Male Reproductive System - Unit 6
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Testes
Endocrine glands that produce sperm and testosterone, contributing to secondary sexual characteristics.
Epididymis
Where sperm are matured and stored.
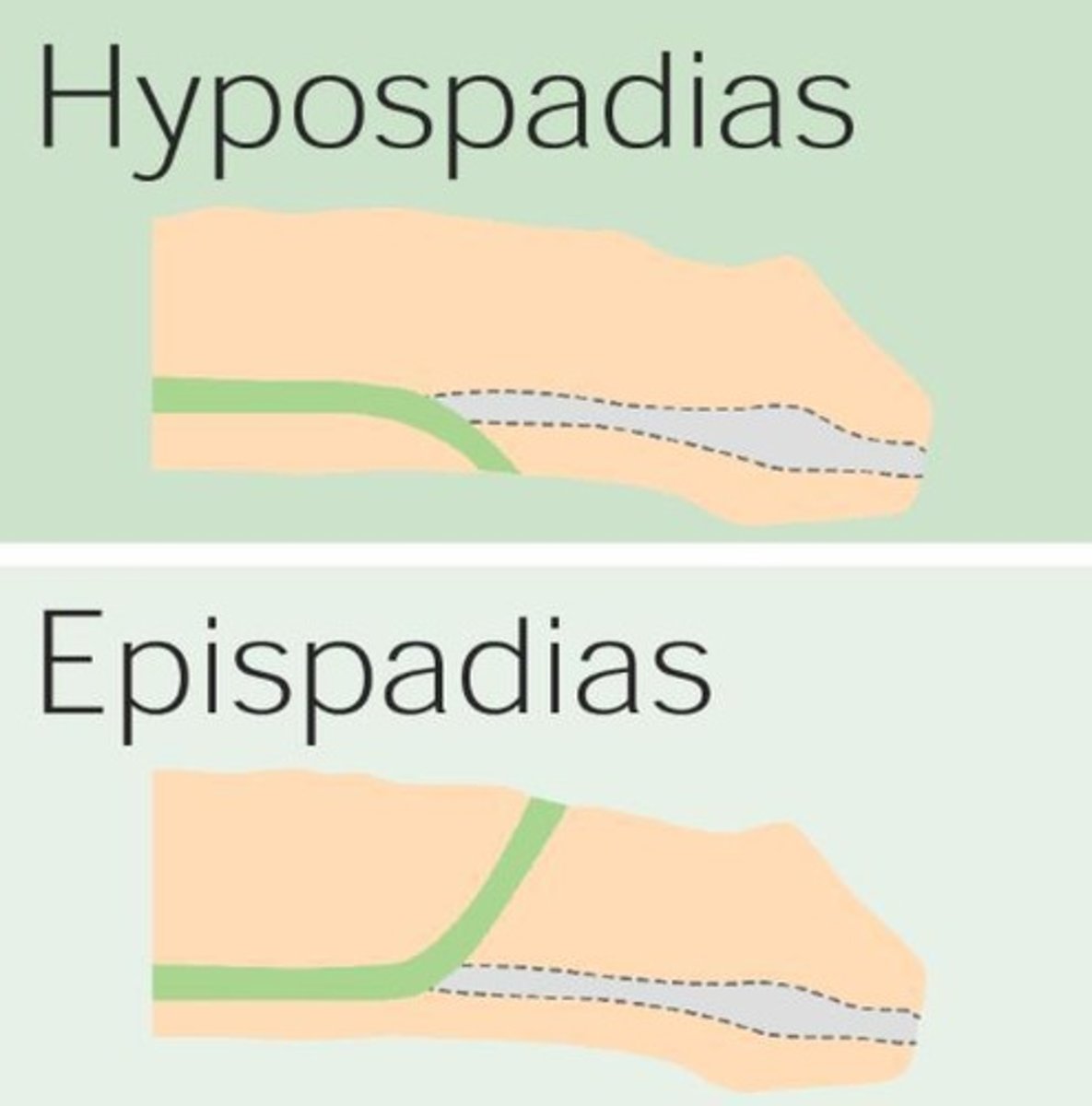
Hypospadias and Epispadias
Conditions affecting the urethra's opening in males.
What is cryptorchidism?
Undescended testes
Which side is most affected by cryptorchidism?
Right side
What percentage of full-term births are affected by cryptorchidism?
3%
What percentage of preterm births are affected by cryptorchidism?
30%
What is the increased risk associated with cryptorchidism?
Testicular cancer
What is infertility?
Inability to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse.
What factors can impair fertility?
Factors in men, women, or a combination of both.
what are testes disorders ?
torsion- twist and cutoff of blood supply
orchitis - acute teste inflammation
hypogonadism - low levels of sex hormones
Hypogonadism
Caused by defects that interrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.
how do we treat hypogonadism
long term hormone replacement
treating underlying causes
what is testosterones action ?
binds to androgen receptors / mimics hormone and binds to site
why is testosterone not addictive
because it is a controlled substance
what do we use testosterone to treat
hypogonadism
delayed male puberty
what is the administration route for testosterone
PO, IM, TD, and topical
what are the side effects of testosterone use
edema
deepening of the voice
decreased libido
clitoral enlargement
decreased breast size
acne and facial hair
what are the adverse effects of testosterone use
deep vein thrombosis
hepatotoxicity
stroke
suicidal thoughts
pulmonary embolism
what are contraindication of testosterone use
heart attack / stoke within past 6 months
males with breast/prostate cancer
what nursing edication needs to be provided for clients on testosterone
educate on signs of stroke, heart attack, DVT, and liver failure
emphasize important follow up
Erectile dysfunction (ED)
Impotence; inability to attain or maintain an erection, more common in older men.
sildenafil action and use
works by relaxing smooth muscle and increasing blood flow
used with ED and BPH
what route and how often can sildenafil be taken
PO , once a day
what are side effects of sildenafil
flushing
dyspepsia - heartburn
headache
dizziness
hyptension
what are adverse effects of sildenafil
priapism - prolonged erection
myocardial infarction - heart attack
vision/hearing loss
what are some contraindication of sildenafil
use of nitrites or tamsulosin (cause life threatening BP drop )
sever hypotension
recent MI or stroke
what nursing education is provided for clients taking sildenaful
dont take more than one daily
report priapism
educate on use of nitrites or tamsulosin since they are both PRN
What is the second most common cancer in men?
Prostate Cancer : mostly slow growing
What are some risk factors for prostate cancer?
Age, black men, obesity, and positive family Hx
how to differentiate between BPH and prostate cancer
blood levels will be up with cancer and not BPH
Orchiectomy
Surgical removal of one or both testes, which may require testosterone replacement therapy.
Orchitis
Inflammation of one or both testes.
Epididymitis
Inflammation of the epididymis.
Phimosis
foreskin cannot be pulled back
Paraphimosis
Inability to return the retracted foreskin to its normal position.
Peyronie disease
Development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis
Balanitis
Inflammed penis