Cell specific: S phase
anti-metabolites: MOA
interfere with synthesis of DNA precursors and DNA synthesis
- effects occur during S phase
antimetabolites: 2 cubclasses
1. antifolates (folate analog)
2. purine/pyrimidine analogs
antimetabolites: drugs
- methotrexate
- 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- 5- fluorouracil (5-FU) /capecitabine
antifolates -- class
antimetabolites
antifolates -- MOA
block DNA precursor synthesis
- structurally similar to folic acid
roles of folic acid
- reduced form (FH4) --> methylation reactions needed in thymidylate/purine biosynthesis
- dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) --> enzyme responsible for the reduction of folic acid into its active form FHR
anti- folates inhibit:
- dihydrofolate reductase (general biosynthesis)
antifolates deplete ....
purine and pyrmidine pools --> preventing DNA synthesis, repair, and RNA transcription
by reducing purine and pyrimidine pools...
the chances of another chemo-drug (that is an analogue of purine/pyrimidine) being incorporated into DNA increases
- antifolates are used concurrently with other antimetabolites (purine/pyrimidine analogs)
Methotrexate -- class
antimetabolite (antifolate)
methotrexate -- MOA
- dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitor --> interferes with DNA synthesis, repair and cellular replication
- also has immune modulator and anti-inflammatory properties
methotrexate -- indications
- cancer (ALL, non-hodgkin lymphoma); part of combination regimen
- autoimmune conditions (RA, chrohns, psoriasis)
- ectopic pregnancy (embryo-fetal toxicity/death)
methotrexate: administration
-PO/IV/intrathecal/IM
methotrexate -- dosing
- fatal errors have occurred with daily dose vs weekly dose
- daily dose --> usually oncology - related
- weekly dose --> usually autoimmune related
can methotrexate be used in pregnancy?
no
methotrexate -- dose adjustments
- hepatic
- renal
methotrexate warnings
- hepatotoxicity
- myelosuppression
- mucositis/stomatitis
- pregnancy (embyro-fetal toxicity/death)
antidote for methotrexate od:
Leucovorin
- metabolite of folic acid that does not rely on DHFR
- referred to as "leucovorin rescue"
- sometimes included as part of chemo regimen with high dose MTX
what may MTX be given with to decrease hematological, GI, and side effects?
folic acid
- given daily on non MTX days
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) -- class
antimetabolite (purine analog)
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) -- MOA
- inhibits de novo purine synthesis
- acts as a false metabolite and is incorporated into DNA and RNA to inhibit their synthesis
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) -- indications
- used in conjunction with MTX in ALL
- effective in curing ~90% of childhood cases
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) -- metabolism
metabolized by xanthine oxidase
- xanthine oxidase inhibitors can be used to treat gout. (allopurinol)
5- fluorouracil (5-FU) -- class
antimetabolite (pyrimidine analog)
5- fluorouracil (5-FU) -- MOA
- prodrug: converd to 5-FdUMP intracellularly
- 5-FdUMP inhibits thymidylate synthase
- decreased thymidine --> imbalance of deoxynucleotides --> decreased DNA synthesis --> apoptosis
5- fluorouracil (5-FU) -- indications
slow growing tumors
what is commonly administered with 5- fluorouracil (5-FU) to enhance its cytotoxic effects?
- leucovorin
5- fluorouracil (5-FU) -- ade
hand-foot syndrome
- tingling, burning, redness, swelling, and blistering on palms and soles
Topoisomerase inhibitors: cell cycle specific?
cell cycle specific: late S/G2 phase
DNA topoisomerases
- enzymes that help relieve torsional strain in supercoiled DNA
topoisomerase I
cutting one strand of DNA
topoisomerase II
cutting both strands of DNA
topoisomerase inhibitors
prevent DNA from becoming relaxed and trap DNA in a supercoiled position
result = overwound DNA until tension tears it apart --> apoptosis
Topoisomerase I inhibitors: drugs
irinotecan, topotecan
Topoisomerase I inhibitors -- MOA
topoisomerase I inhibitor --> leads to overwinding of DNA --> apoptosis
topoisomerase I inhibitors -- ade
- irinotecan can produce severe diarrhea
what can help manage the severe diarrhea of irinotecan
- early onset: atropine (anticholinergic drug) can help manage early onset diarrhea
Topoisomerase II inhibitors -- drugs
etoposide and teniposide
topoisomerase ii inhibitors -- moa
- topoisomerase ii inhibitor --> leads to overwinding of DNA --> apoptosis
topoisomerase ii inhibitors -- adverse effects
- GI distress
- alopecia