The Adolescent brain Week 2 Part 1
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on: Navigating the Social Environment in Adolescence: The Role of Social Brain Development
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What age range is defined as adolescence?
10-24 years
How does the amount of cortical gray matter change during development?
It goes up, peaks in late childhood, and decreases until the mid 20s
How does the amount of white matter change during development?
Linearly increases during childhood and adolescence
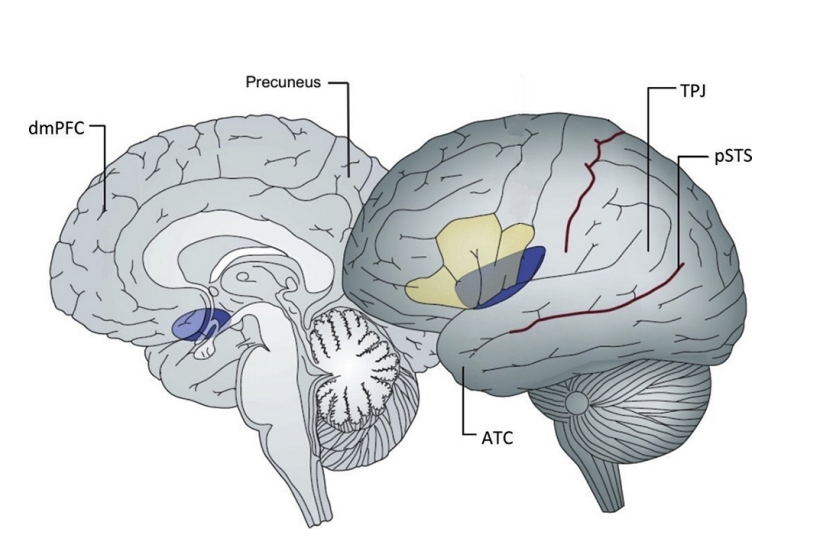
What areas are part of the social brain?
dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC)
anterior cingulate cortex
inferior frontal gyrus
posterior superior temporal sulcus
anterior temporal cortex
amygdala
anterior insula
What happens to gray matter and cortical thickness in the posterior superior temporal sulcas, temporoparietal junction (TPJ), and dmPFC from childhood into early 20s?
They decrease
What happens to the anterior temporal cortex cortical thickness until early adulthood?
It increases
What happens to the gray matter in the anterior temporal cortex until adolescence?
it increases
How much does the amygdala increase in size from late childhood to mid adolescence?
it increases by ~7% stopping growth at ~14 years of age
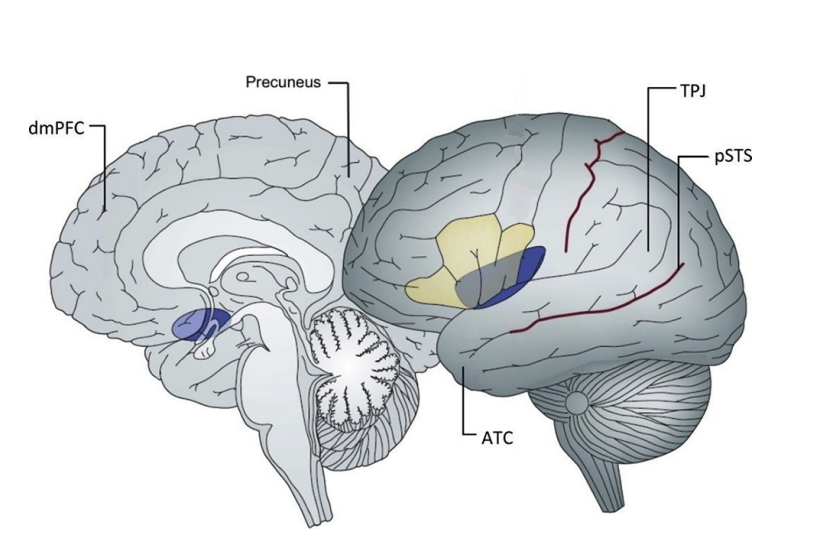
During mentalising tasks, are the temporal posterior regions (TPJ pSTS)more active in adults or adolescents?
In adults
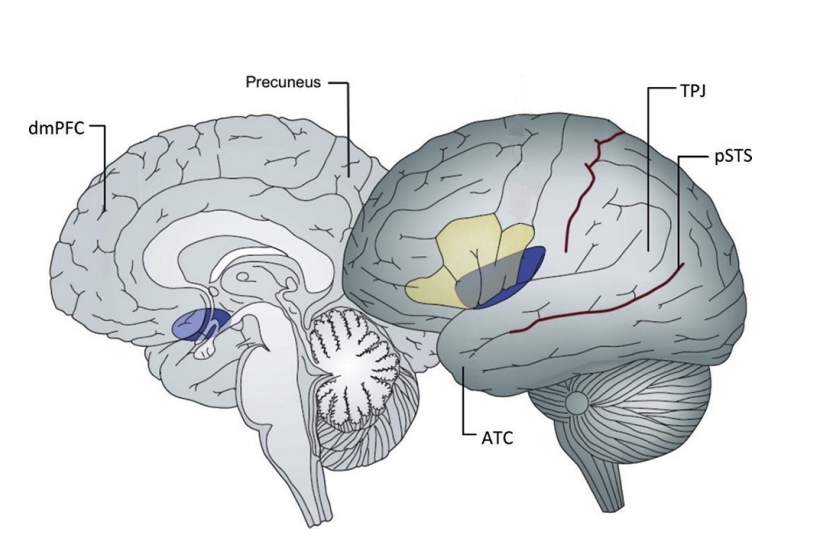
During mentalising tasks, are the anterior rostral PFC regions more active in adolescents or adults?
In Adolescents
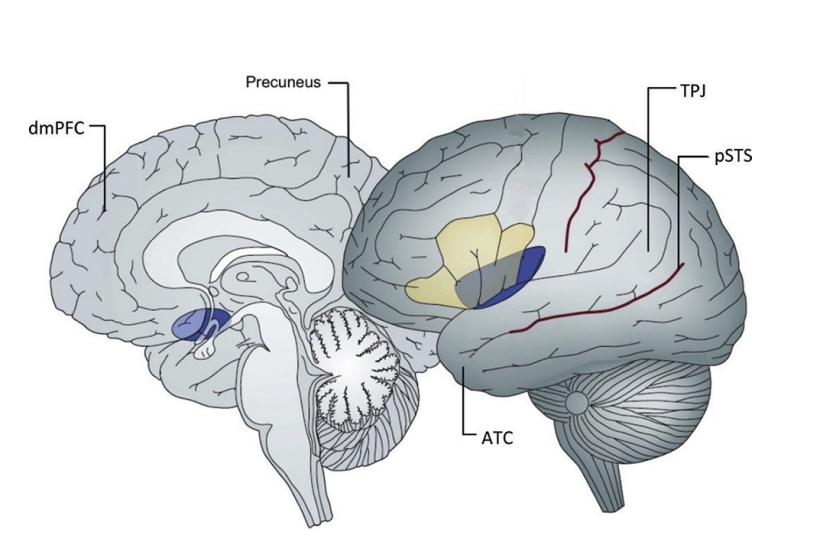
Both adults and adolescents use the Dorsomedial Prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) when taking other people’s opinions into account. What is special about adolescents?
They also use the dmPF during nonsocial situations
When is the mentalising network most used?
During risky social situationsW
What happens in the social brain during social exclusion?
The connections become more active, mentalising (trying to figure out what other people are thinking)
How does having a less dense social network impact the connections in the social brain?
You have stronger connectivity during social exclusion
What happes to the conections between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex by mid adolescence?
They are inversely coupled
How does a stronger inverse connection between the PFC and amygdala show itself?
Less nonclinical anxiety symptoms
How does PFC and ventral striatum activation influence risk taking
Less risk taking
What is the Baloon analogue risk taking task
Participants inflate a virtual balloon for a monetary reward
What disorders do youth with antisocial peers more likely develop?
Externalizing disorders such as antisocial behavior and substance use
What is adolescence a sensitive period for?
Activating genetic predisposition to certain disorders.
What areas are more active when adolescents observe peers be prosocial, and the continue to mirror that behavior?
dmPFC
TPJ
precuneus
superior temporal sulcas
What is prosocial risk taking associated with (Standing up to a bully for example)
lower reward sensitivity, higher punishment sensitivity, and greater school engagement