Cow Eye Dissection
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:20 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
Aqueous humor
A clear fluid that helps the cornea keep its rounded shape
2
New cards
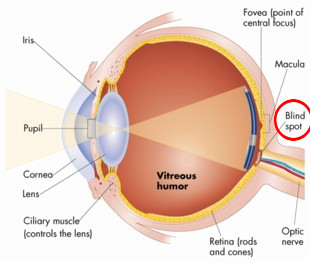
Blind spot
The place where all nerves from the retina join to form the optic nerve. Each eye has one of these where there are no light sensitive cells
3
New cards
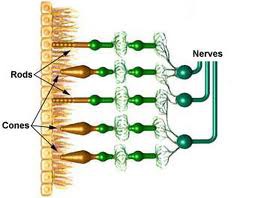
Cones
One kind of light sensitive cell in the retina. These give you color vision in bright light.
4
New cards
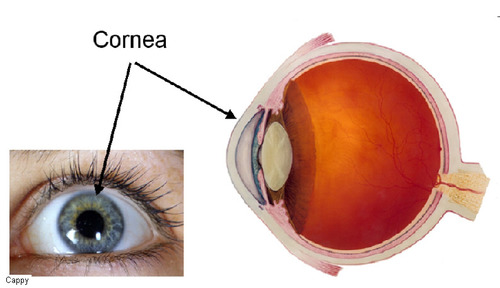
Cornea
A tough clear covering over the iris and the pupil that helps us protect the eye. Light bends as it passes through here. This begins bending light to make an image; the lens finishes the job
5
New cards
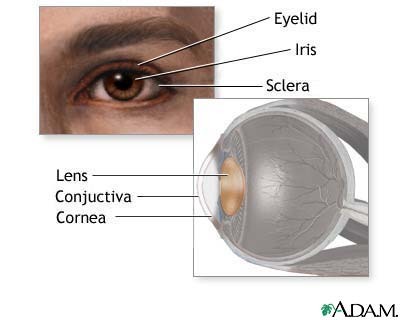
Iris
A muscle that controls how much light enters the eye. It is suspended between the cornea and the lens. A cow's is brown. Human have these that come in many colors, including brown, blue, green, and gray.
6
New cards
Lens
A clear, flexible structure that makes an image on the eye's retina. This is flexible so that it can change shape, focusing on objects far away and close up.
7
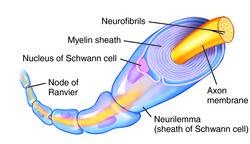
New cards
Myelin
The fatty layer that surrounds each nerve fiber.
8
New cards
Optic nerve
The bundle of nerve fibers that carry information from the retina to the brain.
9
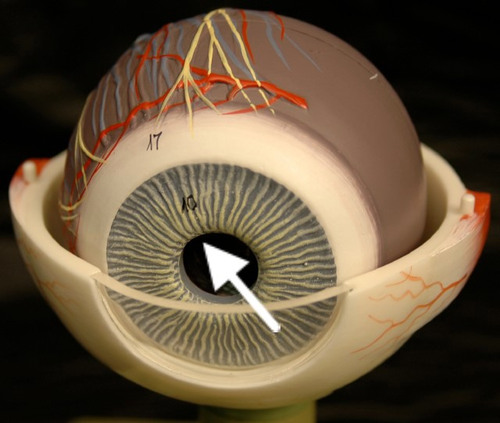
New cards
Pupil
This is the dark circle in the center of your iris. It's a hole that lets light into the inner eye. Your's is round. A cow's is oval.
10
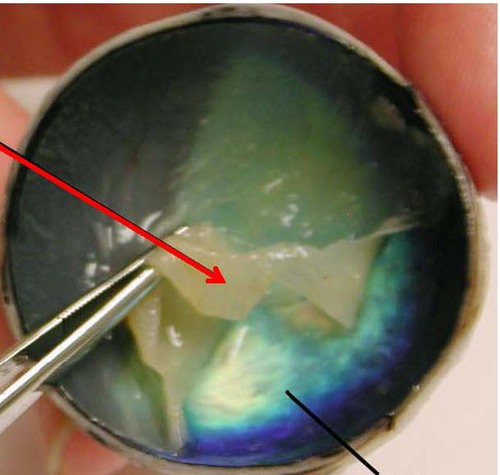
New cards
Retina
The layer of light sensitive cells at the back of the eye. This detects images focused by the cornea and the lens. This is connected to the brain by the optic nerve
11
New cards
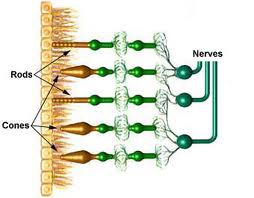
Rods
One kind of light sensitive cell in the retina; respond to dim light.
12
New cards
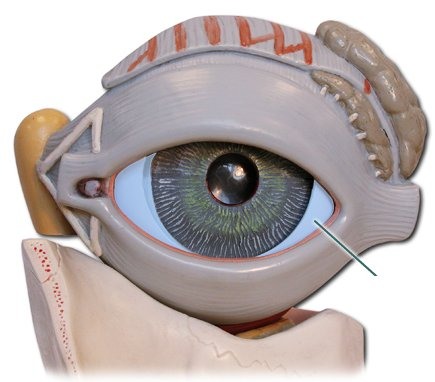
Sclera
The thick, tough, white outer covering of the eyeball.
13
New cards
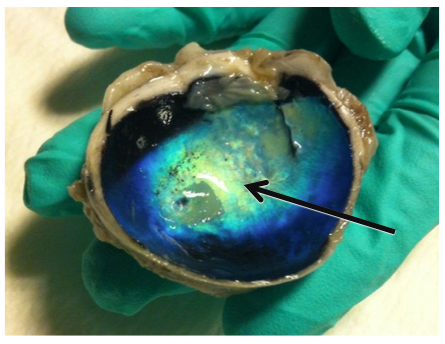
Tapetum
The colorful, shiny material located behind the retina. Found in animals with good night vision; reflects light back through the retina.
14
New cards
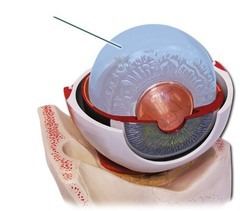
Vitreous humor
The thick, clear jelly that helps give the eyeball its shape.
15
New cards
scalpel
Surgical knife
16
New cards
Formalin
a colorless solution of formaldehyde in water, used chiefly as a preservative for biological specimens