non-protein nitrogen & kidney function
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
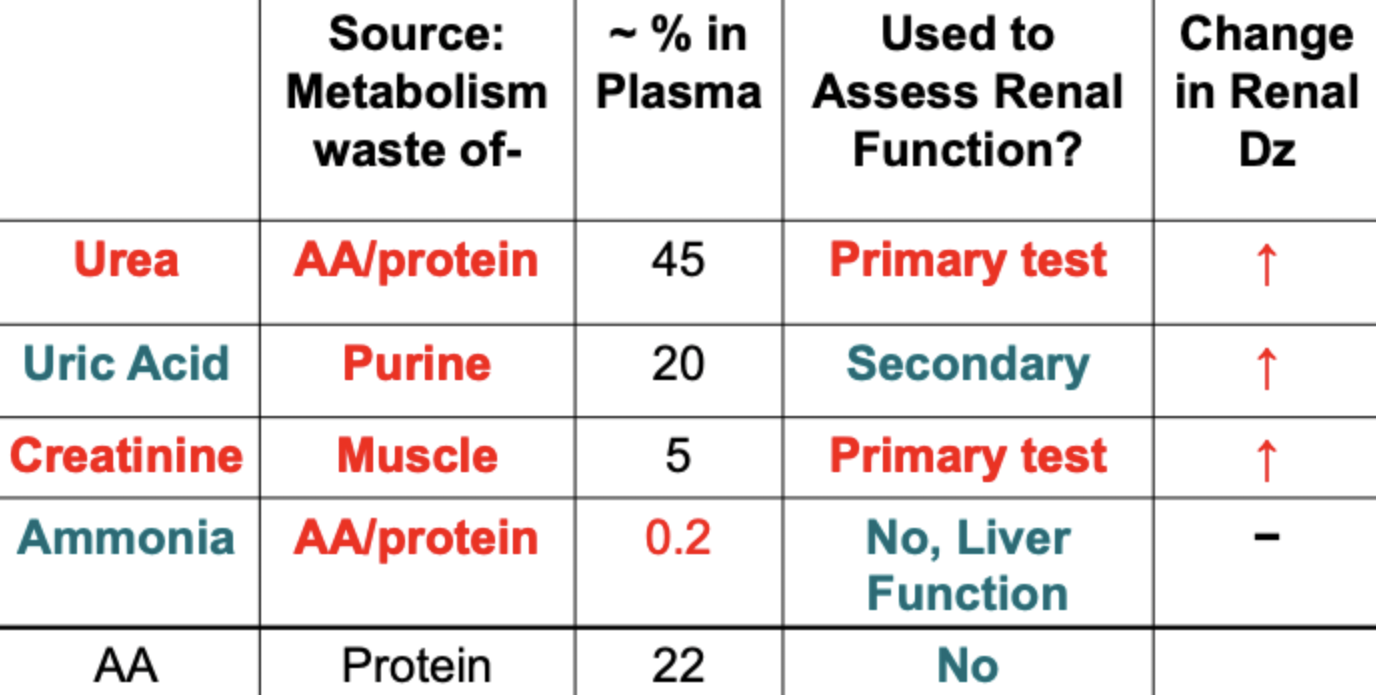
non-protein nitrogen (NPN) compounds
catabolic products = wastes. clinically significant when increased. ex: urea, creatine, uric acid, ammonia
urea
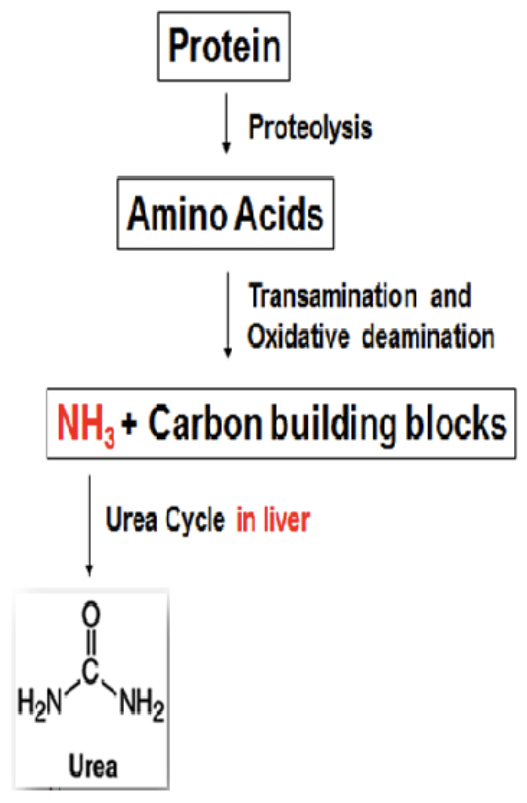
principal excretory form of nitrogen. formed in the liver from toxic NH3 (end product of protein catabolism). kidney is the only significant route for excretion, readily filtered by glomerulus. ~40-50% reabsorbed by tubules
how is urea regulated?
blood levels are directly related to the metabolic function of the liver (urea formation) and the excretory function of the kidney (urea excretion)
urea disorders decrease with…
malnutrition: low protein intake.
dec synthesis: severe liver dz (high NH3).
inc renal loss: not reabsorbed (acute tubular necrosis)
urea disorders increase (azotemia) with…
dehydration.
inc synthesis: high protein diet, tissue breakdown, severe GI bleeding.
dec renal clearance: low renal blood flow (circulatory/heart failure), dec kidney function, obstruction to urine outflow.
clinical utility of urea measurement
increase may indicate renal dysfunction: not specific indicator of renal function, not sensitive to mild renal dysfunction (may not be > RR until advanced dysfunction). increase confirms creatine inc in renal dysfunction. distinguishes causes of AKI as BUN/Cr ratio.
how is urea measured?
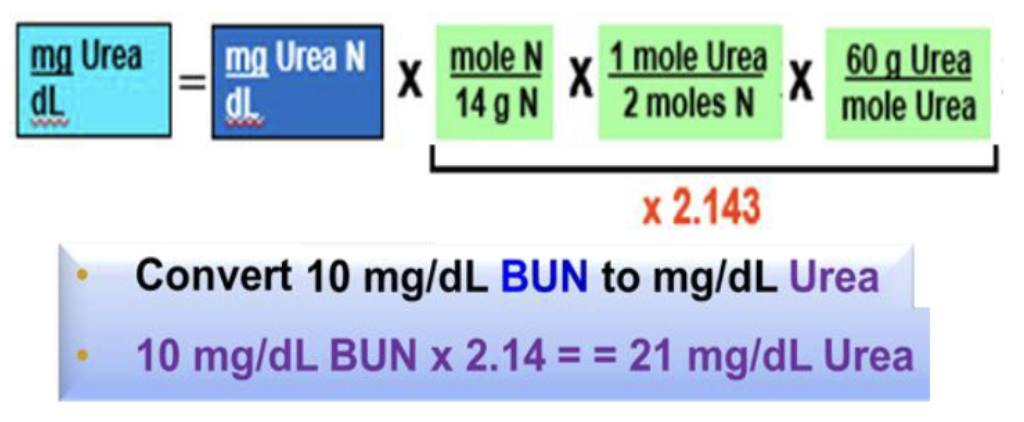
plasma urea measurement reported as blood urea nitrogen (BUN), whoch is in units of urea N. urea = urea N x 2.143
BUN measurement: direct method (spectrophotometric)
combines urea with a reactant → colored complex that is measured
BUN measurement: indirect
1st step: enzymatic using urease to convert urea into ammonia (NH4+). must not use tube w/ NaF additive → inhibits urease. 2nd step: measures NH4+, many methods

creatine
synthesized from glycine, arginine, & methionine in liver. stored in muscle as part of energy pool as phosphocreatine, which is used to fuel muscle contraction. phosphocreatine → H2O + creatinine (muscle waste product)
creatinine
release from muscle into circulation is relatively constant as 1-2% of total creatine pool breaks down each day. kidney is the only significant route for excretion (plasma). readily filtered by glomerulus, not reabsorbed by tubules
3 factors that determine plasma creatinine levels
muscle mass, rate of creatinine turnover, renal function
clinical utility of creatinine measurement
evaluate renal filtering function: plasma creatinine inc w/ dec glomerular filtration, not sensitive test (GFR may be down 50% before plasma creatinine significantly high). determining GFR. used in delta check: current patient values compared to previous ones before reporting, failure = might mean errors
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
volume of plasma filtered by the glomerulus per minute (ml/min) = renal clearance. healthy glomerulus: 120 mL/min at Bowman’s capsule. low = kidneys inefficient, can only clear small volume of plasma of given substance per min. used for early detection of chronic kidney dz
how is GFR estimated?
eGFR calculation. creatinine clearance test
renal clearance test
measures plasma removal of an ideal molecule that is subject only to the renal filtration process.