Lecture 22a: Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy | Skin Conditions 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Examples of skin conditions

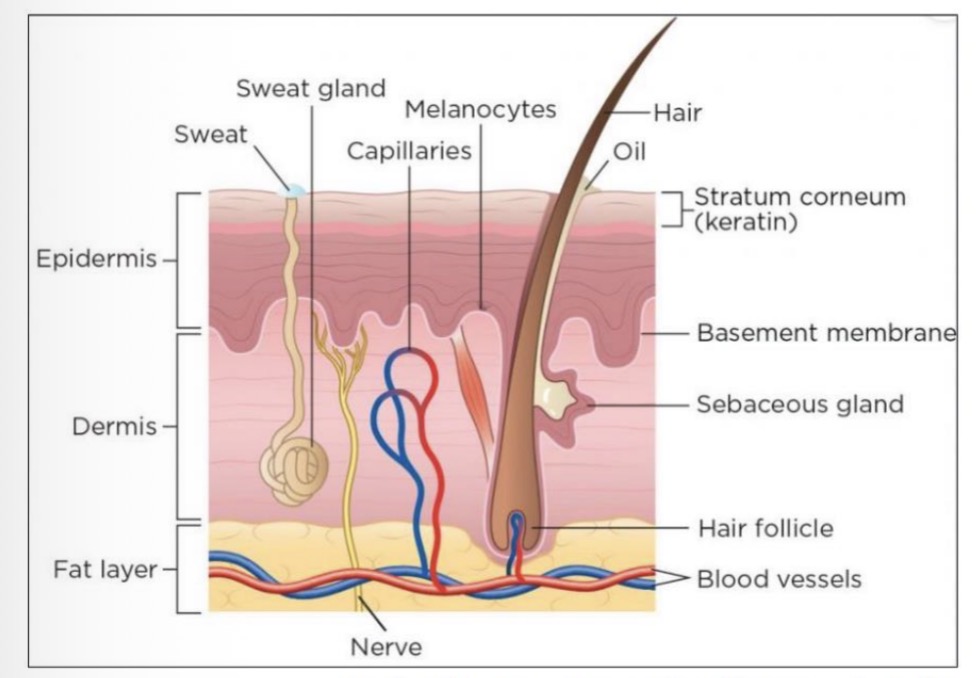
Skin structure
Dermatology
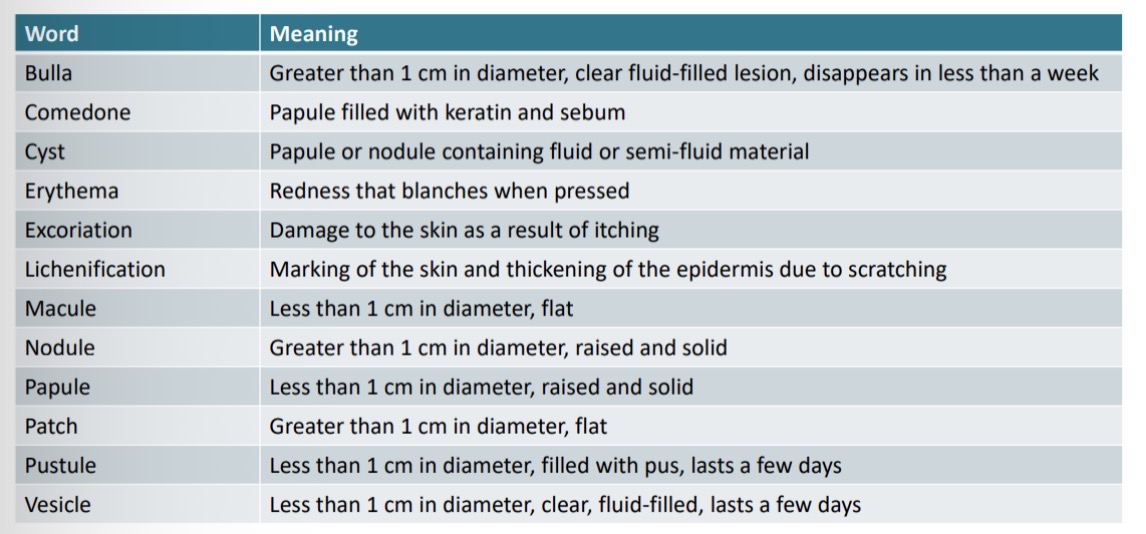
Lesion: single area of abnormal skin
Rash: lesions that are widespread
Dermatosis: disease of the skin
Terminology
Skin conditions
Age
Affected area
Distribution of rash
Appearance
Duration of symptoms
Occupation/contact
Associated symptoms
Medical conditions - asthma, hay fever
Treatment tried
Meningitis and Septicaemia
Meningitis - inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord
Septicaemia - blood poisoning
Bacterial, viral, fungal
Rare but life-threatening illnesses, can lead to sepsis
Can affect all ages, more common in babies and children
Symptoms rapidly worsen, can kill in hours
Rash - may develop at later stage, sign of very severe illness, risk factor for fatal outcome
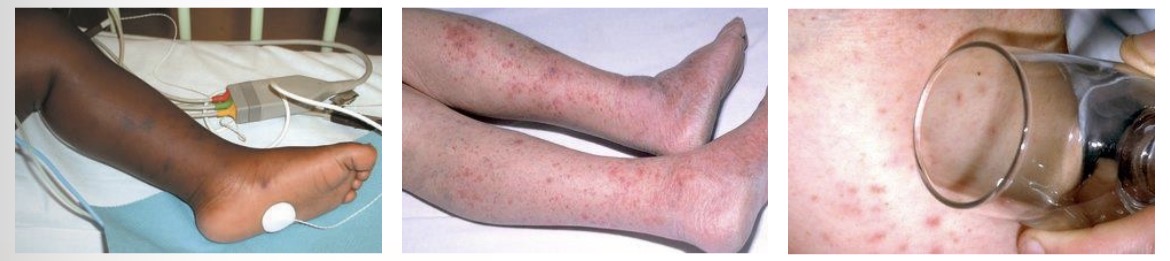
Meningitis and Septicaemia Rash
Starts as small red pinpricks, spreads quickly to become red or purple blotches anywhere on the body
Non-blanching rash - doesn’t fade or lose colour if pressed with the side of a clear drinking glass firmly against the rash
Darker skin - check paler areas of the body
Balancing rash can develop into a non-blanching rash as illness progresses
Medical emergency - call 999 immediately
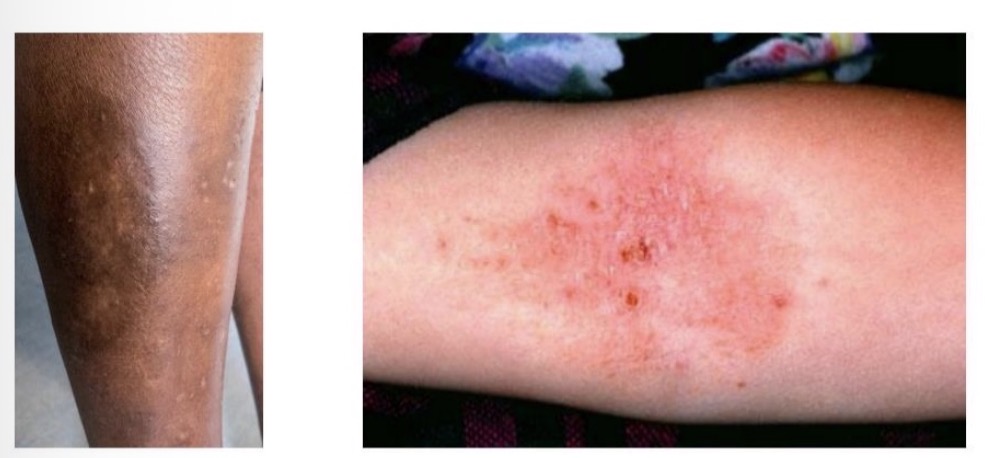
Eczema
Eczema and dermatitis (interchangeable)
Most common - atopic eczema, contact dermatitis
External - irritants/allergens, Internal - genetic cause
Emotional or environmental factors can trigger flare up
Lipid layer that covers skin becomes thin causing water loss
Long term relapsing condition, in children improves with time
Symptoms - redness, dry itchy skin, localised to flexures of limbs, usually symmetrical, scratch marks, damage, thickening
Treatments can control but no cure
Management of eczema
Emollients/moisturisers - first line, moisturisers, smooth hydrate and protect skin barrier
Provide an occlusive layer which reduces water loss
Applied regularly at least 4 times a day, in a downward motion following direction of hair growth, stroke on liberally
Use soap substitutes, bath additives are ineffective
Available as creams, ointments, lotions, gels, sprays, bath oils/additives - ointments most effective
Safety: risk of slipping, paraffin based products are a fire hazard
MHRA alert - aqueous cream causes burning, stinging, itching, detrimental effect on skin barrier
Management of eczema
Topical steroids - reduce inflammation
Choice - severity of eczema/ flare up, patients age, affected area
Apply 20 to 30 mins before emollients
Available as creams, lotions, ointments, gels and foams
Stepped up/down according to need
OTC - Hydrocortisone 1% cream, 10 years and over, not licensed for use on the face, eumovate 0.05% cream, 12 years and over
Atropy and thing of skin after prolonged use
Topical Corticosteriod’s
Finger Tip Units (FTU)
1 FTU - hands, elbows or knees
1.5 FTU - feet including soles
2 FTU - face & neck
4 FTU - hand and arm
8 FTU - one leg & foot, or chest & back
Management of eczema
Itching:
Bandaging - paste bandages, cotton gloves
Antihistamines - chlorophenamine, non sedating usually ineffective
Homeopathy, herbalism, acupuncture - limited evidence
Self-care - avoid scratching, avoid triggers, keep cool, avoid synthetic fibres, avoid detergents e.g. bubble bath
Refer
Bacterial infection - weeping, pus, warm to touch
Eczema herpeticum - rare but life threatening, affects children, rapidly worsens, painful eczema with clustered vesicles, fever, distress
Systemically unwell - fever, generally unwell
Acne
Chronic inflammatory condition
Common in teenagers, onset at puberty, hormonal changes
Lasts few months to several years
Affects mainly face, back and chest
Increased keratin and sebum causes blockages of hair follicle, causes comedowns, papules, pustules
Complications: scarring, hyperpigmentation, depression anxiety
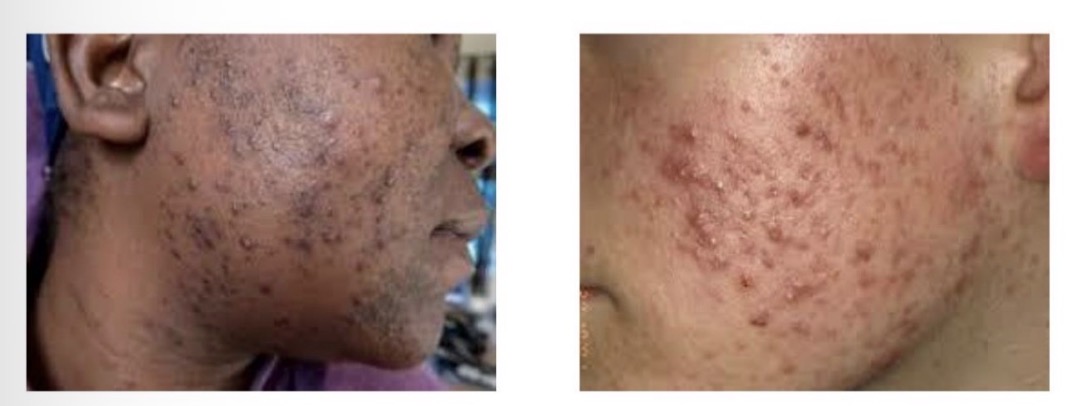
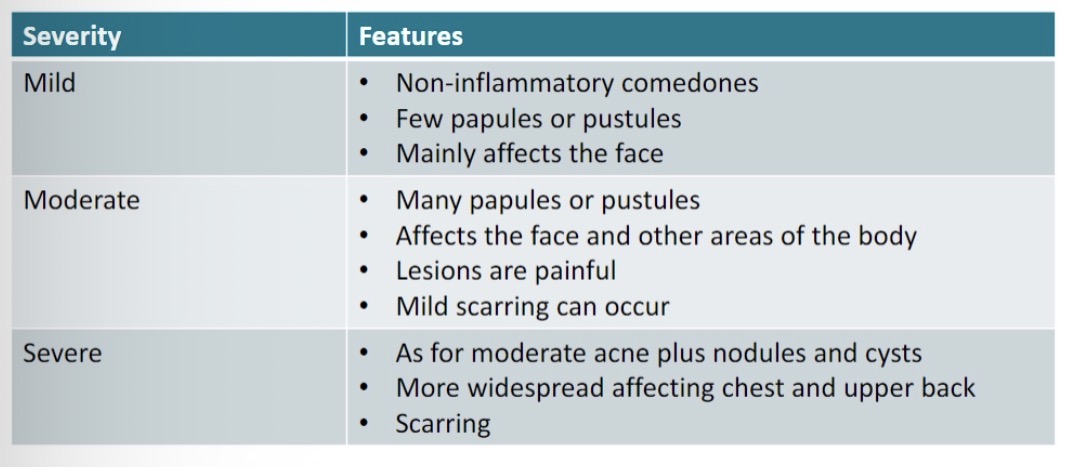
Severity of acne
Management of acne
Mild acne - Treat OTC, may take at leats 8 weeks to work as prevent new lesions forming, OTC treatments likely to irritate skin initially, stinging, redness, skin peeling, will settle with time, start on worst strength, use on alternate days or once daily if occurs
Benzoyl Peroxide (P) - most effective, first line, anti-inflammatory with antibacterial properties, reduces comedowns, available as creams, gel formulation, 2.5%, 5% or 10% strength , apply 1-2 times a day, preferable after washing with soap and water, may bleach fabrics and hair, can make skin sensitive to sun
Nicotinamide (GSL) - anti-inflammatory, reduces swelling, redness, tenderness, available as 4% gel, apply twice daily
Moderate to severe acne - refer to GP
Management of acne
Self-care:
Avoid over cleaning of skin, avoid exfoliants
Avoid oil-based products - skincare, makeup, sunscreens
Remove makeup at the end of the day
Avoid picking.scratching lesions - likely to scar
Use non alkaline cleansing product twice daily
Refer
Moderate or severe acne
Psychological distress
OTC treatments likely ineffective
Acne with scarring
Pigmentary changes
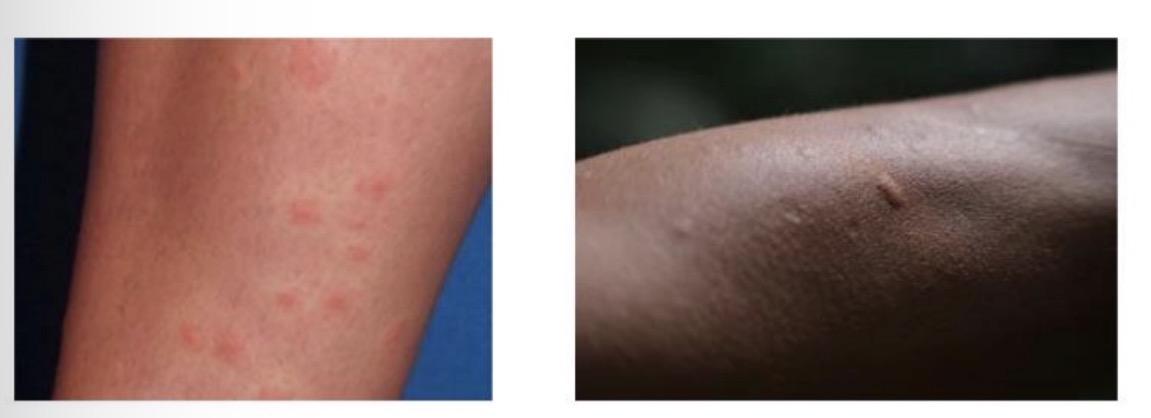
Insect bites and stings
Rapid onset, inflammatory reaction - erythema, tenderness, swelling, itchy papules
Can cause allergic reaction or become infected
Allergic reaction occurs within 24 hours, infection usually develops after 24-48 hours: pus, warm to touch, fever
Complications: urticaria, anaphylaxis, malaria
Tend to overtreat
Management of insect bites & stings
Usually non serious, resolves in few hours or days
Remove stinger, wash area with soap and water
Antihistamines oral, sedating e.g. Chlorophenamine (Piriton) (P), non sedating e.g. Loratadine (P) or topical e.g. Mepyramine (Anthisan) (P)
Steroid cream e.g. Hydrocortisone. 1% cream (P)
Analgesics - paracetamol or ibuprofen
Ice wrapped in a cloth or wet cloth applied for 20 mins
Self-care - avoid scratching to prevent infection
Refer
Anaphylaxis, life threatening allergic reaction - call 999
Systemically unwell
Human or animal bite
Severe pain from wound
Signs of Lyme disease - bullseye rash
Insect bites or stings that occured while travelling abroad
Significant fluid, pus at site of insect bite or sting
Pharmacy First Service
Advanced service in community pharmacy
Urgent medicines supply, minor illness, management of 7 common conditions
Infected insect bites - adults and children 1 year and over
Signs of infection, can supply POM medicines: flucloxacillin, clarithromycin (penicillin allergy) or erythromycin (pregnant)
Warts and Verrucae
Small skin coloured excess growths of akin cause by human papilloma virus (HPV), stimulates basal cell division
Common in children, teenagers
Warts can appear anywhere on the skin, usually hands and feet
Verruca is a wart on the sole of the foot, underlying black dots
Transmitted by skin to skin contact, contact with contaminated surfaces
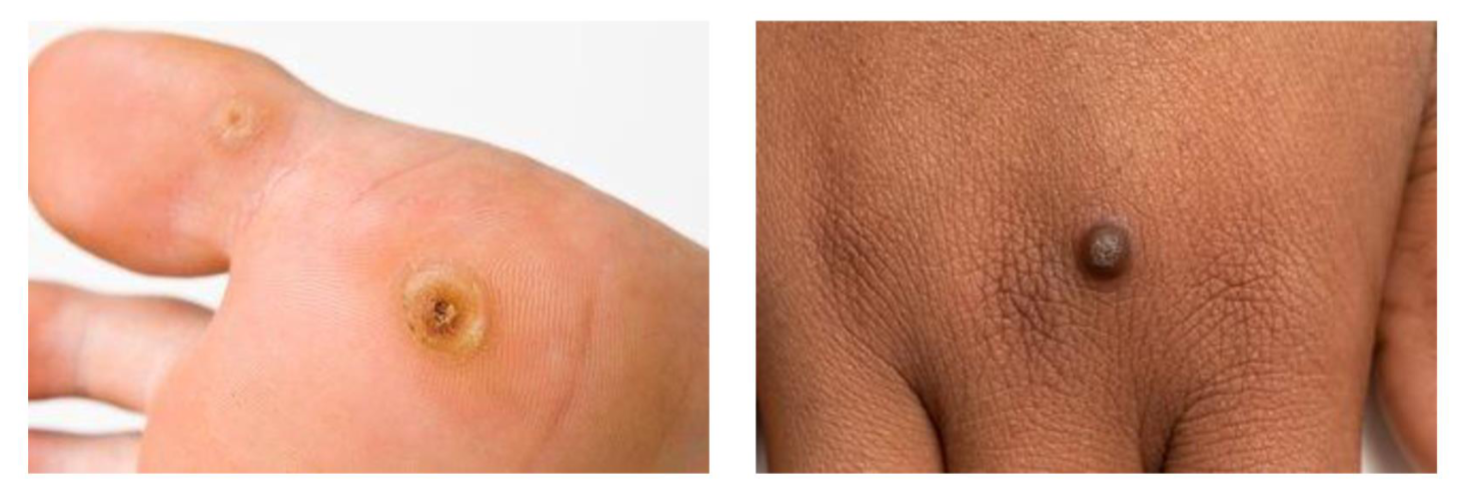
Management of warts & verrucae
Reassurance - clear spontaneously within a few months, can take years
Topical salicylic acid +/- lactic acid, break down keratin in skin e.g. Bazuka 12% pr 26% gel (P), Salatac 12%/4% gel (P), soak the skin, abrade with emery board, protect surrounding skin with vaseline, apply to wart/ verruca daily, can take 12 weeks for full effect
Cryotherapy - extreme cold to freeze abnormal skin
Self-care - avoid picking, scratching of wart, waterproof plasters when swimming
Refer
Facial warts
Anogenital warts
Diabetic patients
Elderly patients
Immunocomprimised patients
Warts that bleed, itch, grow, change colour
Large or painful verrucae