environmental science
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Soil
is the top layer of the Earth’s surface where plants grow. It’s a natural mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, air, and living organisms.
Geologists
Study the earths strength , composition and history
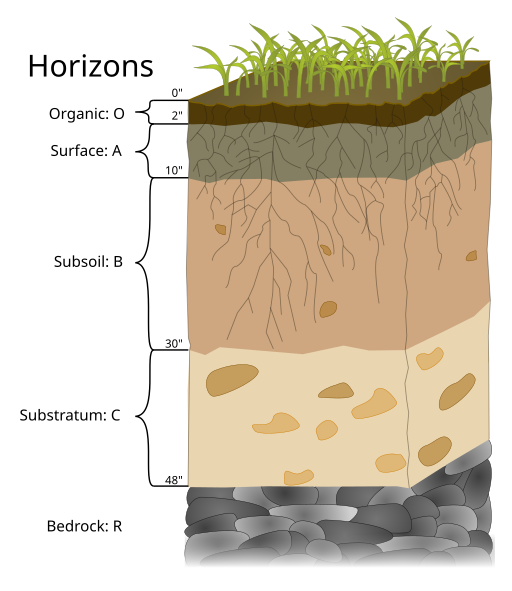
Horzions
Organic
Surface
Subsoil
Substratum
Bedrock
Civil engineering
Focuses on the physical characteristics of the soil in relation to the construction
Ecologists
The interaction between livings things and their environment ecosystems could be on land or water
What is the foundation for ecologists
Soil
What is the foundation for aquatic system
Water
Agricultural scientists
Study interaction between plants soils , livestock and their environment
agroecosystem
Studying farming systems as ecosystems—how plants, animals, soil, water, and humans interact.
Functions of soil ?
Anchoring plants
Supplying air to roots
Supplying water and nutrients
Hydroponics
Growing of plants in water
Aeroponics
Is the growing of plants suspended in air by applying mist
What are plants products used for
Food , feed , clothing and biofuels
What is agriculture main focus
Plants and animal production in sustainable manner
Who is Thomas Malthus and what did he do ?
Wrote on the principle the green revolution (1960) and founder of it as a father and saved billion of lives
What was the green revolution
Initiates to transfer agricultural technologies to developing countries, including high yielding and disease resistant semi dwarf wheat
Biodiversity or biological diversity
The variety of live in world , a specific habitat , or a geographical location
Ecosystem service
Benefit humans gain from ecosystem biodiversity ( food , feed , clean air , water and medicinal )
what is it called when you need to find the grain of a plant weight
Harvest index
what is soil composed for
inorganic minerals and organic compounds
inorganic
portion of soil includes soil minerals , air and water
organic compounds
consists of plant and animal residues / mircorganics
what is decompostion plays a part for
organic compound
what does organic and inorganic soil particles form
granules and cpds
what fills the soil pores
water and air
what is oxgen used for
plants roots for respiration
what does water do
it is the soil solution which caused dissolving and when it filles the pores it displace the air
soil provides
habitatl , home for wide variety of microorganisms and animals
what are present for microorganisms
fungi and bacteria
what are the soil animals
worms,insects, earthworms and nematodes
succesful crop
growth and yield depend greatly on these nutrient recycling processes
what are the layers for the crust
crust,mantle and core
crust
earth outermost
mantle
the layer belong crust
core
the innermost layer
what caused the thickness of the crust
the location
what is the conteints of the crust
30 miles thickness
under ocean floor on the crust is about
2 to 3 miles on thick
what elements crust have
al,fe , ca , na , k and Mg
crust have 74% of what
oxygen and silicon
what is the negative charge oxygen
o2- anion
what is the postive charge oxygen
silicon s4+
rocks
are naturally occurring solid aggregate's of minerals
different types of rocks
igneous,sedimentary and metamorphic
igeneous rocks
created when mollen lava cools and crystallizes (grantile and basalt)
sedimentary rocks
form through accumulation and compaction of sediment often in water( shale and limestone)
metamorphic rocks
undergo structure an compositional changes due to intense heat and pressure(marble)
what are the earth minerals
they have 90% slicates made up of oxygen and silicon
what is mica
is a sicate mineral that contains aluminum and potassium
five differnt soil formation factors
parent material , climate , organisms , relif of topograqphy and time
what does soil forming process caused
physical weather, chemical weathering , leaching and the accumulation of organic matter
what does the climate and organisms act on
parent material and topography
parent materials
primary rocks is the igneous,sedimentary , metamorphic and sediments from water or wind such as sand and slit
types of parent material inogranic materna determines soil properties
rock is low in calicum and the soil becomes acidic
topography
determines water movement and susceprbity to erosion/ soil formed upland is lowland and steep vs flat land
steep land
is susceptible to erosion
weathering
is breaking down of rocks and minerals by natural forces
climate factors
temperature , water
what does soil temp determines
the rate chemical recators
biological processes
minerals break down at higher rates in warm temp
what does high temp does
evapro transpiriation
evaporation
is the loss of water from soil and transpiration is loss of water form plants
preciapation
rain,snow etc dissolving minerals that will be leaching
low precipation
soluble minerals may acculmate in the soil and after soil properties
organisms
plants, animals, microorganisms, microbiome and living in the soil
what does the organisms do
they influence the accumulation of organic matter in soil
bacteria
are dominant in praire veggie
fungi
dorminat of forset vegation
time
time of the soil formation process , with older horizons are older