Inflammatory Conditions
Characteristics:
General history for uveitis: ROS, fever, chills, fatigue, malaise, cough, shortness of breath, joint problems, diarrhea, rash, oral or genital ulcers
TReatment:
: Cyclo 1% TID or atropine 1% bid
Pred forte Q1-6H. Consider loading dose of 1 drop per minute, 5 minutes before bed and upon wakening.
Workup: IOP, gonio, dilation, check vit for cells
RTC: 1-7 days then 1-3 months when stable
Check ant chamber and IOP. Dilation Q3months or sooner if flare up. Taper steroid
Anterior Uveitis: Greater cells in the ant chamber than post chamber. Must do DFE to look for post uveitis
Acute: Pain, red, photophobia and consensual photophobia, tearing, dec vision
Chronic: Dec vision from cataract, vit debris, CME, ERM, floaters. Can wax and wane like JIA
BAB breakdown -> cataracts, less melanin on iris, CME (inflammatory deposit travel to macula), trabeculitis (if chronic the Fuchs, if acute the glaucomatocyclitic), iris swells -> PS and PAS, IOP decrease at first bc CB active secretion inflamed + prostaglandin release, fine keratic precipitates on endo.
Grading:
Cells: 1: 6-15 cells. 2: 16-25 cells. 3. 25-50 cells. 4. >50 cells.
Flare: 1. Faint. Moderate - iris clear. Marked - iris hazy. Intense - fibrin aqueous
Intermediate uveitis: More cells in the vitreous than the AC but no chorioretinal involvement
Posterior Uveitis: Chorioretinal, post vit cells, disc edema and hyperemia, neuroretinitis, vasculitis
Iritis: Cells in AC only.
Iridocyclitis: some cells in anterior vitreous
Hypopyon: accumulation of WBC (pus) in anterior chamber
Conditions that cause this?
Herpes: pinking hypopyon bc some blood in there
Behcet: hypopyon that changes with head positions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Characteristics:
General history for uveitis: ROS, fever, chills, fatigue, malaise, cough, shortness of breath, joint problems, diarrhea, rash, oral or genital ulcers
TReatment:
: Cyclo 1% TID or atropine 1% bid
Pred forte Q1-6H. Consider loading dose of 1 drop per minute, 5 minutes before bed and upon wakening.
Workup: IOP, gonio, dilation, check vit for cells
RTC: 1-7 days then 1-3 months when stable
Check ant chamber and IOP. Dilation Q3months or sooner if flare up. Taper steroid
Anterior Uveitis: Greater cells in the ant chamber than post chamber. Must do DFE to look for post uveitis
Acute: Pain, red, photophobia and consensual photophobia, tearing, dec vision
Chronic: Dec vision from cataract, vit debris, CME, ERM, floaters. Can wax and wane like JIA
BAB breakdown -> cataracts, less melanin on iris, CME (inflammatory deposit travel to macula), trabeculitis (if chronic the Fuchs, if acute the glaucomatocyclitic), iris swells -> PS and PAS, IOP decrease at first bc CB active secretion inflamed + prostaglandin release, fine keratic precipitates on endo.
Grading:
Cells: 1: 6-15 cells. 2: 16-25 cells. 3. 25-50 cells. 4. >50 cells.
Flare: 1. Faint. Moderate - iris clear. Marked - iris hazy. Intense - fibrin aqueous
Intermediate uveitis: More cells in the vitreous than the AC but no chorioretinal involvement
Posterior Uveitis: Chorioretinal, post vit cells, disc edema and hyperemia, neuroretinitis, vasculitis
Iritis: Cells in AC only.
Iridocyclitis: some cells in anterior vitreous
Hypopyon: accumulation of WBC (pus) in anterior chamber
Conditions that cause this?
Herpes: pinking hypopyon bc some blood in there
Behcet: hypopyon that changes with head positions
Keratic precipitates: small, translucent, grayish deposits that are scattered across the corneal endothelium
Seen in Simplex, Zoster, CMV, fuchs, heterochromic iridocyclitis
Types:
Non-Granulomatous KP: UCRAP + trauma + Posner Schlossman + Drugs
Granulomatous KP (larger): Sarcoid, syphilis, TB, JIA, sympathetic ophthalmia, lens induced, VKH
Arlt triangle: Granulomatous KPs at base of cornea but are non specific
Mutton fat KP - granulomatous
Side note: coin based KPs below occur in CMV.
Iris nodule: yellow-white inflammatory nodules
Koeppes seen near pupil, smaller
Bussacca seen near border, larger and more transparent
indicative of granulomatous uveitis
Seen in Sarcoid, syphilis, TB
Posterior inflammatory/uveitis signs
Symptoms: Blur, floaters, scotoma, metamorphopsia, photopsia.
Vasculitis - Retinal sheathing (active) → sclerosed/ghosting vessels (old)
white, cuff-like appearance around the blood vessels, caused by a collection of inflammatory cells and exudates
Associated with inflammatory conditions + BRVO and CRVO
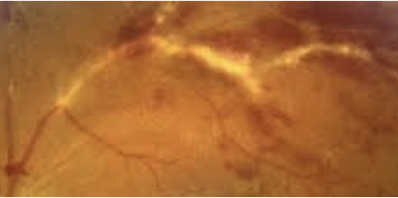
Periphlebitis - candle wax drippings
inflammation of the tissues surrounding a vein (phlebitis)
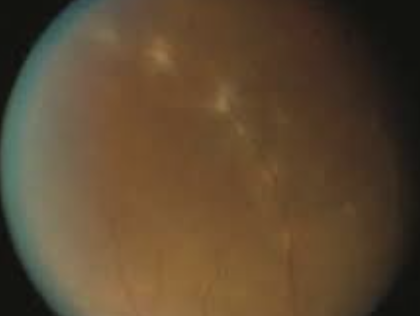
Vitritis: vitreous opacities (string of pearls) or “headlight in the fog” - hazy vitreous, snowbanking/snowballs in vitreous
Retinitis - white patches / ill defined borders + severe overlying vitritis
choroiditis: yellow patches/ regular borders + mild vitritis
Optic Disc Edema/hyperemia
Conditions associated with uveitis/look like uveitis
Band Keratopathy seen in JIA and chronic uveitis.
Calcium deposits in bowmans layer
Poster Schlossman - unilateral, acute infla of TM causing inc IOP, minimal uveitis
Drugs that cause uveitis: Cidofovir, sulfonamide, oral fquin, biologics, chemo drugs
Clare - CL complication due to hypoxia when sleeping in CL. Wake up with red angry inflamed eye + infiltrate
Plan: Tobradex QID 10 days.
Pigment dispersion syndrome: has pigment in AC, differentiate bc smaller than WBC
Lens induced uveitis: lens material escapes capsule leading to uveitis
UGH syndrome: IOL displaced resulting in uveitis/glaucoma/hyphema
Incoming complaints: Blur, floaters. Possible red, photophobia, pain if uveitis
Any flu like symptoms or rash? any history of eating undercooked meat or handling of cat feces? HIV hx? CNS issues?
May have blurred vision, pain from uveitis if active
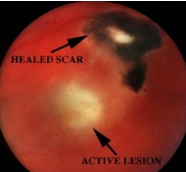
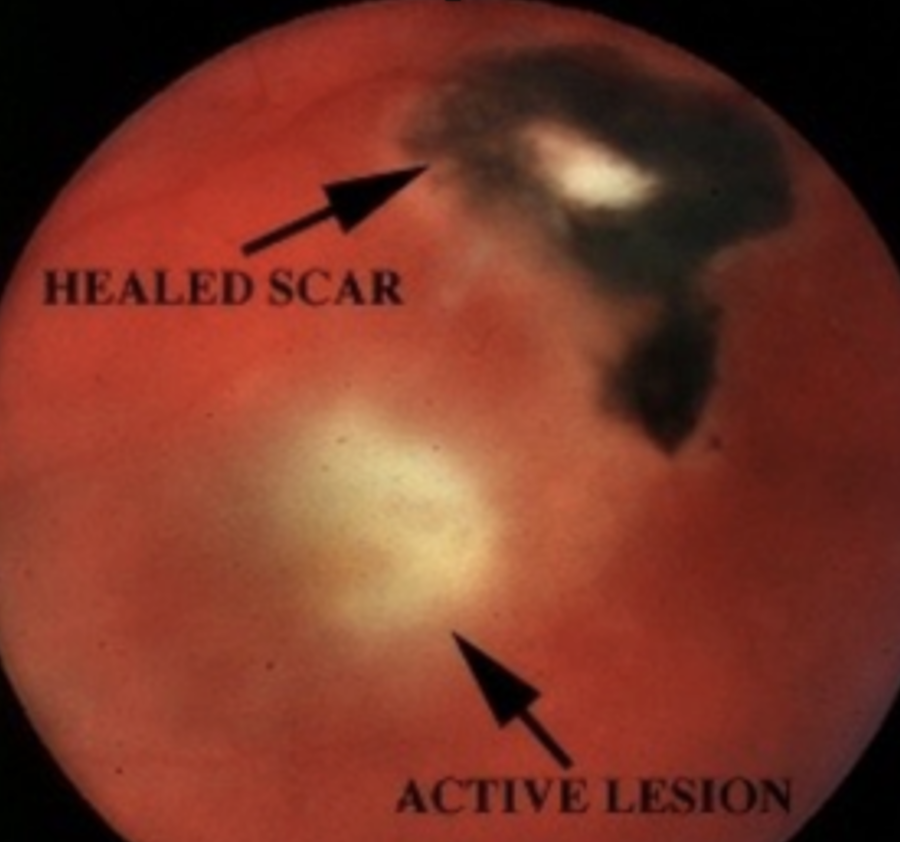
Toxoplasmosis: Infection from parasite transmitted from mom or from undercooked meat or cat feces. most common cause of Posterior uveitis. Causes 90% focal necrotizing retinitis.
Objective: White fluffy lesion with surrounding edema, sign of reactivation -> Chorioretinal scar
Other: Vitritis, uveitis, may have CNVM/RD/mac edema complications
Workup: Order ELISA for toxoplasmosis antibodies and titers. Macula OCT RO edema/CNVM, DFE (may have disc edema).
Serum anti-Toxoplasma antibody IgG or IgM. Optional PCR test of aqueous or vitreous
Plan: treat uveitis/IOP/steroids for toxo - oral prednisone 20mg qd
Pyrimethamine po 200 mg loading dose then 25mg daily + Sulfadiazine 2 g loading dose then 1g qid for 4-6 weeks + Folinic acid 10mg every other day for bone marrow health.
RTC 3-7 days for CBC (to monitor infla reduction) + DFE exam then 1-2 weeks while on meds. Monitor yearly for complications.
Cough, chest pain, intermittent fever, loss of appetite, usually kids
Ocular Signs: poor vision one eye
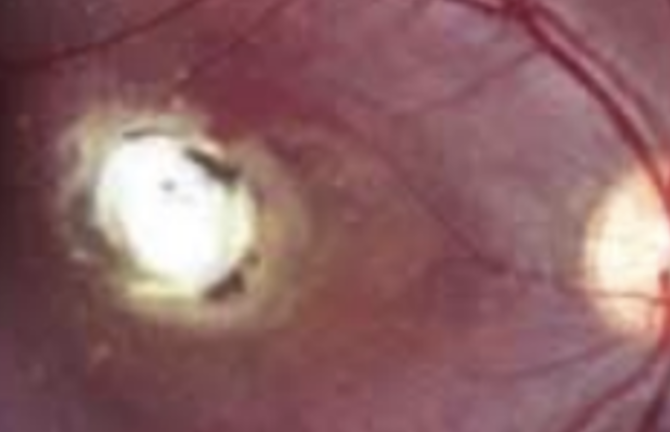
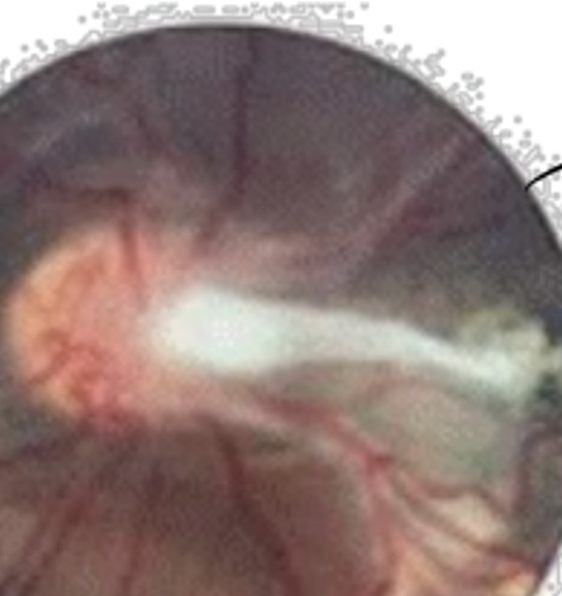
Toxocariasis: Parasite infection from worm transmitted from dog feces or dirt resulting in inflammatory response in the body + eyes.
Objective: Macular granuloma white raised lesion in posterior pole (with RPE hyperplasia). OR unilat intermediate uveitis OR endophalmitis. Traction, macular dragging. Vitritis and ant uveitis. Leucocoria
Workup: Fundus photo, ELISA for toxocara antibody titers and ultrasound of body to see if located anywhere else
Plan: triamcinolone (16 mg for 2 weeks, once a day, and then 8 mg for 1 week, once a day)
Rarely use Albendazole 400 mg po bid for 5 days (kill worm)
RTC if any flare ups or annually. Monitor pt CBC and infla in eye yearly.
If recent, may have flu like symptoms, respiratory issues and CNS issues if severe
Likely no ocular symptoms, my get metamorphopsia or small blind spot/blurred vision
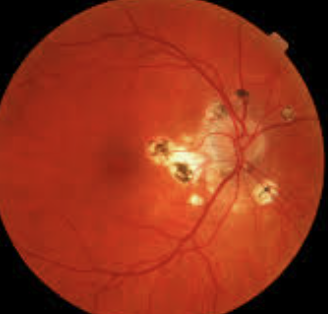
Ocular Histoplasmosis: Inflammation caused by Fungus inhalation from chicken or bat droppings. Prevalent in ohio Mississippi river valley
Objective: Triad: PPA, histo spots (choroidal lesions), CNVM
No anterior uveitis or vitritis
Workup: IVFA to detect CNVM, OCT macula
Plan:
Amphotericin B 3 mg/lg daily for 1-2 weeks if severe
Monitor with Amsler grid and RTC if any vision changes.
RTC yearly for annual exam. q6 months if macula involved.
DDx. Multifocal choroiditis with panuveitis - looks like histo + vitritis. Treat with prednisolone
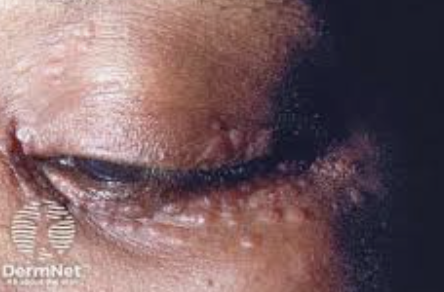
Adult: rash on palms, soles and trunks, sore through →(latent) asymp → CNS/cardio issues
Child: notched teeth, deafness, IK (late signs), Early (bilateral salt and pepper fundus, glaucoma, IK, cataracts
Ocular: Eye pain/redness, blurry vision, photosensitvity, HA, eye discharge, floaters/spot in vision.
Syphilis: sexually transmitted bacterial infection that, if left untreated, can cause serious health problems, including brain damage and heart problems. This can be passed to the fetus when mother is pregnant.
Most syphilis pts won't develop ocular signs. Highest risk for male-male sexual relations
Objective Signs:
Adult: Multiple, non-elevated yellowish grey, ill-defined Chorioretinal lesions -> heals -> Chorioretinal atrophy with hyperpigmentation. Late stage has argyll pupil (light near dissociation), Interstitial keratitis, optic atrophy, Salmon patch: Orange discoloration of the stroma
General: uveitis (uni or bi, post or pan), vasculitis, vitritis, optic neuritis → optic atrophy, retinal necrosis, serous detachment
Child: Salt and pepper fundus, IK, glaucoma
Workup: FTA-ABS (detects If have dx) or MHA-TP (progress checks during treatment), VDRL or RPR, HIV (due to corbidity) VF (constricted)
Plan: penicillin G IV followed by long term treatment of tetracycline 250 mg PO qd.
If uveitis, repeat VDRL at 3, 6, 12 months to ensure nonreactivity.
Treat uveitis if present (topical steroid/cyclo)
RTC daily for uveitis episodes
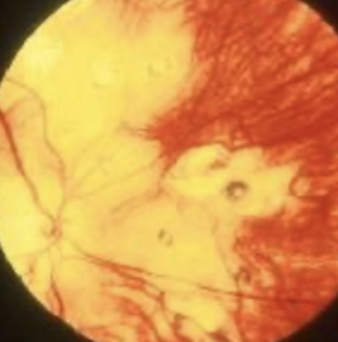
cough, night sweats, recurrent fever, weight loss, pleurisy (inflamed lung lining)
Ocular: Eye pain/redness, blurry vision, photosensitvity, HA, eye discharge, floaters/spot in vision.
Tuberculosis: pulmonary infection that reactivates at any time caused by tuberculosis bacteria.
Workup: PPD, chest X-ray (hilar adenopathy), culture for bacteria, FA, b-scan
Objective: granulomatous uveitis (bi/uni/ant/post), vitritis, periphlebitis, phlyctenule, keratoconjunctivitis, neuroretinits
Plan:
Refer to PCP for management of condition and tested for HIV.
Isoniazid (INH) 300 mg PO qd + NO SYSTEMIC STEROID
Rifampin 600 mg PO qd • Pyrazinamide 25-35 mg/kg PO qd x 2 mos • Ethambutol or streptomycin
RTC q3 months until inflammation resolves?
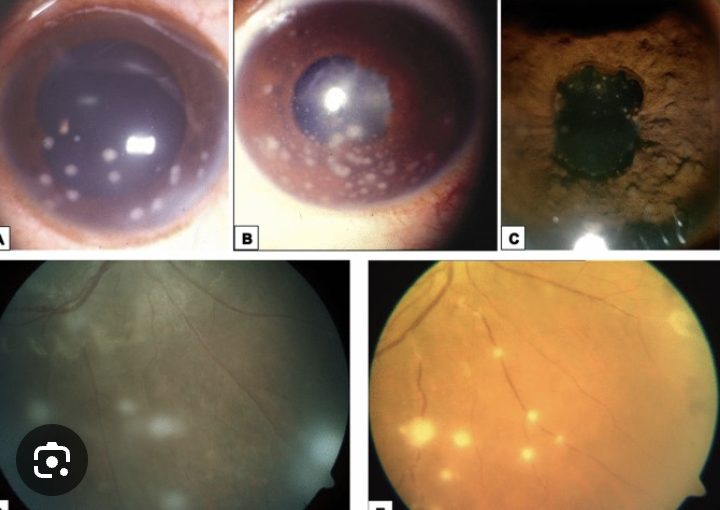
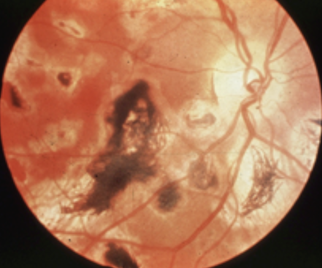
Fatigue, skin granulomas, lymphadenopathy, cardiac issues, arthritis
Ocular: blurred vision, eye pain, red or swollen eyes, light sensitivity, and floaters, as well as dry (lac gland inflamed)
Sarcoid: Idiopathic, causes multisystem granulomatous disorder, common in young black females
Workup: Chest X-Ray to look for hilar adenopathy, Serum ACE (diagnostic), biopsy, PPD, ESR, serum lysozyme, Ca++
Objective: everything inflamed: nerve is edematous, LG affected bc CN 7 palsy, iritis, large mutton fat KP, conjunctivitis, keratitis, ant/post granulomatous uveitis, peiphlebitis, vitreous opacities,
Plan: Refer to PCP for management that includes prednisone 60-100 mg po qd. Treat uveitis, and refer to optho for laser if needed.
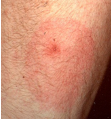
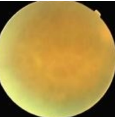
Recent tick bite from great outdoors trip followed by rash, flu, red eye, light sensitivity
Lyme Disease: bacterial infection transmitted through the bite of infected ticks
Objective:
Stage 1: Rash + flu + conjunctivitis + photophobia
Stage 2: Granulomatous uveitis, retinal vasculitis, vitreous infla, stromal keratitis, CN 7 palsy, episcleritis, iritis, exudative RD, papilledema, lid edema
Stage 3: arthritis
Workup: Western Blot + ELISA
Plan:
Therapeutics: Doxycycline 100 mg bid for 2-3 weeks. Alternative 500 mg erythromycin QID. Stage 3: IV penicillin G/ceftriaxone
RTC weekly until resolved?
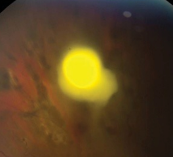
Asymptomatic/blurry vision
Fungal retinitis: fungal infection affecting the eyes. Associated with newborns, immunocompromised patient and drug users.
Objective: dense fluffy localized retinal infiltrate, vitirtis, uveitis, retinal vasculitis, chorioretinitis
Workup: DFE, culture using vitreal tap
Plan: refer to retina for vitrectomy + amphotericin B
RTC?
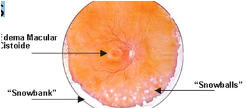
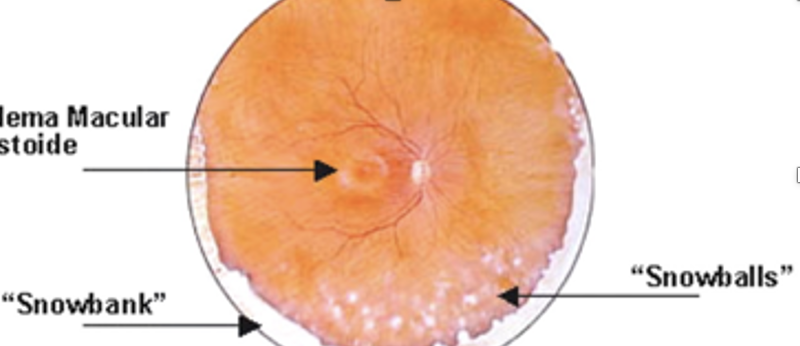
Pars planitis: inflammation in the posterior chamber associated with demyelinating conditions.
Objective: Intermediate uveitis, periphlebitis, snobanking and snowballs in vitreous
Workup: FA + CBC. MRI if suspect MS. inflammatory work up if indicated
Plan: Refer for cryotherapy for snowbanking area. Pred forte 1% or diflurprednate 0.05% Q1-2H. Consider subtenon triamcinolone. Refer to ID or rheum
RTC 1-4 weeks in acute phase, 3-6 months if chronic (look for CME, ERM, glaucoma, cataract)
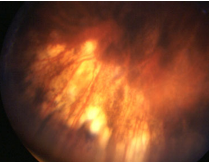
Hearing issues/cns issues , whitening of hair, hair loss
VKH (Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease) - autoimmune dx that affects pigment cells associated with HLA-DR4.
Objective: Granulomatous anterior and posterior uveitis, multifocal choroiditis -“sunset glow” -> choroid depigmentation after 4+ months of uveitis. vitritis, Retinal hemes
Workup: HLA-DR4
Plan: oral prednisone 100 mg PO daily. RTC q2 days? to monitor improvement bc can lead to blindness
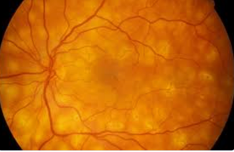
Birdshot chorioretinopathy: autoimmune dx that affects choroid and retina
bilaterally and symmetrically.
Objective: cream-colored flecks that are located surrounding the optic disc and radiate out towards the periphery. Infla throughout the eye with complicatsion including CME, GA, serous detachment
Workup: Visual field (peripheral field constriction or an enlarged blind spot) and HLA-B29 testing
Plan: for acute flare up give oral prednisolone 60-100 mg po daily. if chronic give cyclosporine A . Monitor for CME/CNV
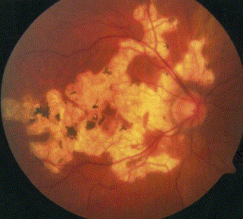
Serpiginous Choroidoapthy: bilateral disease of the choroid thati s idiopthic and uncommon.
Objective: gray-white to yellow-white subretinal infiltrates with hazy borders that typically become brighter over time. Starts at optic disc and radiates towards macula in snake like pattern
Plan: for acute flare up give oral prednisolone 60-100 mg po daily. if chronic give cyclosporine A . Monitor for CME/CNV
IDIOPATHIC MULTIFOCAL WHITE DOT SYNDROMES
Acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE)
Bilateral, painless vision loss over several days with preceding viral illness
Workup: FA and ERG abnormal
Plan: oral predisolone 60-100 mg po (CAN LEAD TO DEATH)
RTC q1-2 weeks (resolution takes up to 6 months)
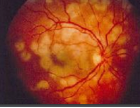
Multifocal choroiditis (MFC) - histo but with vitritis
Retinal and choroidal infla disorder with multiple relapses.
Plan: monitor for CNV/CME/subretinal fibrotic scarring
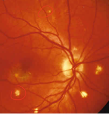
Multiple evanescent white-dot syndrome (MEWDS): retinopathy involving RPE and outer retina
Objective: creamy flat white gray dots in PP, optic dis edema, RAPD, granular macula appearance. Vitritis.
Plan: monitor should resolve on its own 6-12 weeks. May have enlarged blindspot persist following resolutiuon.
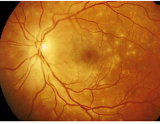
Acute Retinal Necrosis: associated with HSimplexV/HZosterV
Objective: patchy or confluent areas of cream-colored retinal necrosis starting peripherally and moves centrally unilateral or bilateral.
Labs: CBC with diff, sarcoid, syphilis, lyme, toxoP, HIV test, FA, MRI brain
Plan: acyclovir, consider steroid based on symptoms. RTC daily then few weeks-months.
Progressive outer retinal necorsis - associated with decreased ammunity
Acute zonular occult retinoapthy: idiopathyic that resolves on its own. notes strange multicolored lights/sudden vision loss.
Scotoma or dec vision, floaters, photopsias. Often asymptomatic
CMV retinitis: Most frequent opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS but 90% when CD4 count <100 cells/mm^2
Signs of indolent CMV
Peripheral granular opacities. Possible hemorrhage
Signs of confluent CMV
Confluent necrosis with prominent hemorrhage starting in the arcades. Retinal atrophy
Other signs: Ant uveitis, non-gran stellate KPs. Mild vitritis. RPE atrophy and pig clumping. 1/3 patients get RRD
Plan: consider AC paracentesis for viral PCR. Refer to infectious disease physician.
Valganciclovir 900mg BID for 21 days to stabilize the retina, HAART, laser for RD (SE: bone marrow toxicity)
Rare focal scotoma, decreased contrast
HIV retinopathy: Most common ocular manifestation of HIV/AIDS. Occurs in 50-70% patients.
Objective: CWS, intraret hemes, microaneurysms. Rare ischemic maculopathy with significant visual loss
Look for comorbid opportunistic infections bc low CD4 count
Plan: None specifically but resolves with HAART and increased CD4
Pts with CD4<50 should be examined every 3-4 months
Sudden onset dec vision and increasing eye pain after surgery
post op endophthalmitis - infection after surgery. Risk of permanent vision loss.
Objective: Hypopyon, fibrin, severe AC reaction, vit cells and haze, dec red reflex.
Workup: Look for wound/bleb leak, suture, vit in AC, bleph, B-Scan if cant see retina
Plan: hospitalize, intensive steroid/antibiotics, atropine 1% BID. Monito q12-24 hours and should have impromovement. Vitrectomy. Culture with blood, chocolate, sabouraud, and thioglycolate. Smear gram and giemsa
Sudden onset bilat dec vision, floaters, photophobia
Behcet: multisystem vasculitis of unknown etiology. The disease can be found most commonly in the Middle East, silk road. Prognosis if untreated: Blind within 3 days to 4 years.
Objective: oral/gential ulcer with ocular uveitis + bilateral hypopyon that shifts with position. Young adult. iritis, aphthous ulcers, retinal vasculitis
Workup: HLA B51. CT and ACE for sarcoid. PPD or IGRA and RPR or VDRL for TB, FTA-ABS or treponemal specific for syphilis. Then, behcet's pathergy test
Plan: Tx: Pred forte and cyclo for ant uveitis. Oral steroids. Referral for immuno suppression with TNF alpha inhibitor
RTC: Daily for uveitis episodes
HLA B27 conditions
Symptoms: Acute pain. BLur, photophobia. Assoc lower back pain, cervical pain, arthritis, oral ulcers, pain on urination, GI problem rash
Recurrent unilat nongran ant uveitis, Severe cells and flare with fibrin. Most common cause of unilat hypopyon. Post syn, ciliary flush. Men.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Young men, lower back pain, SI joint, inc ESR, +HLA B27, negative RF
IBD: Crohn and ulcerative colitis. Chronic diarrhea, bloody stool, ab pain.
REactive Arthritis: Young men. Conjitis, urethritis, polyarthritis. Inc ESR, pos HLA B27. Arthritis in lower extremities
Psoriatic arthritis: Skin finding plus arthritis in upper extremities
Plan/workup:
Run HLA typing.
Ank spon: SI X-ray.
IBD: consult GI.
ReA: Conj and urethral swabs for chlamydia. Consult Rheum.
Psoriatic: Consult rheum or derm
Treat uveitis
Cat Scratch disease:
Type 1: . Neuroretinitis: consisting of lymphadenopathy and granulomatous inflammation of the retina and optic nerve with classic optic nerve swelling, macular star (neuroretinitis), and possible vasculitis. Unilat stellate macular exudates, optic nerve swelling aka NAION, vit cells, and positive bartonella
Type 2: Parinauds Ocularglanduar Syndrome: consisting of lymphadenopathy and follicular conjunctivitis
Tx nothing, steroid, or doxy/azithro
Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis: bilateral nongranulomatous uveitis, young girls, abdominal pain, fatigue. Manage with nephrologist.
JIA: Young girls with <4 joint arthritis. Bilat, can be painless. Iritis. Positive ANA, negative RF, increased ESR.
Assoc glaucoma, cataract, band K, CME