UWORLD Poisoning Step 2 CK | Quizlet
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is the treatment of large local reactions to insect bites?
Oral antihistamine and topical corticosteroids
What is the next step in management in a patient with spider bite which presents with a erythematous ulcer that progressed to blister and necrotic wound?
Supportive wound care
(Cleanse wound and apply ice)
(The patient most likely has brown recluse spider bite, which are found in warm, dry areas [eg, attics, woodpikes, cellars])
(vs. Black widow spider: muscle pain/cramps, abdominal rigidity)
![<p>Supportive wound care</p><p>(Cleanse wound and apply ice)</p><p>(The patient most likely has brown recluse spider bite, which are found in warm, dry areas [eg, attics, woodpikes, cellars])</p><p>(vs. Black widow spider: muscle pain/cramps, abdominal rigidity)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/251602fd-afb1-4a41-a1be-ab8623cd3828.jpg)
Triad of seronin syndrome
3 A's:
1) Activity (neuromuscular): clonus, hyperreflexia, hypertonia, tremor, seizure
2) Autonomic instability: hyperthermia, diaphoresis, diarrhea
3) Altered mental status (eg, anxiety, restlessness, agitated delirium)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with acute onset
-confusion,
-hyperthermia,
-tachypnea,
-elevated lactate, and anion gap metabolic acidosis?
Acute salicylate toxicity
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with acute onset
-tachypnea
-tachycardia
-hyperthermia
-dizziness
-nausea and vomiting?
Acute salicylate toxicity
What is the management of acute salicylate toxicity?
-Sodium bicarbonate drip: alkalinization of blood and urine
-Glucose: prevents neuroglycopenia
-Activated charcoal: if presentation is within 2 hours
-Dialysis
What is the likely diagnosis if an elderly patient with CKD and using topical salicylate for arthritis presents with
-hyperpnea,
-anion gap metabolic acidosis,
-hyperthermia
-tinnitus
-confusion
-pulmonary edema?
Chronic salicylate toxicity
(more common in young children and the elderly)
(hyperthermia due to dissipated energy byproducts from Krebs cycle dysfunction; noncardiogenic pulmonary edema due to increased pulmonary vascular permeability, not volume overload)
What is the management of chronic salicylate toxicity?
-IV sodium bicarbonate therapy:
alkalinize the urine and serum --- increase salicylate (anion) excretion. However, large volumes are required.
-Hemodialysis: Indicated in patients unlikely to tolerate the large volumes of bicarbonate required, (eg, ESRD, renal failure, and salicylate-induced pulmonary edema)
(Activated charcoal is indicated within 2 hours of acute ingestion)
What is the management of acetaminophen toxicity?
Within 4 hours of ingestion: activated charcoal
4-24 hours after ingestion: N-acetylcysteine
Organophosphate poisoning - Symptoms
1) Muscarinic effects (DUMBBELSS): Diarrhea, Urination, Miosis, Bronchospasm, Bradycardia, Emesis, Lacrimation, Sweating, Salivation
2) Nicotinic effects: Muscle weakness, paralysis, fasciculations
Organophosphate poisoning can be confirmed with ...................
the measurement of RBC acetylcholinesterase activity
What is the recommended treatment for organophosphate or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
atropine (a competitive inhibitor) followed by pralidoxime (regenerates AChE)
(equally important is the removal of any clothes, which may be contaminated with pesticides, and washing of skin to prevent further cutaneous absorption)
What is the recommended treatment for anticholinergic poisoning?
physostigmine (cholinesterase inhibitor)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with elbow and shoulder pain that began an hour after a scuba diving excursion?
Decompression sickness
(Rapid ascent --- formation of nitrogen bubbles in the tissues and bloodstream --- pain and obstruction of blood flow)
High-altitude cerebral edema is diagnosed clinically (eg, drowsiness, confusion, ataxia); treatment is aided by .............., which can decrease cerebral swelling and is administered at the first sign of symptoms.
dexamethasone
Risk factors for lead poisoning include homes built before ............
1978
What is the next step in management for a child that has an elevated lead level on capillary blood testing?
Measure venous lead level
(capillary blood testing is a good initial screen but false-positive results are common)
What is the treatment of asymptomatic lead toxicity?
1) Mild (5-44): No medication (repeat venous blood level within 1 month)
2) Moderate (45-69): succimer
3) Severe (>69): dimercaptol + EDTA
What complications are a child with lead level of 35 μg/dL at greatest risk of developing?
Cognitive impairment and behavioral problems (eg, ADHD)
(Chelation therapy has not been shown to improve neuropsychiatric outcomes in children with lead levels of 5-44 μg/dL. Therefore, primary prevention is critical)
To prevent scalding injuries in children, the water heater temperature should be set to a maximum of ...........
49 C
What is the most effective way to prevent children from drowning in swimming pools?
install a 4-sided fence around the pool with a self-closing gate and latch
What is the likely diagnosis in a child that presents with cyanosis and decreased O2 saturation after using an local/topical anesthetic (e.g. benzocaine)?
Methemoglobinemia
(other oxidizing agents that may induce methemoglobinemia include dapsone, nitrites, sulfa drugs)
Methemoglobinemia
-Pulse oximetry saturation:
-PaO2:
-around 85%
-normal
(arterial blood gas testing analyzes only unbound arterial oxygen [as opposed to hemoglobin-bound oxygen] and displays a falsely elevated oxygen saturation level, shown as normal PaO2.)
Methemoglobinemia is typically treated with ..............
methylene blue
(methylene blue reduces methemoglobin [Fe3+] back to hemoglobin [Fe2+]; high-dose vitamin C is occasionally used as well)
.............. and carbon monoxide (CO) are the 2 major products of combustion in closed spaces.
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with headache, nausea, and dizziness? His wife develops concurrent symptoms.
Carbon monoxide poisoning
What is the cause of metabolic acidosis in cyanide poisoning?
Cyanide binds to ferric iron (Fe3+) in cytochrome oxidase a3 in the mitochondrial electron transport chain --- blocks oxidative phosphorylation --- promotes anaerobic metabolism --- lactic acidosis
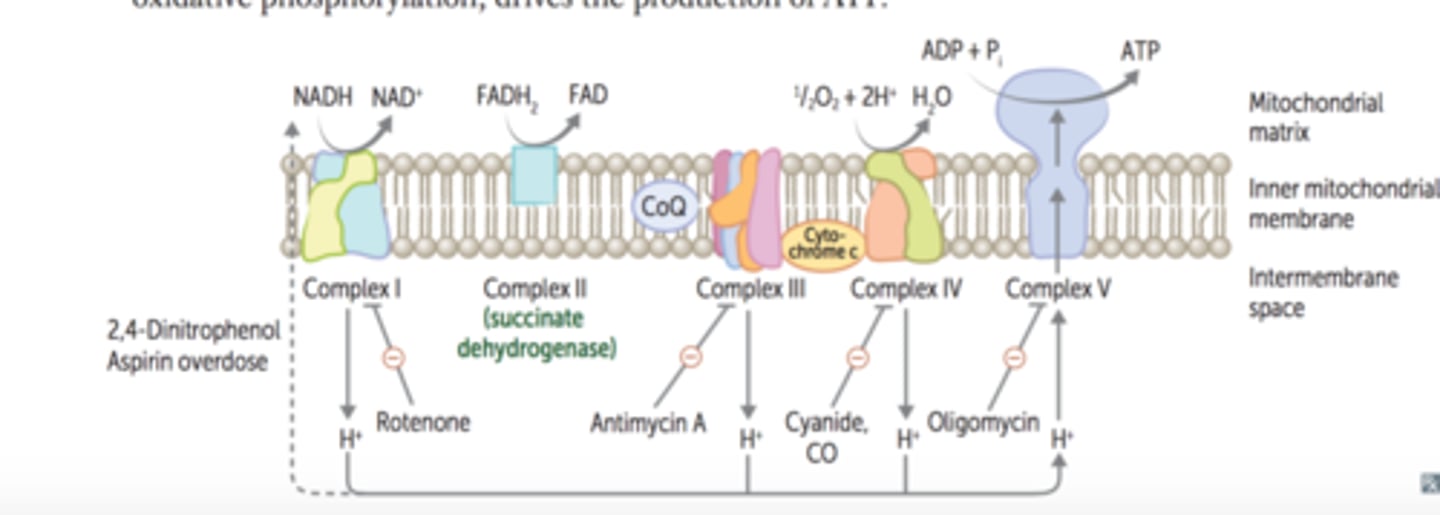
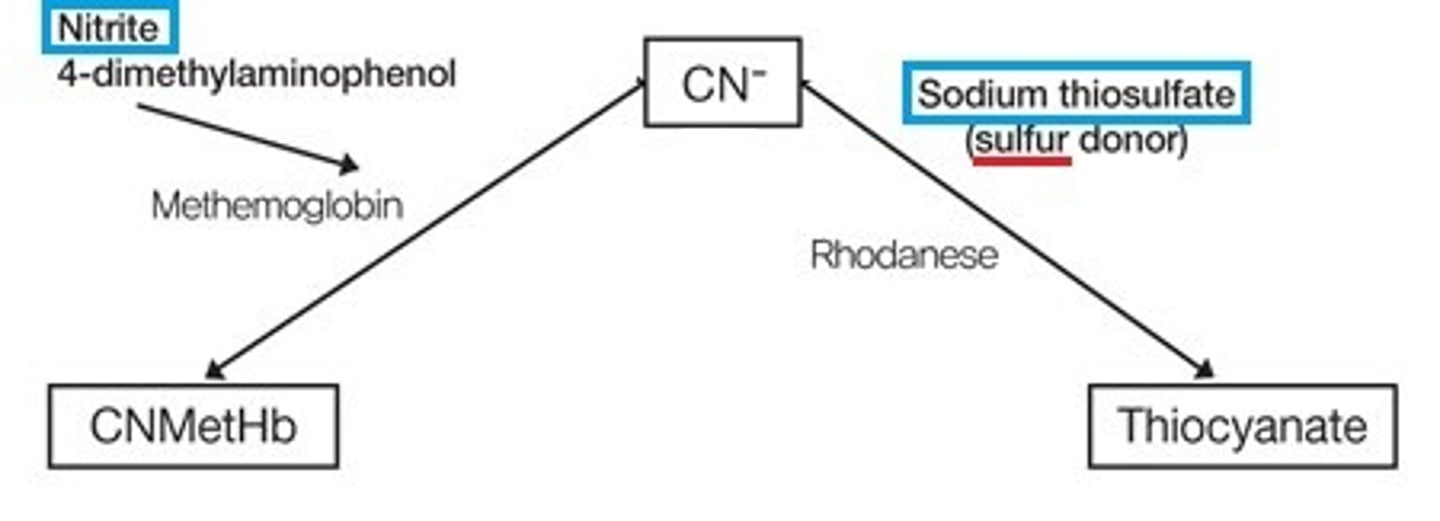
Cyanide poisoning - Treatment
-hydroxycobalamin (preferred) or
-sodium thiosulfate
-alternatively nitrites may be used to induce methemoglobinemia
What is the likely diagnosis in a homeless patient with
-confusion,
-epigastric pain
-blurred vision, optic disk hyperemia
-anion gap metabolic acidosis?
Methanol poisoning
What is the likely diagnosis in a hospitalized patient with
-acute change in mental status, somnolence
-respiratory depression (RR=10)
-hypotension
-miosis?
Opioid intoxication
-Sweating
-Dilated pupils (mydriasis)
-Nausea, stomach cramps, diarrhea ("flu-like" symptoms).
-Piloerection ("cold turkey")
-Rhinorrhea, lacrimation
-Yawning
-Myalgias
Opioid withdrawal
What is the next step in management of caustic ingestion, after airway, breathing, and circulation have been assessed?
Decontamination (e.g. remove contaminated clothing, irrigate exposed skin)
Caustic ingestion causes immediate esophageal injury. In stable patients with no evidence of perforation, ............. should be performed within the first 24 hours.
endoscopy
(to assess the severity of the injury)
What is the likely diagnosis in a soccer player with cystic fibrosis presenting with
-hyperthermia (39 C)
-normal mental status
-profuse sweating
-nausea / vomiting
-tachycardia (136), tachypnea (26)?
Heat exhaustion
................ most commonly affects elderly patients and is characterized by body temperature ≥40 C (104 F) with CNS dysfunction (eg, encephalopathy).
Nonexertional (classic) heat stroke
What is the likely cause of collapse in an athlete after completing the marathon?
Exercise-associated postural hypotension:
When an athlete abruptly stops exercising (eg, finishes a marathon), the muscles are no longer exerting pressure --- sudden decrease in venous return --- fails to meet increased cardiac demand --- postural hypotension and collapse
Patients with cystic fibrosis are at increased risk for dehydration, exertional ...........natremia, and ..........chloremic dehydration
-hypo
-hypo
Circumferential, full-thickness (third degree) burns can result in eschar formation that restricts venous and lymphatic drainage, leading to ..................
acute compartment syndrome
(Pain out of proportion to clinical findings is often the first presenting symptom)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient who works building outdoor fences presenting with
-polyneuropathy,
-pancytopenia,
-mild transaminase elevation (hepatitis)
-hypo- and hyperpigmentation of the skin, and hyperkeratosis and scaling of the soles and palms?
Chronic arsenic toxicity
(toxic exposure is more likely through mining, pesticide manufacturing, metalworking, and working with pressure-treated wood [eg, used in outdoor fences] preserved with arsenic)
(vs. lead poisoning: GI complaints, no skin changes)
In frosbite, what is the next step in management of a patients with persistent signs of tissue ischemia (sensory loss, gray appearance, absent capillary refill) after rapid rewarming of affected tissues in a warm water bath?
Angiography or technetium-99m scintigraphy
(can help assess perfusion within the affected tissues and identify those who would benefit from thrombolysis)
Ethylene glycol ingestion leads to a severe anion gap metabolic acidosis. This causes a typical ..................
rapid and deep breathing pattern known as Kussmaul's respiration
What is the most appropriate treatment of early ethylene glycol ingestion?
Fomepizole (competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase)
(Simultaneous use with ethanol is not recommended.)
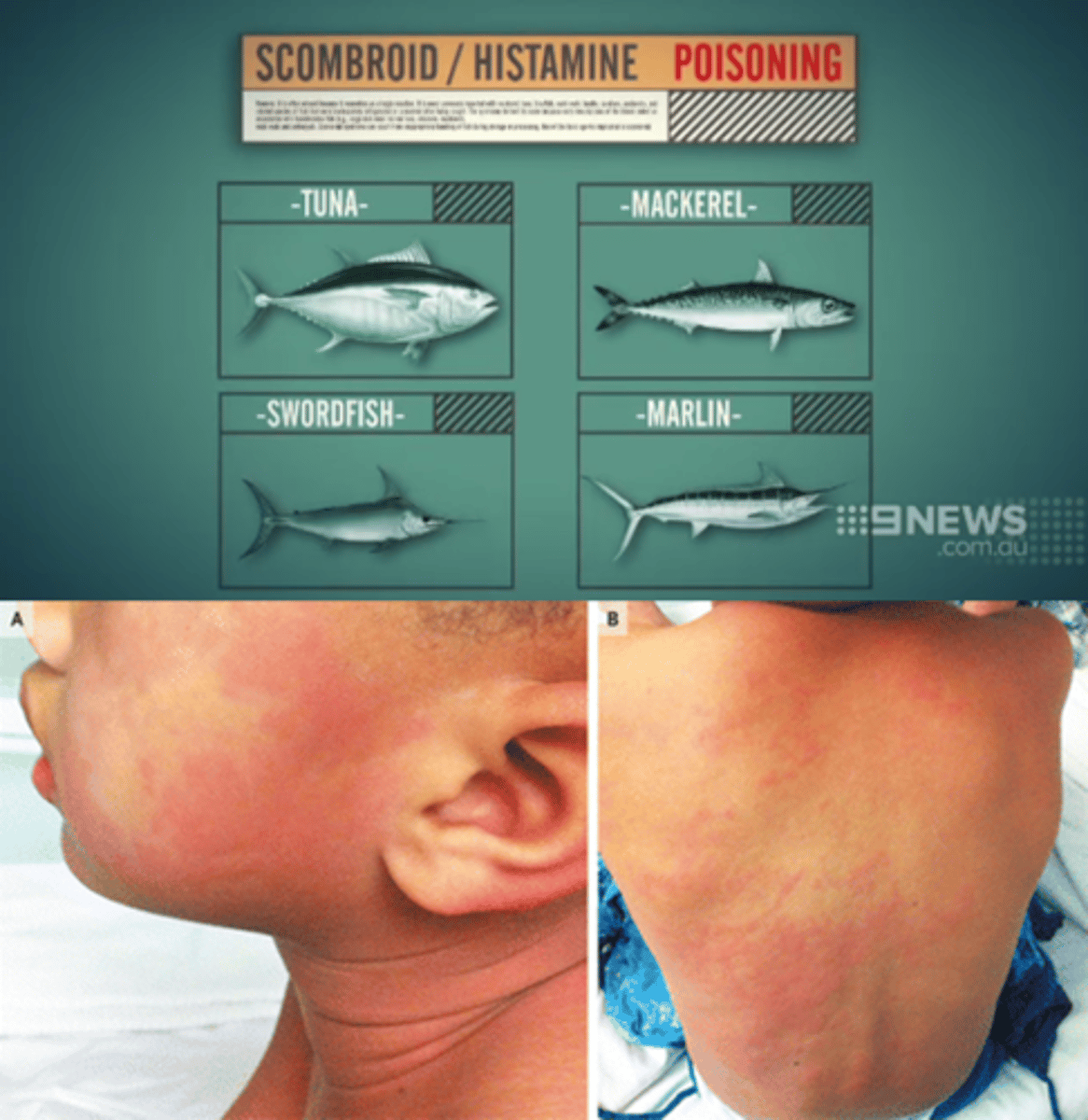
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient who presents with
-acute onset of flushing,
-a throbbing headache,
-palpitations and
-abdominal cramps
30 minutes after eating fish?
His two friends who had the same dinner in the restaurant with him had similar but milder symptoms.
Scombroid poisoning
(vs. acute allergic reaction: no similar symptoms in the patient's friends)
What herbal medication causes hypertension, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis?
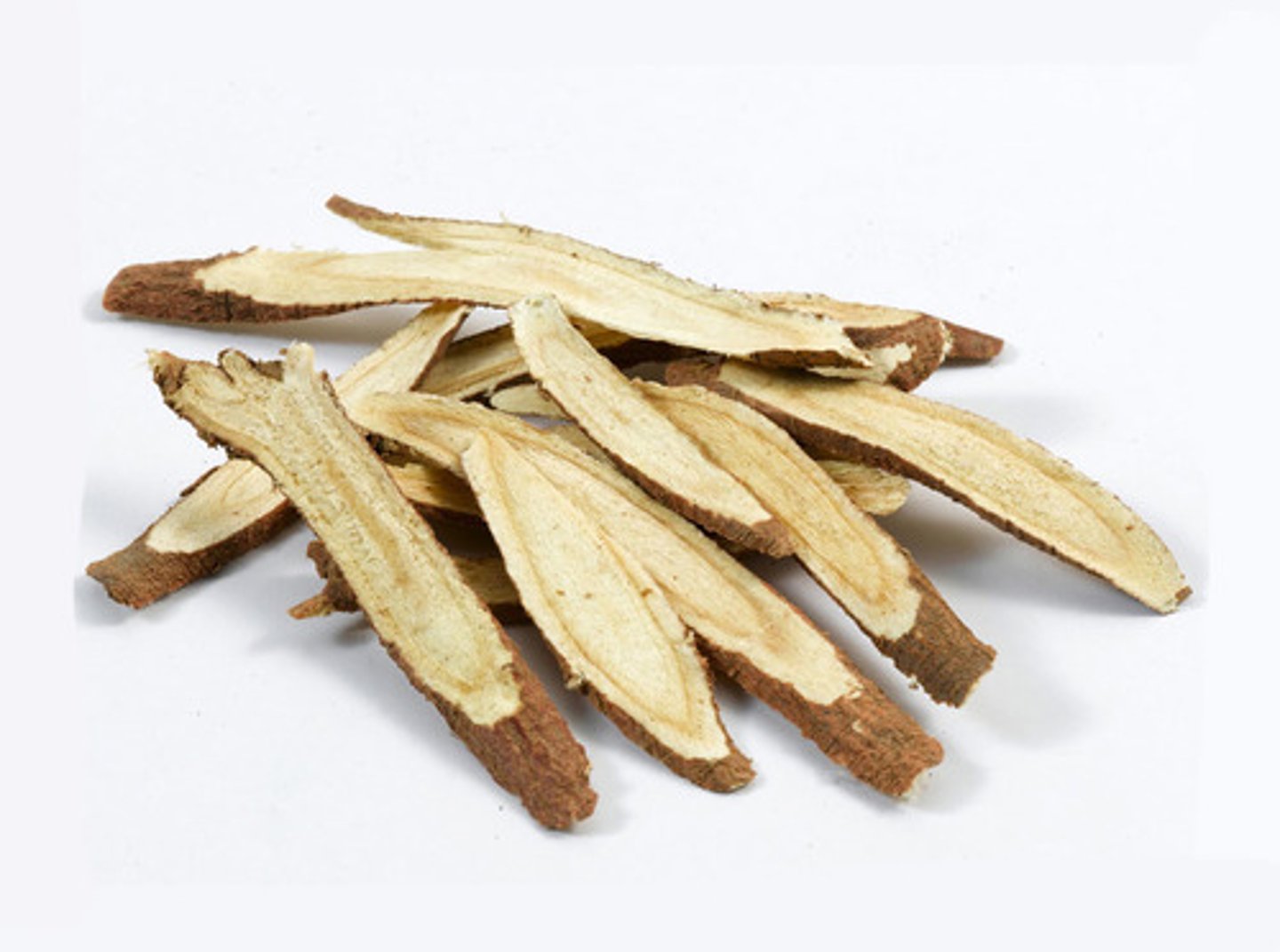
Licorice root
(inhibit the conversion of cortisol to cortisone. The excess cortisol binds to mineralocorticoid receptors.)

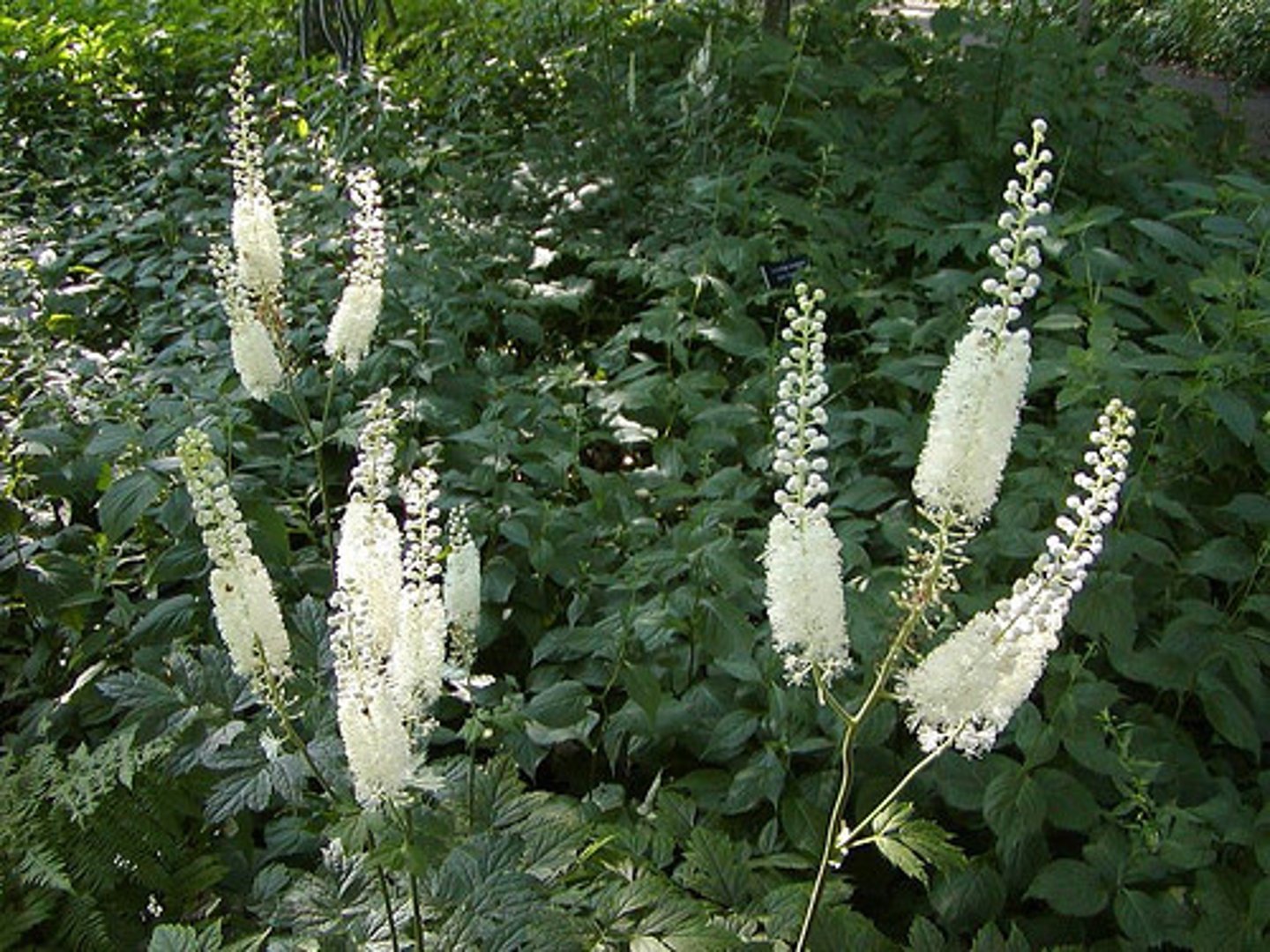
.................... has been promoted for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is generally safe, although it has been associated with possible hepatotoxicity.
Black cohosh

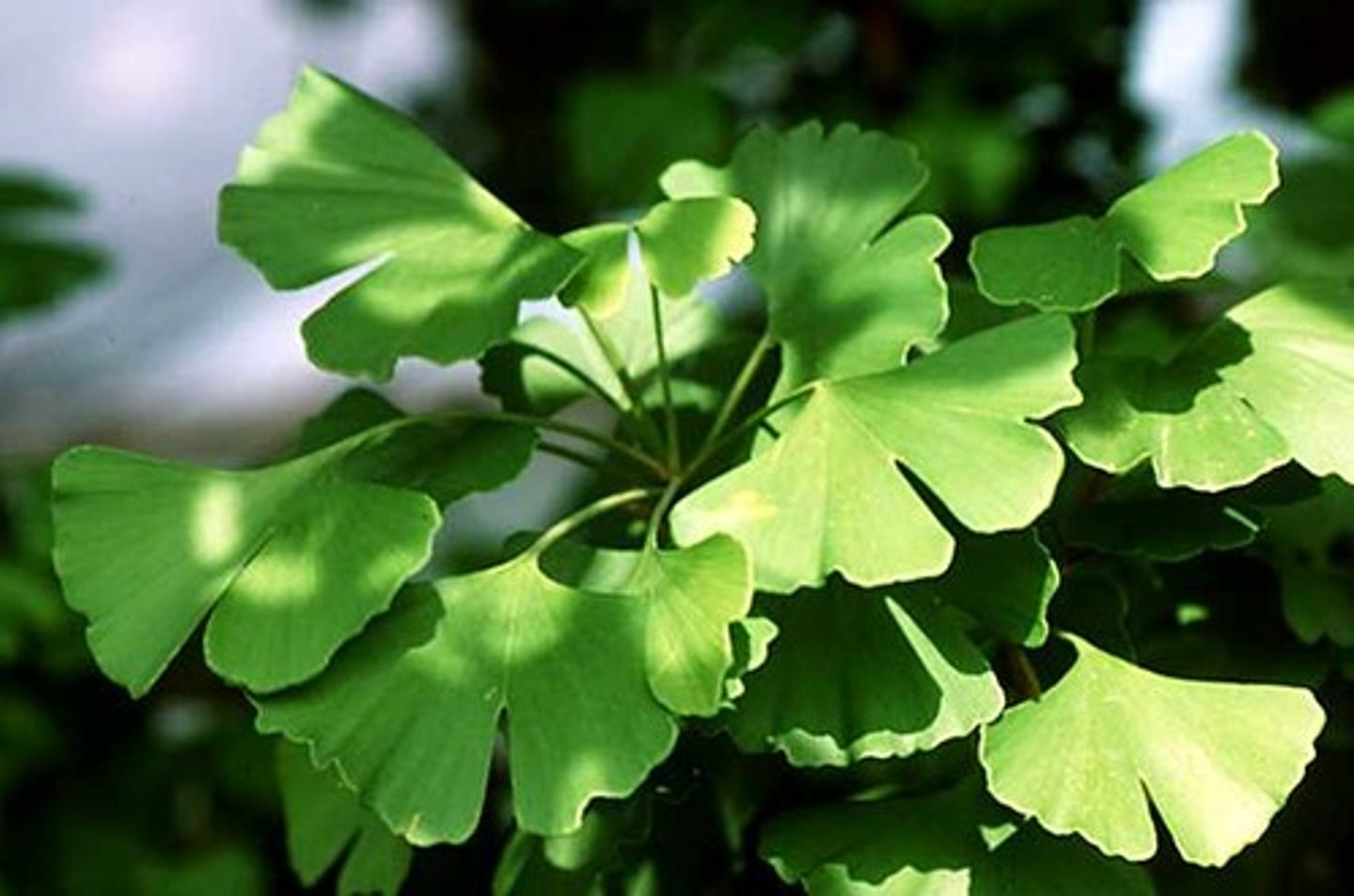
.............. has been advocated for the treatment of mild memory loss and dementia. Potential adverse effects include an increased risk of bleeding, especially in patients who take aspirin or other antiplatelet drugs.
Ginkgo

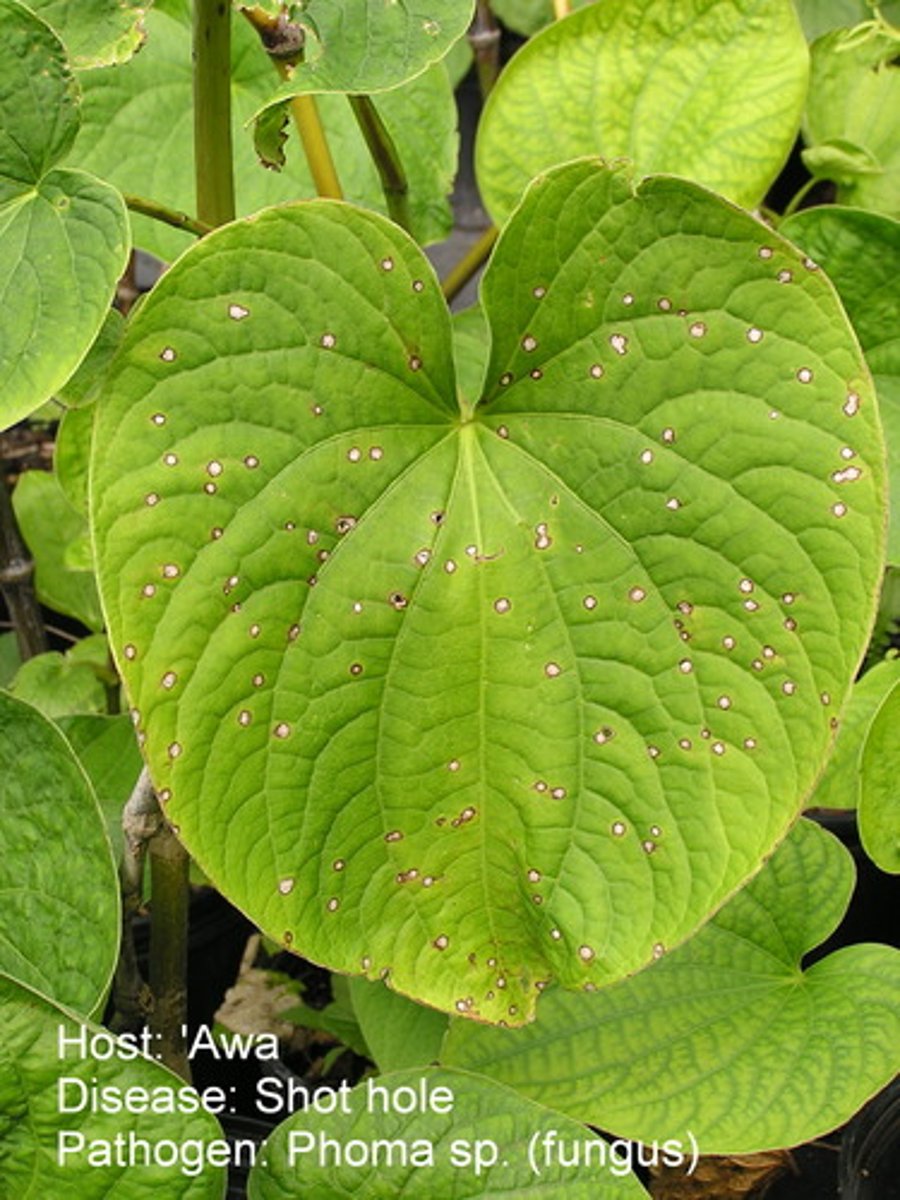
.................. is a supplement that has been used for anxiety and insomnia but may result in hepatoxicity and liver failure several weeks or more after intake.
Kava kava

Saw palmetto is a popular herbal preparation most often used by men to treat ..................
benign prostatic hyperplasia.
(In at least one case, significant bleeding during surgery was attributed to saw palmetto.)
