Chem Chapter 6: Periodic Tables/Periodic Law
1/75
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
John Newlands
Scientists who grouped elements into groups of 8, called the Law of Octaves
Law of Octaves
A principle for classifying elements by arranging them in order of increasing atomic mass. It states that every eighth element has properties similar to the first, much like the notes in a musical octave
Meyer and Mendeleev share what in common?
Both grouped the elements with atomic mass/elemental properties
Why did Mendeleev get credit for the table?
He published first
How did Mendeleev order the table?
In vertical columns based on their reactivity with other elements, also on atomic mass
What was special about Mendeleev’s table?
There were blank spaces for undiscovered elements
How did Moseley change the periodic table arrangement?
Elements arranged according to atomic number
Periodic Law
Elements are arranged according to repititous properties
Groups in the PT
A vertical column of elements; aka a chemical family
How many groups are on the PT?
18
Period
Horizontal row of elements; 7 periods on the table
Elements in the same period have?
A strong resemblance among their member
List the 4 chemical families:
Alkali metals
Alkaline earth metals
Halogens
Noble gases
Alkali Metals (Group, Charge, Examples)
1A, +1, Li/Na…
Alkaline Earth Metals (Group, Charge, Examples)
2A, +2, Be/Mg/Ca
Halogens (Group, Charge, Examples)
7A, -1, Cl/F
Noble Gases ((Group, Charge, Examples)
8A, N/A, Xe/Kr
3 PT Blocks
Representative Elements
Transition Metals
Inner Transition Metals
What block are these elements in?
Representative Elements = ?
Transition Metals = ?
Inner Transition Metals = ?
s/p
d
f
Metals are located?
Around the left side
metals characteristics
Have luster or shine
good conductors of heat/electricity
solid at room temperature
malleable (thin sheets)
ductile (fine wire)
non-metals characteristics
lacks luster; is dull
poor conductors
neither malleable/ductile
many are gases at room temperature (bromine is a liquid)
varied physical properties
semi-metals location
along the staircase, except for aluminum and polonium
semi-metals are also called?
metalloids
semi-metals’ properties
properties intermediate of metals/nonmetals
properties not predictable/different for the different elements
type of electrons
valence electrons (outermost)
core electrons (remaining)
patterns in different groups (1A, 2A, 7A, 8A)
alkali metals end with s1
alkaline earth metals end with s2
halogens end with p5
noble gases end with p6
atoms tend to ___ or ____ electrons to becomea stable noble gas
lose or gain
isoelectronic
elements that have the same e-config
for isoelectronic elements
write the configuration using the previous noble gas
which 2 elements are liquid at room temperature?
Mercury (Hg) and Bromine (Br)
atomic radius
distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost electrons
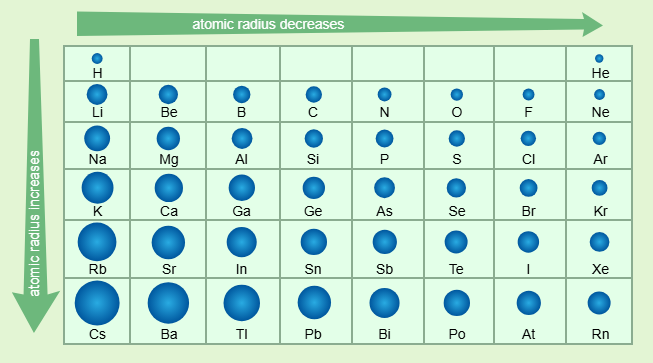
characteristics of atomic radius
strong attractive forces between protons/electrons make the atom smaller going from left to right
electron shielding
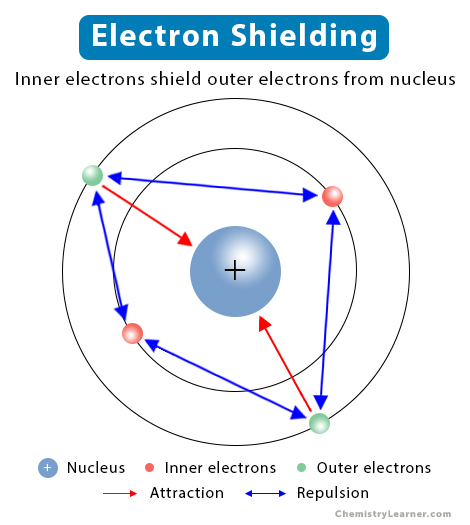
electron shielding
inner core electrons’ attraction to protons causes the outer electrons to be held less tightly (size increases top to bottom)
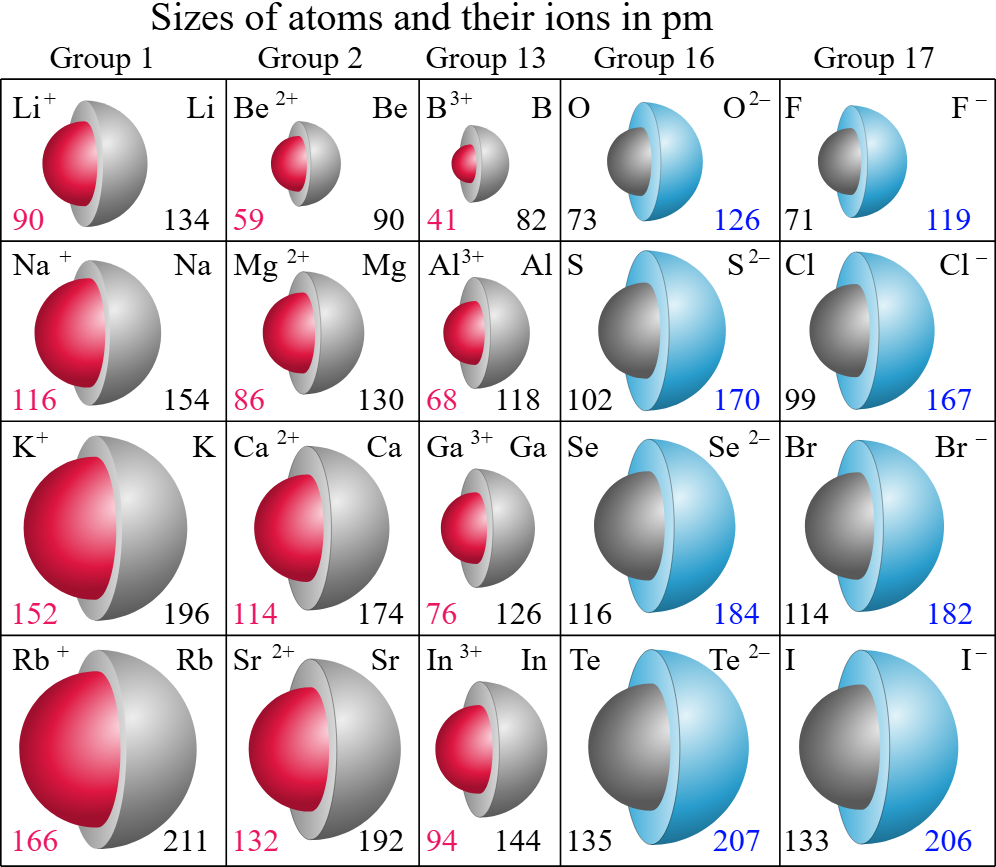
ionic radius
size of the ions
electronegativity
the attraction an atom has for the shared pair of electrons in a bond (pull on electrons)
which group is NOT on the electronegativity table (mostly)
noble gases
ionization energy
energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of neutral gaseous atoms
2 trends go from left to right, bottom to up
Electronegativity & Ionization Energy
successive ionization energy
energy used to remove successive electrons (2nd/3rd/4th)
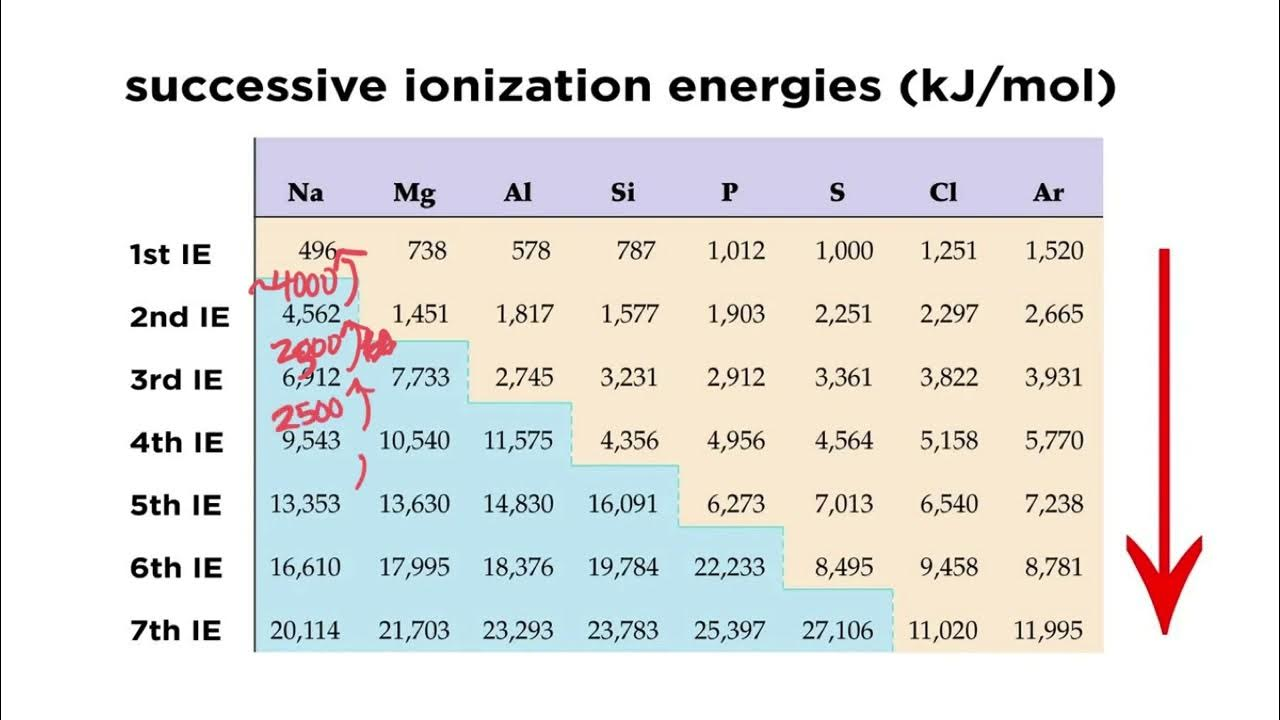
Magnesium’s 3rd IE is high because?
It has a noble gas config (easy to remove 1st/2nd however)
anions v. cations
cations are positively charged, smaller than anions
anions are negatively charged, bigger than cations