Types of Inheritance Patterns in Genetics: Mendelian, Non-Mendelian, and Gene Interactions
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Simple Mendelian
Dominant/recessive relationship
X-linked
Involves inheritance of genes on the X-chromosome
Incomplete penetrance
dominant allele does not influence the outcome of a trait in a heterozygote individual
Sex-influenced inheritance
Recessive dominant phenotype not expressed even in one sex, dominant in the other.
Incomplete Dominance
Heterozygote has intermediate phenotype between corresponding homozygotes.
Sex-limited inheritance
Traits only in one sex (ex. breast development in females, facial hair in males).
Overdominance/Heterozygous advantage
Heterozygote has a trait more beneficial than either homozygote.
Lethal alleles
An allele that has the potential to cause death in an organism.
Codominance
Heterozygote expresses both alleles; w/o intermediate phenotype.
Epistasis
Alleles of one gene mask the phenotypic effect of alleles of a different gene.
Complementation
Two parents with same recessive phenotype produce offspring with a wild-type phenotype.
Gene modifier effect
Alleles of one gene modifies the phenotypic outcome of alleles of a different gene.
Gene redundancy
Loss of function in a single gene has no phenotypic effect.
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Additional patterns of inheritance that deviate from a Mendelian pattern.
Epigenetic Inheritance
A pattern in which a modification occurs to a nuclear gene or chromosome that alters gene expression.
Dosage Compensation
Offsets differences in the number of active sex chromosomes.
DNA methylation
An enzymatic modification performed by DNA methyltransferases.
Histone methylation
Genes are silenced because methylation results in formation of heterochromatin.
Barr body
Highly condensed structure in the interphase nuclei of somatic cells in females.
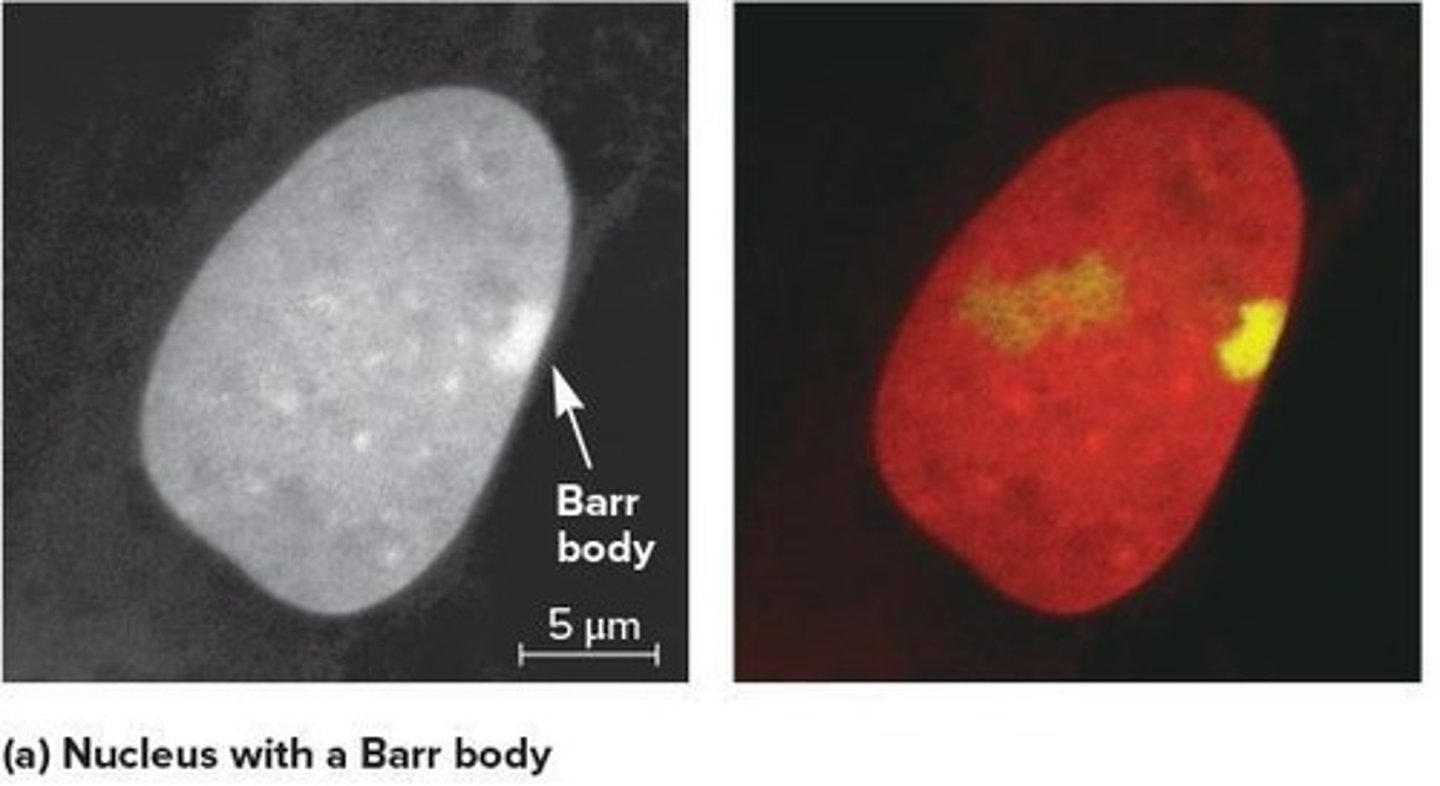
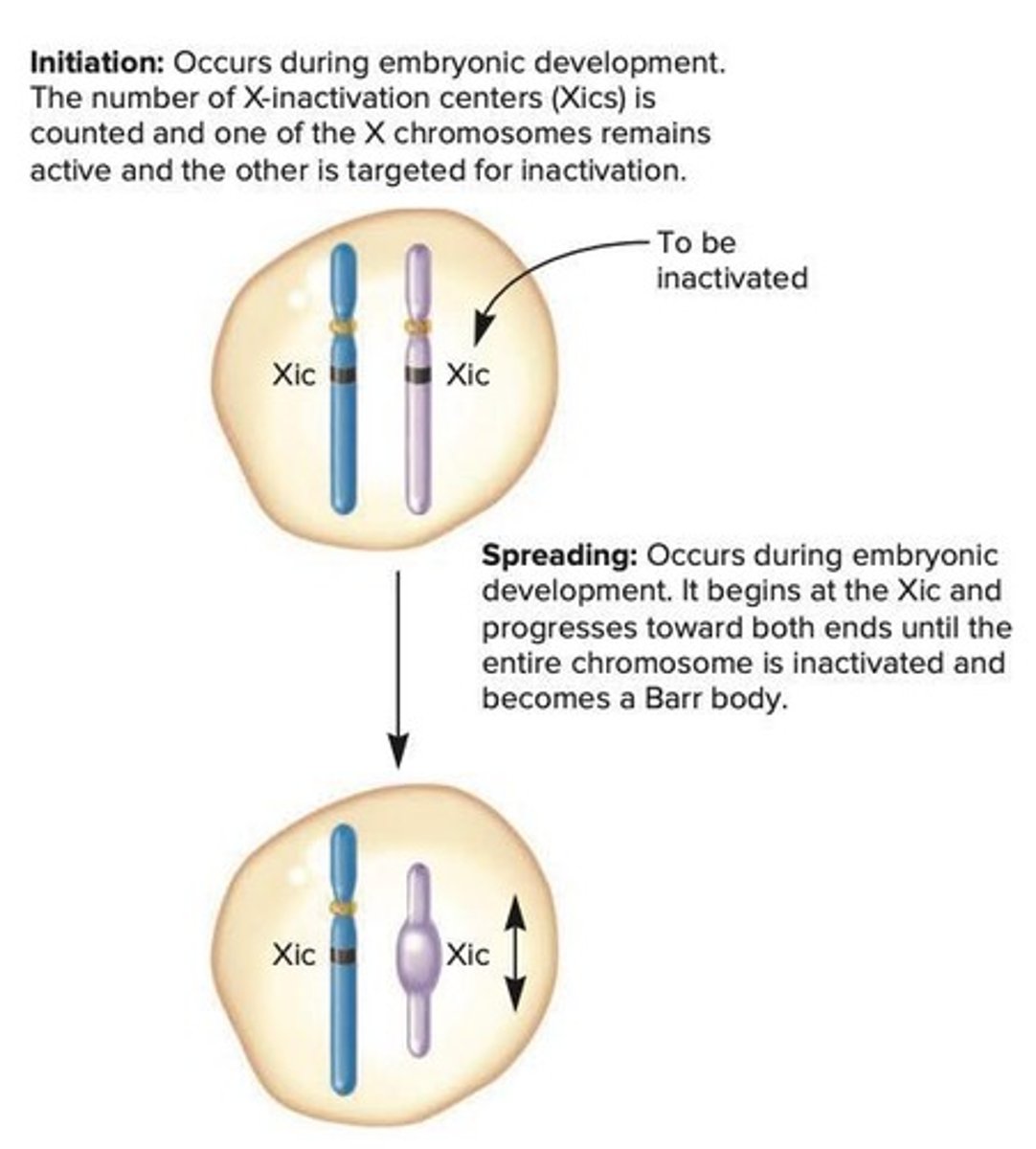
X-chromosome Inactivation
Random X inactivation occurs early in development.
Genomic Imprinting
A segment of DNA is marked and the effect is maintained throughout the life of the organism.
Igf2 Gene
The Igf2 gene for growth hormone: insulin-like growth factor 2.
Functional Igf2
Normal size.
Imprinting
The paternal allele is transcribed into RNA while the maternal allele is not transcribed and not expressed.
Igf2-
A loss-of-function allele: no functional Igf2 protein.
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
Characterized by reduced motor function, obesity, and small hands and feet.
Angelman Syndrome (AS)
Characterized by hyperactivity, thinness, unusual seizures, repetitive symmetrical muscle movements, and mental deficiencies.
Methylation
Causes inhibition of transcription.
Maternal Effect
Involves genes in the nucleus where the genotype of the mother directly determines the phenotype of her offspring.
Extranuclear Inheritance
Inheritance patterns involving genetic material outside the nucleus.
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Females pass mitochondria to all their children; sperm do not contribute mitochondria.
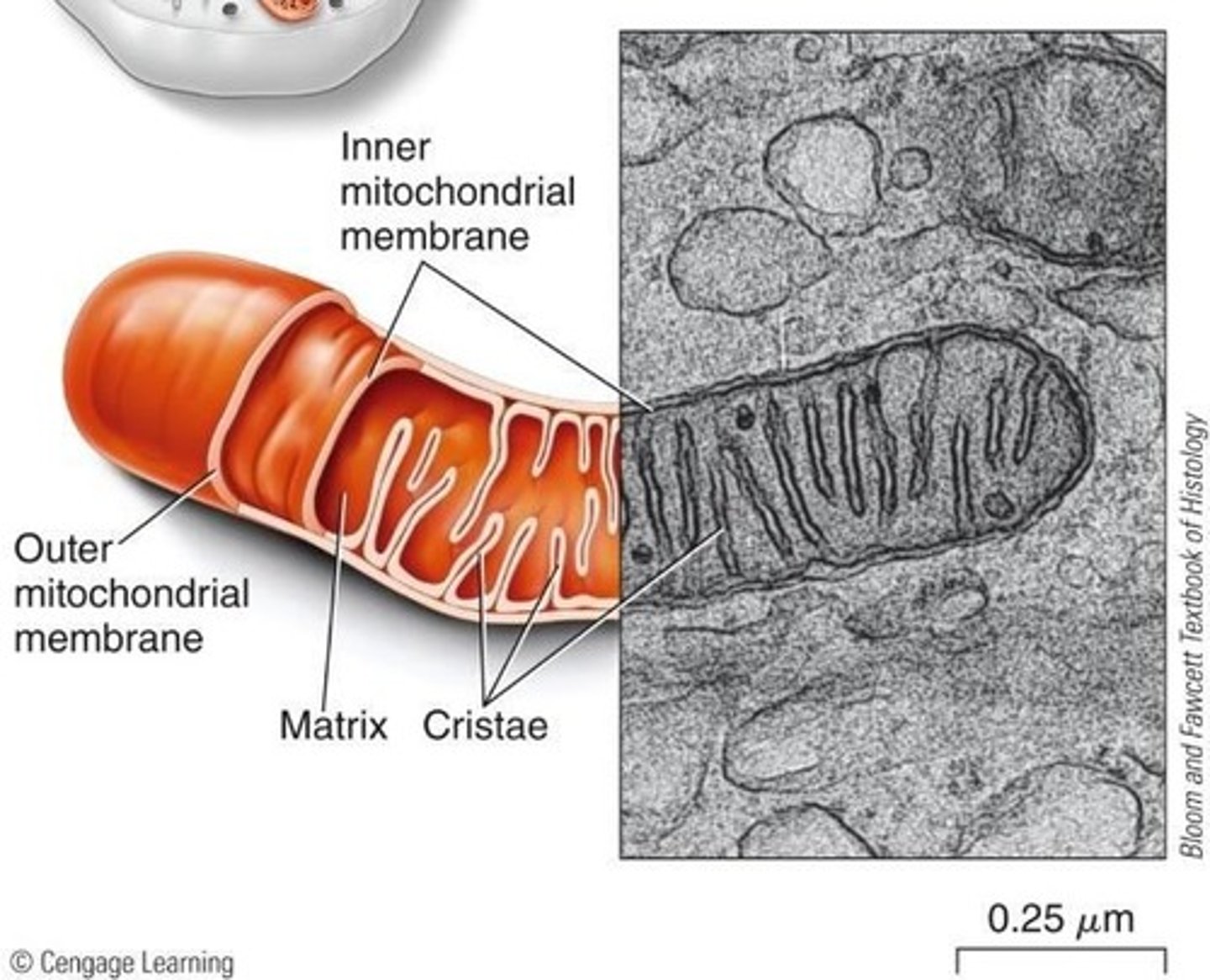
Mitochondrial DNA
Most mitochondrial proteins are encoded by genes in the nucleus.
Chloroplast DNA
The genetic material in chloroplasts (cpDNA) is approximately 10 times larger than the mitochondrial genome of animal cells.
Maternal Inheritance
Pigmentation in Mirabilis jalapa depends only on the maternal parent.
Green Phenotype
The wild-type that makes green pigment.
White Phenotype
The mutant that prevents synthesis of the green pigment.
Probability of Genotype AA bb Dd ff
What is the probability that an offspring will have the genotype AA bb Dd ff?
True-breeding Tall Pea Plant
What is the probability that an F1 individual will be true-breeding?
Inverted Chromosome
An inverted chromosome has a specific sequence that can yield different products if a crossover occurs.
Chromosomal Deletion
Which disorder results from the chromosomal deletion represented in the image?
Deletion Type
What type of deletion is this?
Simple Mendelian inheritance
A single gene with two different alleles that display a simple dominant/recessive relationship.
Wild-type (WT) alleles
Prevalent alleles in a population that function normally and are made in the proper amounts.
Mutant alleles
Alleles that have been altered by mutation and are defective in their ability to express a functional protein.
Simple dominant/recessive relationship
The recessive allele does not affect the phenotype of the heterozygote.
Examples of recessive human diseases
PKU, cystic fibrosis, Albinism, Tay-Sachs disease.
Penetrance
How many individuals in a population carrying a particular allele of a gene also express an associated trait.
Polydactyly
An autosomal dominant trait characterized by additional fingers and/or toes.
Expressivity
The degree to which a trait is expressed, indicating how severe the trait is.
Marfan syndrome
A condition caused by a dominant mutation in the fibrillin 1 (FBN1) gene, affecting connective tissue.
Dominant Mutants
Less common than recessive mutants and can be gain-of-function or dominant negative.
Gain-of-function mutants
Mutants that exhibit a new or abnormal function.
Dominant negative
A mutant allele that inhibits the activity of the wild-type protein.
Overdominance
Heterozygote is more vigorous than both of the homozygotes.
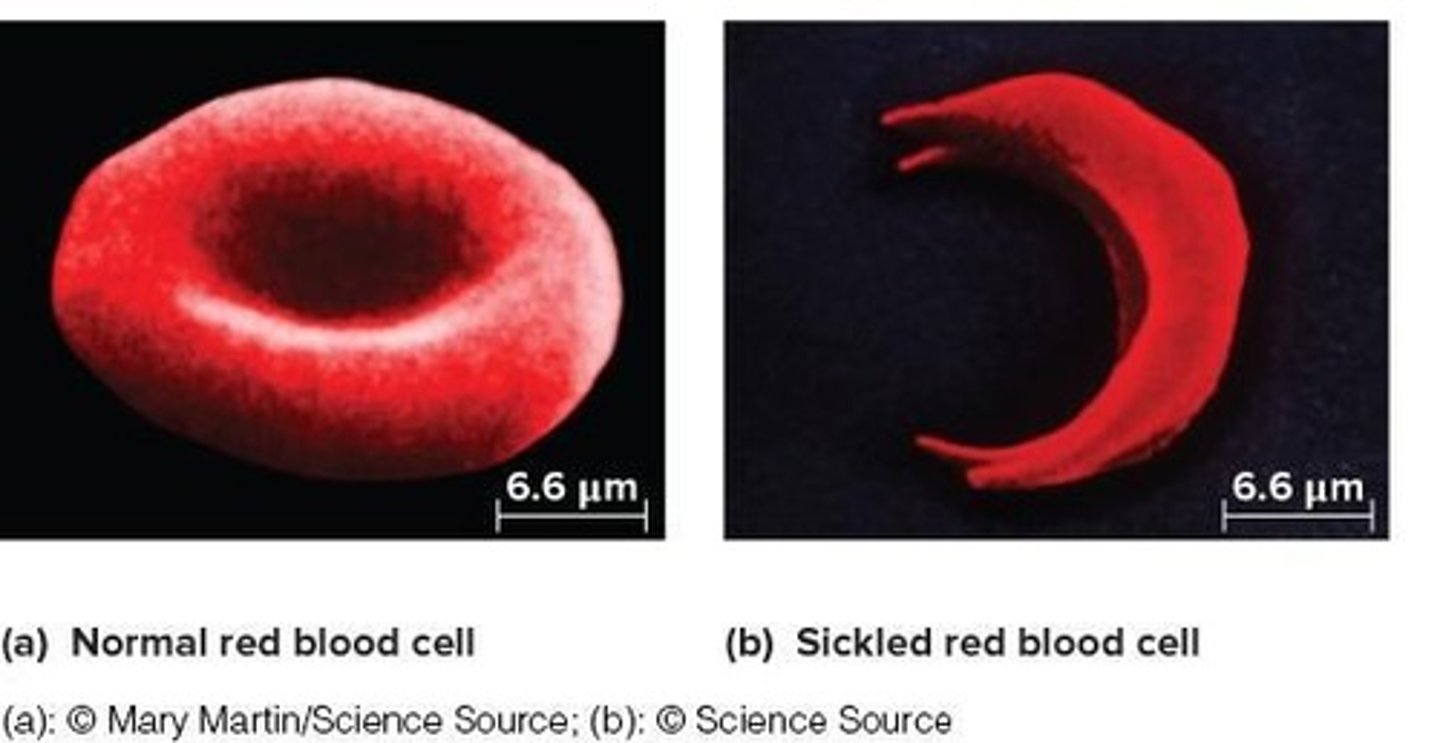
Sickle-cell anemia
An autosomal recessive disorder where affected individuals produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin.
Environmental effects on gene expression
Environmental conditions may impact the phenotype of the individual.
Temperature-sensitive allele
An allele whose expression is influenced by temperature.
Multiple Alleles: The ABO blood group
A system where antigens are present on the surface of red blood cells, with multiple alleles involved.
Antigen A
Encoded by the IA allele and recognized by the immune system.
Antigen B
Encoded by the IB allele and recognized by the immune system.
Sex-linked traits
Traits governed by genes on the sex chromosomes, such as color blindness and hemophilia.
X-linked traits
Traits that are hemizygous in males, making them more likely to be affected.
Y-linked traits
Traits transmitted only from father to son, with relatively few genes in humans.
Sex influenced traits
Traits that differ in expression between males and females but are not on sex chromosomes.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
A genetic disorder characterized by progressive muscle degeneration, often affecting males.
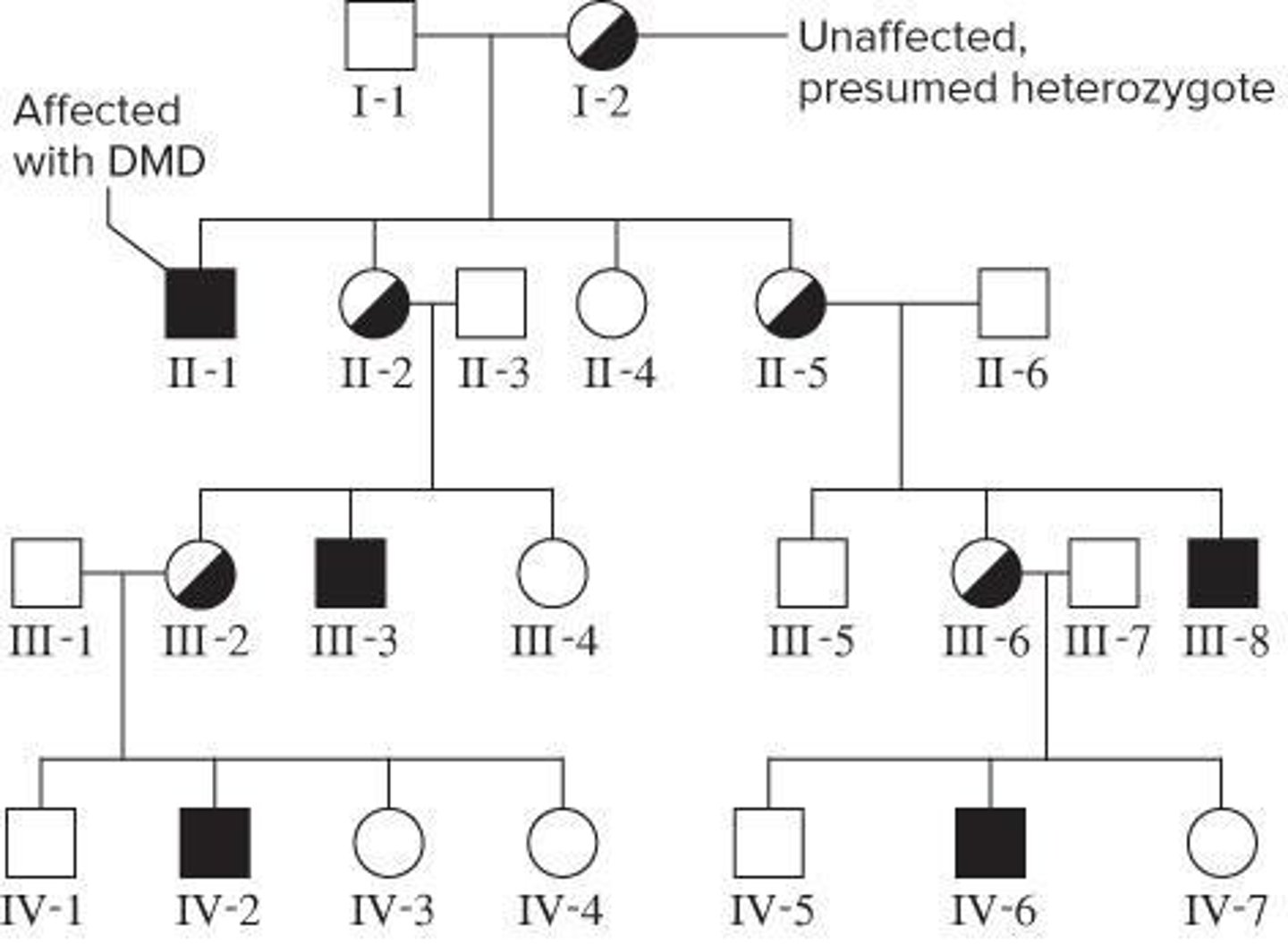
X-linked Inheritance
Affected mostly males that are affected with their mothers as carriers.
Pseudoautosomal Inheritance
Inheritance pattern is the same as the inheritance pattern of a gene on an autosome even though the gene is on the sex chromosomes.
Mic2 Gene
Encodes a cell surface antigen and follows pseudoautosomal inheritance.
Sex-influenced Trait
Allele is dominant in one sex but recessive in the opposite sex.
Scurs in Cattle
Sc is dominant in males, but recessive in females.
Dominant Lethal
Huntington's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that results in death.
Recessive Lethal
Cystic fibrosis.
Conditional Lethal Alleles
May kill an organism only when certain environmental conditions prevail.
Inheritance of Capsule Shape in Shepherd's Purse
Triangular capsule shape requires a dominant allele in one of two genes, but not both.
Gene Interactions
Two or more different genes influence the outcome of a single trait.
Height Genetic Contribution
60-80% genetic and 20-40% environmental.
Phenotype in Males (Scurs)
SS: Scurs, Ss: Scurs, ss: No scurs.
Phenotype in Females (Scurs)
SS: Scurs, Ss: No scurs, ss: No scurs.
Mendelian Inheritance Patterns Involving Two Genes
Epistasis, Complementation, Gene modifier effect, Gene redundancy.
Phenotypic Ratio in Epistasis
F2 generation phenotypic ratio is 9 purple: 7 white.
Agouti Gene in Mice
Heterozygous for the agouti yellow allele: yellow coats; homozygous for the agouti yellow allele: dead.