Plant Cell Walls and Plasmodesmata: Structure, Function, and Development
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are plasmodesmata?
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels that traverse the cell walls of plant cells, allowing for communication and transport between adjacent cells.
What is the primary function of plasmodesmata?
The primary function of plasmodesmata is to facilitate the exchange of materials and signals between plant cells.
What forms during cell division to create primary plasmodesmata?
Primary plasmodesmata form during cell division when the cell plate is established.
How do secondary plasmodesmata differ from primary plasmodesmata?
Secondary plasmodesmata form de novo, independently of cytokinesis, across already formed cell walls, typically between cells that do not originate from the same primary cell.
What structural components are involved in the plasmodesmata channel?
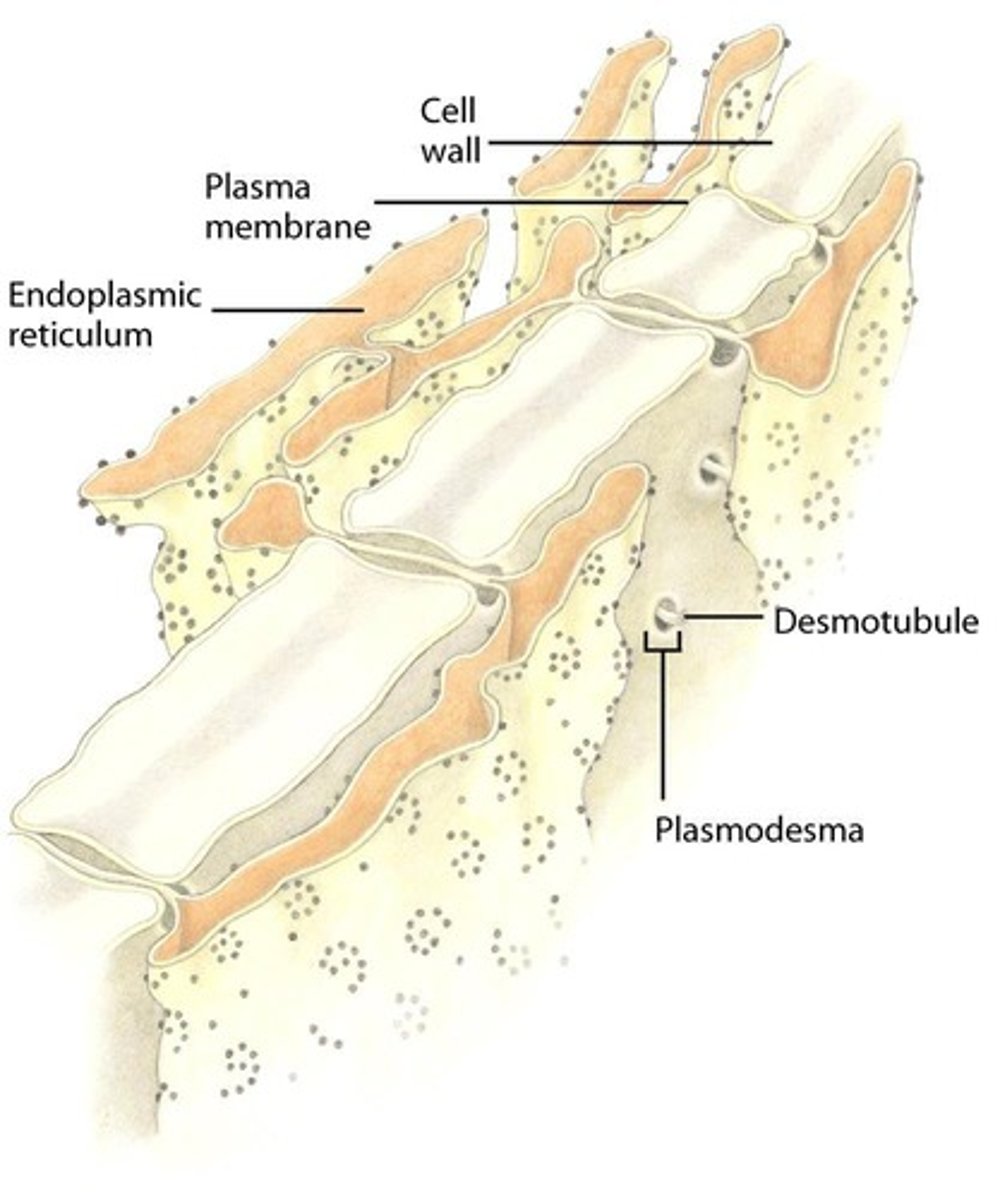
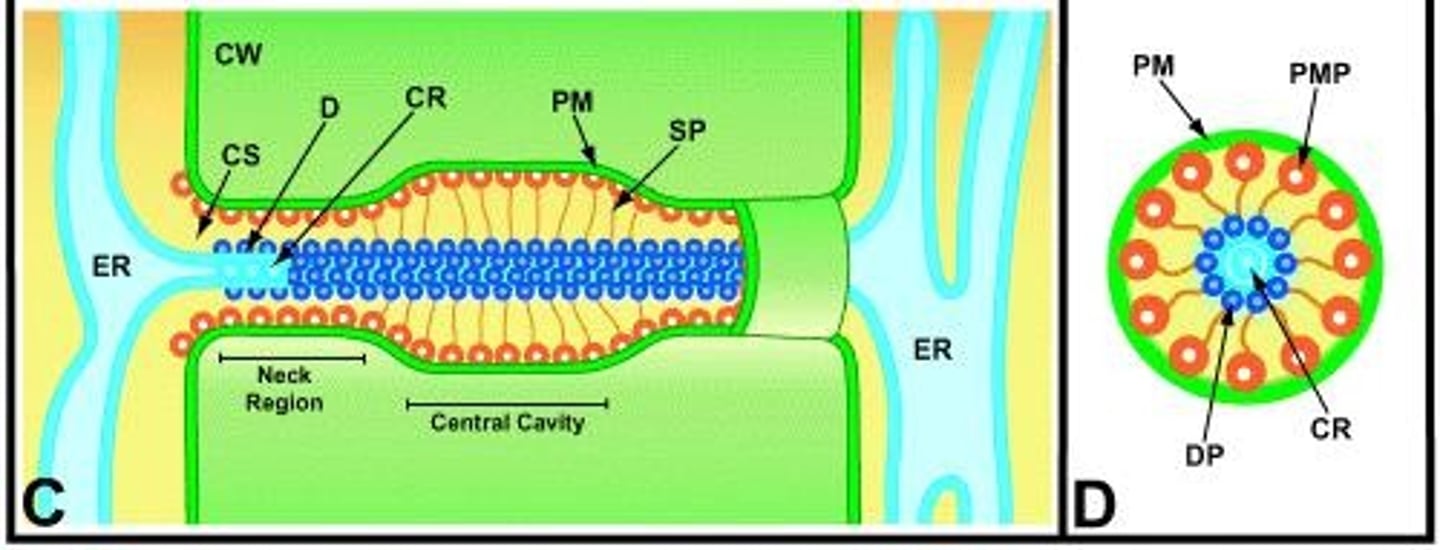
The plasmodesma channel includes a cytoplasmic sleeve and desmotubule, which is derived from the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the size-exclusion limit (SEL) in relation to plasmodesmata?
The size-exclusion limit (SEL) of plasmodesmata determines the maximum size of molecules that can pass through, varying with plant development and tissue type.
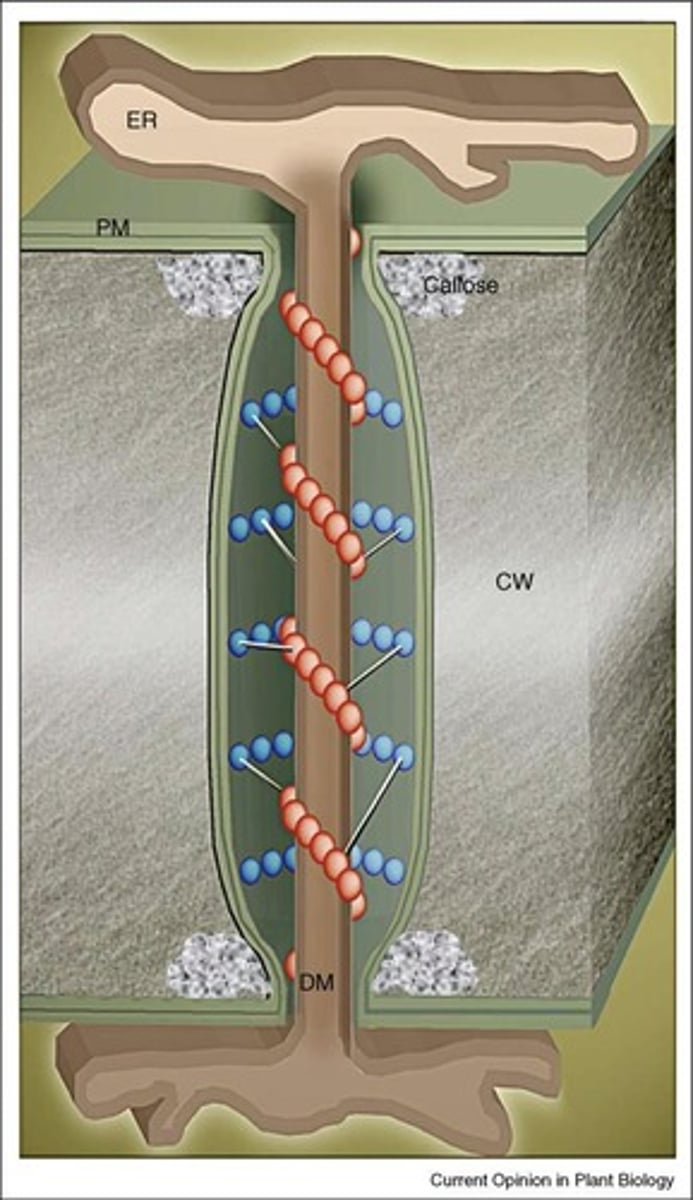
What role does callose play in plasmodesmata?
Callose regulates the size-exclusion limit of plasmodesmata, slows down pathogen spread, and is involved in wound response and sieve-pore genesis.
What happens to plasmodesmata density as cells mature and divide?
As cells elongate, the density of plasmodesmata per unit area decreases due to dilution from cell division and elongation.
What compensatory mechanisms do plants use for plasmodesmata during cell growth?
Plants compensate for the dilution of primary plasmodesmata by modifying existing plasmodesmata and forming branched primary plasmodesmata.
What physiological changes can affect plasmodesmata permeability?
Plasmodesmata can alter their permeability in response to turgor changes and various physiological perturbations.
What is the impact of viruses on plasmodesmata?
Viruses can modify the plasmodesmal size-exclusion limit and induce enzymes that degrade callose, facilitating their spread.
How do actin and myosin contribute to plasmodesmata function?
Actin and myosin may allow constriction and relaxation of the plasmodesmatal pore, participate in pore structure, and assist in the transport of materials.

What is the significance of the cytoplasmic sleeve in plasmodesmata?
The cytoplasmic sleeve allows for the movement of small molecules and may be occupied by globular subunits that influence transport dynamics.
What is the role of ubiquitin in plasmodesmata?
Ubiquitin is involved in the degradation and removal of plasmodesmata during cell differentiation and development.
What types of cells typically have secondary plasmodesmata?
Secondary plasmodesmata are found between cells that undergo extensive elongation or are involved in graft unions.
What is the relationship between plasmodesmata and cell walls?
Plasmodesmata traverse cell walls, connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent cells and facilitating intercellular communication.
What is the effect of cadmium on viral invasion in plants?
Cadmium blocks viral invasion in plants by affecting the function of plasmodesmata.
What happens to plasmodesmata during the differentiation of guard cells?
During the differentiation of guard cells, there is a loss or reduction of plasmodesmata.
What are the components of secondary cell walls?
Secondary cell walls are composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses (like xylans and mannans), low levels of pectins, and lignin.
What are brachysclereids?
Brachysclereids, or stone cells, are a type of sclerenchyma found in plants like pear and avocado, characterized by thick lignified walls.
What is the significance of the phragmosome in cell division?
The phragmosome is involved in the coalescence of Golgi vesicles during cell division, facilitating the formation of the cell plate.
How do plasmodesmata change during plant development?
Plasmodesmata can be sealed off or removed both temporarily and permanently during plant development, affecting cell communication.
What is the role of desmotubules in plasmodesmata?
Desmotubules are extensions of the endoplasmic reticulum that run through plasmodesmata, playing a role in cellular transport.