Unit 2 - Energy Charts (Thermochemistry expanded)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What happens to temperature during a phase change?
The temperature stays constant while heat energy is absorbed or released — energy is used to break or form bonds, not raise temperature.
Heating curve
A graph showing how temperature changes as heat is added to a substance over time.
It includes flat sections (phase changes) and sloped sections (temperature changes).
What are the main segments of a heating curve for water?
1⃣ Solid heating (ice warming)
2⃣ Melting (solid → liquid)
3⃣ Liquid heating (water warming)
4⃣ Boiling (liquid → gas)
5⃣ Gas heating (steam warming)
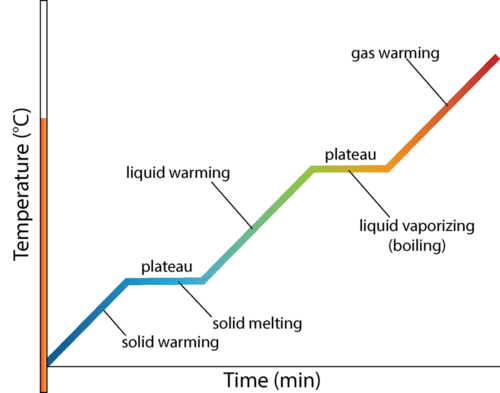
Heating phase plateau
The substance is changing phase — temperature doesn’t rise, but potential energy increases as bonds weaken.
Heating curve slope
The temperature increases — kinetic energy of particles rises.
Is melting endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic — heat is absorbed to break bonds between solid particles.
Is freezing endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic — heat is released as particles form bonds and move closer together.
Is boiling (vaporization) endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic — heat is absorbed to overcome attractions and turn liquid into gas.
Is condensation endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic — heat is released when gas molecules slow down and form liquid bonds.
Is sublimation endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic — solid absorbs heat and turns directly into gas (e.g., dry ice → CO₂ gas).
Is deposition endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic — gas releases heat and turns directly into solid (e.g., frost forming).
What does the area under the flat lines on an energy diagram represent?
The amount of heat absorbed or released during the phase change — proportional to mass × heat of fusion/vaporization.
What kind of energy changes during phase changes?
Potential energy changes — particles move farther apart or closer together, but their average kinetic energy (temperature) stays the same.
The substances that solidify first have __ amount of energy to lose.
Least
Substances that solidify last have __ amount of energy to lose.
Most