11.0 Economic Performance (All in 1)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Why does a positive output gap lead to inflation
Excess demand over capacity causes firms to raise prices
Why does a negative output gap reduce inflation
Unused resources mean low demand pressures, keeping prices stable or falling
How do output gaps affect unemployment
Negative output gaps increase unemployment; positive gaps reduce it
Draw the short-run and long-run Philips curve
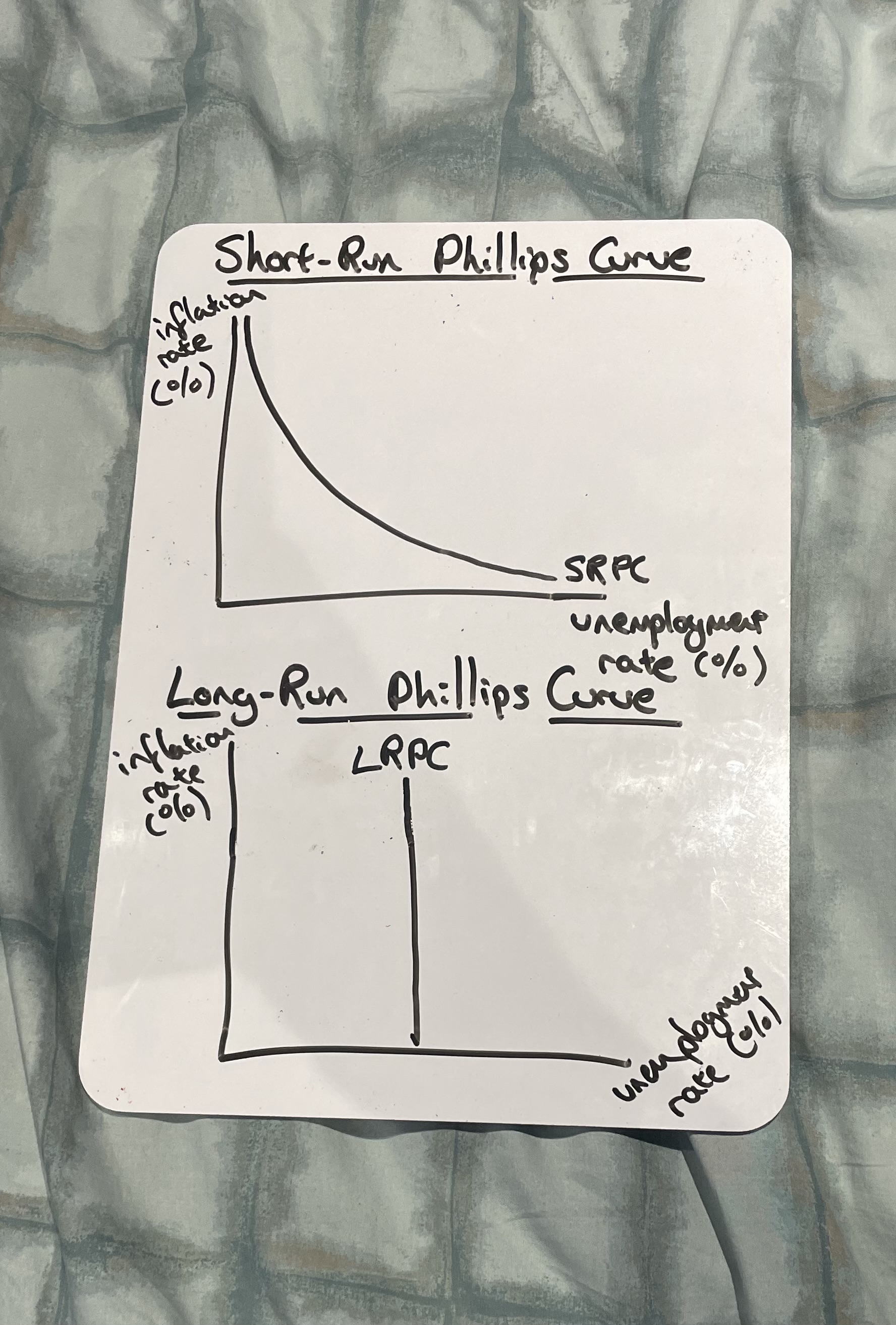
What happens when demand-side policies reduce unemployment in the short run according to Bill Phillips
Inflation rises due to increased consumer spending and wage pressure
Why is the long-run Phillips curve vertical
Because in the long run, unemployment returns to its natural rate, regardless of inflation
Why are demand-side policies ineffective at reducing unemployment in the long run
Because any gains in employment are offset by rising inflation, with unemployment returning to its natural rate
What kind of policies are recommended to reduce long-term unemployment
Supply-side policies like education,training, and labour market reforms to improve workforce skills and flexibility
What is the ‘natural rate of unemployment’
The level of unemployment that persists in the long-run when the economy is at full capacity
Why can economic growth conflict with inflation control
Rapid growth raises aggregate demand, which can lead to demand-pull inflation if the economy is near full capacity
How does economic growth potentially worsen a country’s current account
Increased incomes raise demand for imports, leading to a larger current account deficit, especially in countries like the UK with high import propensities
In what way can economic growth harm the environment
It often leads to higher emissions, pollution, and the depletion of non-renewable resources due to increased industrial actitivity
How does cutting a budget deficit potentially reduce economic growth
It involves reducing government spending or raising taxes, which lowers aggregate demand and slows growth
What is short-run economic growth
It is the annual percentage increase in a country’s real GDP, caused by increases in aggregate demand
What is long-run economic growth
It occurs when the productive capacity of the economy increases, caused by an increase in aggregate supply
What is potential output
The level of output an economy can produce if all resources are fully employed
What is an output gap
The difference between actual and potential levels of output
What characterises a negative output gap
Actual output is less than potential output, leads to unemployment and downward pressure on inflation
What characterises a positive output gap
Actual output is greater than potential output, resources are overused, causing upward pressure on inflation
What is the economic cycle
The fluctuations in economic growth over time, including booms and recessions
Draw the Economic Cycle
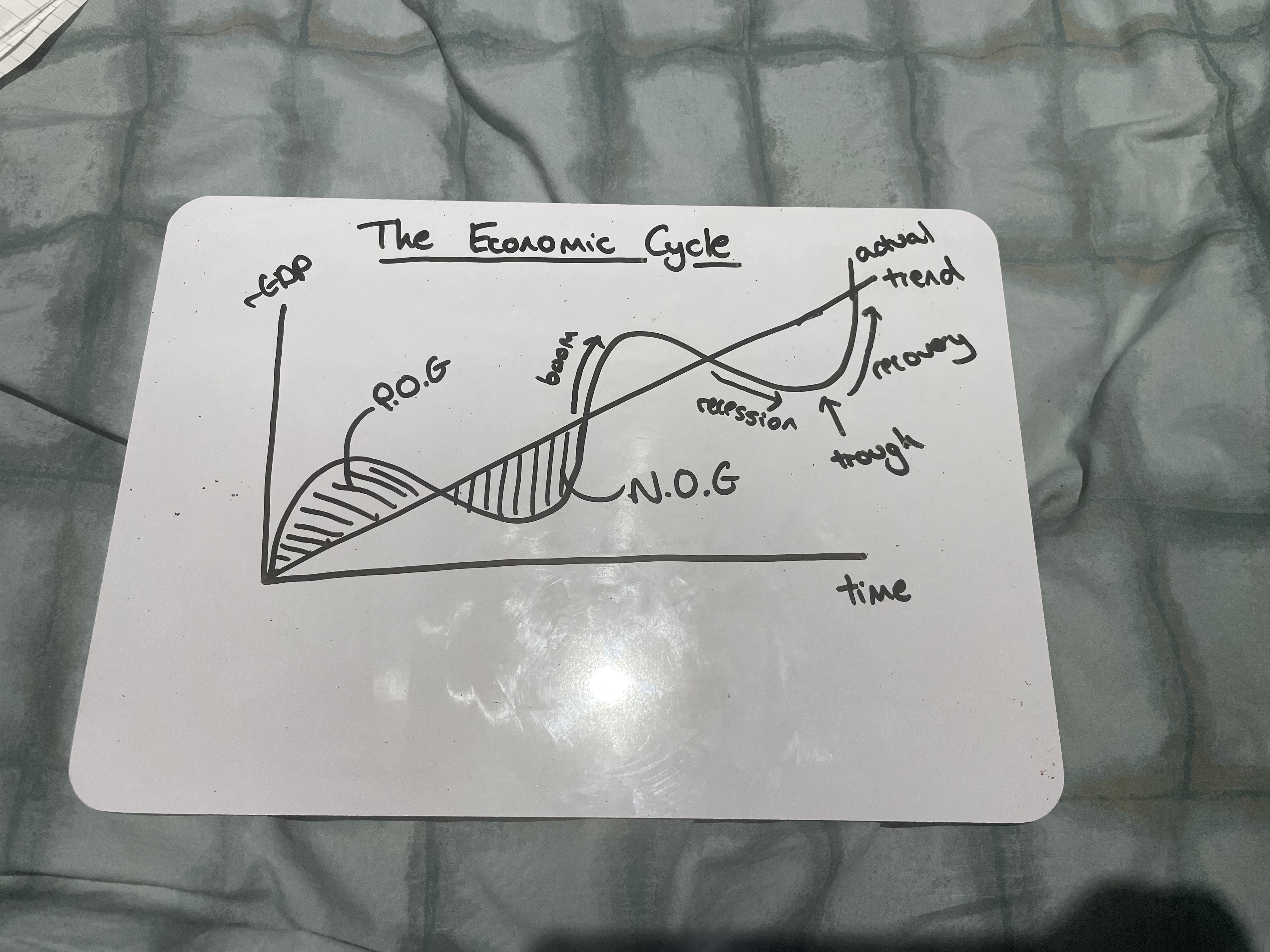
What happens during a boom
Fast economic growth, near full employment, positive output gaps, demand-pull inflation
What happens during a recession
Negative growth over two consecutive quarters, spare capacity, rising unemployment, and lower inflation
How might government respond to a recession
Increase spending, cut taxes, raise welfare benefits to stimulate demand
What benefits do consumers gain from economic growth
Growth increases confidence, leading to higher consumption and living standards
What are consumer costs of economic growth
Higher inflation, greater inequality
What benefits do firms gain from economic growth
Higher profits, investment, economies of scale, better export opportunities
What are menu costs
The costs to firms of changing prices frequently due to inflation
How does economic growth benefits the government
Increased tax revenues, reduced welfare spending which improves the budget
What is the Claimant Count?
It counts the number of people claiming unemployment-related benefits like Job Seeker’s Allowance (JSA), who must prove they are actively seeking work
What are the drawbacks of the Claimant Count
It underestimates unemployment since not all unemployed are eligible for or claim benefits
What is the Labour Force Survey (LFS)?
A survey used by the ILO that asks people if they’ve been out of work for 4+ weeks, are available to start in 2 weeks, and can work at least 1 hour/week
How does the LFS differ from the Claimant Count?
The LFS generally shows a higher unemployment figure because it includes those who are not claiming benefits
What is structural unemployment
Unemployment caused by a mismatch between the skills that workers in the economy can offer and the skills demanded of worker by employers
What is frictional unemployment
Temporary unemployment when people are between jobs or just entering the workforce
What is seasonal unemployment
Unemployment that occurs at certain time of the year
What is cyclical unemployment
Unemployment caused by a fall in aggregate demand, often during economic downturns or recessions
What is real wage unemployment
When wages are above market equilibrium, causing labour supply to exceed demand
What is voluntary unemployment
When someone chooses not to work at current wage levels
What is involuntary unemployment
When people willing and able to work at current wages cannot find employment - often due to cyclical factors
How does unemployment affect consumers?
Reduces disposable income, lowers living standards, and can cause psychological stress
How does unemployment affect firms?
Increases labour supply (lower wages), but reduces consumer spending and may require retraining workers.
How does unemployment affect workers?
Leads to a waste of labour resources and skill loss due to underutilisation.
How does unemployment affect the government?
Increases spending on JSA, reduces tax revenues, and carries an opportunity cost.
What is the natural rate of unemployment
The unemployment level when labour market is in equilibirum, with no cyclical unemployment
What causes the natural rate of unemployment
Supply-side factors - frictional and structural unemployment
What is NAIRU
The Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment - when inflation is stable
Why is the natural rate also called full employment
Because there’s no demand-deficient unemployment - only unavoidable types like frictional or structural
What is inflation
Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time, leading to a decrease in purchasing power of money
What is deflation
Deflation is the opposite of inflation, where the average price level in the economy falls, and there is a negative inflation rate
What is disinflation
Disinflation is the falling rate of inflation, where the price level is still rising, but at a slower rate than before
What is demand-pull inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand grows unsustainably, putting pressure on resources and causing producers to increase prices
Draw demand-pull inflation
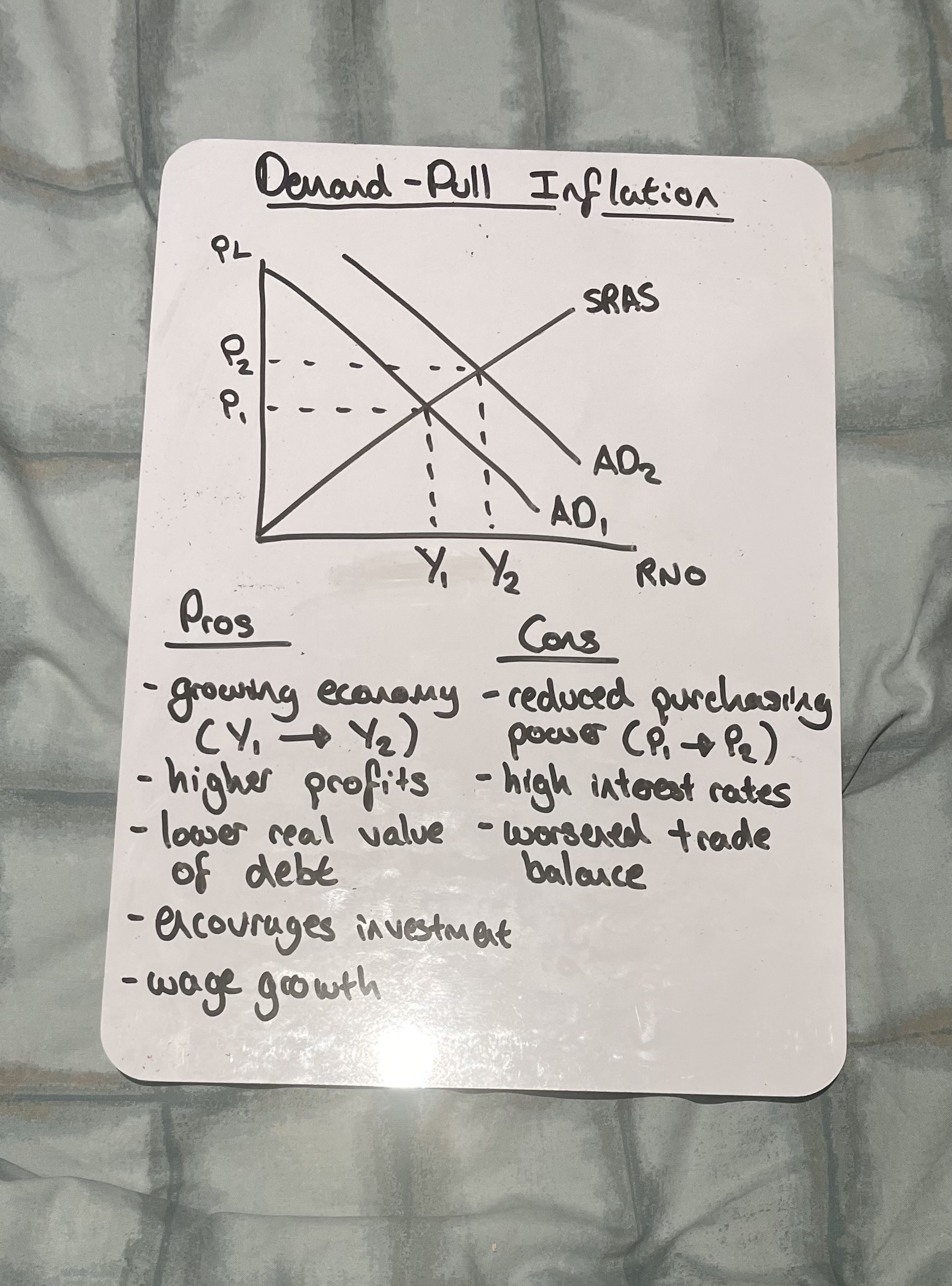
What are the key trigger for demand-pull inflation
Depreciation of the exchange rate
Fiscal stimulus (Lower taxes or more govt spending)
Lower interest rates
High growth in export markets
What is cost-push inflation
Cost-push inflation occurs when firms face rising costs of production, pushing up the general price level
Draw cost-push inflation

What are the key factors causing cost-push inflation
Rising commodity prices (e.g. oil)
Increased labour costs
Indirect taxes
Depreciation of the exchange rate
Effect of inflation on consumers
Consumers on low and fixed incomes are hardest hit by inflation due to the rising costs of necessities, which reduces their purchasing power
Effect of inflation on loans
Inflation reduces the real value of debt, making it easier for consumers with loans to repay them
Effect of inflation on firms
High inflation can make borrowing and investing less attractive
Workers may demand higher wages, increasing production costs
Firms may lose global competitiveness if inflation is higher than in other countries
Effect of inflation on the govt
The government may need to increase state pensions and welfare payments due to the rising cost of living
Effect of inflation on workers
Real incomes fall, reducing disposable income
Firms may make redundancies to cut costs
Economic effects of deflation
Economic decline and rising unemployment
Consumers with high debt face more difficulty repaying loans
Wages may fall, leading to lower disposable income and spending
What is Fisher’s equation of exchange
Fisher’s equation is: MV = PQ
M= money supply
V = velocity of circulation
P = price level
Q = quantity of real goods sold