Year 10 Biology & Chemistry
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
A molecule that is the blueprint of all living things.
Instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
Structure of DNA
2 backbones forming a double helix.
‘Rungs’ made up of bases: Adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
DNA Molecule Structure
A DNA nucleotide (monomer) has 3 parts:
A phosphate group
A deoxyribose sugar
A nitrogenous base (one of A, T, C or G)
DNA Base Pairing
Base pairs are complementary.
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) join together: A–T
Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) join together: G–C
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
Can act as a messenger (mRNA).
mRNA is an RNA copy of our DNA, and is used to send information on protein making from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
Bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
A pair with U instead of T.
DNA and RNA Differences
DNA | RNA |
Double Stranded | Single stranded |
Deoxyribose sugar | Ribose sugar |
A,T,C,G Bases | A,U,C,G Bases |
Longer | Shorter |
Chromosomes
Histone proteins organize DNA by wrapping it around themselves into chromosomes.
Chromosomes carry DNA in units called genes..
Humans have 46 (23 homologous pairs).
Chromosomes are inherited in pairs, one from each parent.
22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (XX in females, XY in males).
Genes
The genome is an organism's complete set of genes.
Sections of DNA molecules that carry instructions for building specific proteins.
Can be inherited, passing down traits.
The order of nucleotide bases within a gene (genetic code), dictates the protein it will produce, and the trait it influences.
The Genetic Coding Process
DNA gets copied onto messenger RNA.
mRNA travels out of the nucleus to the ribosomes.
Bases on the DNA and mRNA are read in triplets.
Each triplet/codon codes for a different amino acid.
Amino acids join to form long chains that make proteins.
DNA Replication
Occurs so there is enough DNA for cell division. Ensures that each new cell gets a copy of the genome.
Semi-conservative, with each strand of the double helix serving as a template for a new complementary strand.
The hydrogen bonds DNA double helix unwinds, and each strand acts as a template for the synthesis of a complementary strand.
Complementary base pairs are added to each template strand during replication.
Replication results in two identical DNA double helices, each with one old and one new strand.
Mitosis
Division of somatic (not sex) cells; autosomes.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase: PMAT
Interphase
Cells spend most of their life in this stage.
DNA replicates, so each daughter cell has the same amount of DNA as the parent cell.
Prophase
Chromatids condense into chromosomes and the nucleus starts to break down.
Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell, and spindles form from microtubules.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell.
Centromeres are attached to a spindle fiber.
Anaphase
Chromosomes separate and are pulled away from each other by spindle fibres.
Telophase
Two nuclei form, each with its own set of identical DNA, within two new daughter cells (cytokinesis).
Chromosomes decondense, and chromatids unwind.
Meiosis
Produces sex cells, through fertilisation of gametes.
Two cycles of cell division (meiosis I and II), resulting in four daughter cells.
Passes on genetic information from parents to children during sexual reproduction.
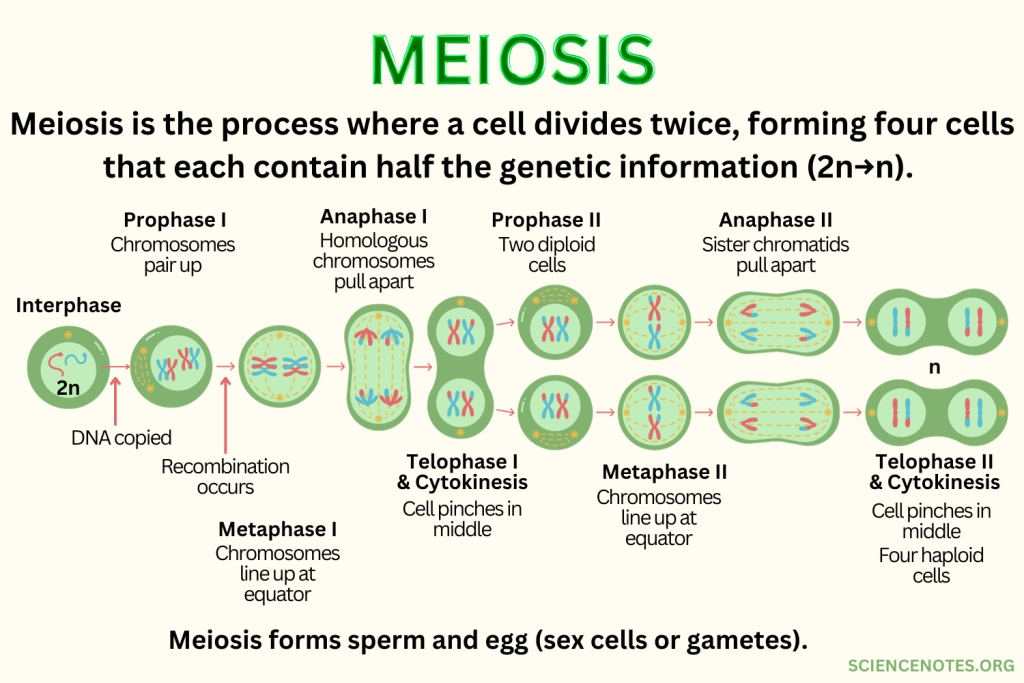
Meiosis Extended
Meiosis produces haploid cells (23 individual) to form gametes for sexual reproduction, ensuring correct chromosome numbers in offspring. Chromosomes are halved from diploid (46) to haploid (23).
Genetic variation arises from independent assortment and crossing over (genetic exchange between homologous chromosomes).
Nondisjunction is where chromosomes fail to separate properly leading to an abnormal number of chromosomes. It can lead to trisomies like Down syndrome, affecting genetic health.
Mitosis and Meiosis Differences
Mitosis | Meiosis |
Genetically identical | Genetically diverse |
Diploid (23 pairs, 46 individual) | Haploid (23 individual) |
Growth and Repair | Sexual Reproduction |
Longer | Shorter |
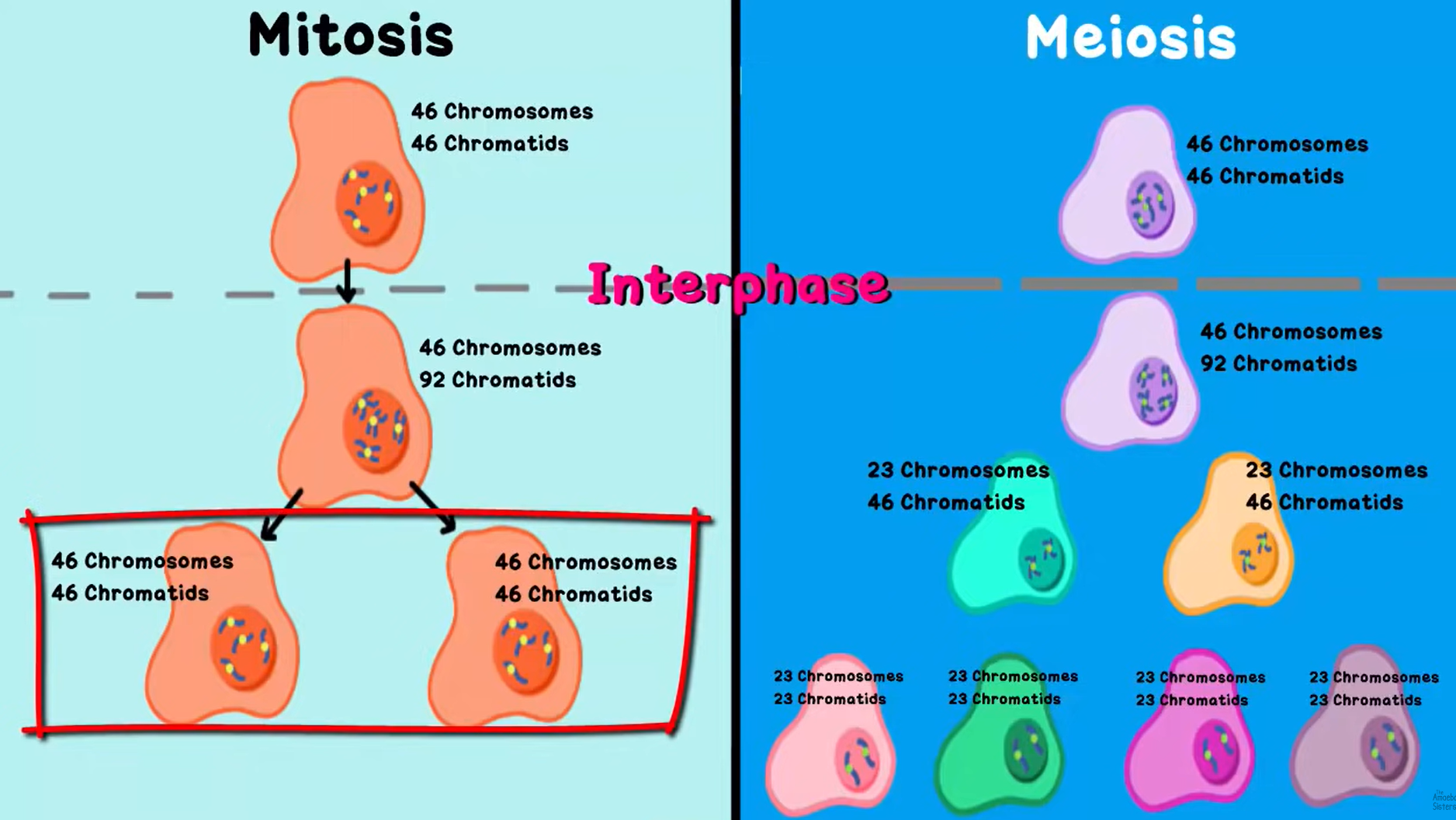
Number of Chromosomes
Number of chromosomes | Single-stranded or double-stranded | |
Before interphase | 46 | Single stranded (46 chromatids) |
After DNA is copied during interphase | 46 | Double-stranded (92 chromatids) |
After meiosis I | 23 | Double-stranded (46 chromatids) |
After meiosis II | 23 | single-stranded |
Mendelian Inheritance (Gregor Mendal)
The transmission of genetic traits from parents to offspring through the passing of genes. Genes are the unit of inheritance that allows living things to pass on traits to their offspring.
Alleles
Different versions of a gene. Eg. green and yellow seeds.
Dominant Traits
Always expressed when individual has one dominant allele.
Recessive Traits
Only show if there are no dominant alleles present. If there is a dominant allele present, the trait is hidden.
Phenotype
Observable traits in an organism.
Genotype
A pair of alleles that influence the appearance of a trait. Eg. Ff
Homozygous
A genotype where the alleles are the same.
Heterozygous
A genotype where the alleles are the different.
Pedigrees
A pedigree is a “family tree” that we use to track traits throughout generations.
Pedigree Symbols
Atoms
The smallest particle of an element.
Composed of a nucleus with protons, neutrons and electrons, and outer shells containing electrons.
Subatomic Particles
Protons (+) Neutrons, Electrons (-)
Subatomic Particle Masses
Electrons are 1/840 of a proton. Neutrons and protons are heavier with a similar mass.
Mass Number
The weight of neutrons and protons.
Atomic Number
Number of protons (identifies the element).
Electrons are the same number of protons (usually)
Elements
Substances made from the same kind of atom
Molecules
Substances that are chemically bonded to the same kind of atom.
Compounds
Substances that are chemically bonded to different kinds of atoms.
Groups
↓Number of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell).
Tells the reactivity of an element.
Periods
→Number of shells
Periodic Table Trends
Electronic Configuration
Shell | Maximum number of electrons |
1st | 2 |
2nd | 8 |
3rd | 8 (18 rarely) |
4th | 32 |
Ions
Charged particles, so they are gaining/losing electrons
Anion
If an atom gains an electron, the overall charge is negative, making it becomes an ANION
Cation
If an atom loses an electron, the overall charge is positive, making it a CATION
Isotopes
An element that has the same atomic number but a different number of neutrons, therefore, the mass number is different. (Number of neutrons= Mass number- atomic number)
The more neutrons, the more unstable the isotope becomes
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonds form between a metal and a non-metal when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
The transfer of electrons from one atom to another results in two ions with opposite charges.
The attraction between these opposite charges is what makes an ionic bond.
What happens to metal and non-metal atoms when bonding?
A metal loses electrons to form a cation, with a positive charge. A non-metal atom gains electrons to form an anion with a negative charge.
Chemical Bonding
Atoms are joined together by attractive forces called chemical bonds to form larger structures: molecules or lattices. Molecules are fairly small groups of bonded atoms such as oxygen (O2) or water (H2O). Lattices are continuous arrangements of bonded atoms in regular patterns, found in metals like iron (Fe) and crystals like quartz (SiO2).
Why do atoms form chemical bonds?
Atoms form chemical bonds to obtain full valence shells. By bonding together in chemical reactions, atoms can reach a more stable state.
Solute
The substance that dissolves in a solvent to produce a homogeneous mixture.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving into one or more other substances.
Solubility
The ability of solute to dissolve in solvent and form a solution.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction mass is neither created nor destroyed.
Independent Variable
The factor that is changed.
Dependent Variable
The factor that is measured.
Controlled Variable
The factors that are the same.