Microbial Classification and Identification Methods
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
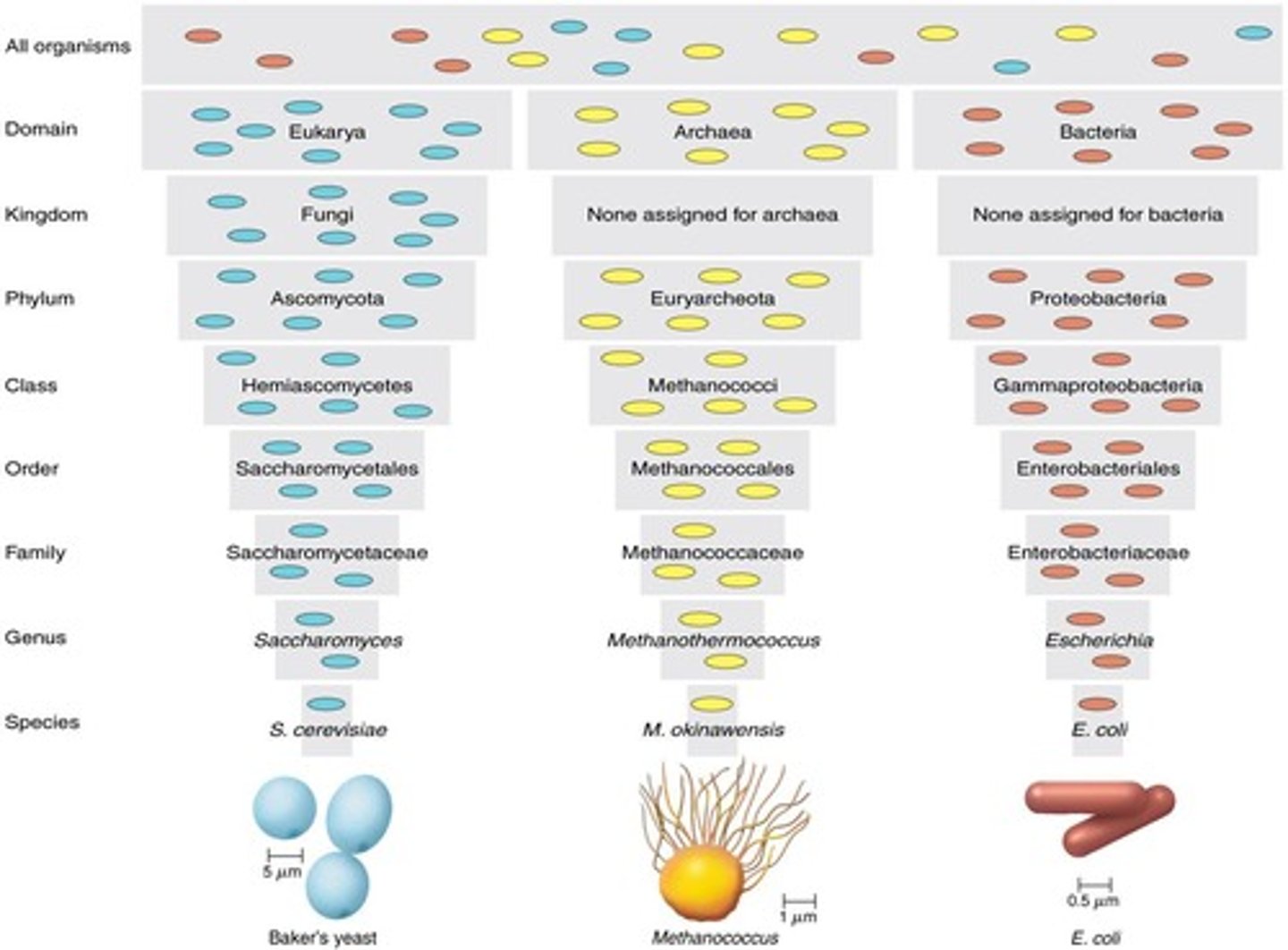
Three Domains
Classification system by Woese based on rRNA sequences. (eukarya, bacteria, archaea)
what is common to all life
ribosomes
Eukarya
Domain including animals, plants, and fungi.
Bacteria
Domain consisting of prokaryotic microorganisms.
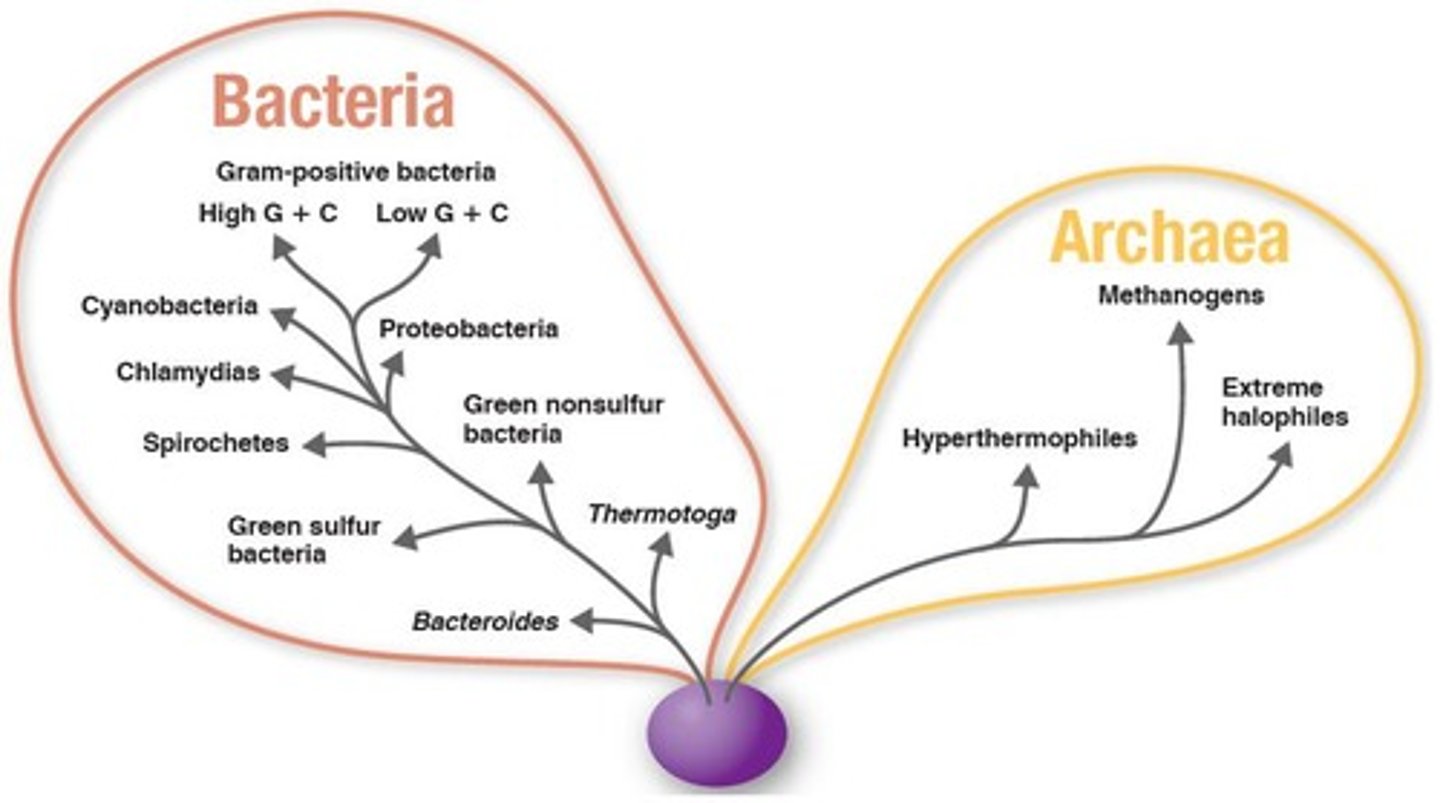
Archaea
Domain of prokaryotes with extreme environments.
Methanogens
Archaea producing methane in anaerobic conditions.
Extreme Halophiles
Archaea thriving in high-salt environments.
Hyperthermophiles
Archaea that live in extremely hot environments.
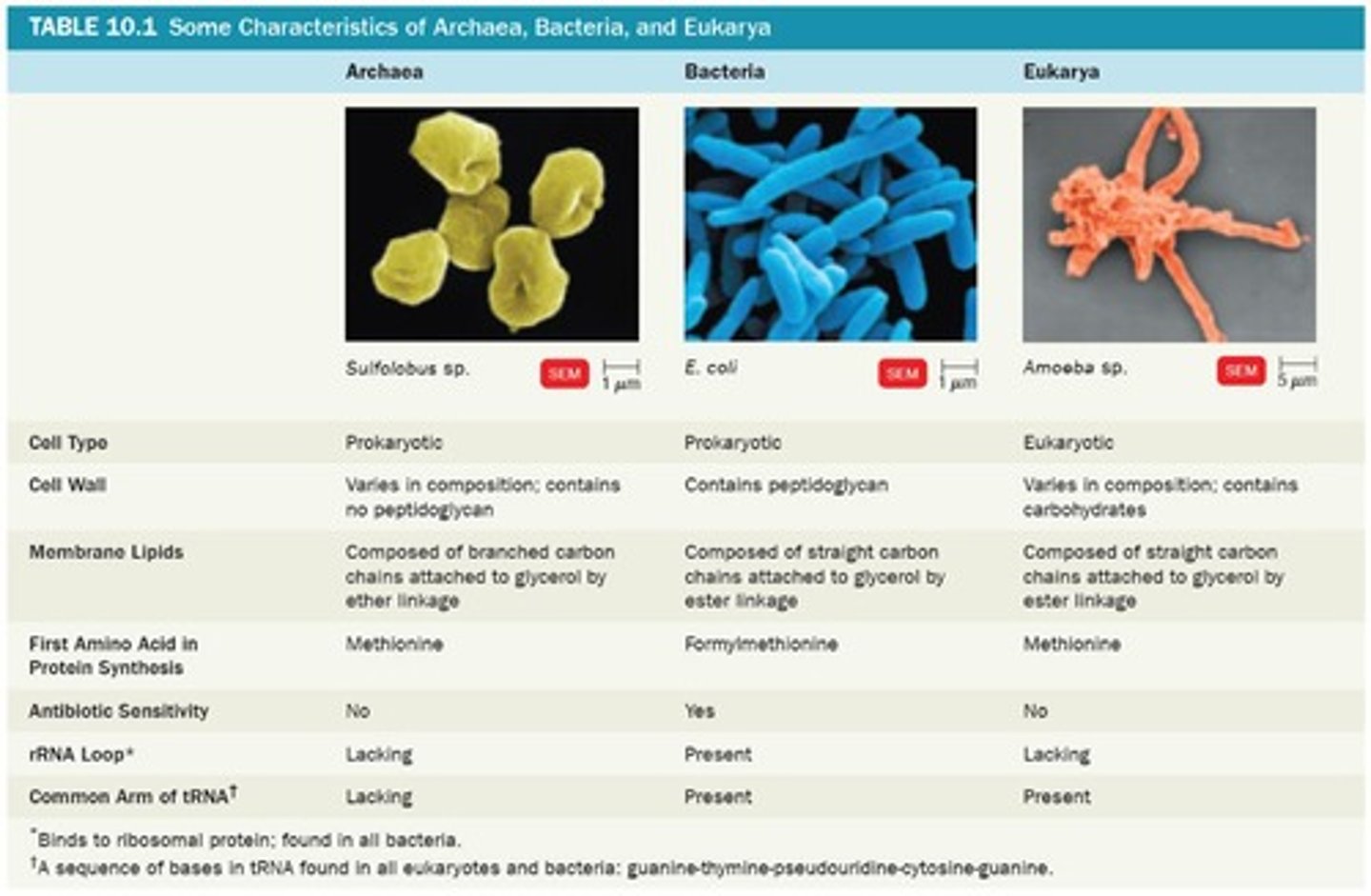
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a defined nucleus or organelles.
Eukaryotic Organelles
Membrane-bound structures within eukaryotic cells.
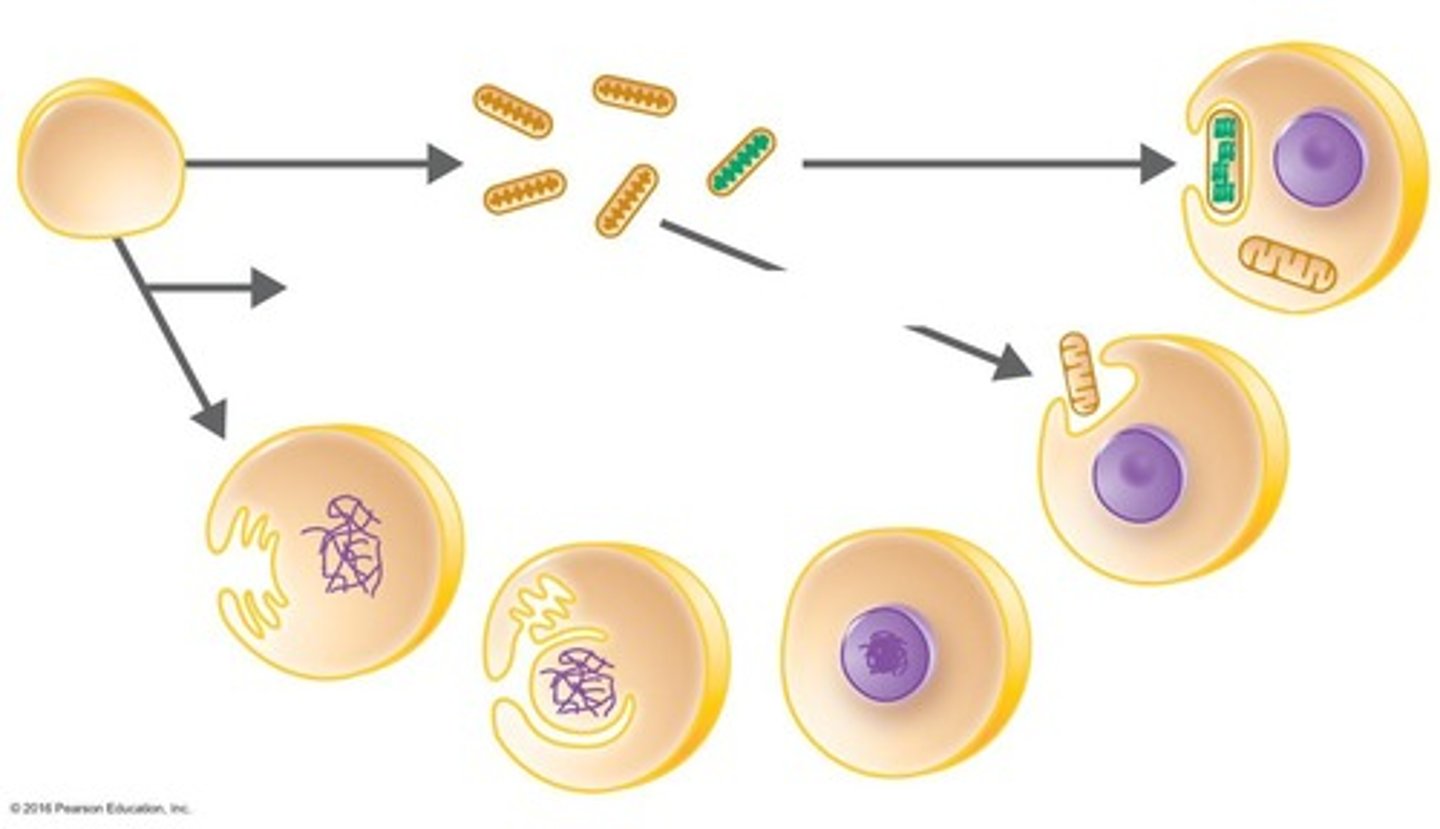
Endosymbiotic Theory
Eukaryotes originated from symbiotic prokaryotes.
Prokaryotic cell wall
contains peptidoglycan
eukaryotic cell wall
contains carbohydrates
Phylogenetic Tree
Diagram showing evolutionary relationships among organisms. (common ancestor)
endosymbiotic theory
a theory that states that certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside of larger cells and evolved into the organelles of modern-day eukaryotes
Molecular Clock
Method using mutation rates to estimate evolutionary time.
stromatolites
Oldest known fossils formed from many layers of bacteria and sediment. (>2billion years)
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part naming system for organisms, genus and species.
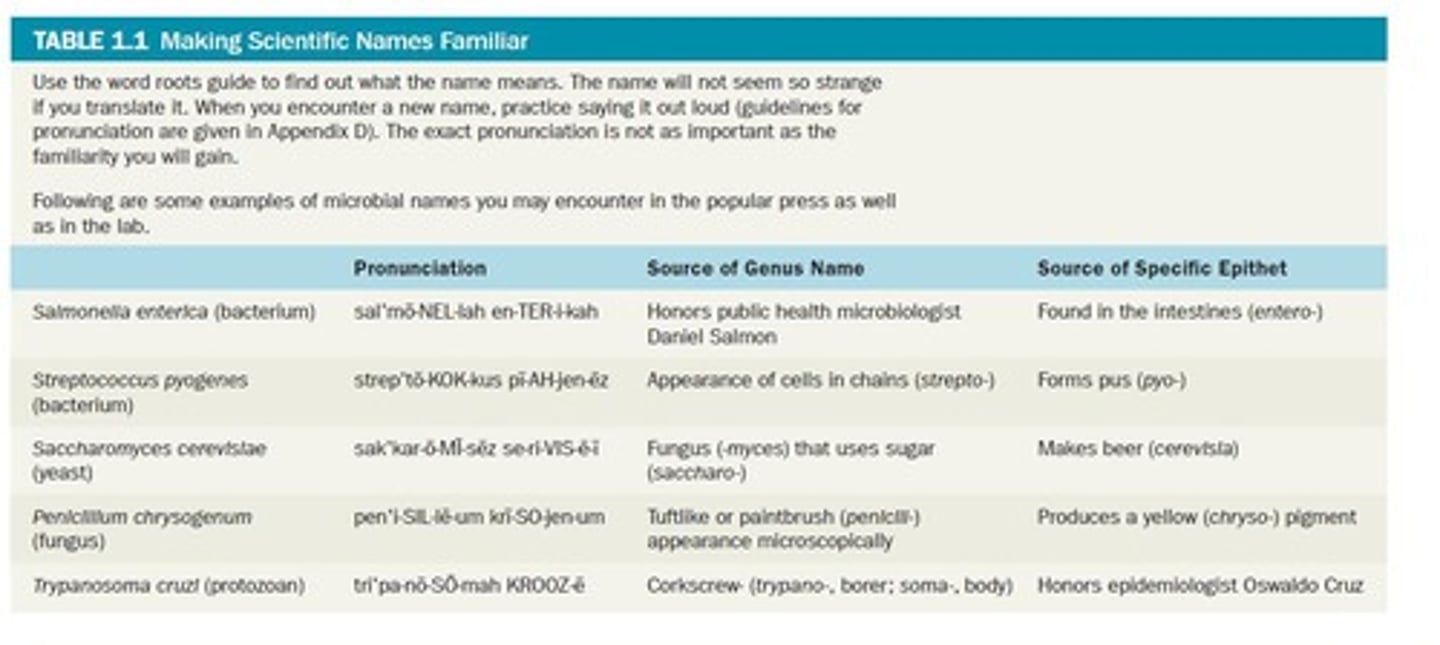
Taxonomic Hierarchy
System of classification from domain to species.
Prokaryotic Species
Population of cells with similar characteristics
eukaryotic species
a group of closely related organisms that breed among themselves
Culture
Bacteria grown in laboratory media for study.
Clone
Population derived from a single parent cell.
Strain
Genetically distinct cells within a clone.
Protista
Diverse kingdom of autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms.
clades
a group of organisms believed to have evolved from a common ancestor, according to the principles of cladistics.
Fungi
Chemoheterotrophic organisms with chitin cell walls. (uni/multicellular) develop from spores or hyphen fragments
Plantae
Multicellular organisms with cellulose walls, photosynthetic.
Animalia
Multicellular organisms lacking cell walls, chemoheterotrophic.
chemoheterotrophic
an organism that uses organic molecules as a source of carbon and energy
Viral Species
Population of viruses with similar characteristics that share ecological niches.
Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology
Reference for identifying bacteria and archaea.
transport media
used to maintain and preserve specimens that have to be held for a period of time before clinical analysis
morphological characteristics
useful for identifying eukaryotes; tells little about phylogenetic relationships
phylogenetic relationships
Connections between species based on evolutionary history.
Differential Staining
Techniques like Gram staining to identify bacteria with cell walls
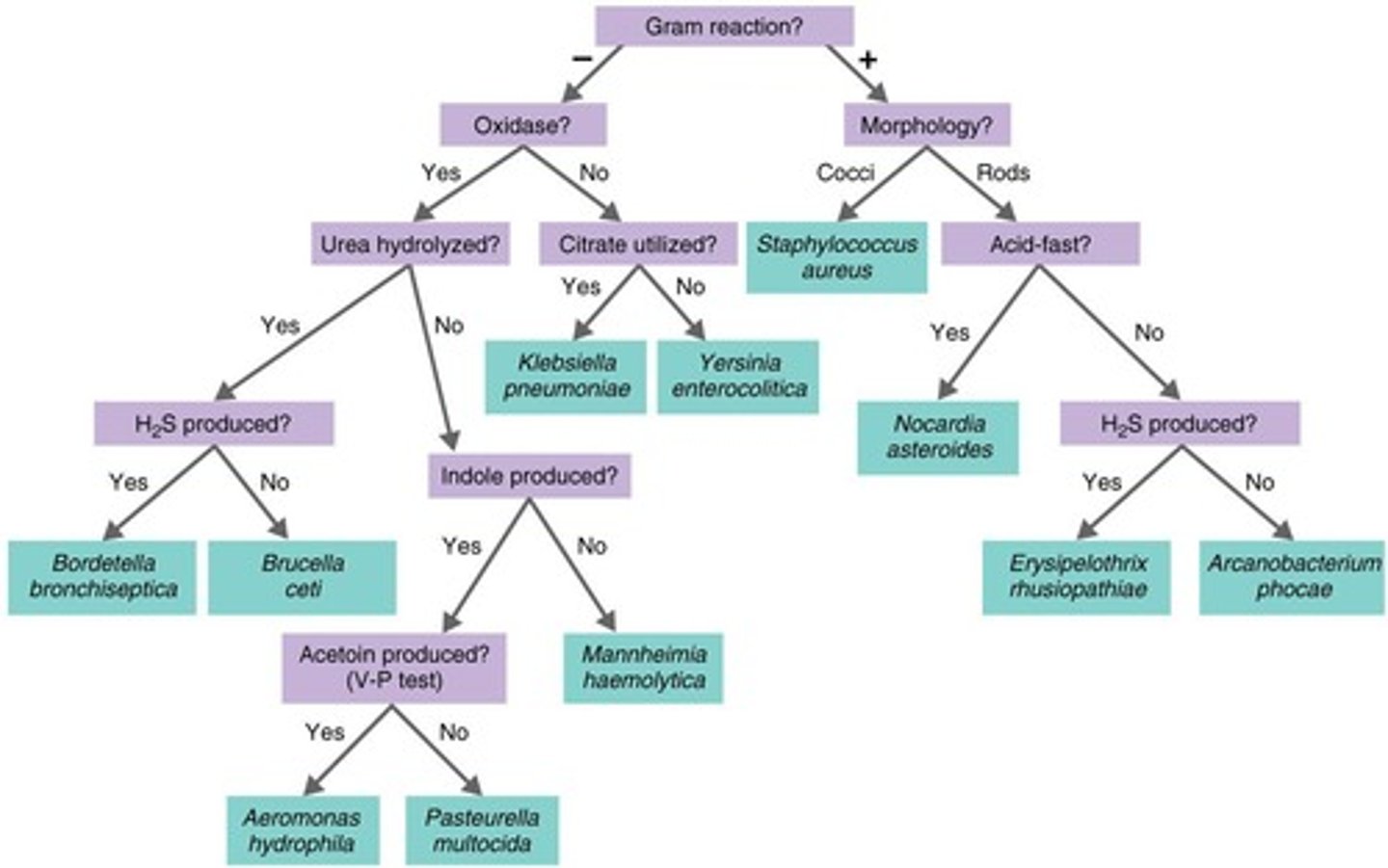
Biochemical Tests
Tests determining presence of specific bacterial enzymes without cell walls
rapid identification methods
perform several biochemical tests simultaneously
automated rapid identification system
available for medically important bacteria and yeast
EnteroPluri Test
Rapid identification method for enteric bacteria.
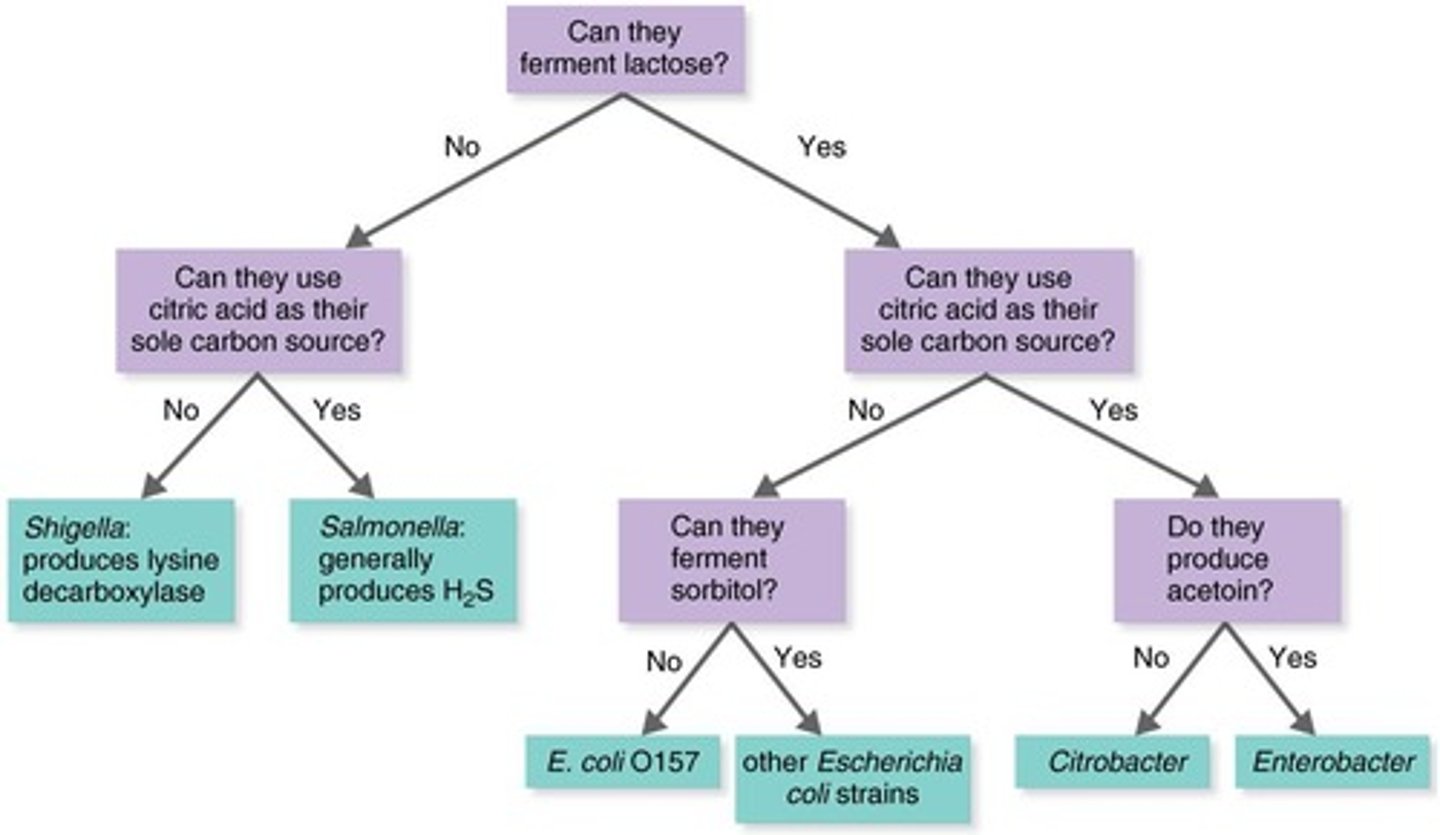
Code Number
Unique identifier derived from test results.
Mass Spectrophotometry
Technique comparing cellular proteins to databases.
Serology
Study of serum and immune responses.
Antiserum
Solution of antibodies tested against unknown bacteria.
Slide Agglutination Test
bacteria agglutinate (clumping) when mixed with antibodies produced in response to the bacteria
serological testing
can differentiate between species and strains within species
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Test using known antibodies to identify unknown bacteria.
Western Blotting
Technique to identify antibodies in patient serum. (ex. HIV, Lyme disease)
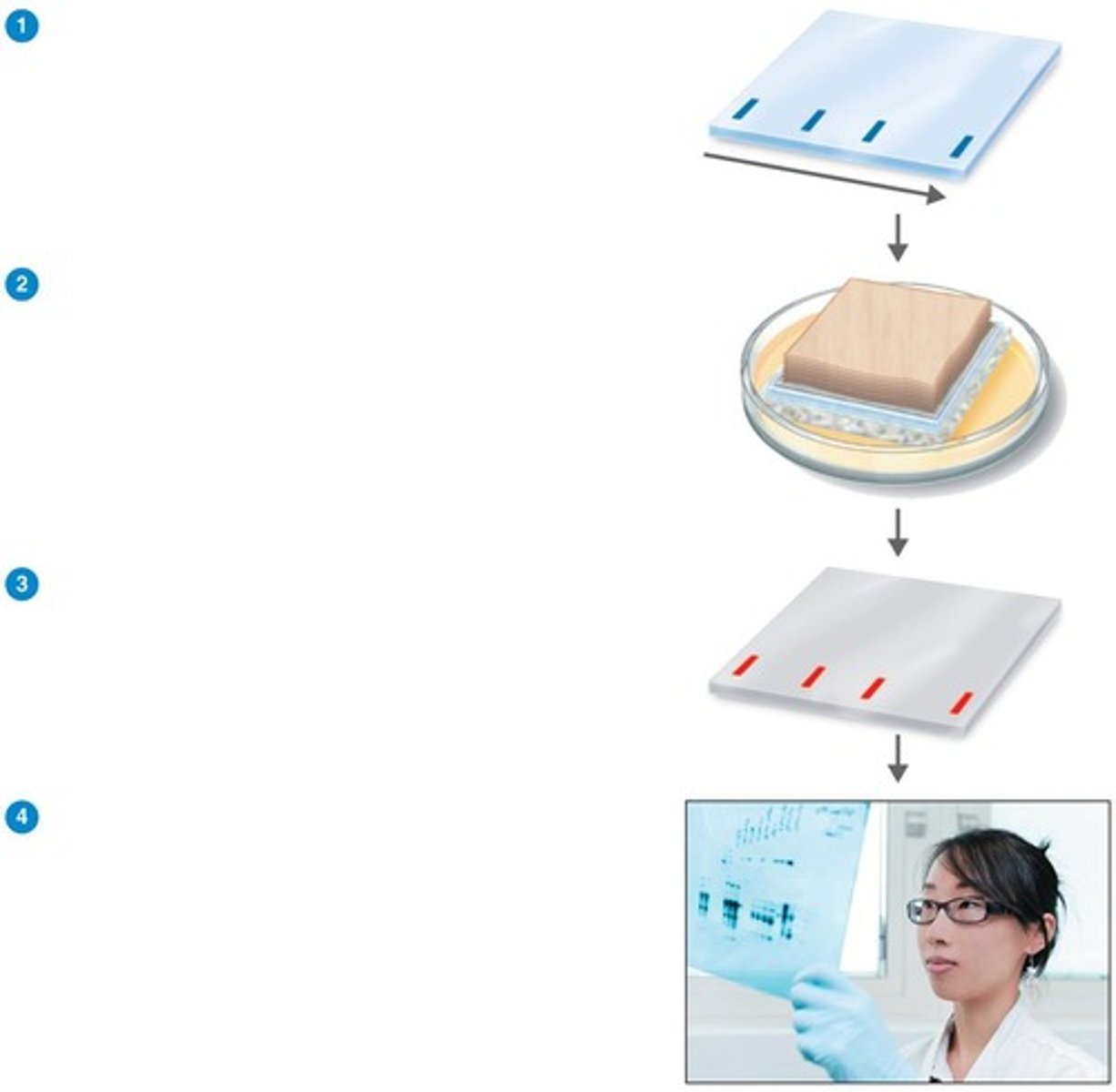
Electrophoresis
Separates proteins based on charge and size.
Phage
a type of virus that infects and kills bacteria. (to eat)
phage typing
test for identifying which phages a bacterium is susceptible to
Nitrocellulose Filter
Medium for transferring proteins from gel.
Antigen
Substance that induces immune response.
Fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs)
provide profiles that are constant for a particular species
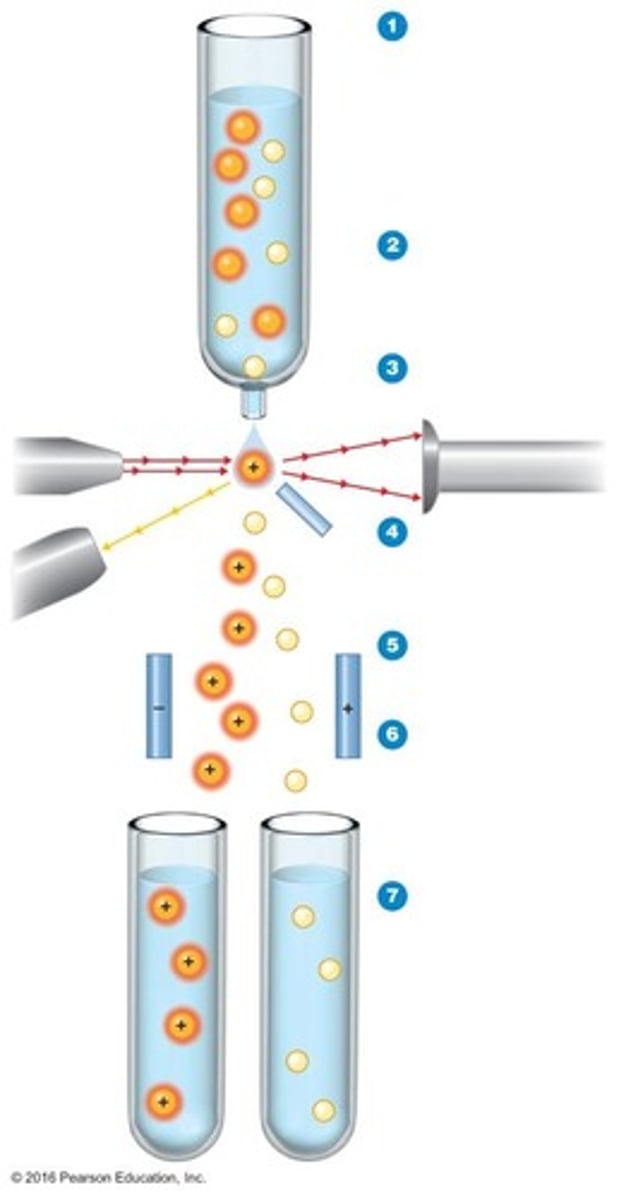
Flow Cytometry
Technique using electrical conductivity and fluorescence.
Fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS)
A device that can count cells and sort them according to differences in fluorescence.
Plaques
Clearings on plates where phages lyse bacteria.
Antibody Reaction
Visible indication of antigen presence in tests.
Lysed Bacteria
Bacteria broken down for antigen detection.
Antihuman Antibodies
Antibodies tagged for detection in serological tests.
Gel Electrophoresis
Technique to separate proteins by size.
Patient Serum
Blood component used in serological testing.
Fluorescent-Antibody Markers
Labels specific antigens for detection in flow cytometry.
Laser Beam
Strikes droplets for cell identification in FACS.
Fluorescence Detector
Identifies cells based on emitted fluorescent light.
Electrically Charged Plates
Directs positively charged cells towards negative plate.
Collection Tubes
Holds separated cells post-sorting in FACS.
DNA Sequencing
Determines base composition of DNA samples.
Online Databases
Resources like NCBI for genomic information.
DNA Fingerprinting
Analyzes DNA fragments for genetic comparison.
Nucleic Acid Hybridization
Measures DNA strand hybridization between organisms.
Hybridization Degree
Indicates relatedness based on DNA strand pairing. (greater degree of hybrid =greater degree of relatedness)
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)
a lab test that looks for DNA or RNA from a virus or bacteria by making lots of copies of it so it can be easily detected
Southern Blotting
Identifies microorganisms using DNA probes.
DNA Probe
Labeled DNA fragment used for hybridization detection.
DNA Chip (Microarray)
a small, flat surface with thousands of DNA probes attached that can be used to detect specific DNA or RNA sequencesin a sample all at once.
Ribotyping
Uses rRNA sequencing for microbial identification.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)
uses fluorescently labeled DNA probes to find and visualize specific DNA or RNA sequences directly inside cells or tissues under a microscope.
Dichotomous Keys
Identification keys based on successive questions.
Cladograms
Maps showing evolutionary relationships among organisms.