Chap 5C - Enthalpy
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Calculations
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
State the formulas between H and Hc and Hf and q
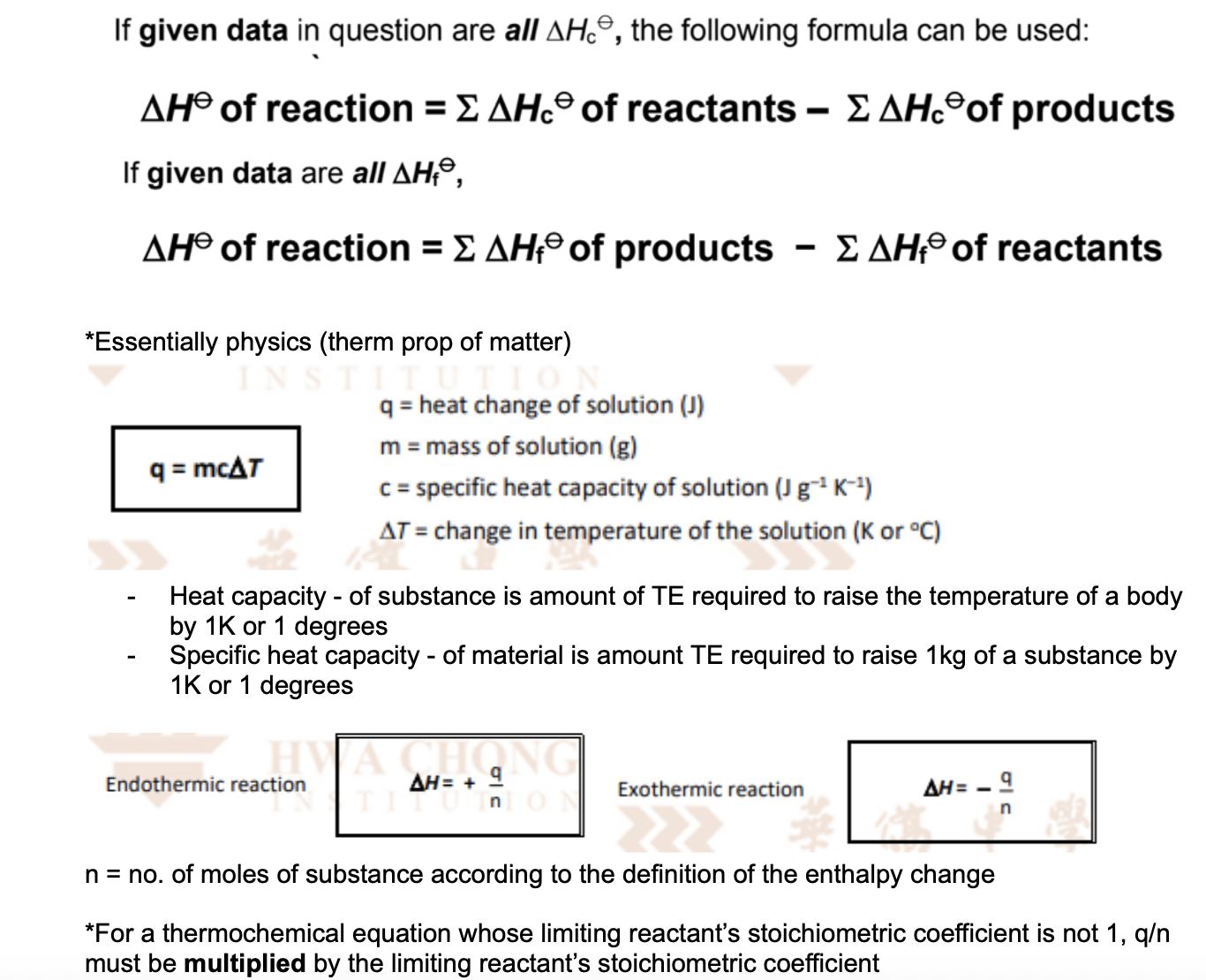
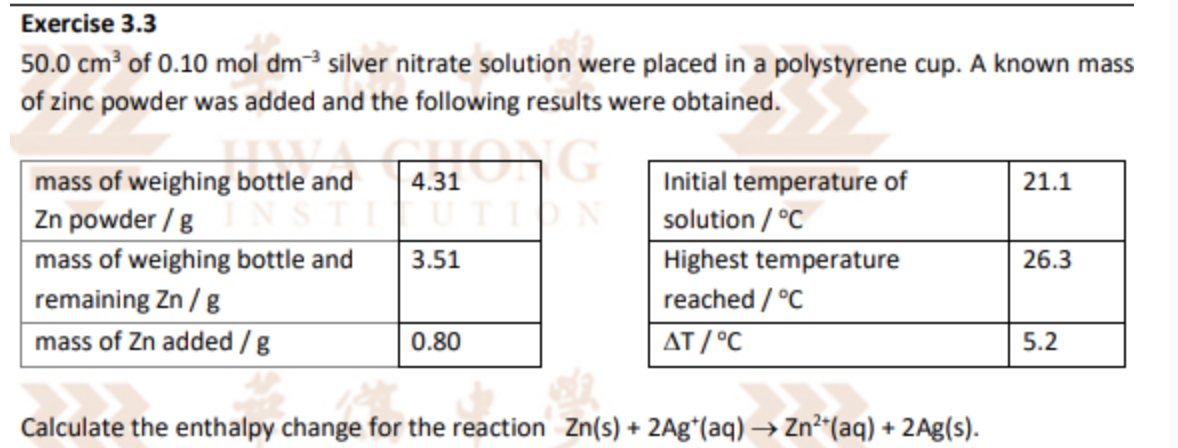
In this reaction, the reaction between Zn and Ag+ heats up the solution it is in -> reaction between Zn and Ag+ is treated as the ‘system’
The water or solution is treated as the ‘surrounding’
When calculating mcT, mass m refers to the ‘surrounding’ which in this question is the 50 cm3 solution

State assumptions in calculations
No heat loss/gain from surrounding air
Heat capacity of the calorimeter is omitted
More convenient to measure the volume of the solution : To calculate the mass of the solution, assume that the density of the solution is the same as that of water (1.00 g cm–3 ) since the solution is very dilute
Specific heat capacity of the solution is the same as that of water (4.18 J g–1 K –1)
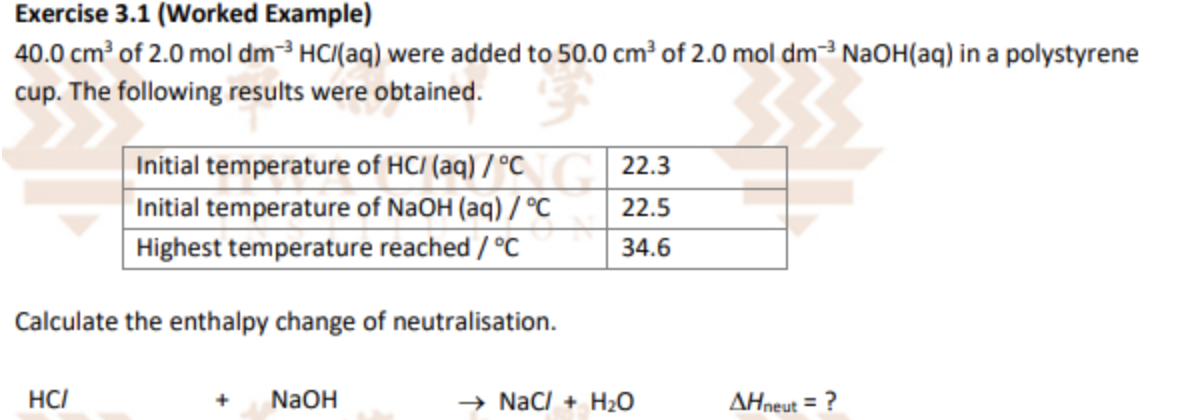

Describe Hess’s Law
To make used of Hess’ Law, the enthalpy changes in a reaction can be represented either in the form of an energy cycle or an energy level diagram.
Definition : Hess’ Law states that the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is independent of the pathway which the reaction takes place, provided that the initial and final states of the system remains the same
Simpler words : Total enthalpy change of a reaction is the same, regardless of the path taken, as long as the initial and final states are the same
Sum of clockwise arrows = sum of anticlockwise arrows
State some impt stuff abt energy cycles
Direction of the arrow DOES NOT indicate whether reaction is endothermic or exothermic
Need to point arrows in the right direction to correctly indicate the enthalpy change that occurs
Must include state symbols
State some impt stuff about energy level diagrams
Direction of arrows = reaction is exothermic or endothermic
Upward arrows are used for endothermic reactions and downward arrows for exothermic reactions
Length of arrows = magnitude of enthalpy change (so length matters!)
Always include the y-axis, which is labelled as the energy content of the substances
Describe the born-harder cycle
The Born-Haber Cycle is a technique of applying Hess’ Law to the standard enthalpy changes during the formation of an ionic compound
Lattice energy can be calculated from born-haber cycle
The cycle begins with the elements in their standard states, which is the 'zero reference line’
State formula relating LE, f, atom,
