L21: Arthropods III (Vet/Med Significance)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are the three primary groups, of insects, of veterinary importance?
– Lice
– Fleas
– Flies
Definition:
Hooked tarsi
– Terminal segments of legs, grip hair
What do chewing lice feed on?
– Mammals
– Birds
– Feed on skin
What do sucking lice feed on?
– Mammals only
– On blood
Summary:
lice (3)
– permanent ectoparasites
– Small, wingless dorso-ventral (DV) flattened body
- Host specific
How do lice cause harm to the host? (4)
– Irritation and skin damage
– Anemia
– Vectors of disease, organisms, like typhus, trench fever
– Intermediate host of parasites, like tapeworms
What does it mean to be host specific? (lice)
– lice will only attach to a specific host
Where does the lice lifecycle occur?
– On the host
What is the lice lifecycle?
1st nymph → 2nd nymph → 3rd nymph → female or male adult → female lays an egg
Life cycle is completely on host
Lice of animals (3)
– Sheep body louse
– Feeds on skin and wool
– Causes intense irritation
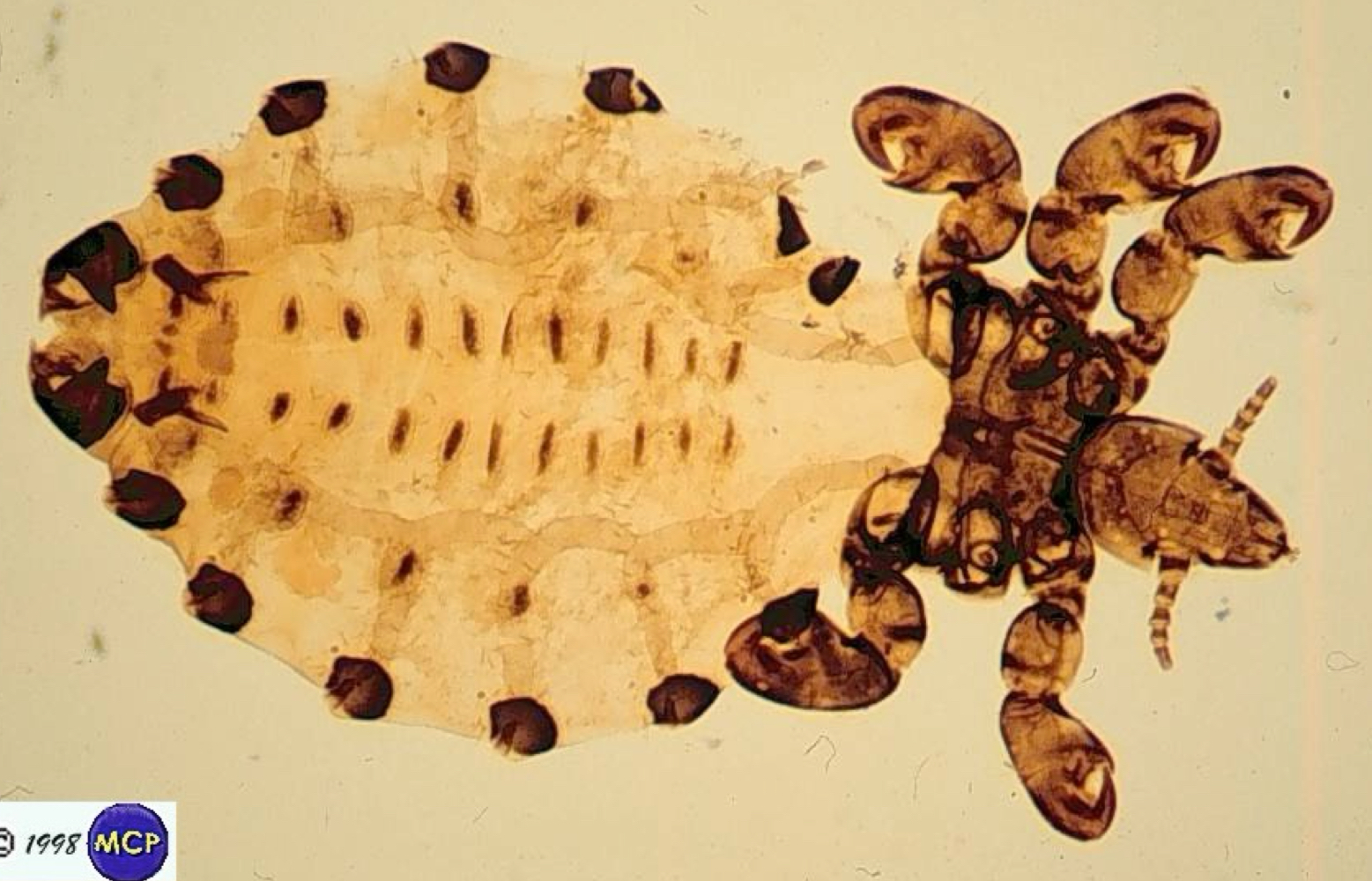

Hematopinus - blood sucking louse (pigs & rumiinants)
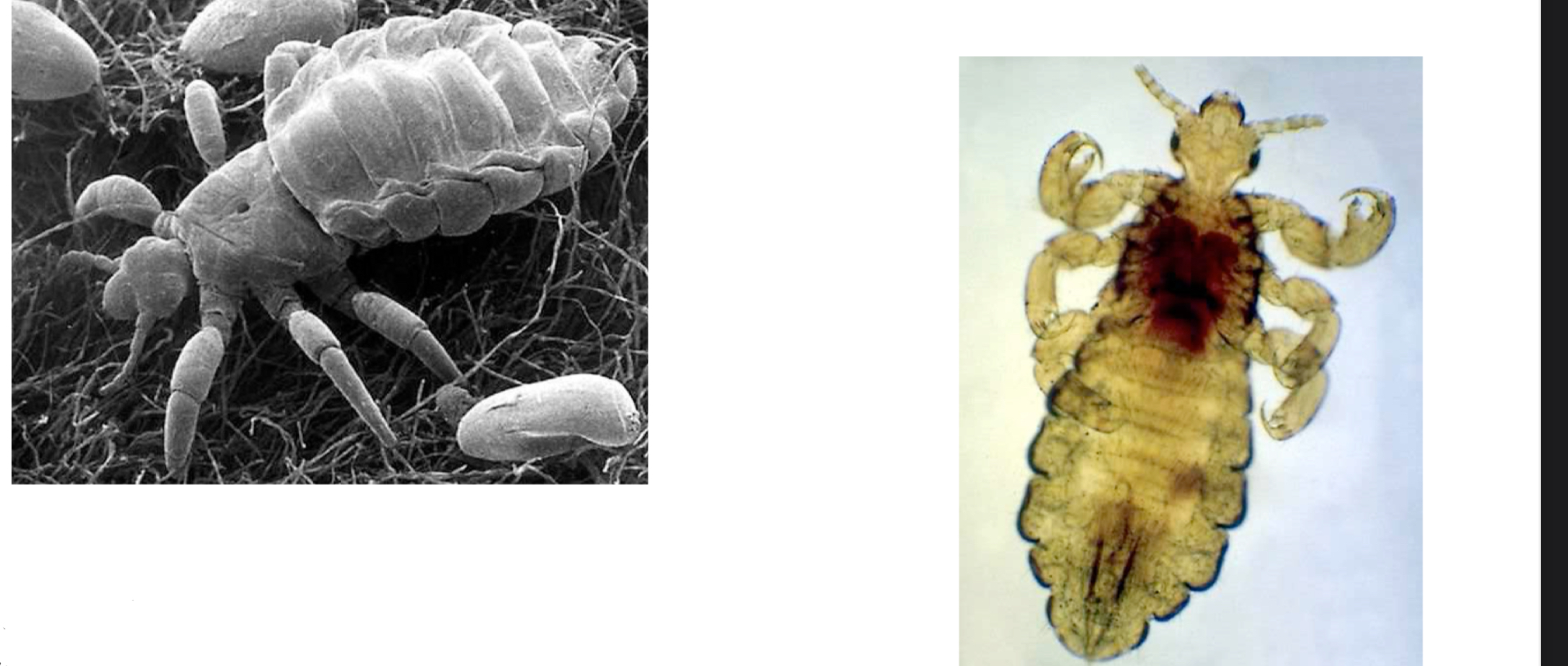

-lice that feeds on humans
-Pediculus humanus
-P. capitis
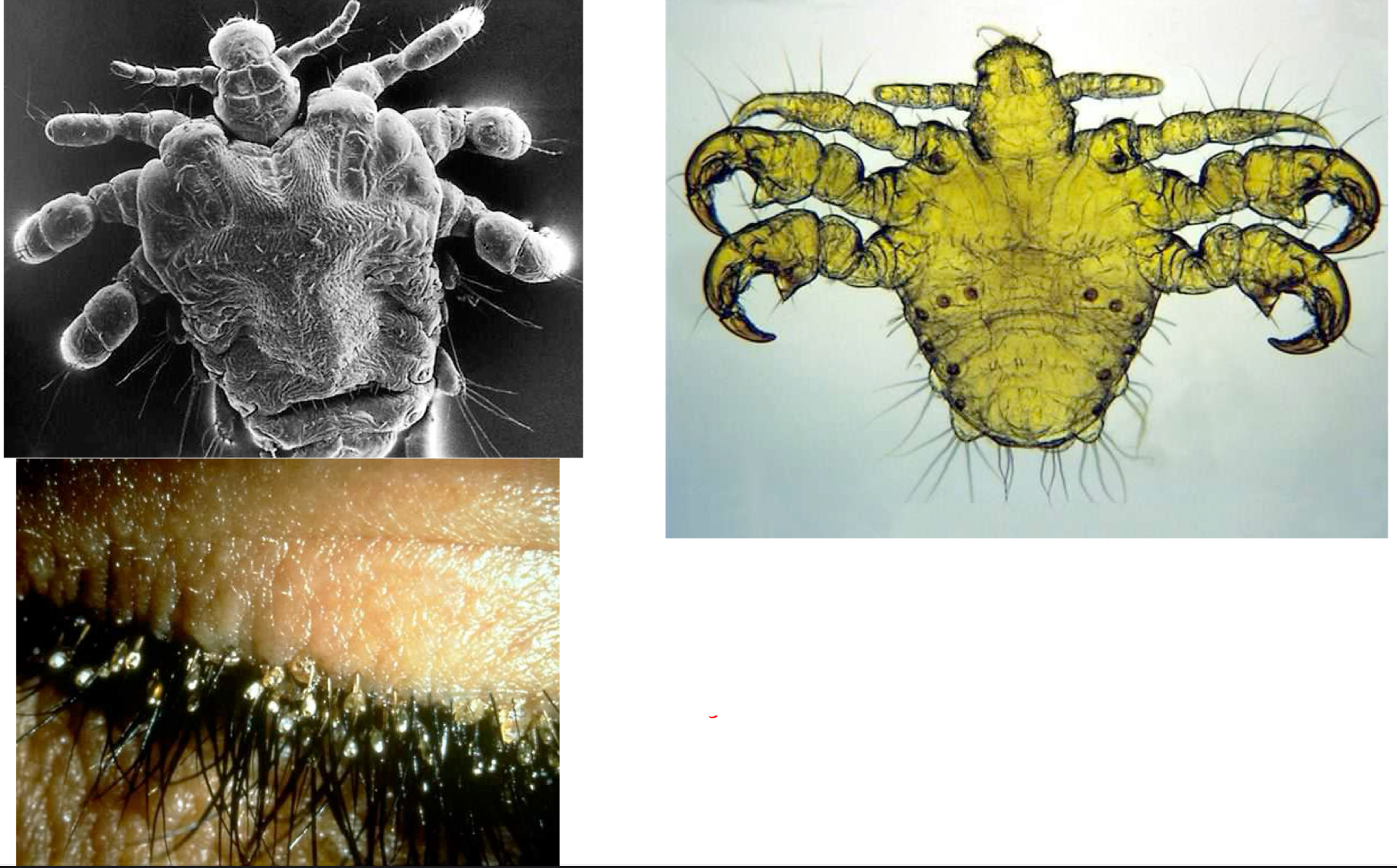
Phthirus pubis - pubic louse
Host specific
Sexual transmission
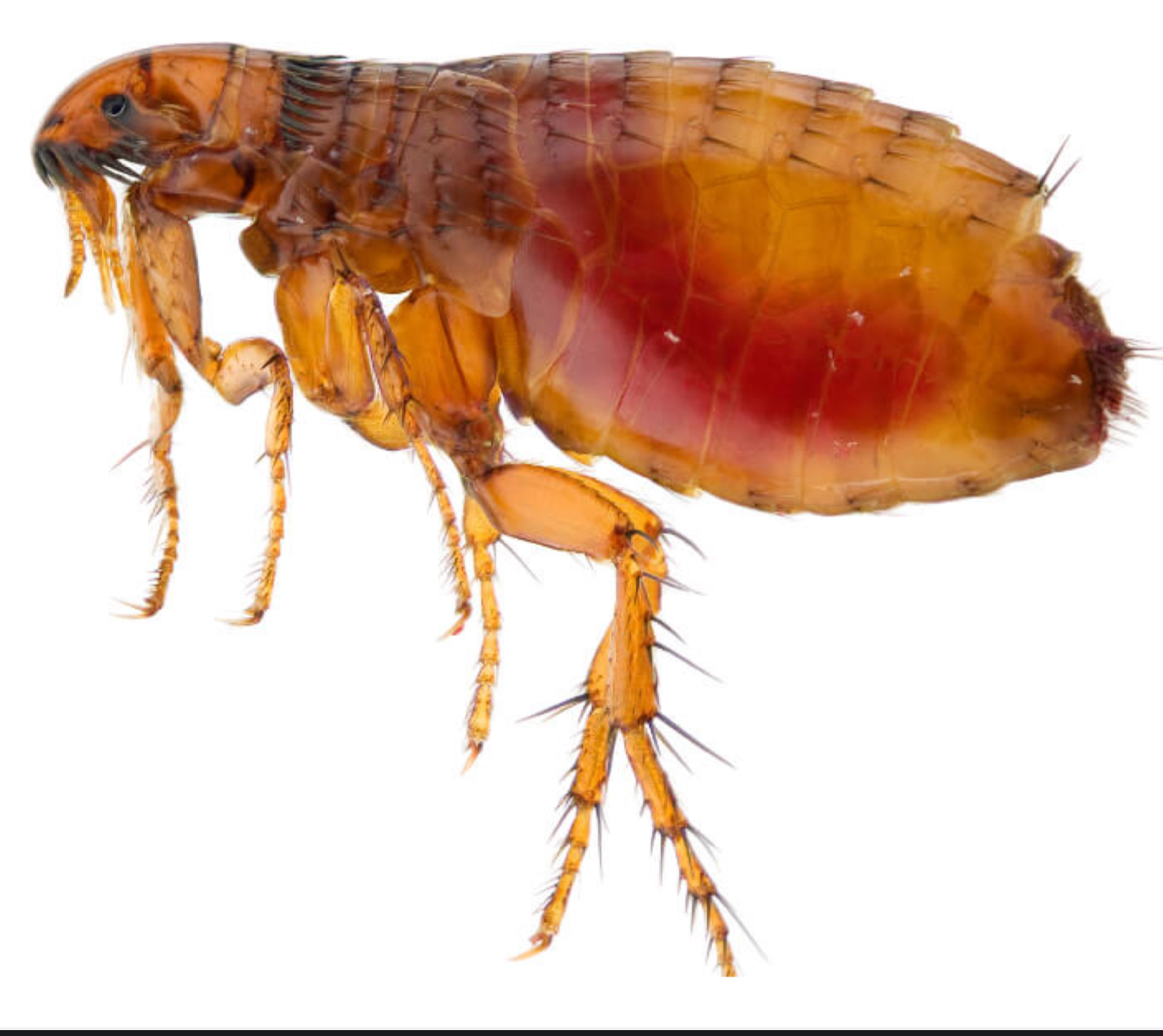

flea
summary:
fleas (3)
– non-permanent ectoparasites
–small laterally compressed adults
–muscular hind legs
Fleas:
Hosts
– Birds
– Mammals (dogs, cats, poultry, humans)
Fleas:
Eggs
Laid on host or in nest of host (kennels, blankets, etc.)
Fleas:
Larva (4)
– Detritus feeder
– Not on hosts
– Chewing mouth parts
– Feed on adult flea faeces and gain nutrition from blood in faeces (cats and dogs)
Adult flea
Blood feeder they have sucking mouth parts, adapted to piercing skin and feeding on blood
How do fleas cause harm to the host? (5)
–allergy or hypersensitivity
–Blood loss (especially in juveniles and elderly animals)
– Bacteria
– Virus
– Intermediate host to cucumber tapeworms
Fleas as bacterial vectors
– Plague
– Cat scratch fever (Bartonella)
Fleas as viral vectors
– Myxomatosis
dipylidium caninum
– Cucumber tapeworm of dogs and cats
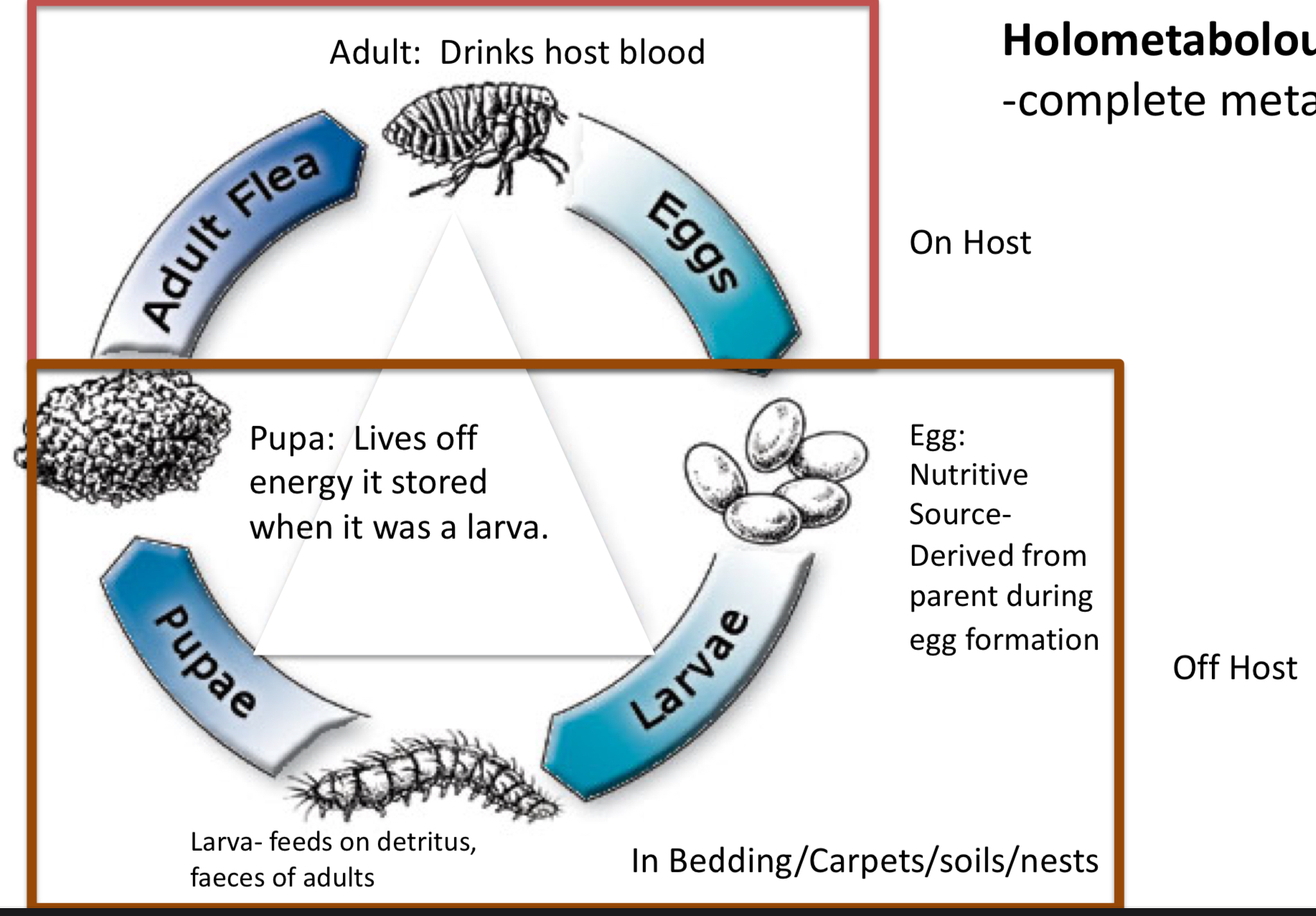
– Life cycle of cat flea
Ctenocephalides felis
Examples of filth flies
– House flies
– Blowflies
flies and mosquitoes:
Blood sucking adult summary
– Stable flies and horseflies cause blood loss
– Vectors for malaria and heartworm and trypanosomiasis
Where do the larval stages of flies of mosquitoes live? (4)
– Blowfly and flesh fly maggots live in decomposing flesh
– Strike fly maggots live in living tissue
– bot fly maggots live in internal organs
Summary:
Crustaceans (3)
– Dominantly aquatic arthropod
– Some live in moist terrestrial environments
– Extensively specialized appendages
Definition definition:
Plankton (4)
– Passive drifter
– Weak swimmers
– Small, some are microscopic
– Includes larval forms of larger crustaceans
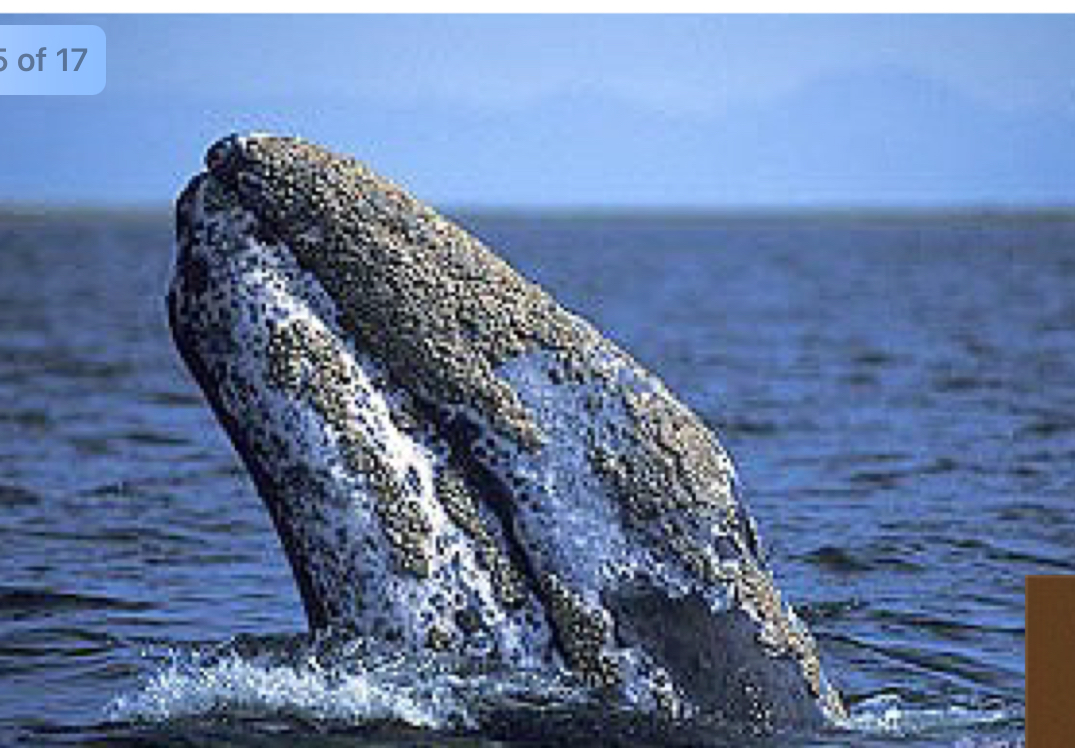

Crustaceans
– Barnacles on whale
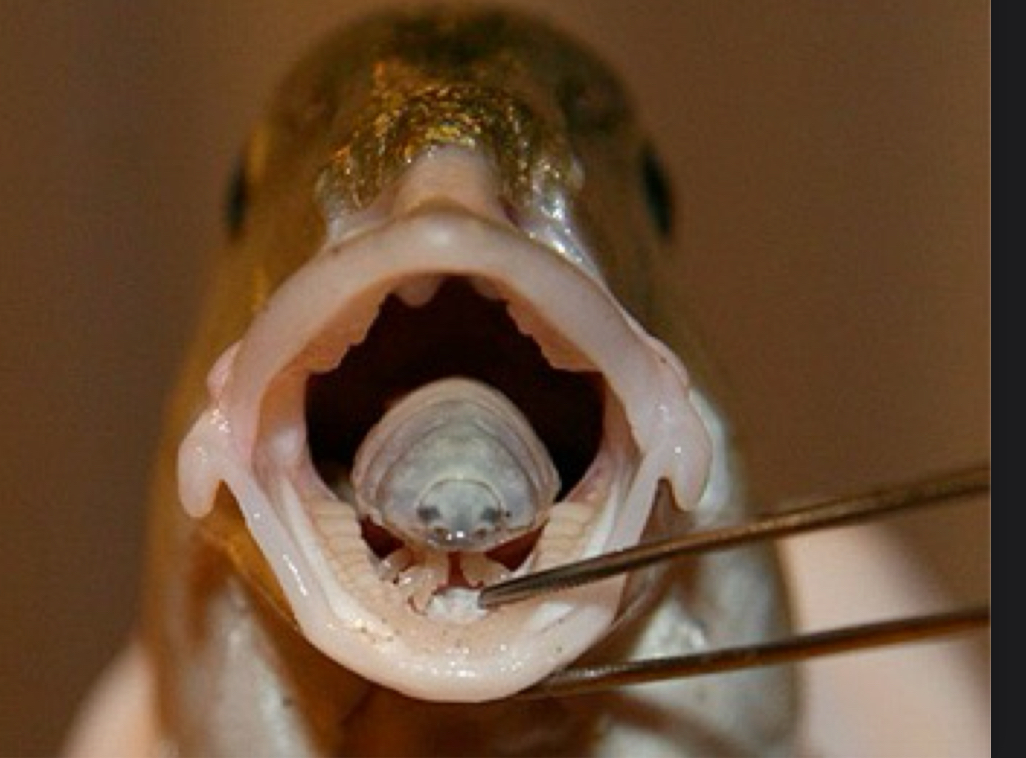
Crustaceans
-Cymothea (isopod)
Summary:
copepods
– Important food source in aquatic systems
– Some predatory (can be used to control populations)
– Can be parasitic on fish
What is an example of a copepod that is predatory?
Mesocyclops used to control dengue mosquito