India: Political History and Notable People (inc. Politicians, Generals, Inventors, Explorers, etc.)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1700 BCE - 28 BCE - Maghada Kingdom / Empire (All Facts)
Located in North India
The history of the monarchs of Magadha, particularly in the Pre-Mauryan period, is shrouded in mystery and legend with various sources claiming different things
1700 BCE - 682 BCE - Brihadratha Dynasty (All Facts)
1st Dynasty of Ancient India
544 BCE - 413 BCE - Haryanka Dynasty (All Facts)
2nd Dynasty of Ancient India
544 BCE - 492 BCE - Bimbisara (All Facts)
1st King and Founder of the Haryanka Dynasty
Led the Kingdom of Magadha against the Vrjji in a war over the Ganges River Valley, which he won
Was a firm friend of Buddha
Established a hierarchical system of administration whose goal was to
maintain order in the provinces
organize the collection of taxes
492 BCE - 460 BCE - Ajatasatra / Ajatashatru (All Facts)
2nd King of the Haryanka Dynasty
Deposed his father and had him imprisoned before making himself king
Secured the final defeat of the Vrjii people
Fortified his capital at Rajagrha
Built a fort at Pataligrama
400’s BCE - Panini (All Facts)
Indian scholar who analyzed and organized the grammar of the Sanskrit language, having formulated 4,000 grammatical rules
322 BCE - 185 BCE - Mauryan Empire (All Facts)
Dynasty of Notable Kings including
Chandragupta
Bindusara
Ashoka
Brihadratha
322 BCE - 298 BCE - Chandragupta Maurya (All Facts)
1st King and Founder of the Mauryan Dynasty / Empire
Destroyed the previous Nanda Dynasty in the Ganges River Valley and consolidating and controlling much of central and northern India
Unified the Indian sub-continent
Established the Mauryan capital at Pataliputra (Patna) in the east of the country
Organized northern India into 16 large states under one monarch but with decentralized government, in which daily decision-making was relegated to local deputies
Under his rule, Buddhism and Jainism greatly flourished
Signed a peace treaty with Seleucus Nicator and the Seleucid Empire in 302 BCE, which established friendly relations between the two empires
Before he did this, he had initially fought against him and Alexander the Great’s Greek garrisons, of which he drove out of India
After he did this, he also exchanged gifts and ambassadors with Seleucus Nicator
Near the end of his reign, he converted to Jainism
Abdicated his kingship to become a Jain monk, in which he claimed he was firmly resolved to pursue an ascetic existence for the rest of his life
Gave the throne to his son
298 BCE - 272 BCE - Bindusara (All Facts)
2nd King of the Mauryan Dynasty / Empire
268 BCE - 232 BCE - Ashoka the Great (All Facts)
3rd King of the Mauryan Dynasty / Empire
Converted to Buddhism
Shocked by the horrors of the Kalinga War, in which 100K were slain
He merged spiritual and temporal power in order to establish a state based on “universal order”
Made his conversion clear across all the rocks and stone pillars erected during his rule with inscriptions announcing his conversion
These rocks and pillars wrote that he pledged that he would rule his empire through the principles of kindness, liberality, truthfulness, and purity of deed and thought
Was the first Indian monarch to be converted to Buddhism
Ruled over a vast empire that was divided into four provinces, each administered by a prince of royal blood
Divided his population into seven castes
Brahmans monopolized spiritual power
Kshatriyas monopolized temporal power
Rule was
Paternal
Carried out by a centralized bureaucracy
Built Stone Palaces at Pataliputra, the capital of the Mauryan Empire
Founded monasteries
Founded the Shrine of Sanchi in the state of Madhya Pradesh, which became one of the great religious centers of Indian Buddhism after his death
Financed irrigation schemes
Established public health services
Created a welfare state
Based on the teachings of the Buddha
Impoverished the treasury
Practiced the principle of universal toleration to all religions in his kingdom
In other words, he allowed tolerance of other religions within the empire during his reign
Administered enlightened policies, which arguably sowed the seeds of decline of the Empire whose peak was represented by his rule, including
Concentration of power which created an administration that was too brittle and distant to adapt to changing circumstances
War with Bactria, a Greek kingdom, made him and his Empire suffer greatly
He lost the Punjab region from it
187 BCE - 185 BCE - Brihadratha (All Facts)
9th and Final King of the Mauryan Dynasty / Empire
Assassinated by his commander-in-chief at a military review who would succeed him and found a new imperial dynasty
His death seemed inevitable, the logical conclusion of the decline of the Mauryan Dynasty / Empire
185 BCE - 75 BCE - Shunga Dynasty / Empire (All Facts)
Dynasty of Notable Kings including
Pushyamitra
185 BCE - 149 BCE - Pushyamitra Shunga (All Facts)
First King and Founder of the Shunga Dynasty / Empire
165 BCE - 130 BCE - Menander (All Facts)
Indo-Greek king who ruled parts of India
Was a contemporary of the Shunga Emperors, although he ruled over a different part of the Indian lands
Led an expedition into the Ganges River Valley reaching Pataliputra (Patna)
Best remembered for his conversion to Buddhism by a scholar-priest named Nagasena
100s BCE - 200s CE - Satavahana / Andhras Empire / Dynasty (All Facts)
Empire / Dynasty of India founded by Simuka
It covered modern-day Central India
30 CE - 375 CE - Kushan Empire (All Facts)
Empire / Dynasty of India founded by Kujula Kadphises
It covered modern-day Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Western Nepal, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan
25 CE - 85 CE - Kujula Kadphises (All Facts)
First King and Founder of the Kushan Empire / Dynasty of India
He laid the basis for the Kushan Empire / Dynasty after he forcibly established unity among the five Indo-European tribes in Bactria known as the Yuezhi and seized control of the Kabul Valley and adjacent regions from the Pahlavas
He set himself up as ruler of Bactria and Sogdiana
By the end of his reign, the Kushan Empire stretched from beyond the Hindu Kush to northwest India
He died and was succeeded by his son
113 - 127 - Vima Kadphises (All Facts)
3rd King of the Kushan Empire
Conquered and ruled over the north of India as far as Benares and the Indus River Delta and eventually extended his kingdom’s possessions in India as far as Mathura
He sent a delegation to Rome to arrange a surprise attack on the Parthian Empire
127 - 150 - Kanishka the Great (All Facts)
4th King of Kushan
Under his reign,
Buddhism flourished across the Kushan Empire
He presided over the Fourth Buddhist Council
He sent a delegation to Rome to arrange a surprise attack on the Parthian Empire
100s - Gautamiputra Satakarni (All Facts)
King of the Satavahana Empire and the Andhra Dynasty
Under his reign, he and his dynasty occupied the whole o central India from coast to coast
Destroyed the Saka Kingdom of Maharashtra near Bombay
He and his dynasty dominated the eastern Dekhan region, between the Godavari and Krishna Rivers since 100 BCE
150 - 190 - Huvishka (All Facts)
5th King of Kushan
During his reign, the Kushan Empire had a golden age
275 - 897 - Pallava Dynasty (All Facts)
Dynasty remembered for its
great sculptures and reliefs in the Mahabalipuram caves
its countless “rathas”
its magnificent temples
Constant conflict with the Pandyas, a neighboring empire, weakened it and the Pandyas
The emergence of the Chola Empire in the 800s further weakened it
They eventually allied with the Chola Empire to destroy the Pandyas, only to be destroyed themselves by the Chola who killed their king and army
320 - 550 - Gupta Empire (All Facts)
Founded by Chandragupta
Dynasty which oversaw
Tolerant rulers
The transformation of Hindu art into Buddhist art
The building of the first small temples
The peak of Buddhist artistic development, with distinct iconography
Dynasty which oversaw
The Golden Age or “Classical Era” of Indian history
Upon its collapse, disunity returned to the region for most of the next 1,000 years in which Northern and Southern India developed separate political structures
320 - 335 - Chandragupta (All Facts)
First Emperor and Founder of the Gupta Empire
335 - 375 - Samudragupta (All Facts)
2nd Emperor of the Gupta Empire
He ruled the largest empire yet seen by India
Extended his rule from a tiny kingdom to an empire dominating all northern and central India and into the Ganges plain
He was a warrior leader who fought against and defeated
The Vakatakas in central India
The Nagas in northern India
The Maghas of Kausambi
The Kosalas of the Ganges
The Kushan Empire (its remnants)
Other territories he consolidated under his rule came through
Strategic marriages
Political alliances
He used his family to govern his provinces
He maintained compliant rulers in his tributary nations
Known as the “Poet King,” he was a patron of the arts
Tributes that extolled his virtues were engraved on the stone pillars of Ashoka the Great of the Mauryan Empire
Under his reign, the common people had a currency of gold coins which depicted him playing the lute
Although a fervent worshipper of Vishnu (Hindu), he maintained a policy of religious toleration
On his return from an expedition in the Dekhan, he performed the ancient Vedic ritual of Ashvamedha (horse sacrifice), which had been abandoned since the 100s CE
In so doing, he proclaimed himself universal monarch
375 - 415 - Chandragupta II (All Facts)
3rd Emperor of the Gupta Empire
Under his reign of tolerance,
Sanskrit literature enjoyed a renewal, especially when the namesake named the poet Kalidasa as one of his “nine jewels”
415 - 455 - Kumaragupta (All Facts)
4th Emperor of the Gupta Empire
455 - 467 - Skandagupta (All Facts)
5th Emperor of the Gupta Empire
During his reign, he successfully defended his empire against the Hephtalite Huns
Upon his death, the Gupta Empire began to dissolve under pressure from the Hephtalite Huns, who had by that point conquered a large part of western India
476 - 495 - Budhagupta (All Facts)
8th Emperor of the Gupta Empire
Upon his death
the empire continued due to decline due to the advancement of the Huns
various small kingdoms within the empire tried in vain to lay claim to the Gupta Dynasty
543 - 753 - Chalukya Dynasty (All Facts)
Repulsed by the Rashtrakuta Dynasty by 907, they regrouped around the Vengi
630 - 668 - Narasimhavarman (All Facts)
Pallavan Emperor who ruled when Pallavan art, literature, and political power was at its zenith
606 - 647 - Harsha of Kanauj (All Facts)
Emperor of Kanauj
He inherited a small principality north of Delhi
He gradually built a vast empire in northern India, which stretched from the Indus River Valley in the West to Orissa in the East
Unified India under one ruler
He was known for his letters and his three dramas, written in Sanskrit
He was a disciple of Shiva (Hinduism)
Despite this, one of his three dramas showed his interest in Buddhism
After his death, India fragmented into tiny states
He had created an empire in the north comparable to the previous Gupta Empire
647 - 1200s - Rajput Kingdoms (All Facts)
Series of successor states in northern India during the Middle Ages / Medieval Ages which gradually formed and changed in northern India and present-day Pakistan representing the much greater upheaval experienced by northern India compared to southern India during the Middle Ages / Medieval Ages
These kingdoms were all
Located in northern India
Hindu
Led by leaders of numerous clans who were often at war with one another
Because of the competition among clans, no centralized government arose
This demonstrates the diversity and regionalism of South Asia at the time, the lack of a centralizing power leaving the kingdoms vulnerable to attacks by the Muslims
Its princes skillfully wielded their power to limit the Muslim conquerors’ influence in the region
By the 1000s, however, Islamic forces had plundered their Hindu Temples and Buddhist shrines for their riches, erecting mosques on previous Hindu and Buddhist holy sites throughout northern India, much to the anger of followers of those faiths
730 - 1036 - Gurjara Pratihara Dynasty (All Facts)
Dynasty which is remembered for its successful repulsion of the Arab-Muslims from it ten years into its ascendancy
700s - 1500s - Chandela Empire / Dynasty (All Facts)
Empire which reached new heights of influence and prosperity around 950
753 - 982 - Rashtrakuta Empire (All Facts)
Ruled most of the Indian subcontinent
Ruled by Maharajas (Kings)
By 907, they occupied most of the Dekhan Plateau, in which they repulsed the Chalukyas to the east, who regrouped around Vengi
756 - 774 - Krishna (All Facts)
2nd Maharaja of the Rashtrakuta Empire
Oversaw the construction of the Temple of Kaliasa at Ellora
This was carved entirely out of the living rock, as if it were a statue
750 - 1161 - Pala Empire (All Facts)
Empire / Dynasty founded in Bengal and Magadha
731 - 796 - Nandivarman II (All Facts)
King of the Pallava Dynasty
736 - 1152 - Tomara Dynasty (All Facts)
Founded the city of Delhi in India in 994
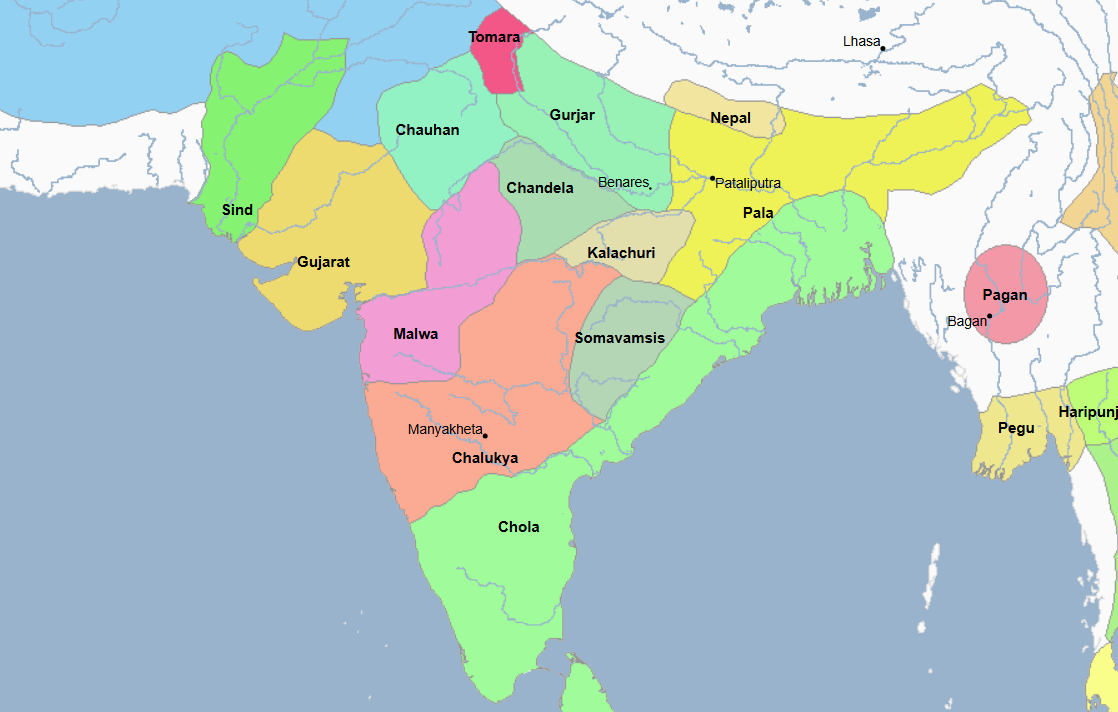
831 - 1315 - Chandela Dynasty (All Facts)
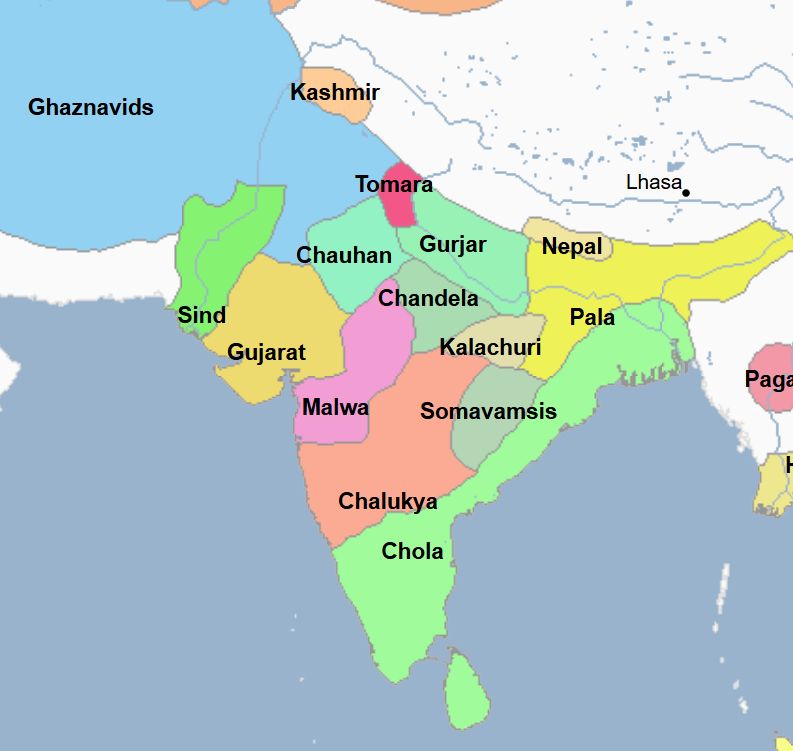
848 - 1279 - Chola Empire (All Facts)
Founded by King Vijayalaya
Located in Tamilnadu
By 888, they had displaced the Pallava Dynasty
By 985, they achieved hegemony over the Dekhan and part of the Indian Ocean
By 1024, their “Tamil Kings” unified southern India and took Ceylon (Sri Lanka) and Bengal (Bangladesh)
It represented southern India being more stable than northern India during the Middle Ages / Medieval Ages
Under this Empire, improved meta-casting techniques enabled notable achievements in figurative images, especially in portraying the complex and balanced poses of the dancing Shiva
848 - 871 - Vijayalaya Chola (All Facts)
First Emperor and Founder of the Chola Empire
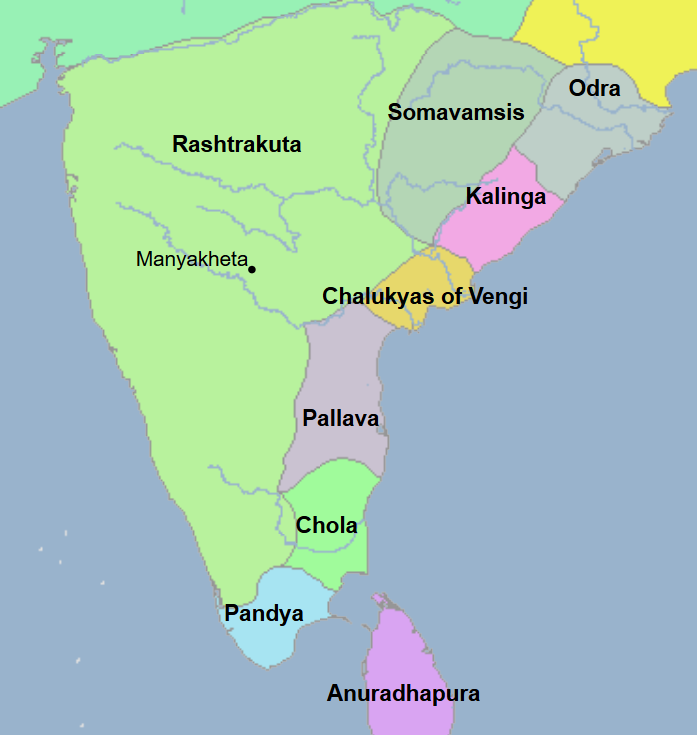
880 - 897 - Aparajita Varman (All Facts)
Final King of the Pallava Dynasty
He was killed in battle, leading his army on his war elephant
871 - 907 - Aditya (All Facts)
2nd Emperor of the Chola Empire
The land he inherited upon his assumption to the throne was an impoverished statelet squashed between the Pallavas and the Pandyas
He astutely played the Pallavas and the Pandyas against each other, dividing them and then conquering and defeating both the Pallavas and the Pandyas
He expanded his empire until it embraced all of southeast India, for which his son would inherit, becoming one of the most powerful empires in India
He married a Pallavan princess
His sepulcher and namesake temple had its foundations laid down at Tondaimanad near Kalahasti
985 - 1014 - Rajaraja (All Facts)
8th Emperor of the Chola Empire
He was nicknamed “The Great”
He made the Chola Empire the most supreme in southern India at the time
Under his reign,
The Chola Empire had extended its domains to all of southern India and became the most powerful and prosperous region of India
He reasserted the Empire’s power after it had previously lost territory, turning south and defeating a revived Pandya power
He then invaded Sri Lanka
He then fought and defeated the Gangas
He reduced the powerful Vengi state to the north to a mere protectorate
He oversaw the construction of the Brihadisvara Temple that was 200 feet high and completed in the capital Thanjavur, a symbol of Chola grandeur
He built a navy that dominated the Indian Ocean, making the Chola Empire rich from trade with China and the Near East
1014 - 1044 - Rajendra (All Facts)
9th Emperor of the Chola Empire
Under his reign,
He and his forces conquered Sri Lanka
He and his forces invaded Bengal
He oversaw
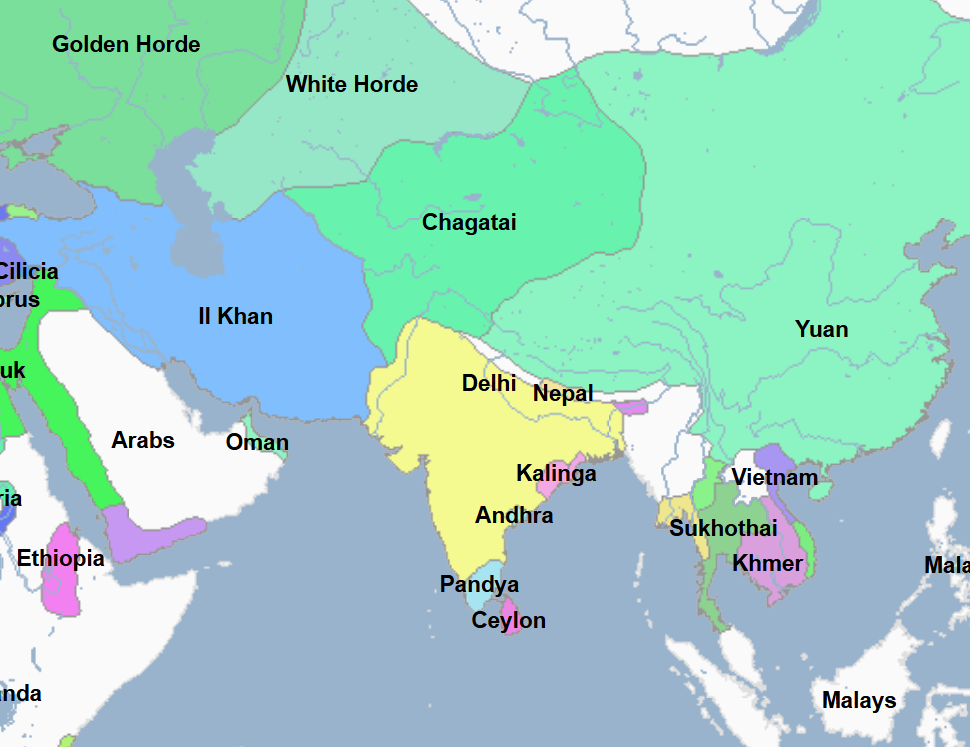
1206 - 1526 - Delhi Sultanate (All Facts)
Dynasty which brought Islam into India, it was the first to do so
Dynasty which began when Islamic forces managed to conquer the namesake Indian city
Dynasty which reigned for 300 years
Throughout its reign
The interaction of Islam and Hinduism in northern India dominated its political history where some Hindus converted to Islam, while others resented Islam and considered Muslims foreigners
It never organized an efficient bureaucracy (like that of the Chinese), so its sultans had difficulty imposing their policies in a land as vast and diverse as India
Despite the strong Islamic presence throughout the regions it controlled, local kingdoms continued to play a major role in India’s decentralized political landscape
They successfully defended themselves against the Mongols, preventing the Mongols from conquering South Asia
However, by the end of their reign, their sultans lost power to the Mughal Empire, whose leaders were descended from Mongols
1336 - 1646 - Vijayanagara Empire (All Facts)
Empire which began with the arrival of two brothers, Harihara and Bukka, from the prior / concurrent Delhi Sultanate in north-central India
The brothers were sent to the area because the Delhi Sultanate wanted to expand its rule to southern India
The brothers were born Hindu but converted to Islam for the sake of upward mobility
When they left the region controlled by the Delhi Sultanate, they once again embraced the religion of Hinduism and established their own Hindu Kingdom
It was Hindu
Its name comes from the word for “the victorious city”
It fell due to Muslim invaders which eventually overthrew it