PDTI Module 13
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Enzyme multiplicity:
several different enzymes may be involved in biotransformation of one drug
Product multiplicity:
Drug is metabolized into several different metabolites
Polyfunctionality
drug may undergo several different reaction types
Phase one metabolism in the liver is done by ___ and makes drugs more ____
CYP450s; hydrophillic
Phase two metabolism in the liver is done by ____ and causes ____
Conjugation: UGTs, ST, NAT2, COMT
Further increases compounds solubility
Most metabolism is done by what cyp?
CYP3A
Label the parts of CYP2D6×2A
CYP: Superfamily
2: Family
D6: Subfamily
6: Individual member/isoform
2A: allele/Haplotype
+
P450s from the same ____ share more than 55% sequence homology
subfamily
Intrinsic factors of drug metabolism?
GENETICS, age, sex, disease
Environmental factors of drug metabolism?
DIET, CONCOMINANT (simultaneous use of) DRUGS, chemical exposure
How does high enzyme activity effect amount of drug in the body?
There will be less drug in the body
What enzyme is high in infants and lower in adults?
CYP2619
Drug exposure is related to what 2 factors?
Cmax and AUC
What is the “wild type”/reference allele for CYP2D6?
CYP2D6×1
What are the allele functional statuses?
uncertain function, unknown, no function, decreased function, normal function, increased function
What are the drug metabolizing phenotype standard definitions?
poor metabolizer, intermediate, normal, rapid, and ultrarapid metabolizer
Phenotype=
allele 1 + allele 2
Two increased function alleles=
ultrarapid
Two no function alleles=
poor
Two normal function alleles=
normal
One no /decreased function + normal function =
intermediate
What is the result of an ultrarapid metabolizer on an active drug to the inactive state?
The drug will become inactive faster. The will be low amount of active drug
What is the result of an ultrarapid metabolizer on an inactive drug to the active state?
Most of the drug will be in the active state
Tmax and Cmax happen quickest with ____ metabolizers as opposed to IM and PM
normal metabolizers
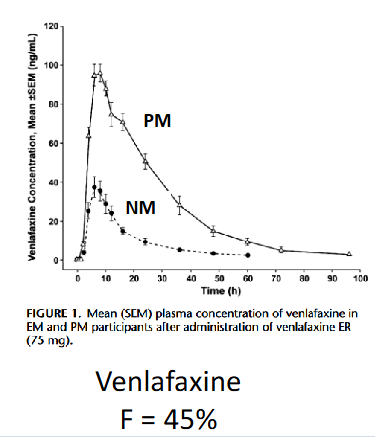
When bioavailability is high, _____ is increased
Half life
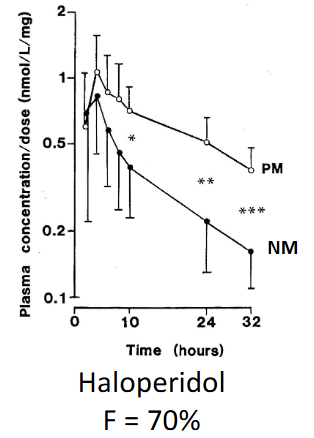
When bioavailability is low, _____ is increased
Cmax
What is the largest mammaliam CYP family and contributes to 50% of all drug metabolism?
CYP2 gene family
What is the major substrate, inhibitor, and inducer of CYP1A2?
Substrate: Tizanidine
Inhibitor: Fluvoxamine
Inducer: Smoking
What is the CYP enzyme where PM phenotype more common in Asian populations compared to Caucasian?
CYP2A6
What allele is responsible for gene deletion/ no function in CYP2A6?
*4
What is the substrate and inducer of CYP2A6?
Substrate is NICOTINE and inducer is St. Johns Wort.
No inhibitors
How is nicotine broken down by CYP2A6?
Nicotine > nicotine-iminium ion > Cotinine
What CYP2A6 allele point mutation yields inactive protein in Caucasians?
CYP2A6*2
What CYP displays gene duplication?
CYP2A6*1/*1x2
What are the substrates of CYP2B6?
Efavirenz, Methadone, Sertraline
What are the inducers of CYP2B6?
Efavirenz, rifampin, carbamazepine
Poor metabolizers have the least amount of ____ but the most amount _____
clearance; under the curve
What CYP is polymorphic?
CYP2C8
Given the close proximity of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9, some _____exists between these genes
linkage disequilibrium
What are substrates of CYP2C8?
Glitazones (e.g.,
rosiglitazone,
pioglitazone)
Ibuprofen
What are inducers of CYP2C8?
Rifampin
What are the substrates of CYP2C9?
warfarin, Phenytoin, NSAIDs (e.g.,
ibuprofen
What are inhibitors of CYP2C9?
Amiodarone
Fluconazole
Miconazole
What are inducers of CYP2C9?
Rifampin
St. John’s wort
What are the phenotypes for CYP2C9?
poor, intermediate, and normal?
What are CYP2C9 phenotypes based on?
Activity Score. Poor is 0-0.5
Intermediate is 1-1.5
Normal is 2
What CYP2C9 allele is for decreased function?
*2
What CYP2C9 allele is for no function?
*3
What are the substrates for CYP2C19?
Clopidogrel (pro
drug)
PPIs (e.g.,
omeprazole)
Select SSRIs: Sertraline, Escitalopram, Citalopram
Voriconazole
What are inhibitors of CYP2C19?
Fluvoxamine
Fluoxetine
What are inducers of CYP2C19?
Rifampin
St. John’s wort
What are no function alleles for CYP2C19?
*2, *3
What is the increased function allele for CYP2C19?
*17
What does the AUC of PM look like for Clopidigrel?
It has lower AUC because it is a prodrug???
How do proton pump inhibitors like Omeprazole affect H.pylori?
Poor metabolizers have higher cure rate. Experts suggest to increase dose in NM
What are the substrates for CYP2D6?
Codeine (pro drug)
Tramadol (pro drug)
Paroxetine
Fluvoxamine
Desipramine
What are inhibitors of CYP2D6?
Bupropion
Duloxetine
Quinidine
Fluoxetine
What are inducers of CYP2D6?
None. Not inducible
What are the phenotypes for CYP2D6?
PM, IN, NM, UM
Allele function is measured by what in CYP2D6?
activity score
_____ results in increased function for CYP2D6?
Duplication
What are the substrates for CYP3A4/5?
Tacrolimus
Quetiapine
What are inhibitors of CYP3A4/5?
Ketoconazole
Verapamil
Grapefruit
juice
What are inducers of CYP3A4/5?
Rifampin
Carbamazepine
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
St. John’s wort
What is a clinically relevant variant for CYP3A4?
*22
What is a functional variant conferring expresser phenotype (NM or IM) for CYP3A5?
*1
What CYP3A5 variant causes splicing defects and truncated protein?
*3
CYP3A5 expresses most commonly in ____
African Americans (2/3)
What are non expresser star alleles for CYP3A5?
*3/*3. Majority of population
What is a phase 1 enzyme that is the rate limiting step for fluoropyrimidines metabolism?
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), encoded for by DPYD
DPYD is rare and highly ____
polymorphic
Variation leading to _____DPD activity increases exposure to drug and increases risk of life-threatening fluorouracil toxicity
decreased
Why are DPYD variants important?
Variants are rare with low population frequency but have severe clinical consequences
What are substrates of DPYD?
Fluoropyrimidines
(e.g., 5-FU and
capecitabine)
What are the substrates for UGT1A1?
Atazanavir, bilirubin, irinotecan
What is an inducer of UGT1A1?
Rifampin
What are decreased function star alleles for UGT1A1
6 and 28
What ethnic group is frequently a poor metabolizer of UGT1A1?
African americans
SN-38 is transformed into SN-38 glucuronide by what enzyme?
UGT1A1
NAT poor metabolizers
slow acetylators
NAT intermediate/normal metabolizers
fast acetylators
NAT2 substrates
Isoniazid,
hydralazine,
amifampridine
______ acetylators generally have higher plasma levels of hydralazine and require lower doses to maintain control of blood pressure
Slow
What does TPMT do?
Thiopurine Methyl Transferase. Catalyzes the s-methylation of thiopurine drugs
What are the substrates for TPMT
Thiopurines (e.g., Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine)
What are phenotypes for TPMT?
PM, IM, NM
What does NUDT15 do?
NUDT15 converts a cytotoxic metabolite to a less toxic one
What are phenotypes for NUDT15?
PM, IM, NM
What are substrates for NUDT15?
Thiopurines (e.g., Azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine)
What are substrates for COMT?
Catecholamine
neurotransmitters
How are Vmax and Km affected in competative inhibition?
Substrate Vmax unchanged, Km increase
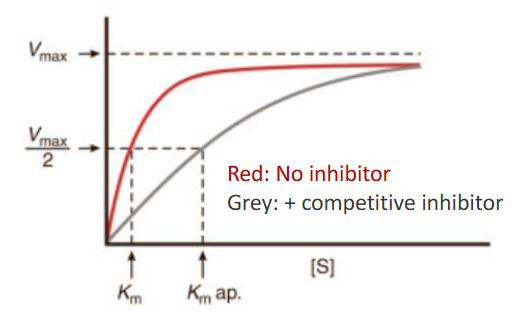
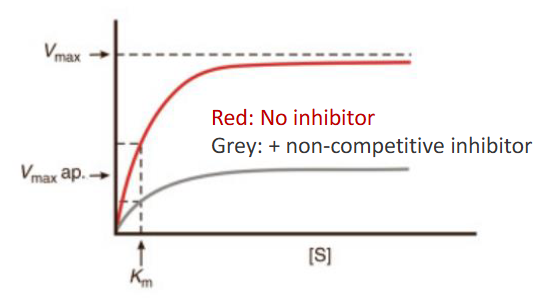
How are Vmax and Km affected for non-competitive inhibition?
Vmax and Km both change (Km might not though)
What is AUC ratio and what classifies strong, moderate, and weak?
AUCinhibitor/AUCno inhibitor
Strong: AUC> 5
Moderate: equal to 2< AUC <5
Weak is 1.25-2
Describe the onset of enzyme inhibition
Fast onset and offset. Direct chemical effect
Describe the onset of enzyme induction
Slow onset and offset. Signals protein synthesis
What is the effect of St Johns wort at acute levels?
Inhibits P-gp/CYP3A4
What does grapefruit juice inhibit?
CYP3A4 and OATP
______ is a great resource that has information on the gene, pathways, and dosing recommendations all in one place
PharmGKB