Chap 15 parasitism and mutualism (cont.)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Mutualism
DEFINITION (RECAP):
- an interaction between members of two species that serves to benefit both parties involved
----------------
TYPES OF BENEFITS (CAN VARY)
- provision of essential resources (food and shelter)
- may involve protection from predators, parasites, and herbivores
- may reduce competition with a third species
- may involve reproduction benefits such as dispersal of gametes or zygotes
obligate mutualists
cannot survive or reproduce with out the mutualistic interaction
----------------
IS DIFFERENT FROM FACULTATIVE MUTUALISTS
Facultative mutualists
can survive or reproduce without the mutualistic interaction
----------------
OPPOSITE OF OBLIGATE MUTUALISTS
Degree of specificity of mutualism
varies from one interaction to another
----------------
TYPES OF MUTUALISTS:
- specialist mutualists
- generalist mutualists
specialist mutualists
ranges from one to one species-specific association
generalist mutualists
mutualist that associate with a wide diversity of mutualistic partners
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- plant-animal pollinator systems
degree of intimacy
also varies among mutualistic interactions
----------------
TYPES OF INTIMACY:
- nonsymbiotic
- symbiotic
Nonsymbiotic
free living individuals
symbiotic
individuals coexist and their relationship is more often obligatory
----------------
FEATURES:
- at least one member of the pair becomes totally dependent on the other
- distinction between the two organisms becomes blurred
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- Reef-forming corals
reef-forming corals
individual coral animals: polyps occupy little cups, or corallites, in the larger skeleton that forms the reef
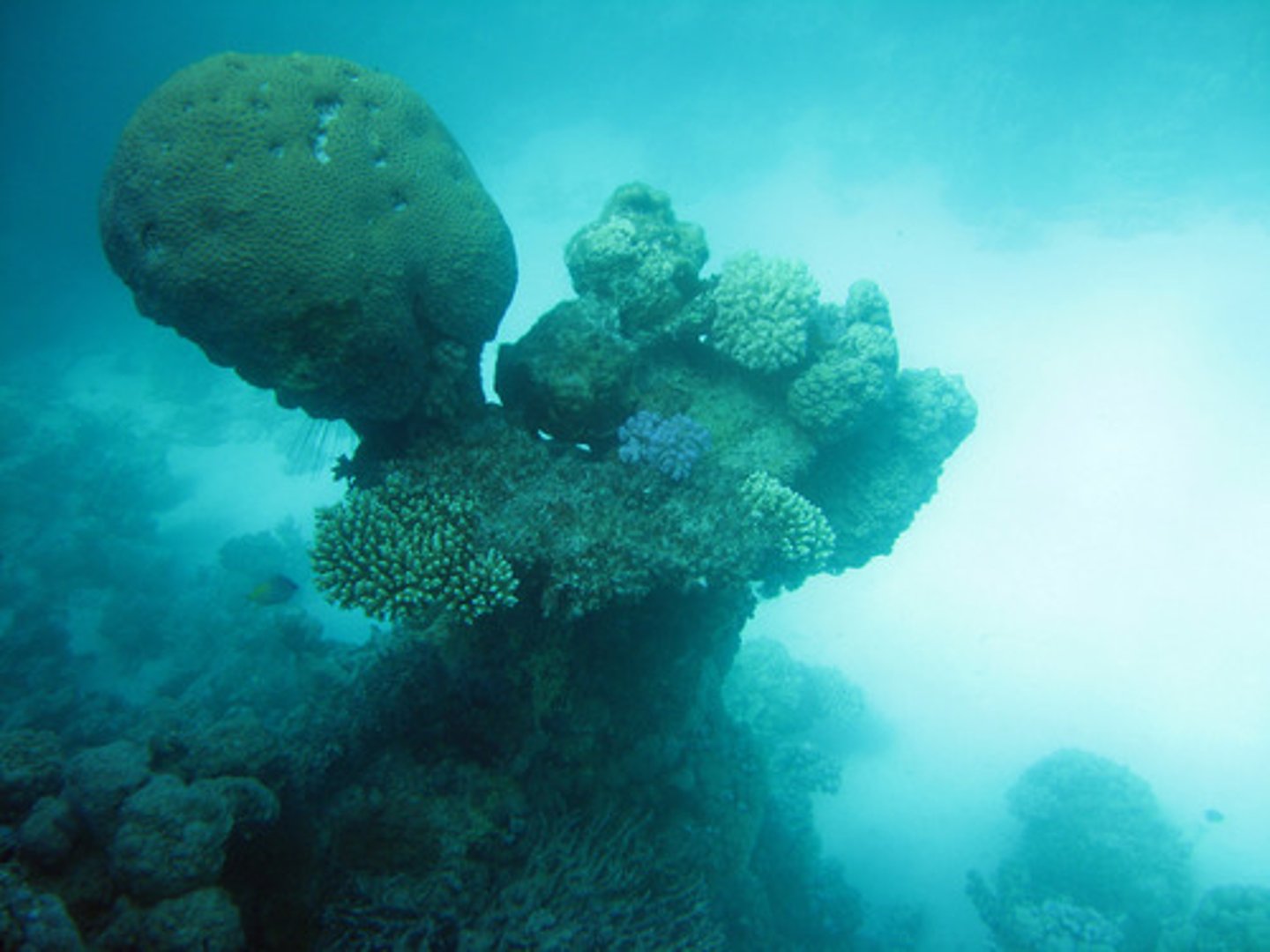

zooxanthellae
the symbiotic algae in the reef-forming corals tissue
----------------
FEATURES:
- can obtain 90% of its energy from the carbon produced by the symbiotic algae through photosynthesis

how are reef-forming corals symbiotic with algae
corals can provide the algae with shelter and mineral nutrients
----------------
TYPES OF NUTRIENTS:
- nitrogen in the form of nitrogenous wastes
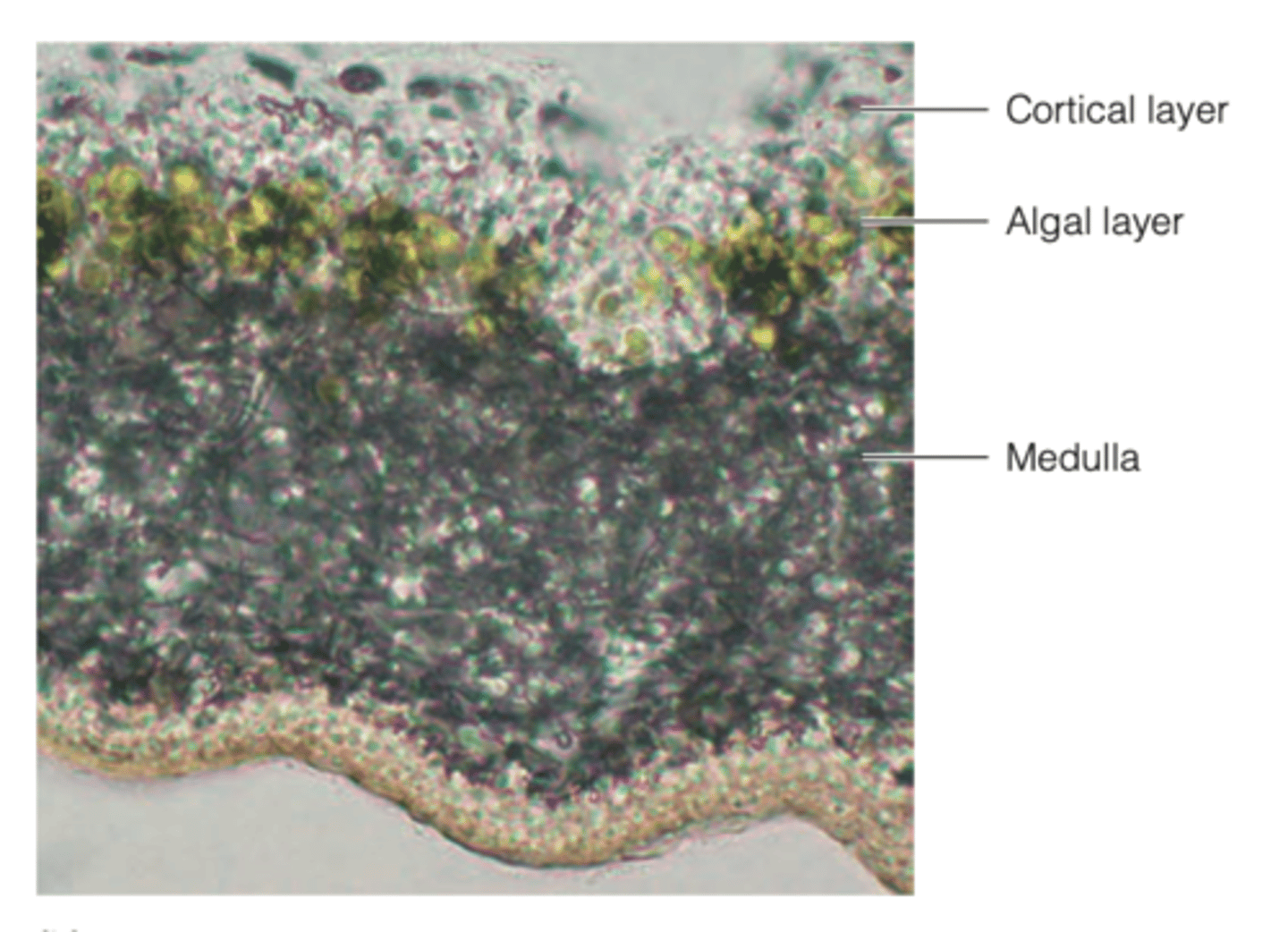
lichens symbiotic relationship between fungus and photosynthetic algae/cyanobacteria
- they are fused into a single body
- the fungus protects the algae from harmful light intensity
----------------
BENEFITS:
- can produce a substance that accelerates photosynthesis in the alga
- can absorb and retain water and nutrients for both organisms
nonsymbiotic mutualism
2 organisms do not physically coexist
----------------
BUT:
- they depend on each other for some essential function
----------------
FEATURES:
- may be obligatory (but most aren't)
- they are facultative (doesn't involve the interactions between two species)
- involves a variety of plants, pollinators, and seed dispersal
digestive system of herbivores
is inhabited by a diverse community of mutualistic organisms
----------------
SO WHAT?:
- they play a crucial role in the digestion of plant materials
----------------
EXAMPLES:
- Ruminant mammals
Ruminant mammals
FEATURES (LEC)
- have a complex stomach with multiple chambers, which house bacteria and protists (mainly anaerobes) that can break down plant material
Which insects also rely on heavily on gut microbes for digestion
termites
Legumes
a group of plant species that have a symbiotic relationship with a type of nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Rhizobium
----------------
FEATURES:
- are able to convert nitrogen gas into solid ammonia
- can secrete chemicals from their roots to attract rhizobia
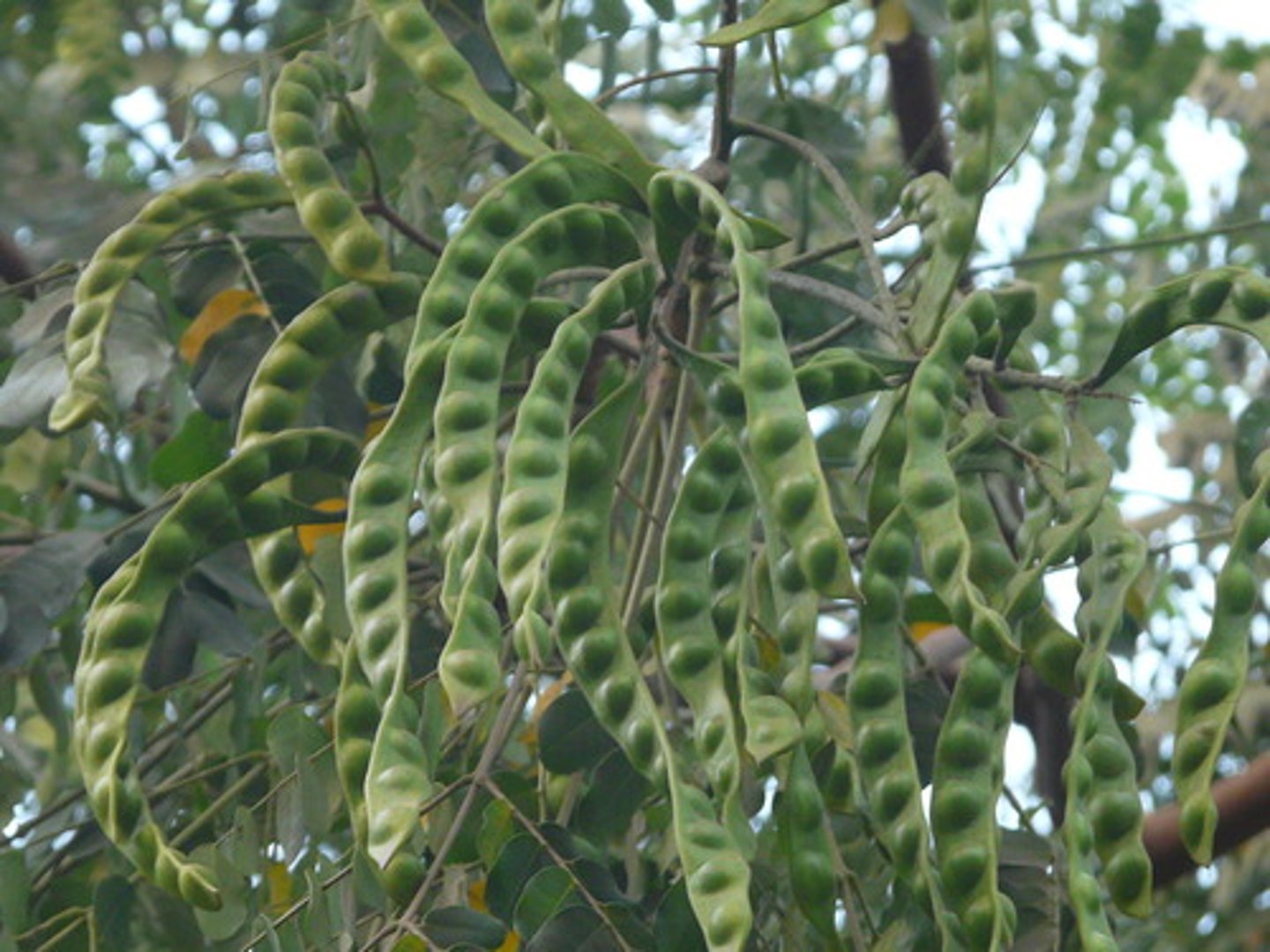

Rhizobia
nitrogen fixing bacteria that enters the root hairs of legumes and multiply to increase in size
----------------
LEADS TO
- the formation of rood nodules that house these bacteria
in some mutualism examples (LEC)
one species provides a resource that can be used as a defense by the second species
----------------
EXAMPLE:
- Epichloe
Major problem for livestock producers
is the toxic/infecting effects of certain grasses
----------------
PARTICULARLY
- perennial ryegrass and tall fescue
----------------
EXAMPLE:
Fungi (clavicipitacceae and ascomycetes)
Fungi (clavicipitacceae and ascomycetes)
fungi that produce alkaloid compounds in the tissue of the host grasses
---------------
FUNCTIONS:
- can make grass have a bitter taste which can be toxic to grazing mammals and insect herbivores (results to death if eaten)
acacia trees
FUNCTION:
- provides food and shelter for ants
---------------
IF ACACIA TREE IS EVER DISTURBED BY INTRUDER:
- the ants will swarm out of the shelters, and emmit a repuslive oder and attack the intruder until it is driven away.

Cleaning mutualism
WHICH ANIMAL HAS THIS TRAIT?
- found between clearner shrimp or cleaner fishes
---------------
HOW DO THEY BENEFIT FROM IT
- they can obtain food by cleaning ectoparasites and diseased and dead tissue from the host fish (allows for the removal of unwanted material)
Cross pollination
to transfer pollen from one individual to another of the same species
---------------
WAYS POLLEN CAN BE TRANSFERED?
- wind
- animal pollinators
Wind (cross pollination)
ADVANTAGES:
- cost little when plants grow in homogenous stands
---------------
DISADVANTAGES:
- range of dispersal distance is variable and is non specific

animal pollinators (cross pollination)
ADVANTAGES:
- more reliable direct transmission to another plant
- range of dispersal can reach to longer distances
---------------
DISADVANTEGES:
- plants are more dependent on animals
- plant must use it energy to stay intact while being moved by an animal rather than grow
nectivores
Animals that feed on nectar
---------------
HOW ARE THEY AN EXAMPLE OF ANIMAL POLLINATORS:
- nectivores pick up the pollen and carry it to the next plant they visit
Nectivores are
generalists that feed on may differnt plant species
---------------
- nectivores depend on the progression of flowering plants through the season
types of "plant generalist"
- blackberries
- elderberries
- cherries
- goldenrods
plants being "specialist" (LEC)
flowers that attract or can be accessed by only one type of pollinator
seeds
can be dispersed by both types of cross-pollination
- wind
- animal
what features are seen in seed of plants that rely on animals for seed dispersal?
"Plants with seeds too heavy to be dispersed by wind depend on animals to carry them some distance from the parent plant and deposit them in sites favorable for germination and seedling establishment." (BOOK)
seed predators (seed dispersal)
Plants may also depend on these type of species
---------------
WHY?
eating the seed will benefit the predator as they are gaining nutrients
---------------
FACT:
- even if most seed are eaten some will survive
some plants
enclose their seeds in a nutritious fruit that attract fruit-eating animals (frugivores)
---------------
plants that attract frugivores are considered as "mature seeds"
frugivores
fruit eaters
---------------
FEATURES:
- are not seed predators because they eat only the fruit surrounding the seed

unripe fruits
contains immature seeds
- are often green (cryptic coloration example)
---------------
FEATURES:
- may have a hard outer coat
- has a unpalatable texture to discourage consumption

ripe fruits
contain mature seed and may be colorful
---------------
OTHER FEATURES:
- has a soft texture
- has an attractive odor smell
- has higher sugar and oil content to encourage consumption
---------------
EXAMPLE:
- Coffee beans
-
effect of mutualism on populations can be modeled
in a similar way to competition
---------------
HOW?
- population growth rate will increase with increasing density of another intoduced species
- interaction will allow both populations to exist in higher numbers
How could you test for the effect of an obligate mutualism?
remove the population of one species and see if the population of the other species persists
facultative mutualism effects
are more subtle
- requires more detailed demographic data to determine the consequences for the fitness of each species
cases where mutualistic interaction is diffuse
can be challenging to determine the effect of interactions between particular species
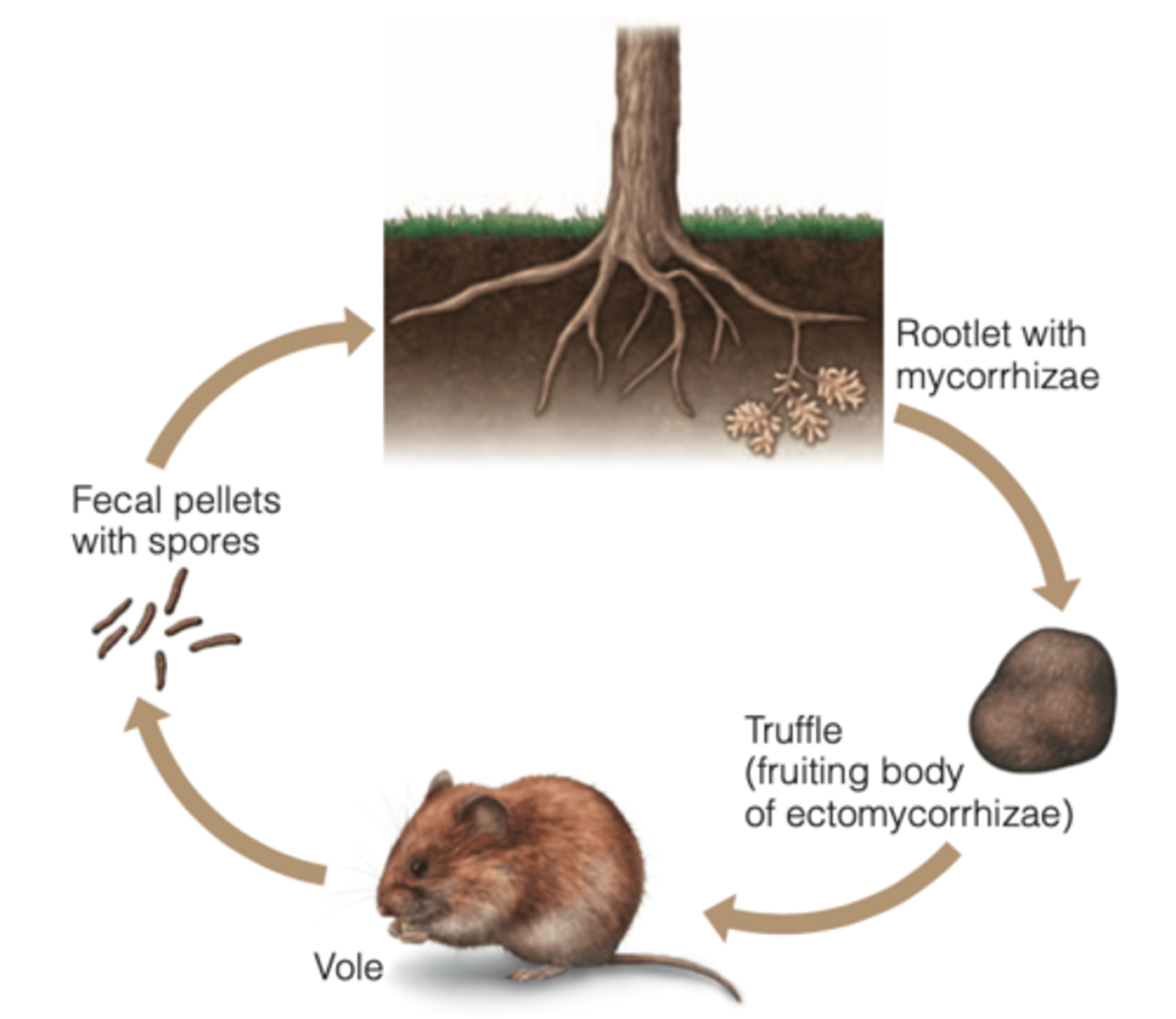
mutualistic relationship between 2 species may involve
a 3rd species
---------------
BENEFITS
- will facilitate or mediate the interaction
---------------
SIMILARITES:
- much the same as for vector organisms and intermediate hosts in parasite host interactions
---------------
EXAMPLE:
- mutualistic relationships between confers, mycorrhizae, and voles
clearing forests for agriculture and urbanization
has long been associated with declining plant and animal populations and the reduction of biological diversity
---------------
- land use changes are directly impacting human health because they facilitate the expansion of infectious disease
---------------
EXAMPLE:
- Lyme disease
Lyme disease
CAUSED:
- caused by a parasite bacterium called (borrelia burgdorferi)
- is transmitted by the bite of an infected black legged tick
---------------
FACT
infectious disease that has been dramatically increased through out N Amer.
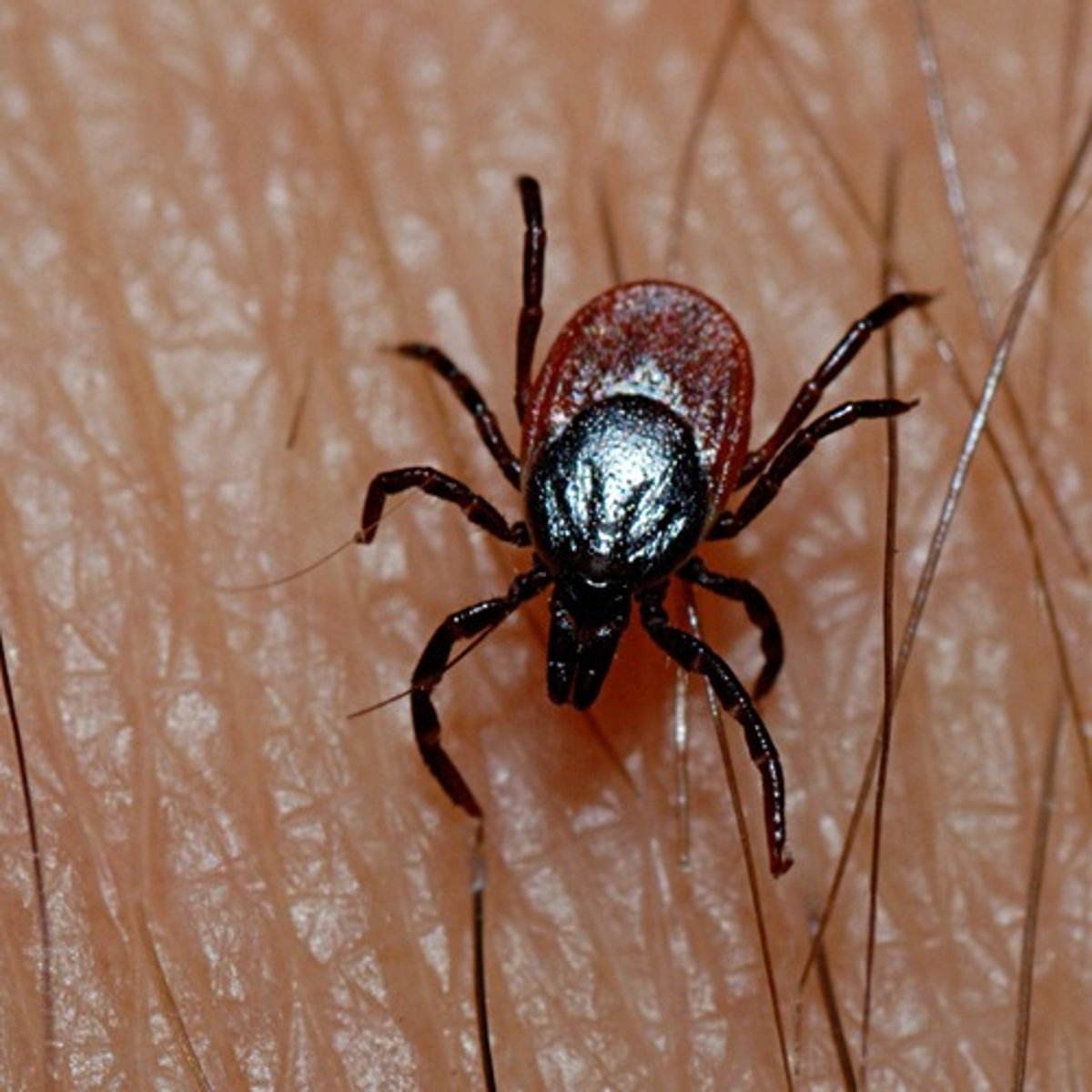

larval ticks (Lyme disease)
species that are uninfected when they hatch
---------------
HOW DO THEY BECOME INFECTED?
- they feed on infected host animals
(host animal will most likely transmit the bacterium to the feeding tick)
---------------
MOST COMMEN IN
- White footed mouse
forest fragmentation
involves the reduction in total forested area and reduction in the average size of remaining forest patches
---------------
IMPACTS ON SPECIES:
- can have have a negative impact in species diversity (however some can thrive in this type of landscape)
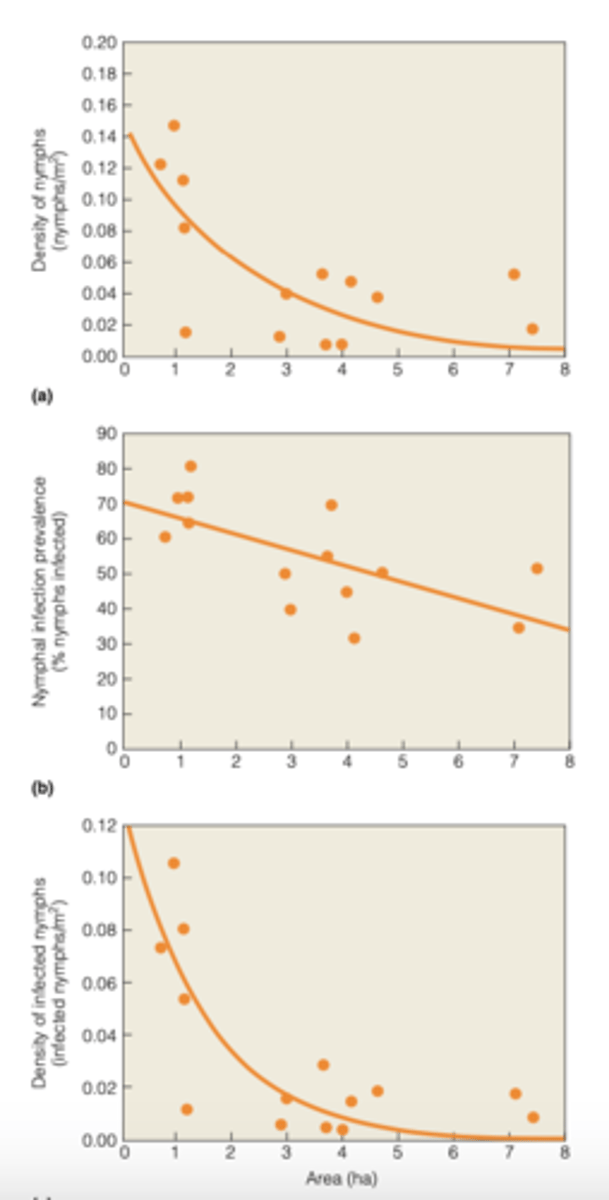
Forest clearing and fragmentation
leads to a potential increase in the transmission of Lyme disease
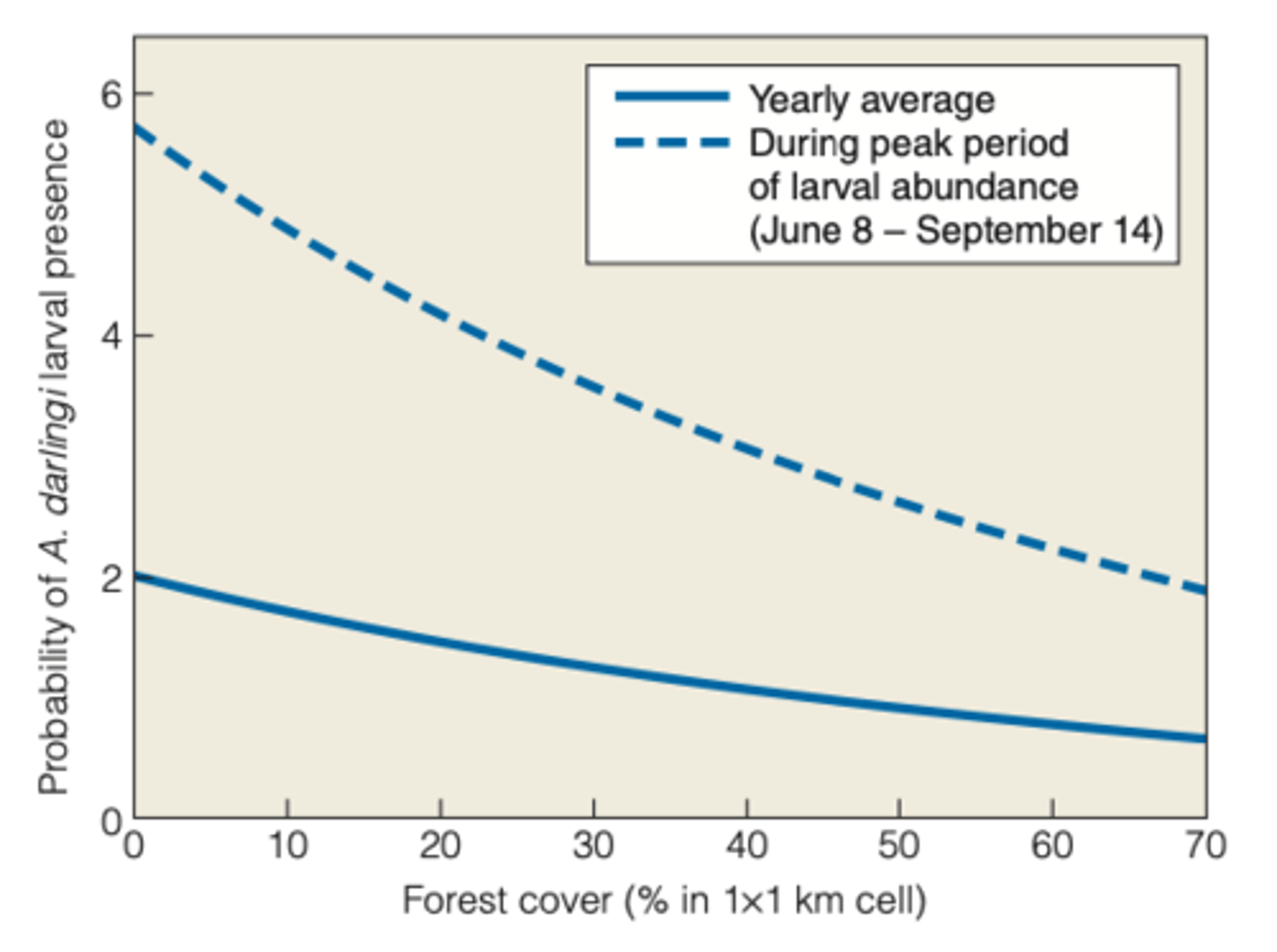
deforestation
can lead to an increase in the prevalence of malaria
---------------
INSECTS INVOLVED:
- parasite - protist
- vector - misquito
- host - humans
Facts about Malaria
- 40 % of the worlds population is at risk
- more than 2 million people die from it
---------------
OTHER FIELD STUDY
- field study that occured in basin brazil showed similar results where deforestation from 1997 to 2000 associated with a 48% chance of getting Malaria.