CNS
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
There are ___ cerebral hemispheres
2
Each cerebral hemisphere includes...
cerebral cortex
subcortical structures
The white matter matter bundle joining the two hemispheres is known as the
corpus callosum
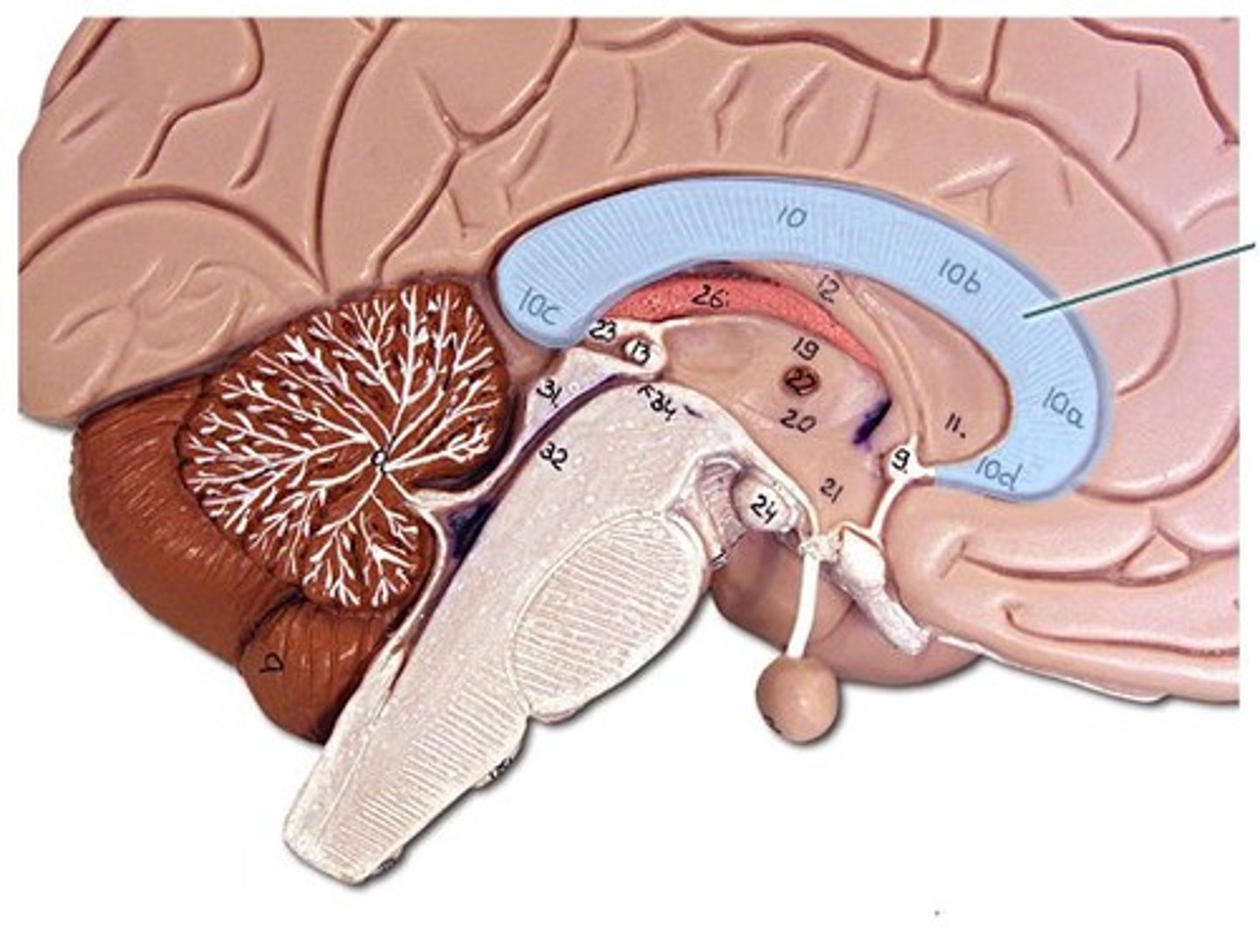
Basal ganglia are a collection of
nuclei (gray matter)
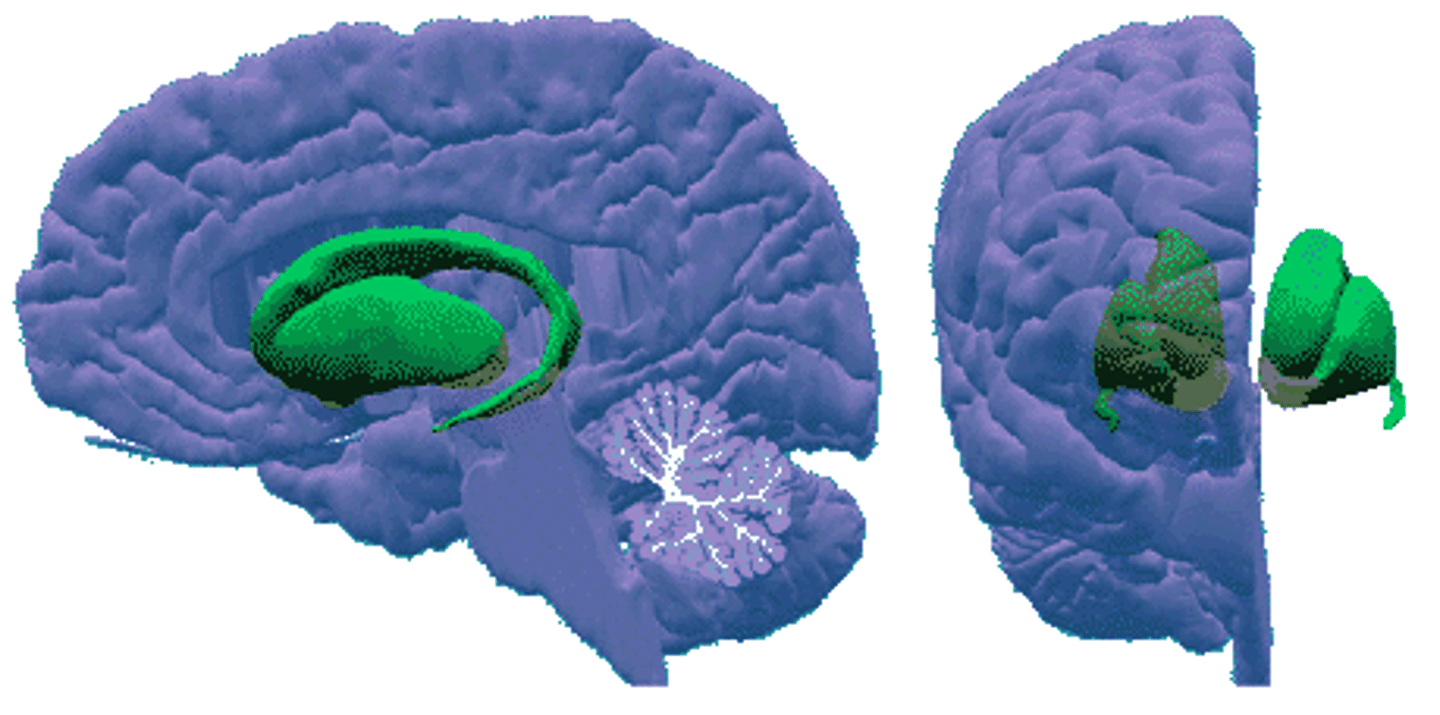
Basal ganglia play a vital role in
initiation and control of movement
The basal ganglia are associated with ______ ________
movement disorders
The hippocampus and amygdala are part of which system?
limbic
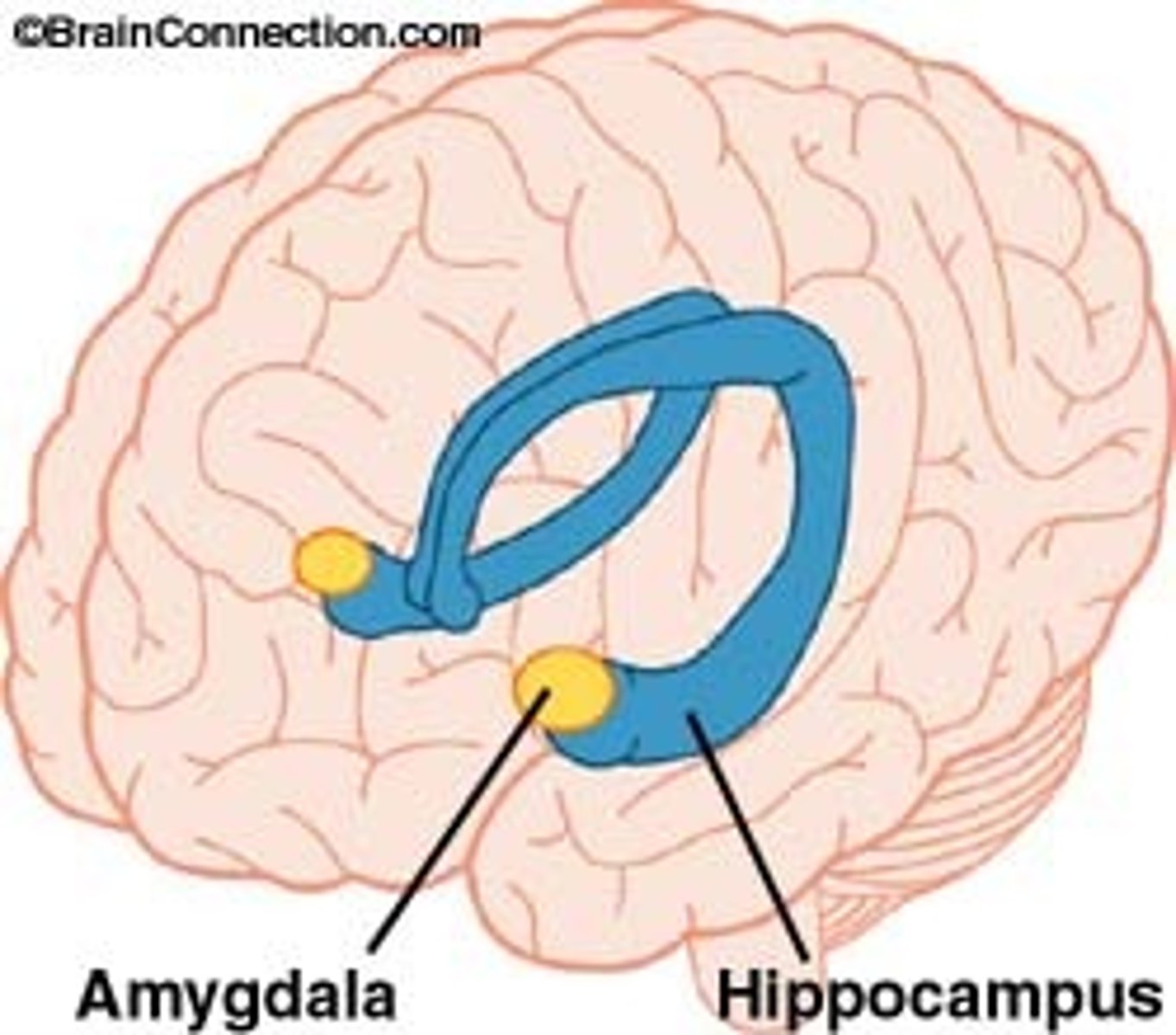
The hippocampus and amygdala are located in which lobe?
temporal
The hippocampus and amygdala play a role in...
motivation
emotion
memory
learning
behavior
The thalamus is a critical processing station for...
all sensory information on its way to the cortex (except olfactory)
The thalamus plays a key role in...
processing motor information and integrating higher-order cognitive and emotional information
The thalamus can be considered the "____" of the cortex
gatekeeper
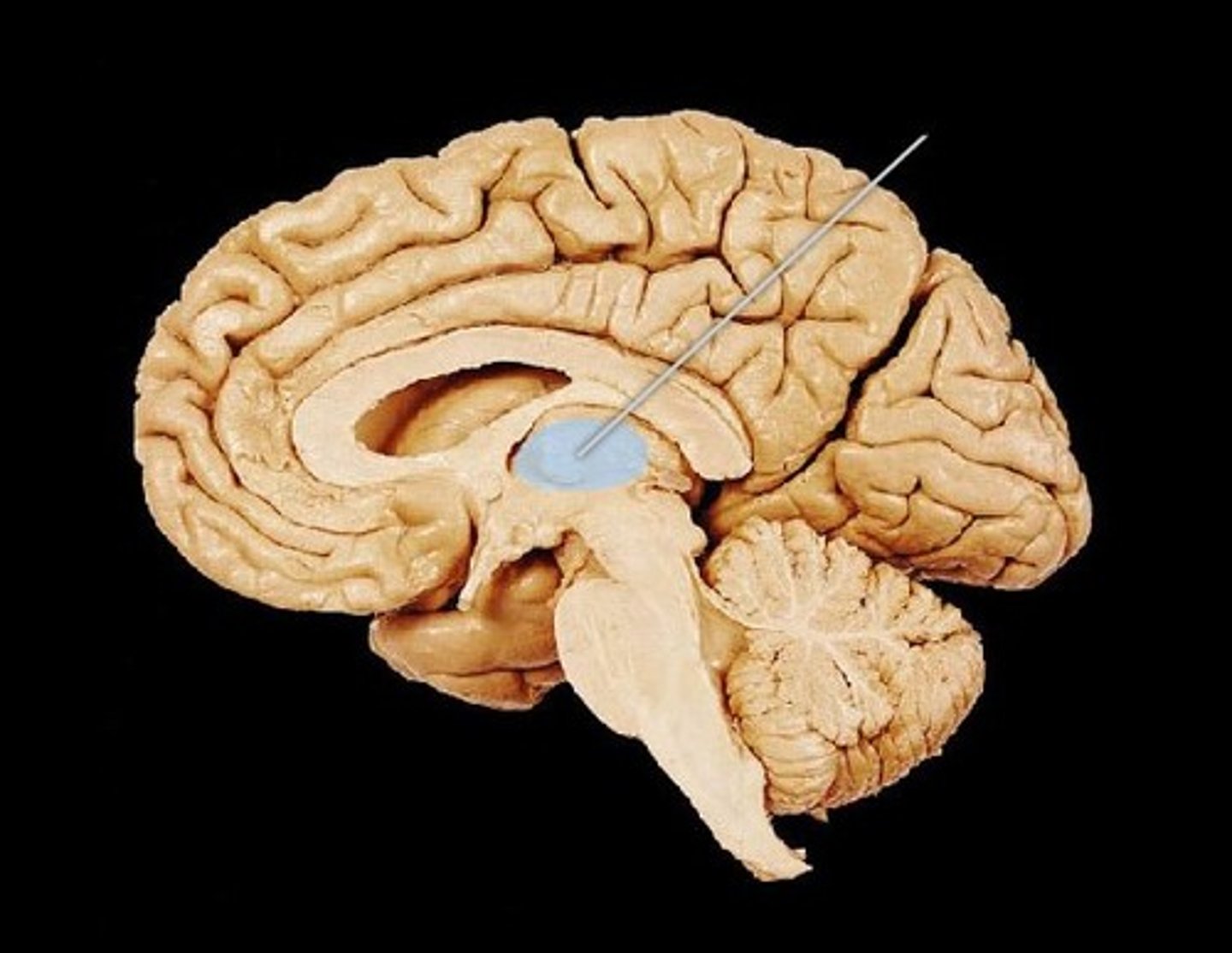
The hypothalamus has an important role in which system?
endocrine
Another gland that has an important role in the endocrine system is the...
amygdala
The hypothalamus assists with...
homeostasis
emotions
behavior
The hypothalamus assists which division of the nervous system?
autonomic
The hypothalamus secretes ________
hormones
Brainstem lies between the _____ and _____ ____
cerebrum
spinal cord
Brainstem includes...
midbrain
pons
medulla
6 enlargements of the midbrain
2 cerebral peduncles
2 superior colliculi
2 inferior colliculi
Cerebral peduncle
connects midbrain to cerebrum
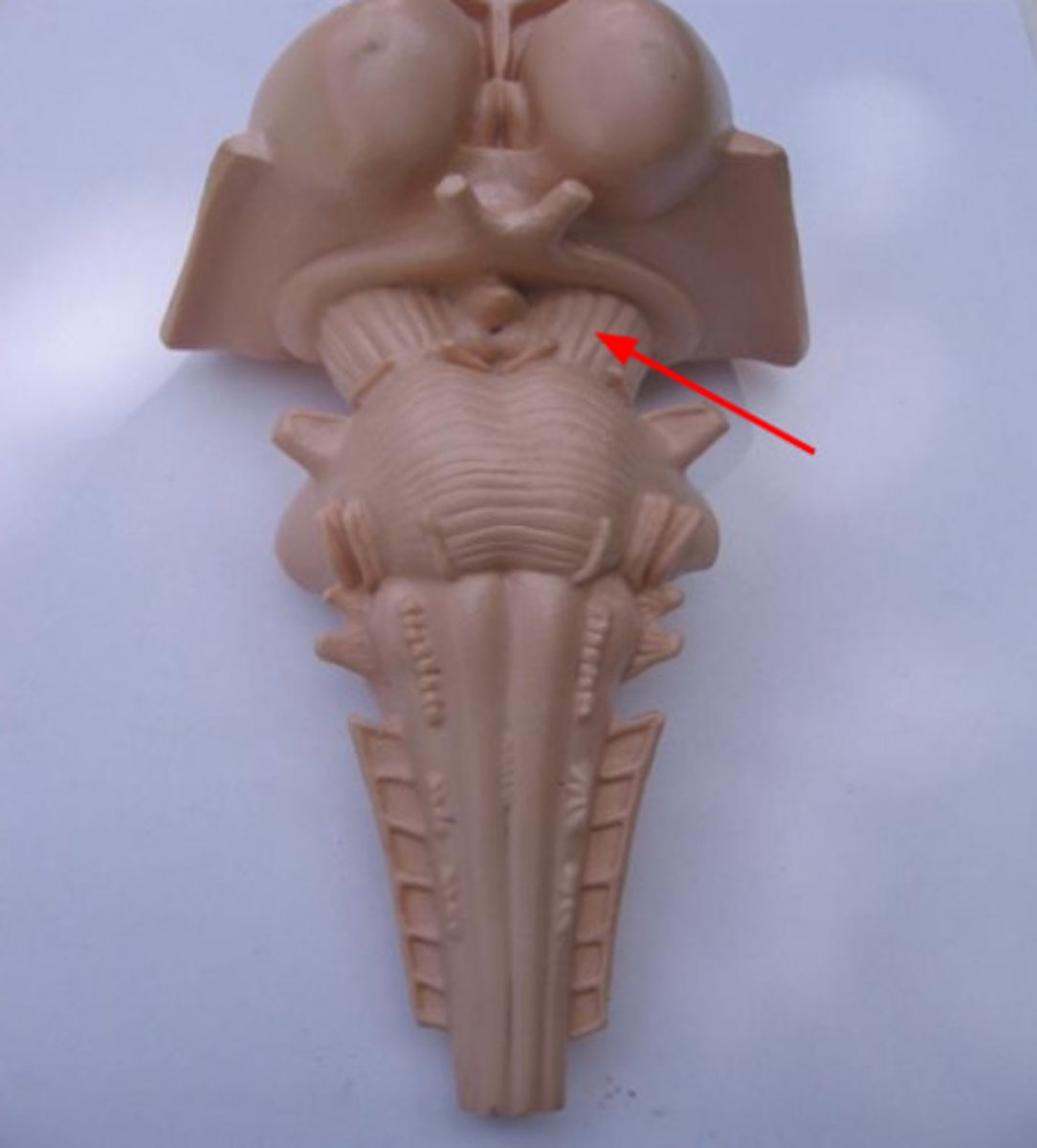
Superior and inferior colliculi
paths for tracts
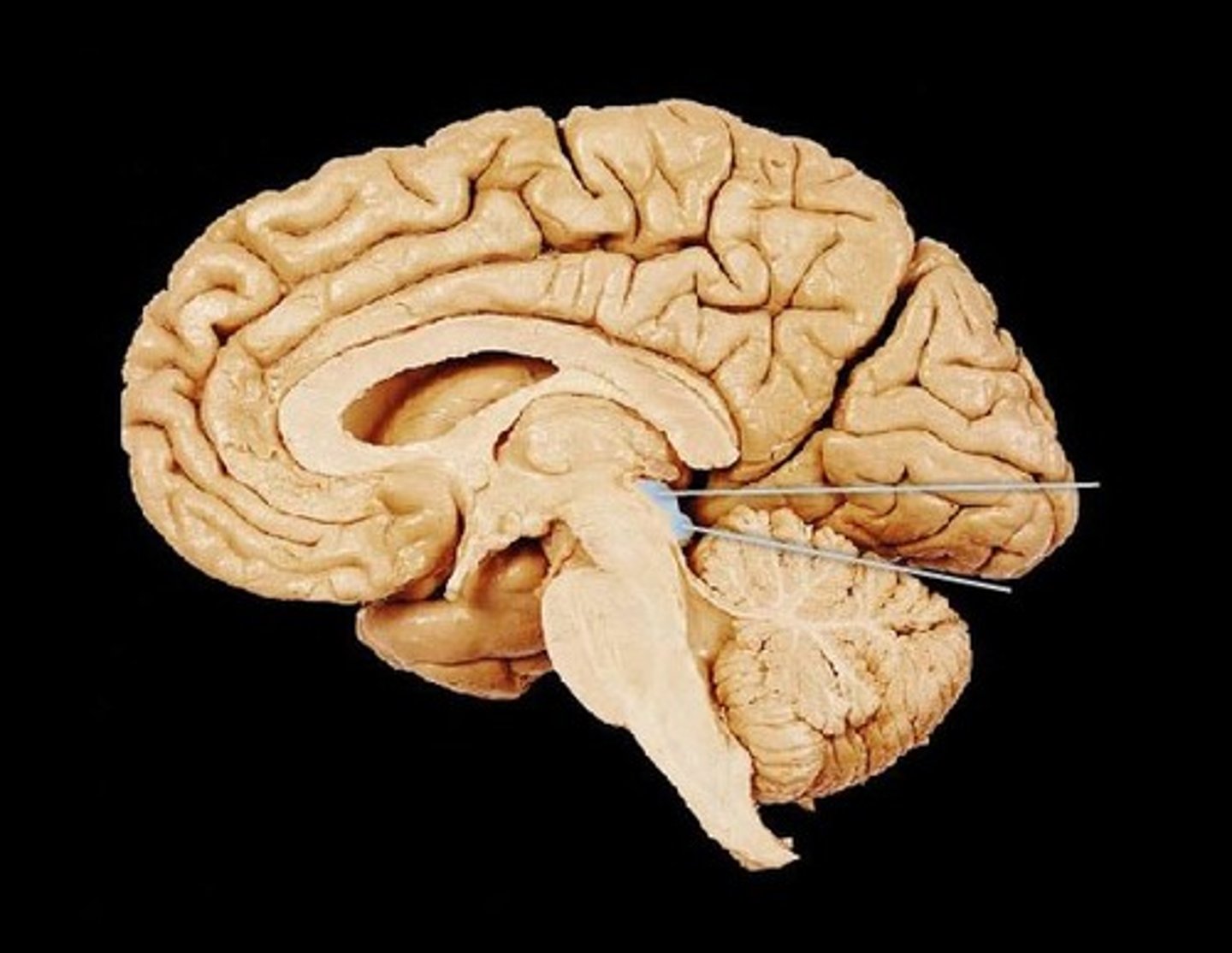
Cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Are the cerebral peduncle anterior or posterior
anterior
Are the superior and inferior colliculi anterior or posterior
posterior
Pons
relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
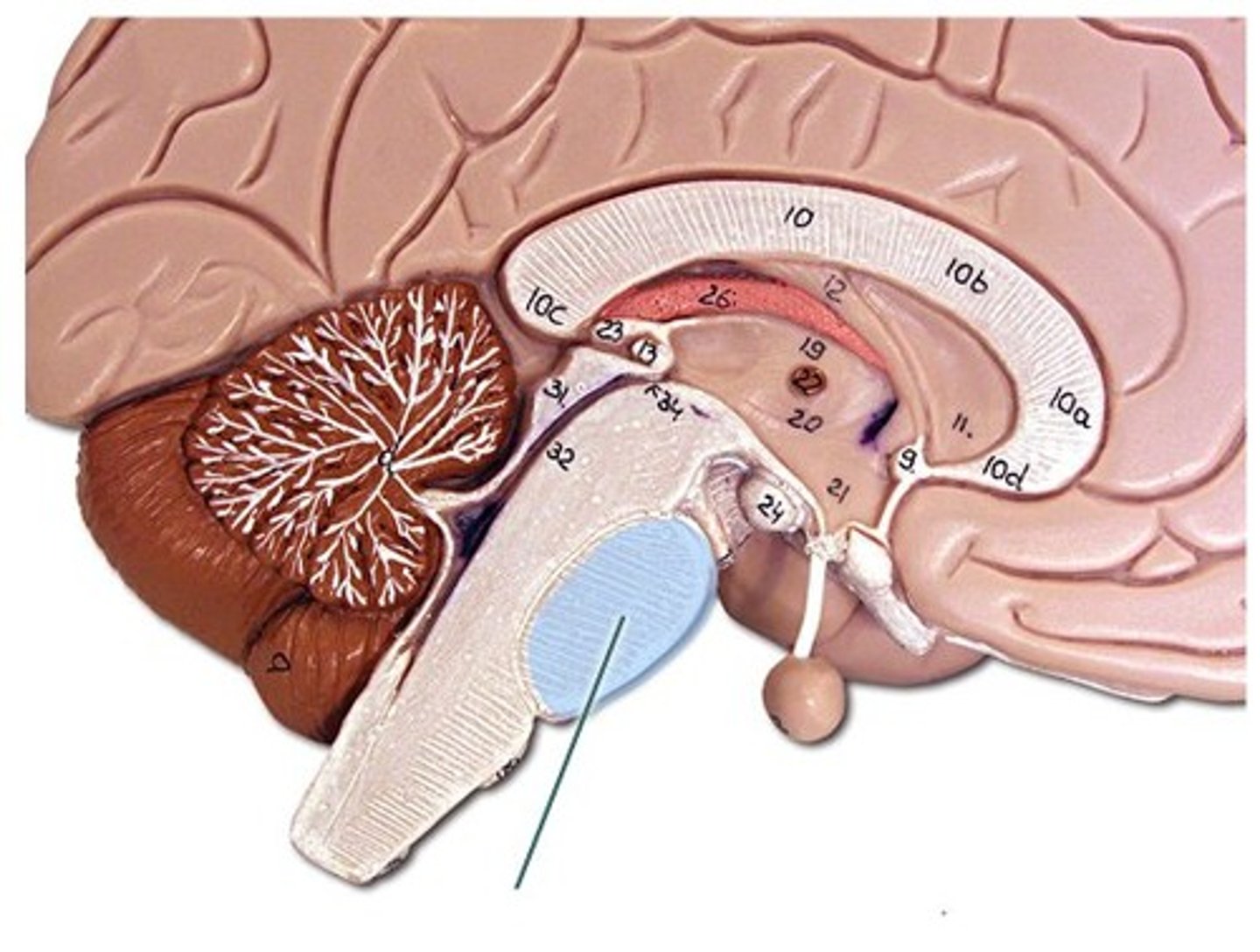
Basal pons
bulge on anterior surface of pons
Features of the pons
basal pons
superior cerebellar peduncles
middle cerebellar peduncles
inferior cerebellar peduncles
Superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles
connect pons with the cerebellum
Superior cerebellar peduncle
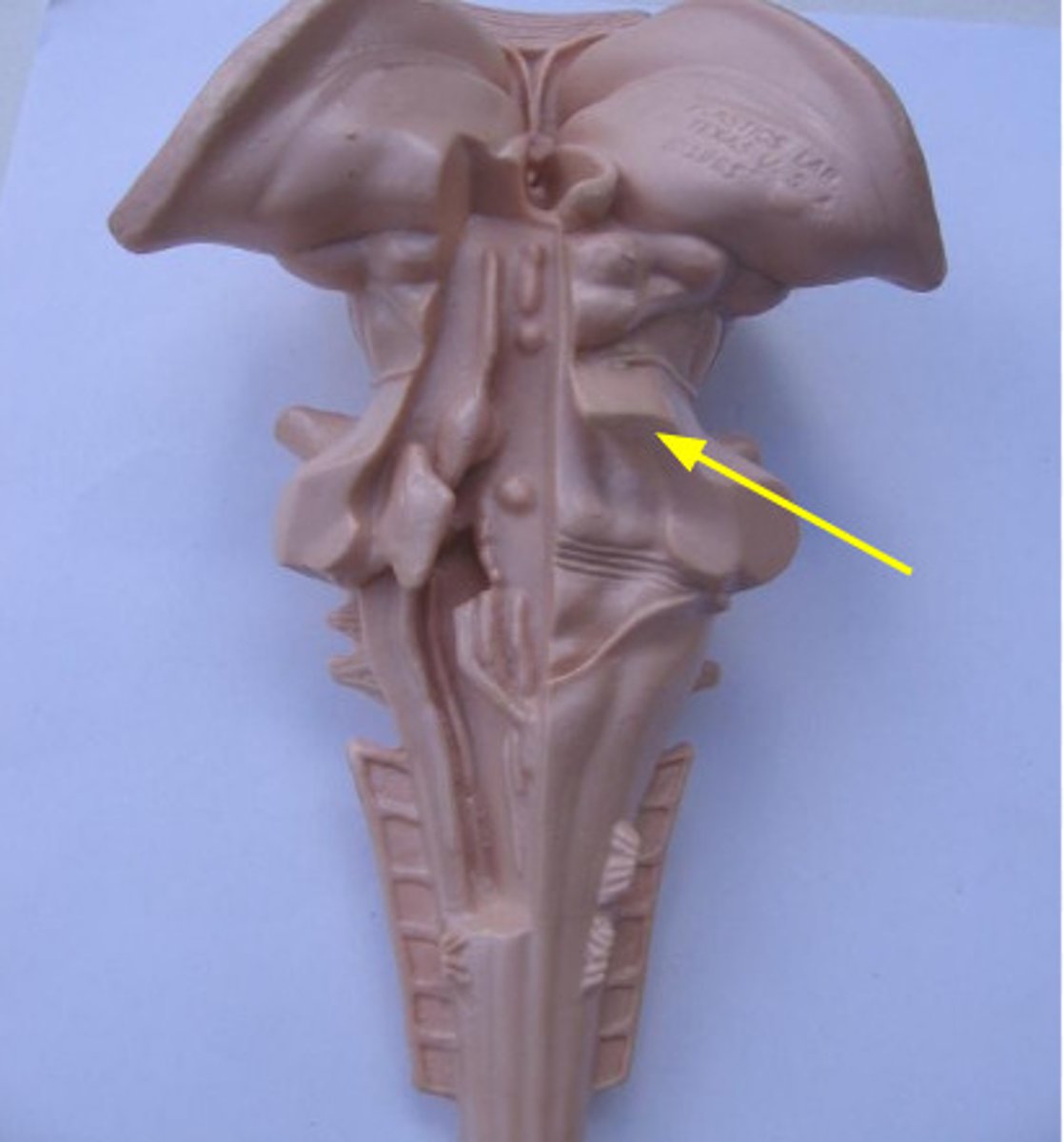
Middle cerebellar peduncle
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
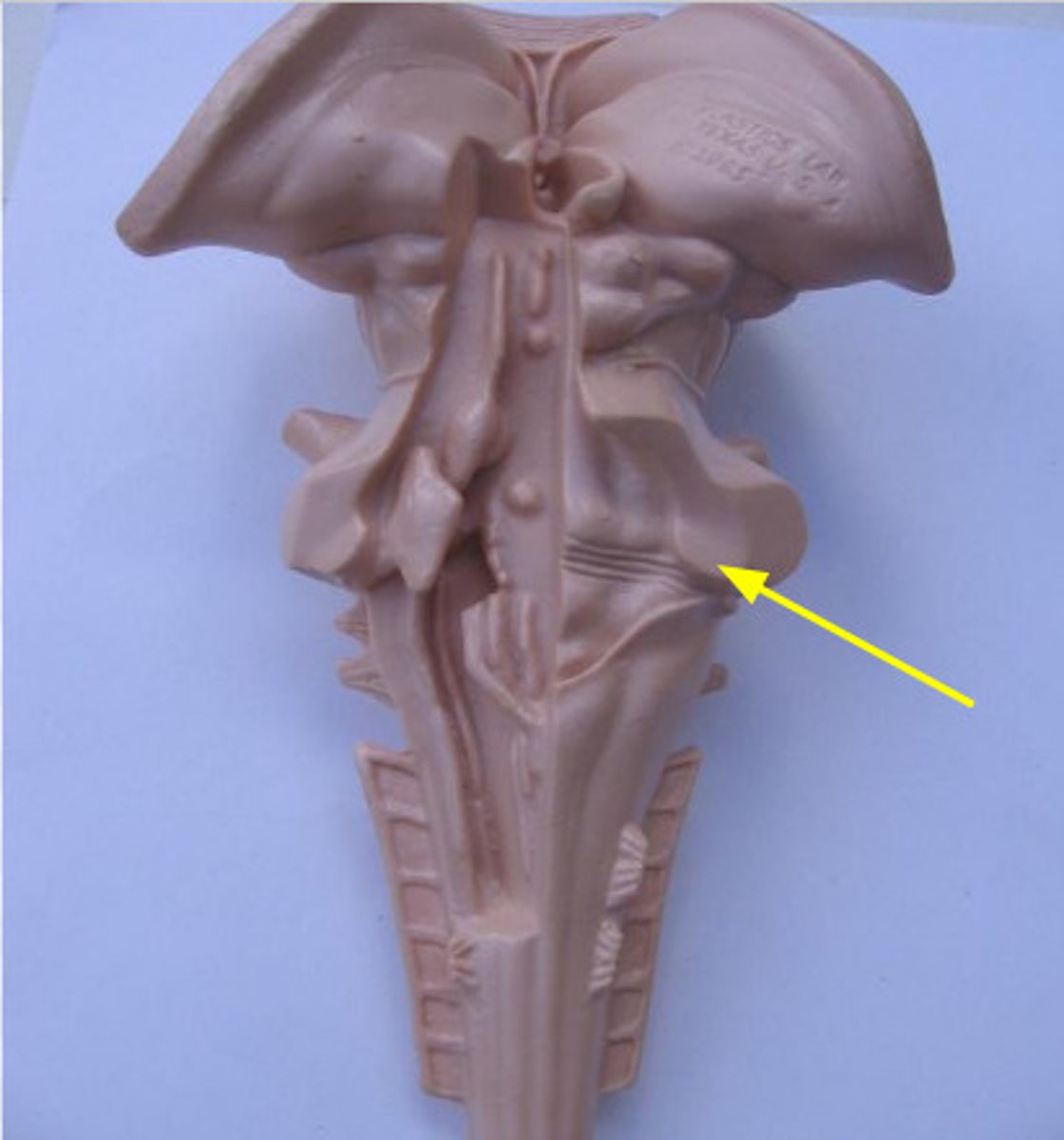
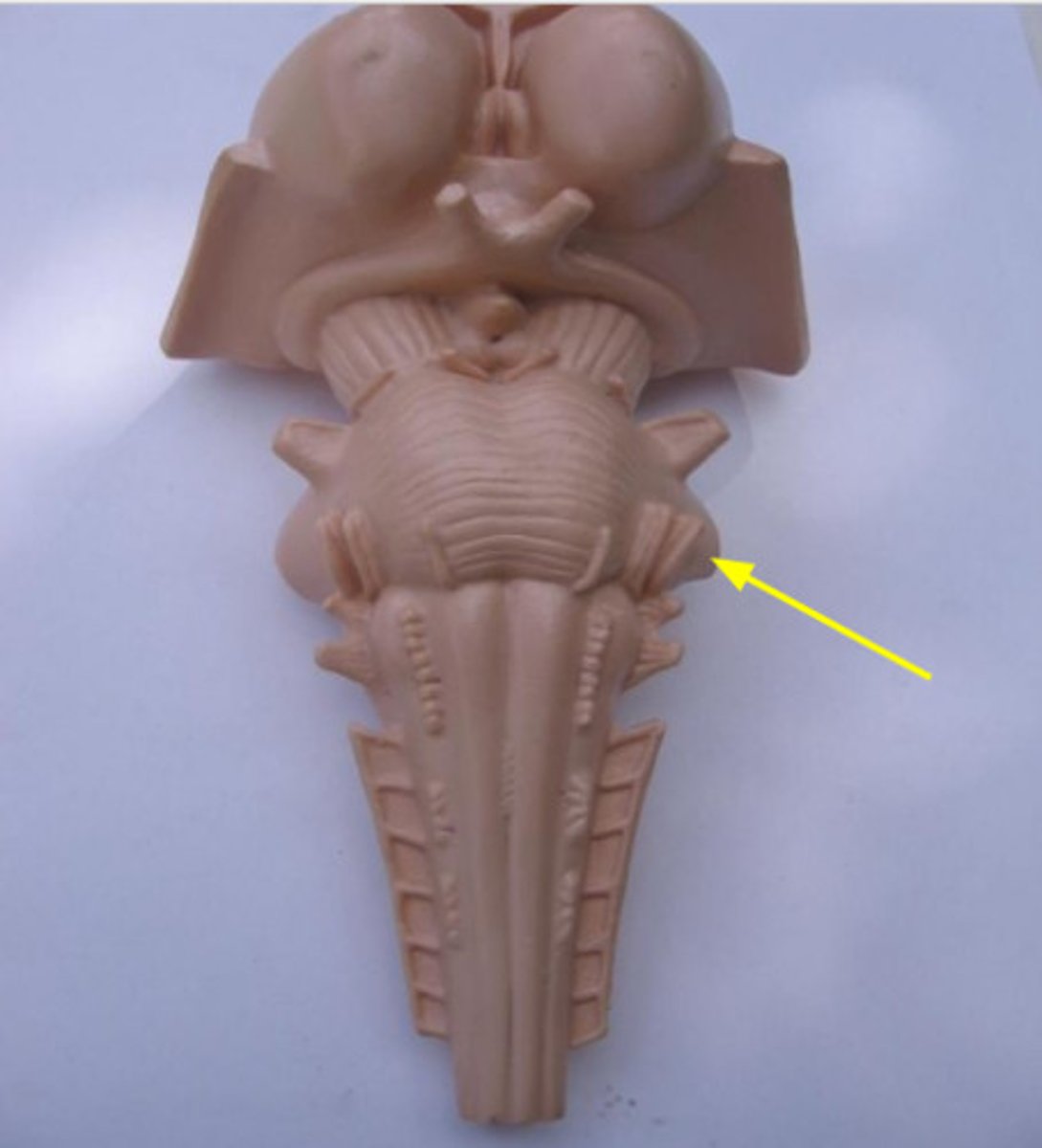
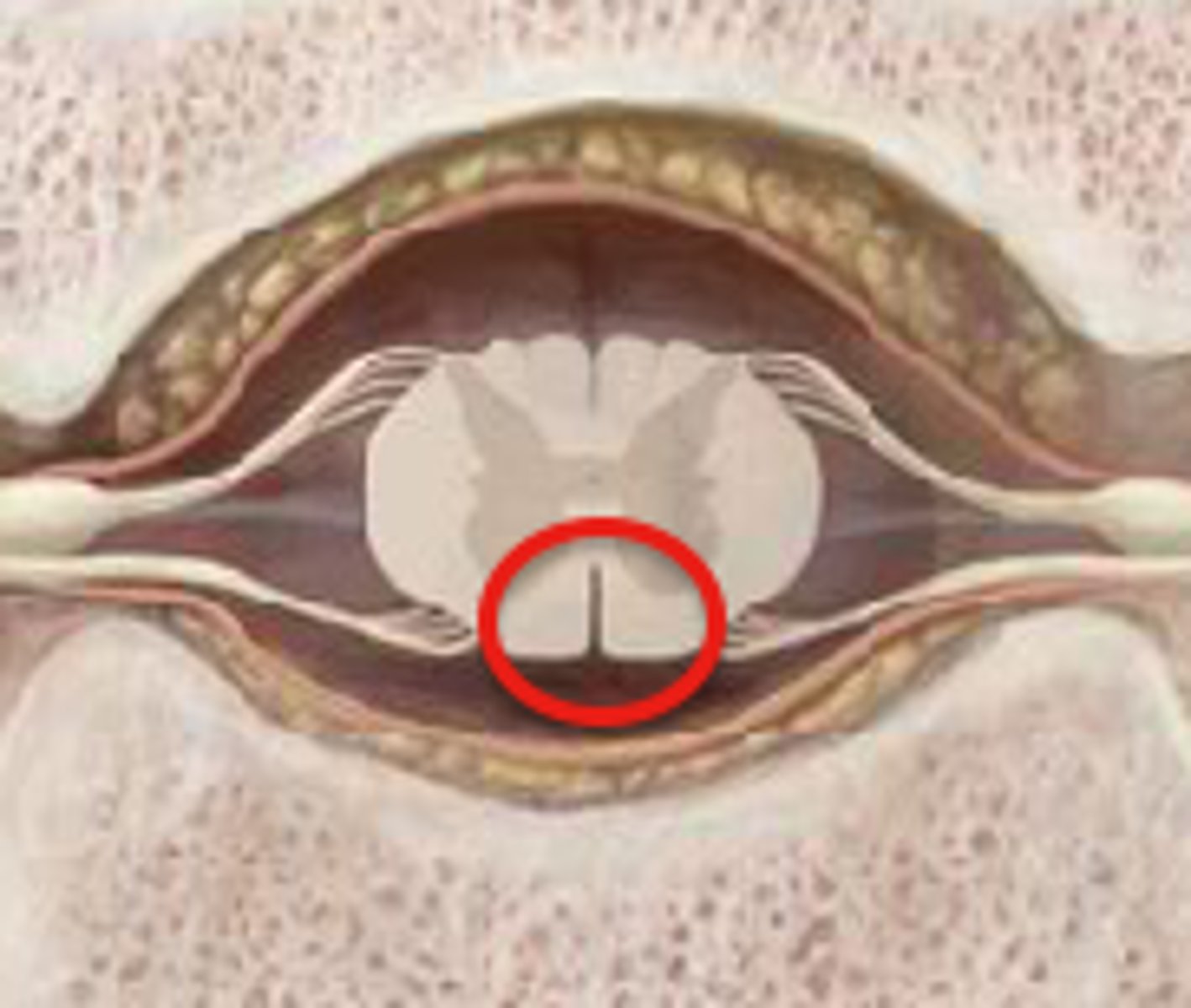
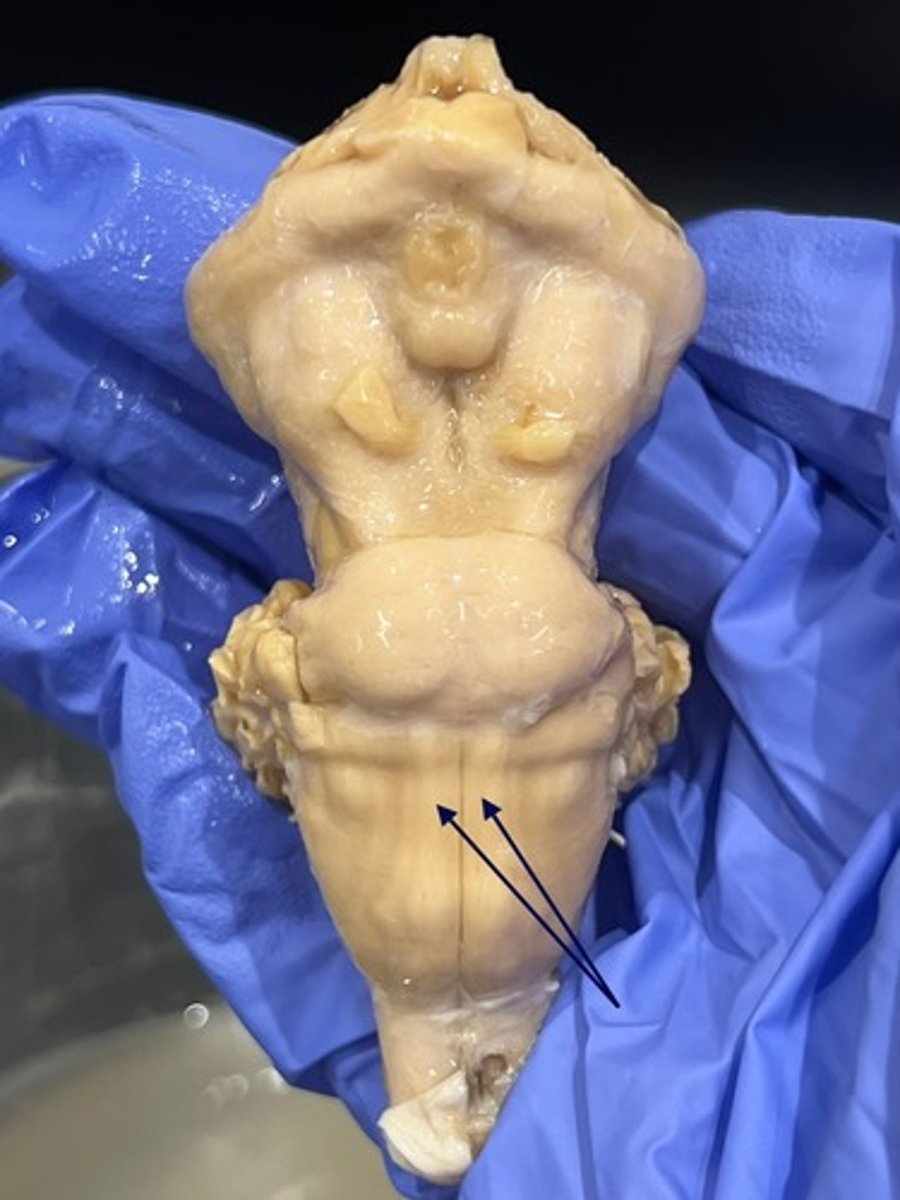
Features of the medulla
anterior median fissure
pyramids
pyramidal decussation
olives
fasciciulus gracilis
fasciculus cuneatus
Anterior median fissure
Pyramids
where tracts are
Pyramidal decussation
crossing of fibers
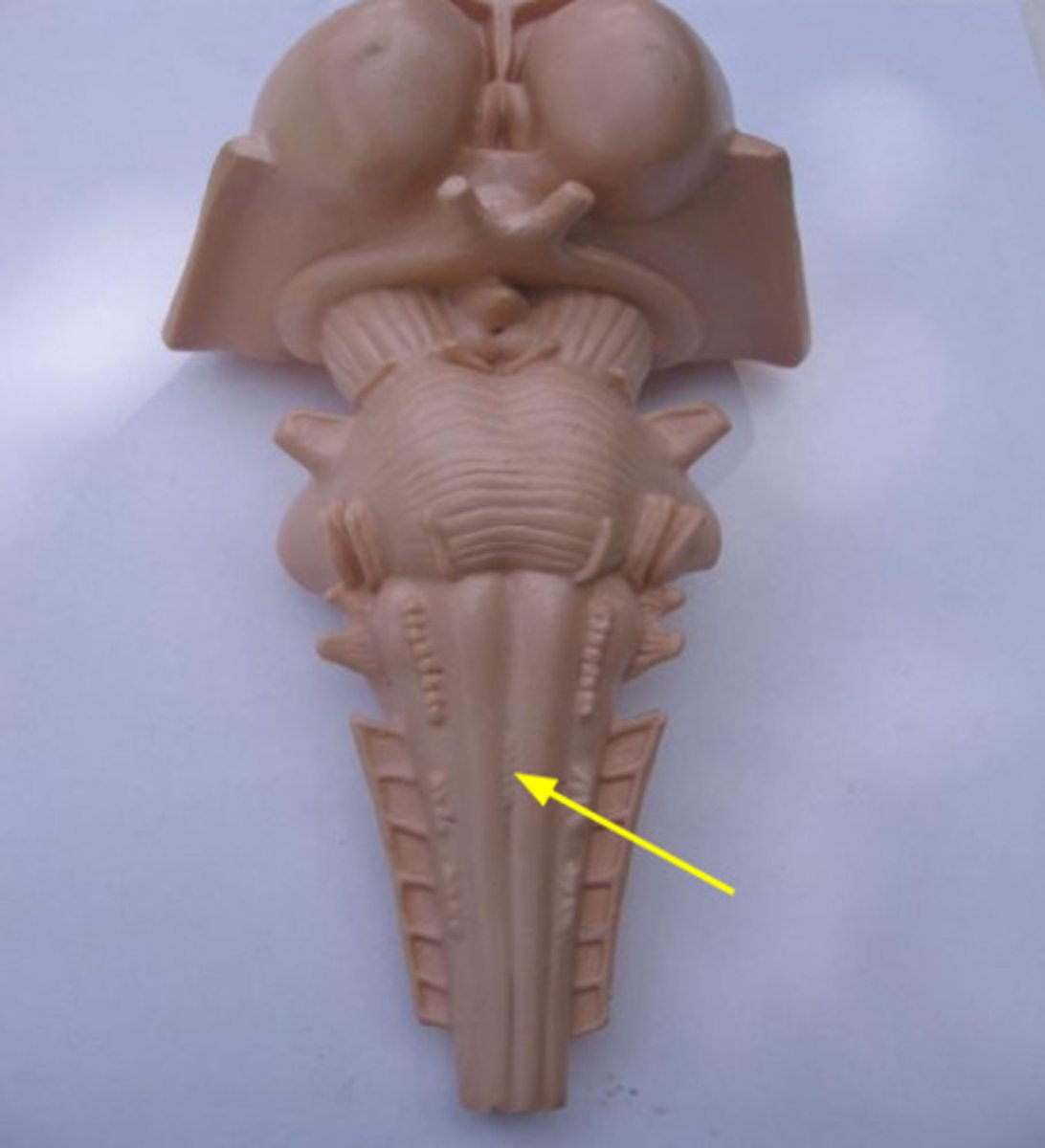
Olives are in the _____ medulla
rostral
Olives are formed by...
inferior olivary nucleus
The fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus are in the _____ medulla
caudal
Tectum
contains superior and inferior colliculus
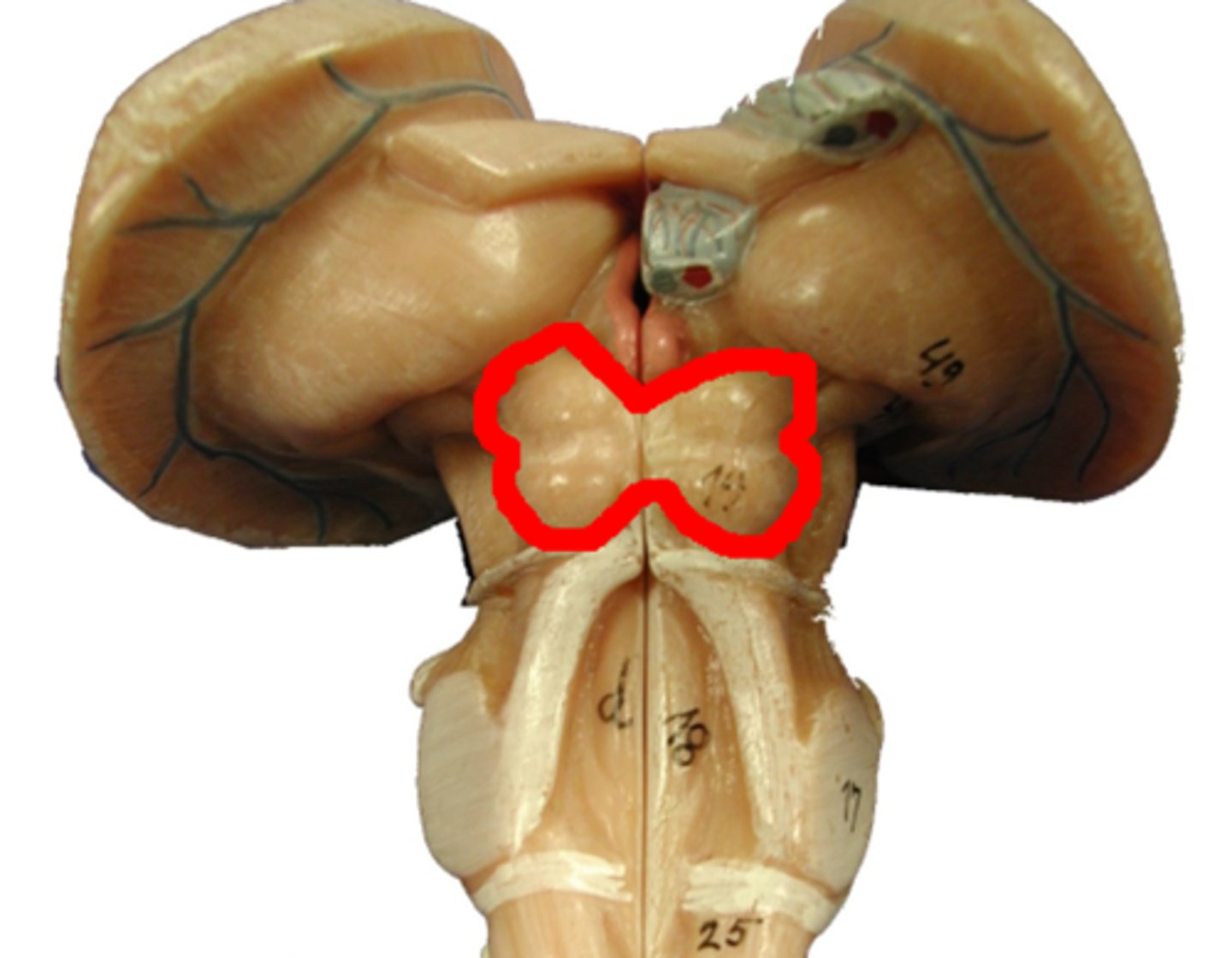
Tegmentum
"hood" covering all three regions of brainstem
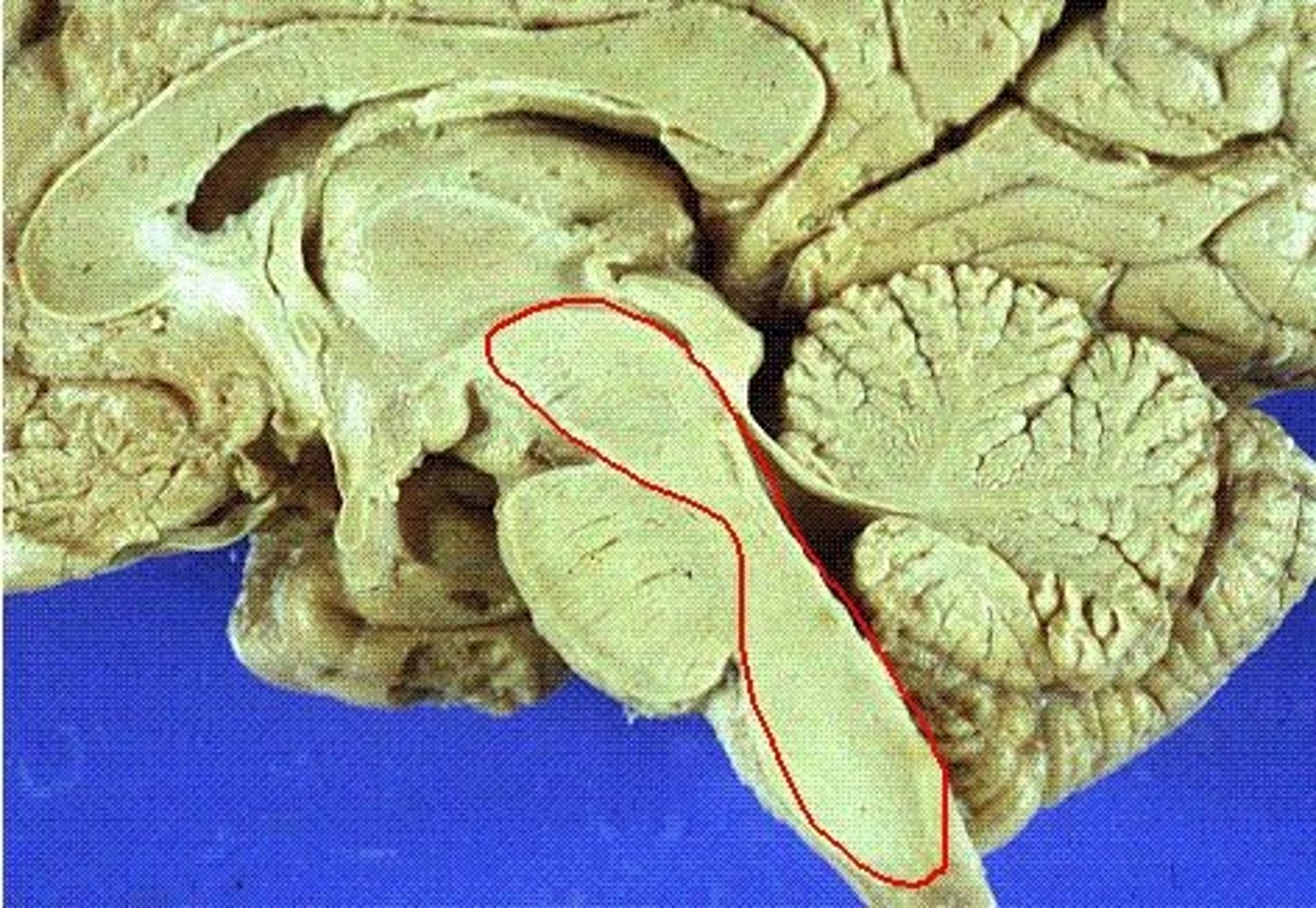
The tegmentum is ______ to the ventricular space
anterior
The cerebellum is ______ to the midbrain
posterior
Cerebellum is in line with the _____ and _____ ______
pons
fourth ventricle
Cerebellum has __ hemispheres
2
Cerebellum plays important role in
coordination
balance
vestibular control
Spinal cord extends from the ____ _____ to the _____ _____
foramen magnum
conus medullaris
The spinal cord is surrounded by the ____ _____
vertebral column
3 meninges
dura
arachnoid
pia
Subarachnoid space is filled with...
cerebrospinal fluid
Funiculi of spinal cord
columns of white matter
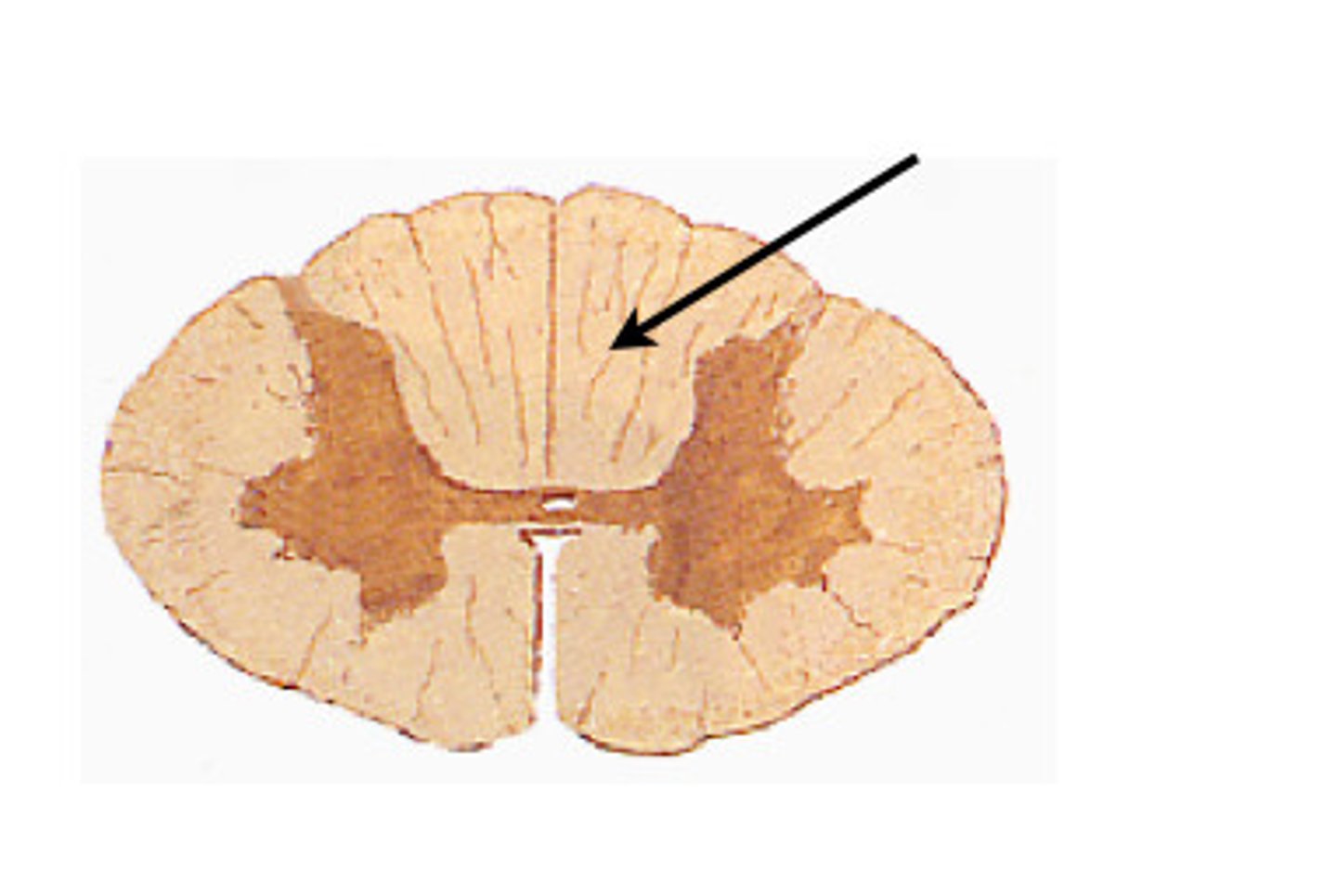
The lateral column (gray horns) are only visible in spinal sections...
T1-L2
S2-S4
Sensory information enters the spinal cord through...
posterior roots
Motor information leaves the spinal cord through...
anterior roots
Spinal cord is divided into ___ segments
31
Which segments of the spinal cord are enlarged to accommodate upper and lower limbs
cervical
lumbar
Dermatomes (sensory)
an area of the skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal root
Myotomes (motor)
muscle or groups of muscles innervated by a specific motor nerve
Microfilaments
bind to cell membrane and maintain cell shape
Neurofilament
structural support within the cell
Microtubules
provide a mean of transport of elements toward or away from the cell body
Acetylccholine
excitatory
Glutamate
Excitatory
GABA
Inhibitory
Dopamine
excitatory and inhibitory
Serotonin
Excitatory and Inhibitory
Continuous Conduction
occurs in non myelinated axons, slower
Saltatory Conduction
occurs in myelinated axons, faster
Ganglion
collection of cell bodies outside the CNS
Nucelus
collection of cell bodies within the CNS
Nerve
collection of nerve fibers (axons) that carries information to and away from the CNS
Tract
collection of nerve fibers (axons) within the CNS
Glial Cells
non neuronal cells within the nervous system that perform a wide variety of support functions
Astocytes
transform from a dormant to reactive state in response to CNS injury, support and nurture neurons
Microglia
transform from a dormant to reactive state in response to CNS injury, remove foreign and degenerative cellular elements through phagocytosis, return to resting state once process is over, immune cells
Oligodendrocytes
form myelin in CNS
Schwann Cells
form myelin in PNS
Grey matter
cell bodies, continuous conduction
White matter
axons, saltatory condition, myelin
CNS
brain and spinal cord
gyrus
ridge
sulcus
groove
Pre central Gyrus
frontal lobe
Post Central Gyrus
parietal lobe
Central Sulcus
separates front and parietal lobe
Frontal Lobe Info
largest lobe, primary motor area, premotor cortex and supplementary motor area
Frontal Lobe Function
executive functions, voluntary motor functions, emotion, motivation, judgement, brocas area (left hemi) - expressive speech
Patieal Lobe Facts
post central gyrus, wernickes areas - language comprehension(receptive speech), spatial orientation and perception, sensory homunculus
Occipital Lobe
important for vision, visual area and visual association areas
Temporal Lobe
processing auditory information, hearing, language interpretation
Limbic Lobe
hippocampus (learning and memory) and amygdala (emotion)