Chapter 3 - Cell Division & Chromosome Heredity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Last updated 7:47 PM on 12/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Diploid/2N
Two copies of genetic material, two homologous chromosomes, same genes in same order
2
New cards
Haploid/N
One copy of genetic material, nonhomologous
E.g. human gametes
E.g. human gametes
3
New cards
Diploid dominant life cycle
Humans - diploid phase is long
4
New cards
Haploid dominant life cycle
Most fungi - haploid phase is the mature form
5
New cards
Blend of diploid/haploid dominant life cycles
Some algae - sporophyte (2N) and gametophyte (N) stages
6
New cards
Mitosis is how ________ cells replicate
somatic
7
New cards
Meiosis produces ___________ cells
haploid gametic
8
New cards
M phase
Cell division occurs
9
New cards
Interphase
Period between cell divisions
10
New cards
G0 phase
Cell division stops, cell is specialized but no longer divides & eventually dies
11
New cards
S phase of interphase
Chromosome duplication & synthesis of DNA
12
New cards
Prophase
Mitotic spindle begins to form
Asters extend microtubules
Chromosomes are joined by a centromere
Asters extend microtubules
Chromosomes are joined by a centromere
13
New cards
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope disappears
Non-kinetochore microtubules begin to line up chromosomes along center of the cell
Non-kinetochore microtubules begin to line up chromosomes along center of the cell
14
New cards
Metaphase
Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate
Spindles reach from centriole to chromosomes
Spindles reach from centriole to chromosomes
15
New cards
Anaphase
Chromosomes are pulled in opposite directions
16
New cards
Telophase
Nuclear envelopes reform
Cleavage furrow appears
Cleavage furrow appears
17
New cards
Cytokinesis
Splitting of cells
18
New cards
DNA content
G1 and mitosis phases are roughly equal in
19
New cards
S phase has double the...
chromatids
20
New cards
G1 check point
Adequate cell size, nutrient availability is sufficient, growth factors are present
21
New cards
S phase check point
DNA replication is complete, screened to remove base pair mismatch/error
22
New cards
G2 check point
Cell size is adequate and chromosome replication is successfully complete
23
New cards
Metaphase check point
All chromosomes are attached to mitotic spindle
24
New cards
Meiotic cell division begins with a...
diploid cell after chromosome duplication
25
New cards
Meiosis I results in...
two cells each with one isolated homologous chromosome
26
New cards
Meiosis II results in
four haploid gametes
27
New cards
Recombination
More common at the ends of chromosomes
28
New cards
Mutation
More common in males
29
New cards
Lowest allelic diversity
After meiosis II in the four haploid daughter cells
30
New cards
Oogenesis
Formation of egg cells
31
New cards
7 million
Number of primary oocytes in female fetuses
32
New cards
Prophase I
Primary oocytes stay in this stage until puberty
33
New cards
Metaphase II
During ovulation oocytes move to this stage
34
New cards
Meiosis II in oocytes
Only completed if fertilization occurs
35
New cards
Law of Independent Assortment & Meiosis
After many rounds of meiosis, there are ~equal proportion of each pair of alleles (GR, Gr, gR, gr)
36
New cards
500
Number of mature oocytes produced over lifespan
37
New cards
60-80k
Number of oocytes per ovary at the beginning of puberty
38
New cards
1-2 million
Number of primary oocytes at birth
39
New cards
Atresia
Form of apoptosis causing number of oocytes to decrease during fetal maturation
40
New cards
1 gamete & 2-3 polar bodies
Oogenesis results in
41
New cards
4 gametes
Spermatogenesis
42
New cards
Sperm
Motile gamete
43
New cards
Egg
Non-motile gamete
44
New cards
Oogenesis cell division is...
Unequal
45
New cards
Spermatogenesis cell division is...
equal
46
New cards
~70 days
Growth phase for spermatogenesis
47
New cards
Years-decades
Growth phase for oogenesis
48
New cards
Millions
Number of sperm produced each day
49
New cards
One
Number of eggs produced during each menstrual cycle
50
New cards
Homozygous
Alleles are the same
51
New cards
Heterozygous
Alleles are different
52
New cards
Hemizygous
Only one allele
53
New cards
Reciprocal cross
Allows one to examine effects of sex on phenotype, same cross with different sexes
54
New cards
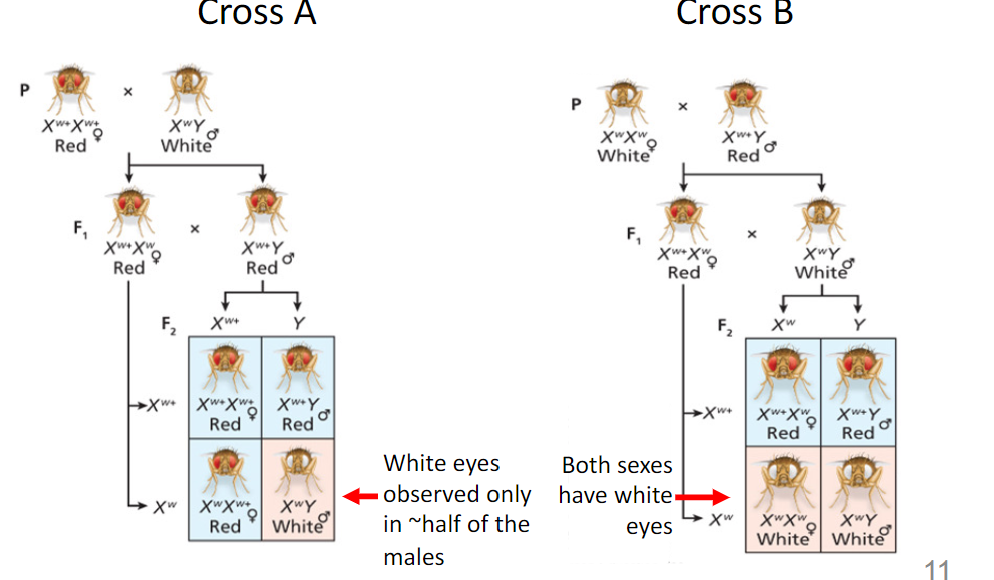
Males express recessive phenotype because they have one X chromosome
55
New cards
X linked disorders in humans
Colour blindness, hemophilia A, Duchenne muscular dystrophy
56
New cards
Non-disjunction
Failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis, can happen at meiosis I, II, or both
57
New cards
Kleinfelter syndrome (XXY)
Male phenotype, tall stature, delayed or absent puberty, low muscle tone, small penis & testes
Could be caused by XX egg or XY sperm
Could be caused by XX egg or XY sperm
58
New cards
Turner syndrome (XO)
Female phenotype, short stature, webbed neck, delayed or absent puberty, infertility
Could be caused by egg without X or sperm without X
Could be caused by egg without X or sperm without X
59
New cards
Jacobs syndrome (XYY)
Male phenotype, variable symptoms, tall stature, curved pinky finger, widely spaced eyes, behavioral disorders, delayed development of social language & learning, large head, large testes, large feet, most are fertile
60
New cards
Trisomy X (XXX)
Variable symptoms, some developmental delays, taller than average, some kidney problems
61
New cards
XYYY syndrome
Very rare, similar symptoms to XYY
62
New cards
X tetrasomy (XXXX)
Tall stature & mild intellectual disability
63
New cards
YO syndrome
Not viable
64
New cards
Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
~0.3% of newborns & ~25% of spontaneous abortions
Most common mental disability
Least severe autosomal trisomy
Most common mental disability
Least severe autosomal trisomy
65
New cards
Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
Severe intellectual disability, decreased muscle tone, low-set ears, internal organ defects
66
New cards
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
Severe intellectual disability & other problems
~90% die within first year of life
~90% die within first year of life
67
New cards
Autosomal trisomies other than 21, 18, & 13
Occur but are not viable
68
New cards
Crossing over
More frequent in males
69
New cards
Non-disjunction is sometimes associated with...
Chromosomes that did not recombine resulting in improper chromosomal segregation
70
New cards
Other mechanisms of non-disjunction
Checkpoint failure, age related degradation of cohesion complex
71
New cards
Chance of trisomy
Positively correlated with older mothers
72
New cards
Y linked inheritance
Male-male transmission, every son will have the gene/trait
73
New cards
~800
Number of genes on human X chromosome
74
New cards
~80
Number of genes on human Y chromosome
75
New cards
X inactivation
One X chromosome is randomly inactivated & varies throughout the cells of a multicellular organism
E.g. Calico cats, orange & brown express on different areas of female cat (or XXY male cat)
E.g. Calico cats, orange & brown express on different areas of female cat (or XXY male cat)
76
New cards
XIST
X linked gene required for X inactivation
Encodes long RNA molecule that covers chromosome to be inactivated
Encodes long RNA molecule that covers chromosome to be inactivated
77
New cards
XIST transcript
acts in cis - only affects the chromosome from which it is transcribed
78
New cards
X upregulation
Males produce twice the X coded proteins in order to cause X dosage to be equal in males and females
79
New cards
Dosage of X does NOT have to be the same as...
autosomes