Cardiac Electrophysiology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
SA Node
Natural pacemaker of heart, determines heart rate
AV Node
Electrical gateway to ventricles, ensure atria eject all blood to ventricles
Bundle of His
Right and left bundle branches conduct impulses toward apex of heart
Purkinje Fibers
Signals from Bundle of His spread through ventricles
Via this
Conducting cells
SA node, AV node, His-Purkinje fibers
Contractile cells
Atrial and ventricular cardiac muscle
Pacemaker, AV, SA
SA and AV nodes have __ action potentials
Although the __ node is slower than the __ node
HCN, If
1 - __ channels open (I_)
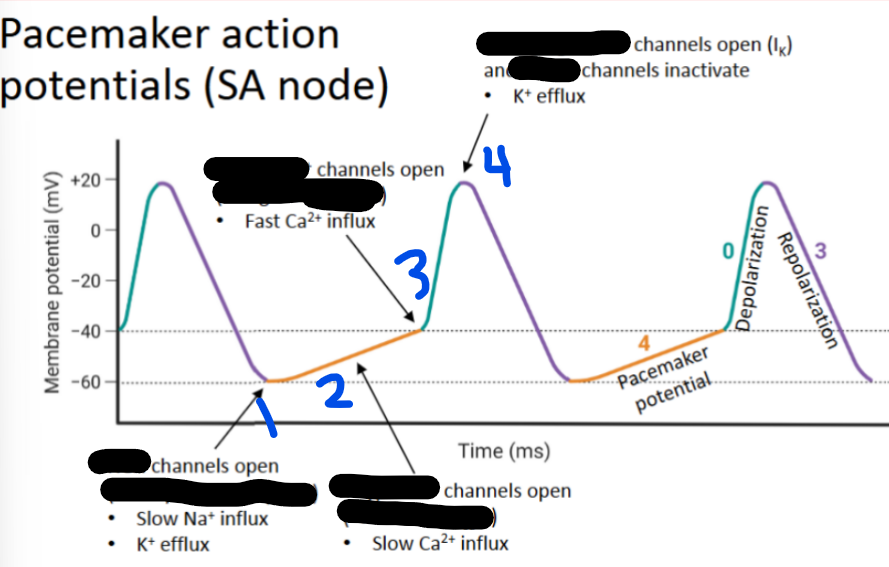
T-type Ca2+, ICaT
2 - __ __ channels open (I_)
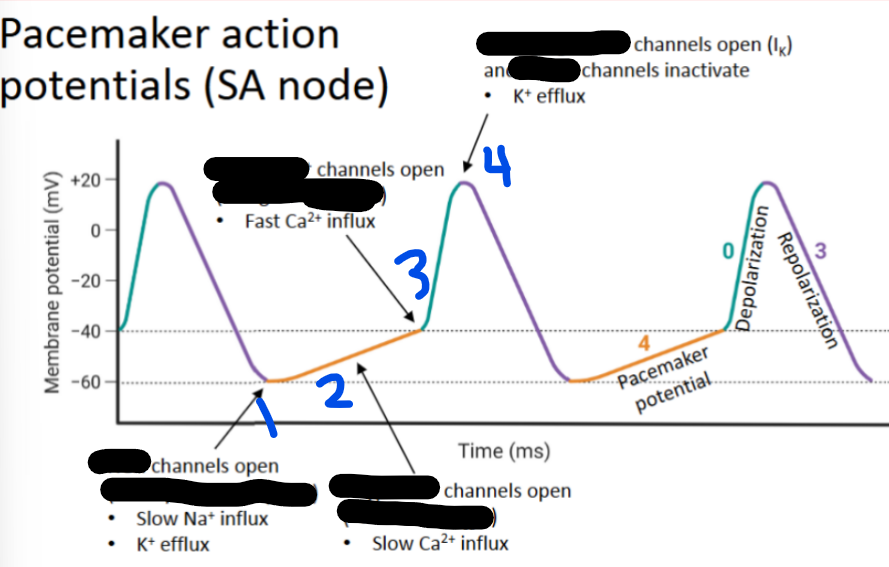
L-type Ca2+, ICaL
3 - __ __ channels open (I_)
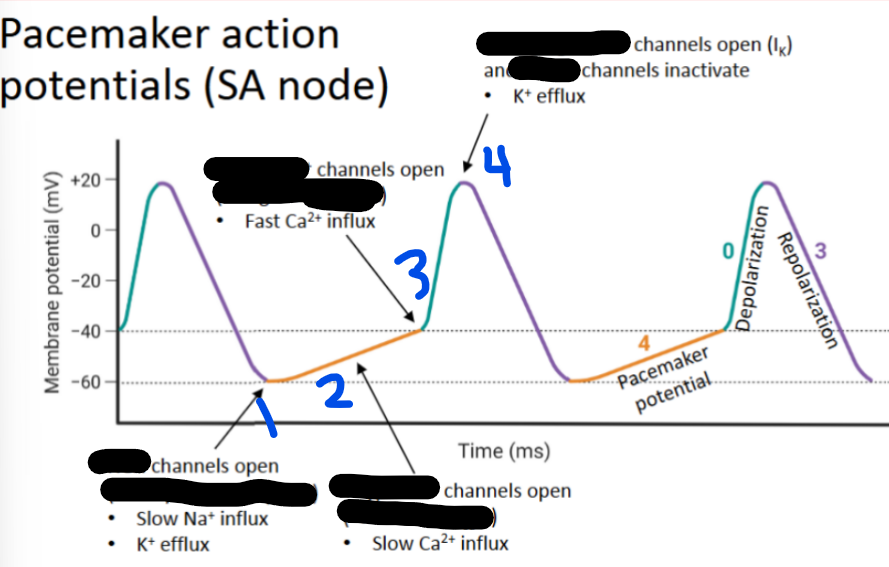
Voltage-gated K+, L-type, Ik
4 - __-__ __ channels open and _-__ channels inactivate (I_)
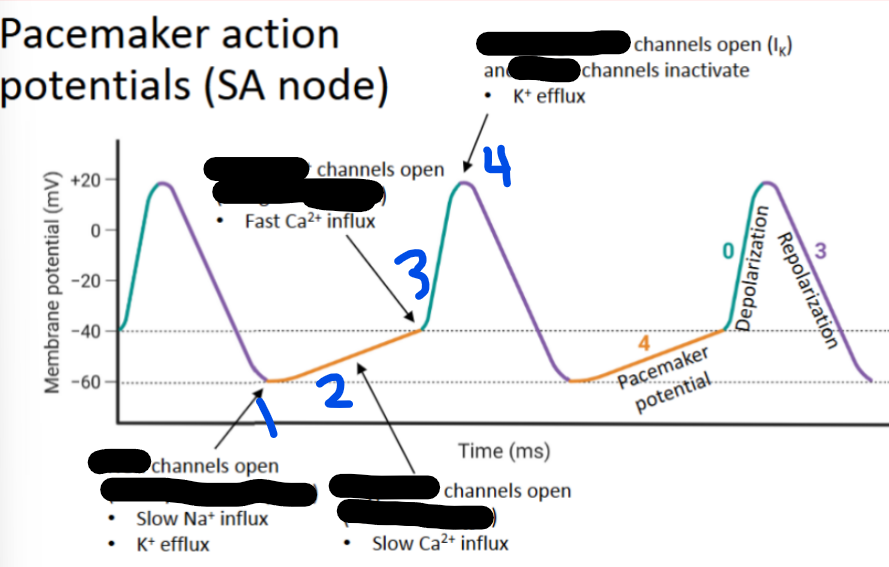
Gradual, funny
HCN channels move to a __ depolarization of SA node
As they do not follow the rules of action potentials, they are nicknamed “__ current”
Na+
__ channels do NOT contribute to pacemaker action potentials in SA node
automaticity, resting MP
SA node has “__” with pacemaker potential and NO true __ __ __
Long-lasting (L-type)
After reaching threshold, SA node has more gradual phase 0 from __-__ Ca2+ DHPR channels opening
Hyperpolarization, cAMP, depolarization, Na+
HCN channels
Open in response to __ (super negative MP)
Regulated by __ (2nd messenger) for opening channels
When HCN channels are open, Na+ moves into cell and K+ moves out
Net effect = Gradual __ by increasing __ (ion) percent of the vote at a slowed rate
60-100, 40-60
SA node firing rate is at __-__ bpm
Whereas AV node + Bundle of His firing rate are at __-__ bpm
AV, atria, ventricles, decrease
What would happen if SA node is ablated/destroyed?
__ node would take over as the pacemaker
However depolarization of __ and __ at the same time → Not very conducive
__ (increase/decrease) HR
Ventricles, depolarization, firing
What would happen if AV node is ablated/destroyed?
Destroys main communicator to the heart’s __ (atria/ventricles)
Uncontrolled __ of myocytes with no supervisor node
Means discoordinated __
Chronotropy, HCN, L
__ (autonomic) affects impulse rate (time)
Via influence on opening of __ channels and _-type Ca2+ channels (more cAMP)
Dromotropy, AV
__ (autonomic) affects conduction speed
Important in __ node
Ionotropy, DHPR, RyR
__ (autonomic) affects myocyte contractility
Via influence on __s (Receptor) and __s (Receptor)
Increase cytosolic Ca2+
Lusitropy, SERCA, NCX
__ (autonomic) affects myocyte relaxation
Via influence on __ and __ for reuptake
Decrease cytosolic Ca2+
M2, HCN, decrease, increase, hyper, pacemaker
Parasympathetic influence on chronotropy
ACh effects via __ receptors
Decrease in __ channel opening due to __ in cAMP
__ in K+ permeability (Vm more negative)
__polarization leads to a decrease in heart rate
Slower rise in __ potential (cardiac)
0.5 m/s
Atrial muscle and ventricular muscle conduction velocity
(Same for both)
0.05 m/s
AV node conduction velocity
2 m/s
Bundle of His conduction velocity
Atrial, conduction, ventricles, bundles, Purkinje fibers, ventricular
Cardiac Electric Cycle
Depolarization of the SA node spreads rapidly thru __ muscle
AV node slows impulse __ to allow complete systole of atria and filling of all __ before they depolarize
Impulse travels down __ and up from apex thru __ __
Depolarization then spreads rapidly thru __ muscle
external, current, all, APs
Electrocardiogram (EKG) is a __ (internal/external) recording of summed net __ towards or away from a sensor/lead
Summed electrical activity of __ heart cells and NOT individual __ __
Mass, lead
Amplitude of a deflection on EKG recording depends on:
__ of tissue involved
Direction of electrical activity relative to the __