SE 4351 Requirements Engineering (INTRO)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the 3 kinds of wares?
Hardware
Software
Peopleware
What is Peopleware?
OF The People - Owner
BY The People - Developer
FOR The People - Customer/Client
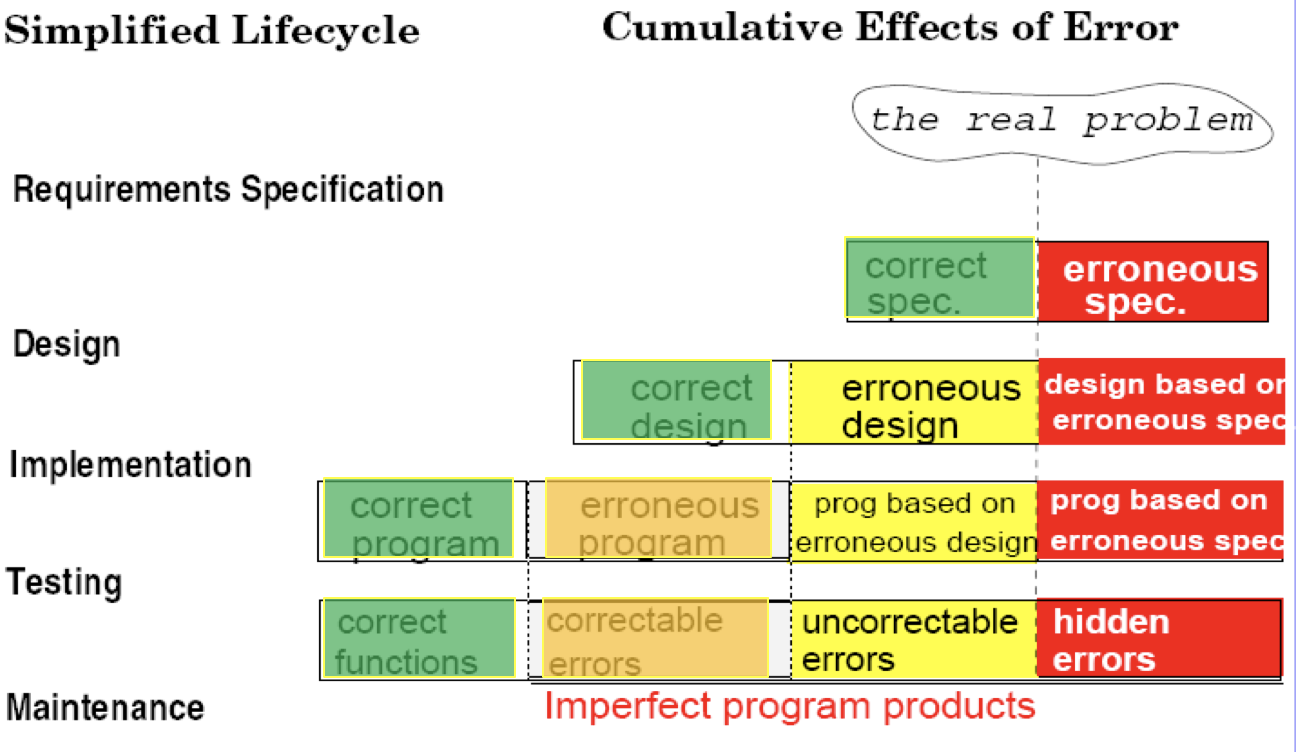
Error Propagation in Lifecycle
What factors contribute to Project Success?
Completed on time and on budget (28%)
Canceled before completion (23%)
Overran original estimates (49%)
The Chaos Ten Project Failures
Lack of User input/involvement
Incomplete/changing requirements & specifications
Unrealistic Expectations
Unclear Objectives
Didn’t need it any longer
Technology illiteracy
The Chaos Ten Project Success
User Involvement
Clear Business Objectives
Minimized Scope
Firm Basic Requirements
Formal Methodology
Reliable Estimates
How costly are Requirement Errors?
COST = 100 x COST
COST(correcting design/implementation errors) = 100 X COST (correcting requirement errors)
What are three most frequent problems plaguing large software systems?
Communication & Coordination
Thin spread of domain application knowledge
Changing & Conflicting requirements
Defining the problem is The Problem
What three key metrics can pinpoint a project’s success potential? (The Standish Group)
Project Size
Team Size
Project Duration
In requirements management: Smaller Projects have….
smaller teams.
fewer requirements.
fewer communication issues.
easier to manage.
usually target more focused business objectives.
What will be the Key?
Changing Requirements
What is RE?
Requirements Engineering is the branch of System Engineering concerned with real world goals to provide services and constraints on software system.
What is Role of Requirements?
Agreement regarding the requirements between the system developers, customers, & end-users.
Should be written in user language
basis for software design
support for verification/validation
support for system evolution
What is essential?
Modeling
“A model is a pattern, plan, representation, or description designed to show the main object or workings of an object, system, or concept”
Systematic Decision Makings
“Decision making can be regarded as an outcome of mental processes (cognitive process) leading to the selection of a course of action among several alternatives. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice
Software Architecture is called?
high-level/preliminary design
Component is called?
low-level/detailed design
What describes how components connect to each other?
software architecture specification
What Is Murphys Law?
Anything that can go wrong will go wrong
Is requirements engineering about the problem or the solution?
It is about Both
What are 3 types of defects?
Program
Design
Specification
80% of defects come from what Phase?
Requirements Phase
What error does RE focus on?
Erroneous Spec