year 10 geography
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Environmental Worldview
How people think the world works, what they think their role in the world should be, and what they believe is right and wrong environmental behaviour (environmental ethics).
ecological services
any beneficial natural process from ecosystems, such as purification of water and air, pollination of plants and decomposition of waste
earth centred environment worldview
our dependency on and part of nature and that earth's support system exists for all species.
4 types of ecological services
Provisioning Services,Regulating Services,Supporting Services,Cultural Services
Provisioning Services
supply us with resources, such as food, water, and timber
Regulating Services
benefits of biodiversity that include climate regulation, flood control, and water pollution
Define biocapacity
the capacity of an area to generate renewable resources and absorb wastes
Define ecosystems
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Describe the coastal zone
area where land meets the ocean or sea, and it encompasses a variety of ecosystems such as estuaries, beaches, dunes, mangroves, coral reefs
Explain how waves are created
wind speed, fetch, wind duration
fetch
The distance that the wind has traveled across open water
wind speed
how fast the wind is blowing
wind duration
The length of time the wind blows over the ocean surface
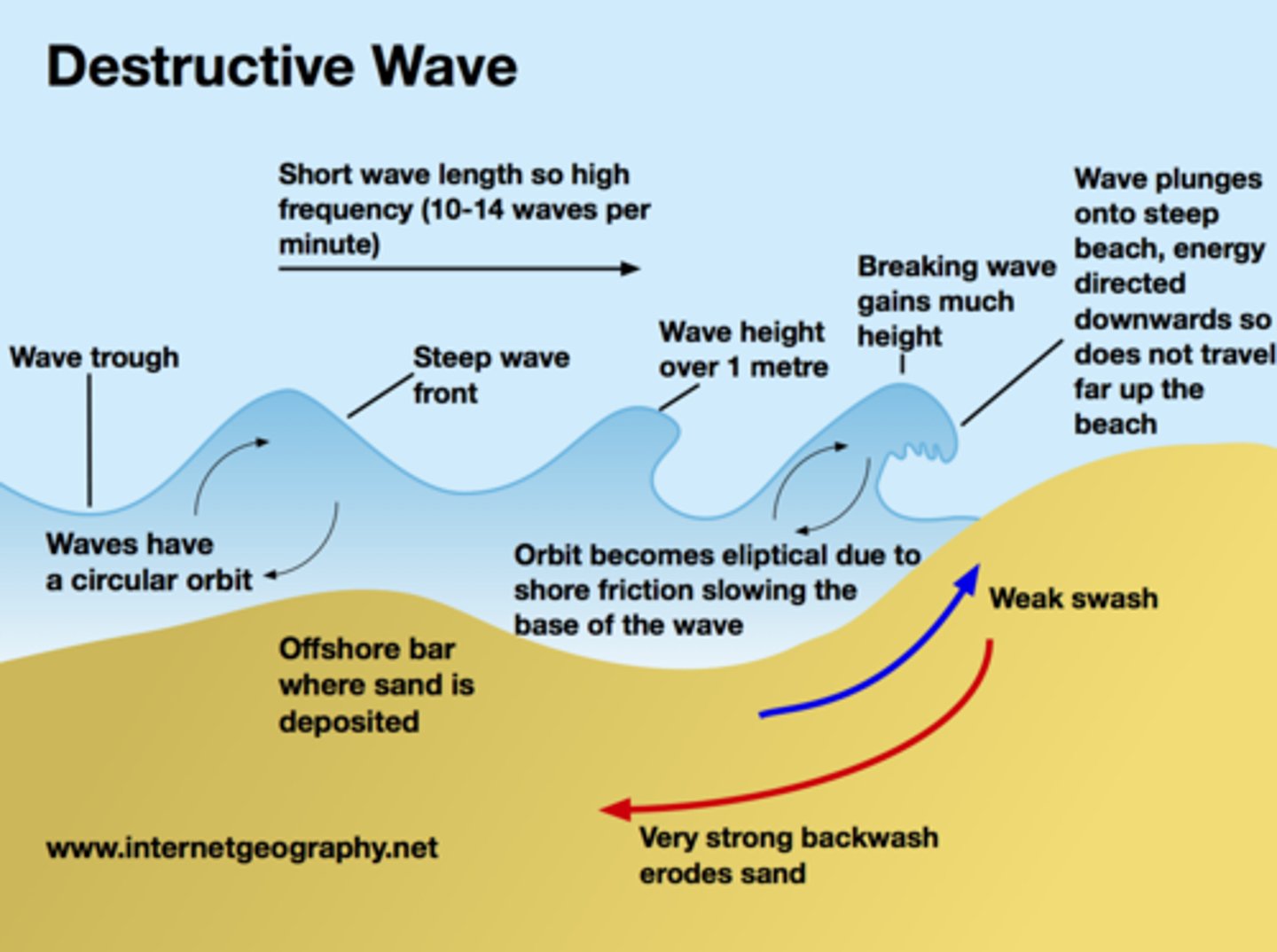
labelled destructive wave
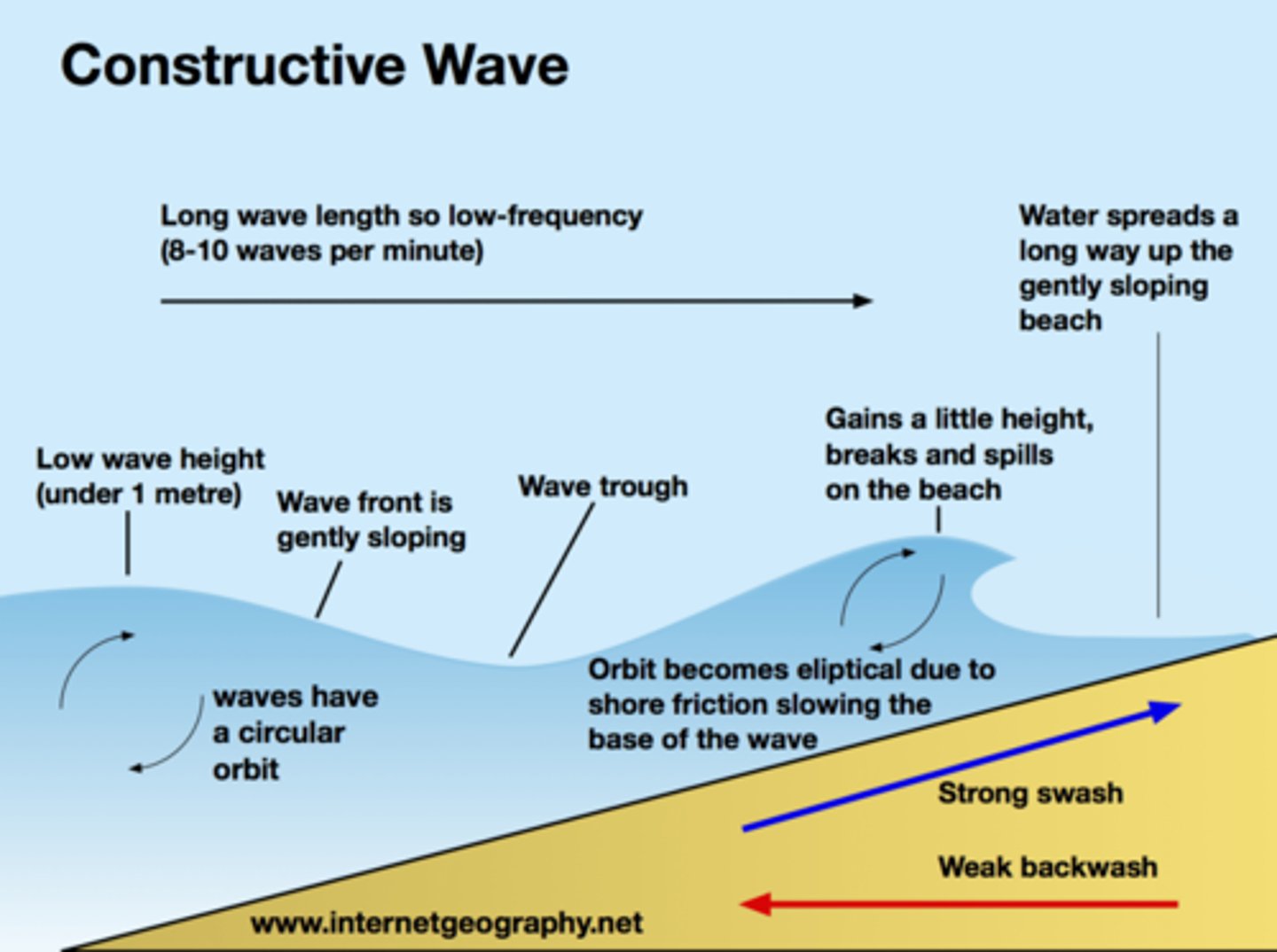
constructive wave
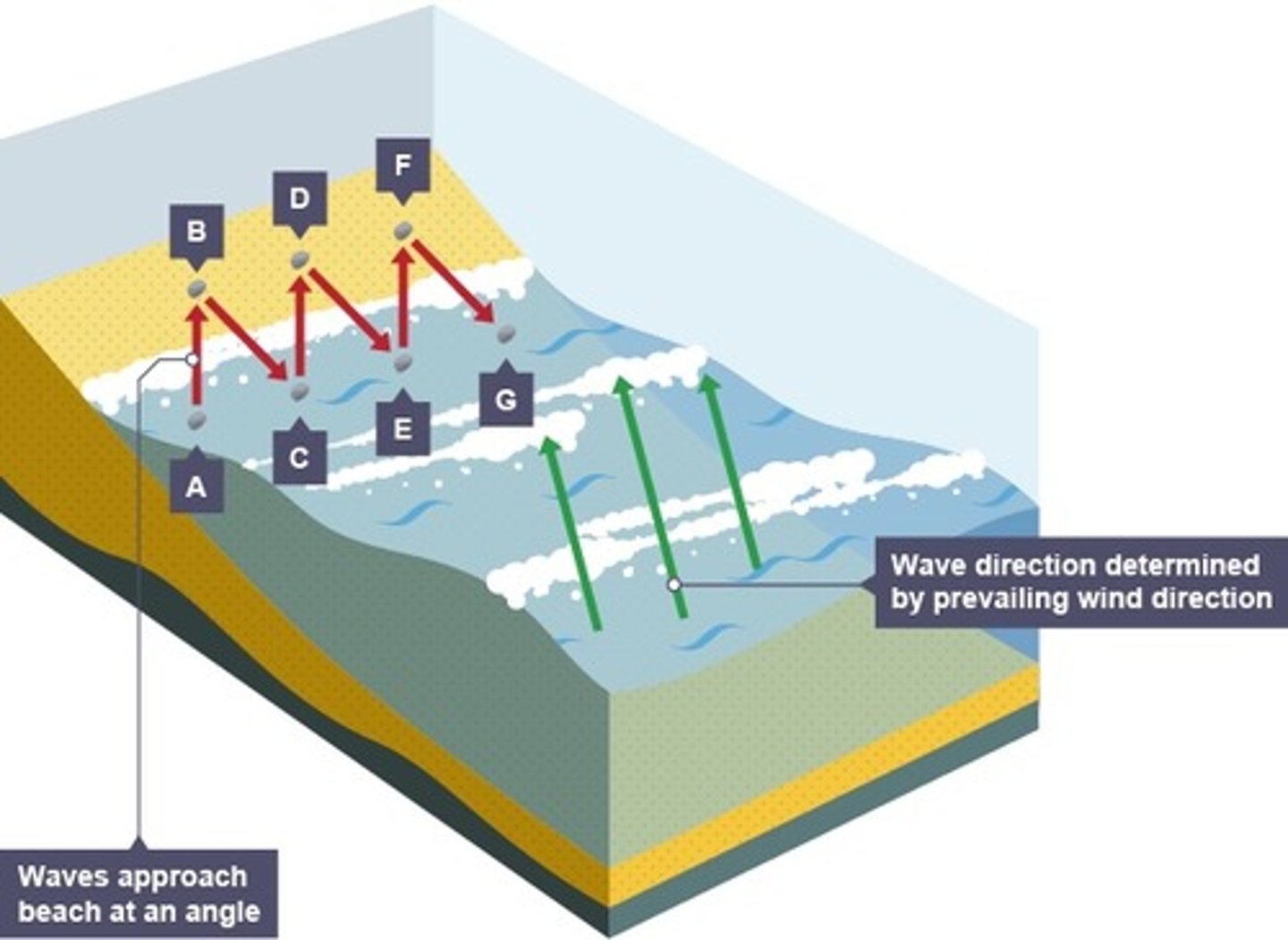
process of longshore drift
The winds caused the waves to approach the shore at an angle
The material carried by the sea is moved up the beach
backwash receded at a 90 degree angle due to gravity.
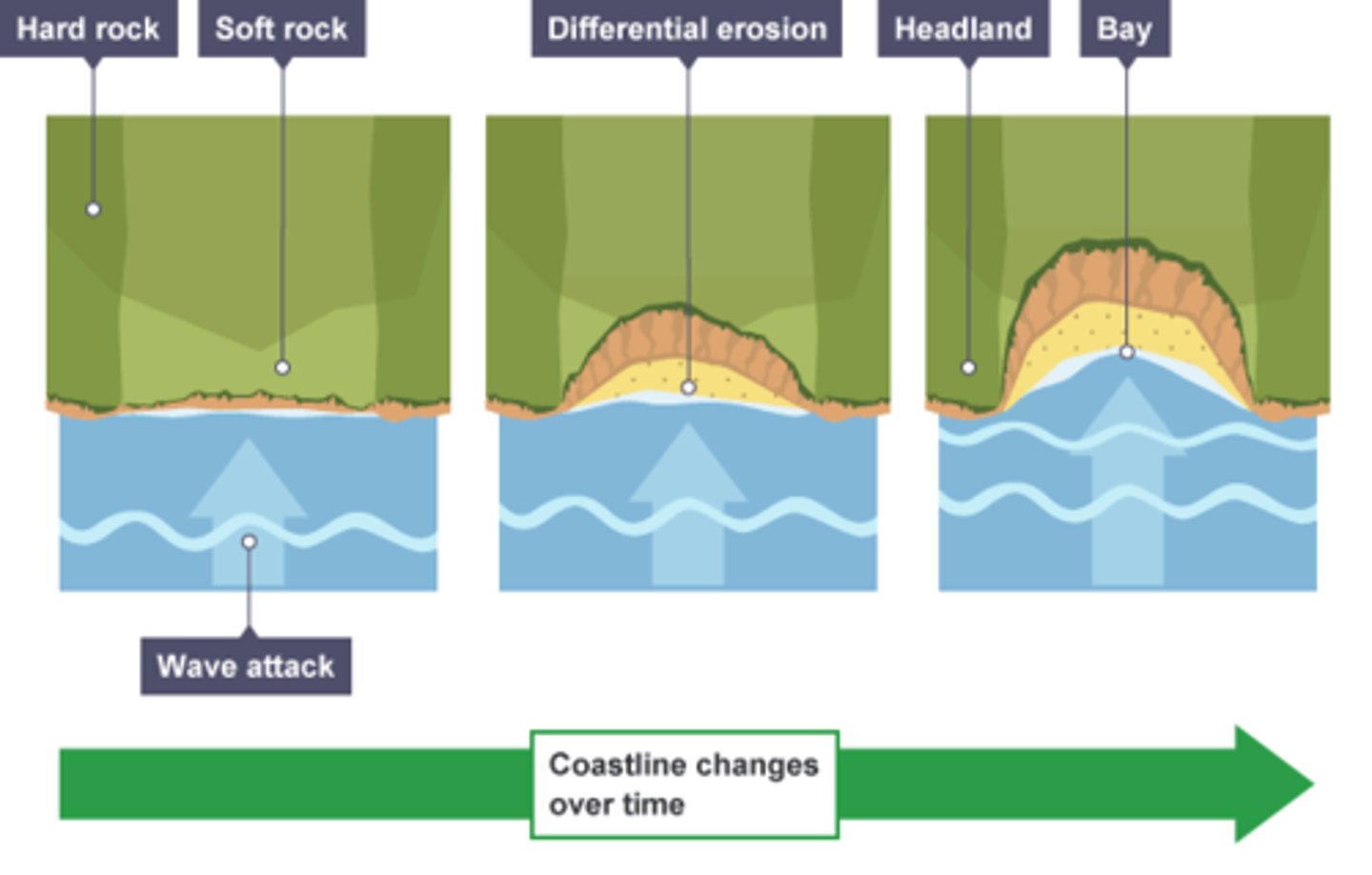
how headlands and bays are created
destructive waves erode soft rock to create bays remaining hard rock becomes headlands
how cliffs and rocky platforms are created
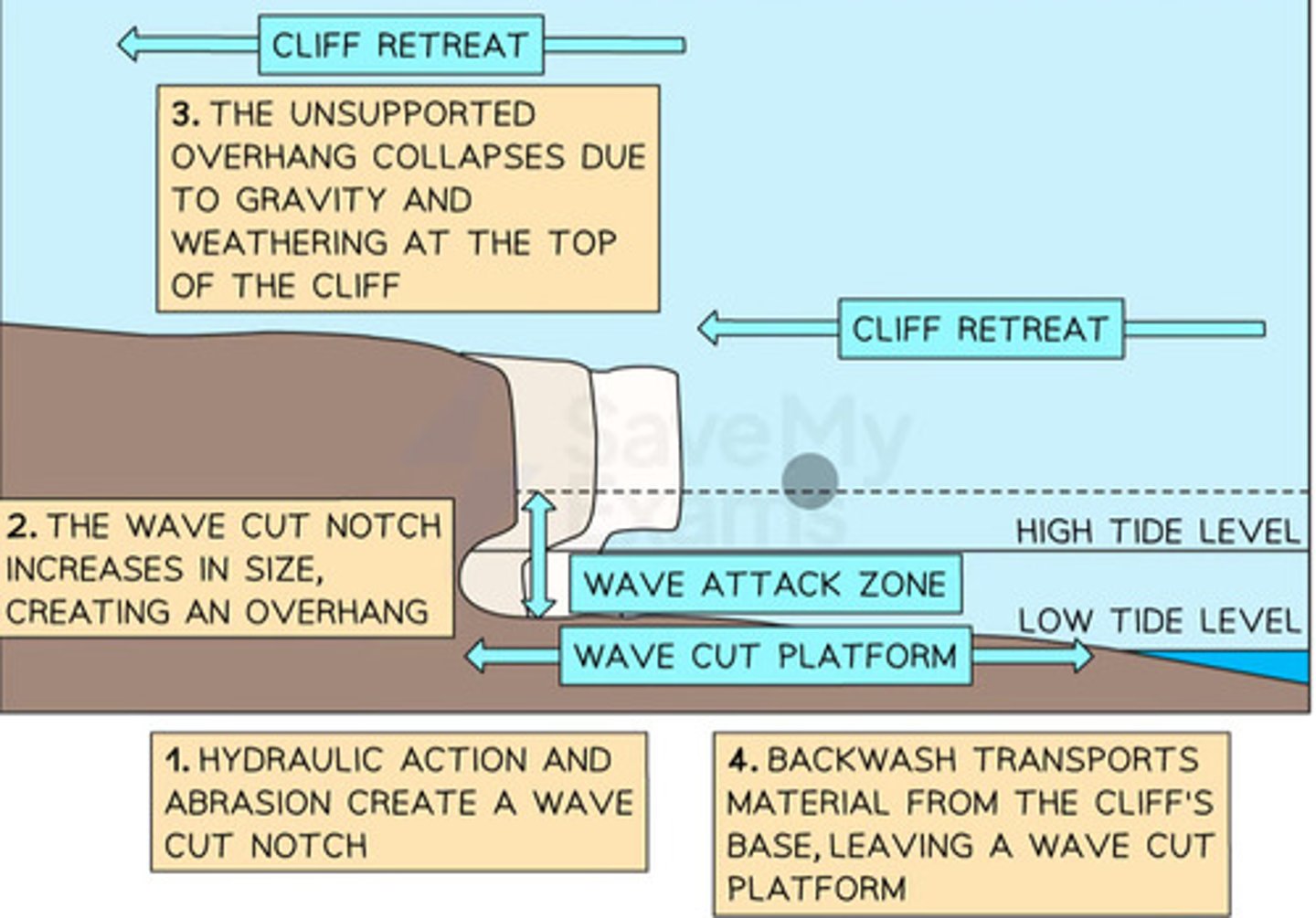
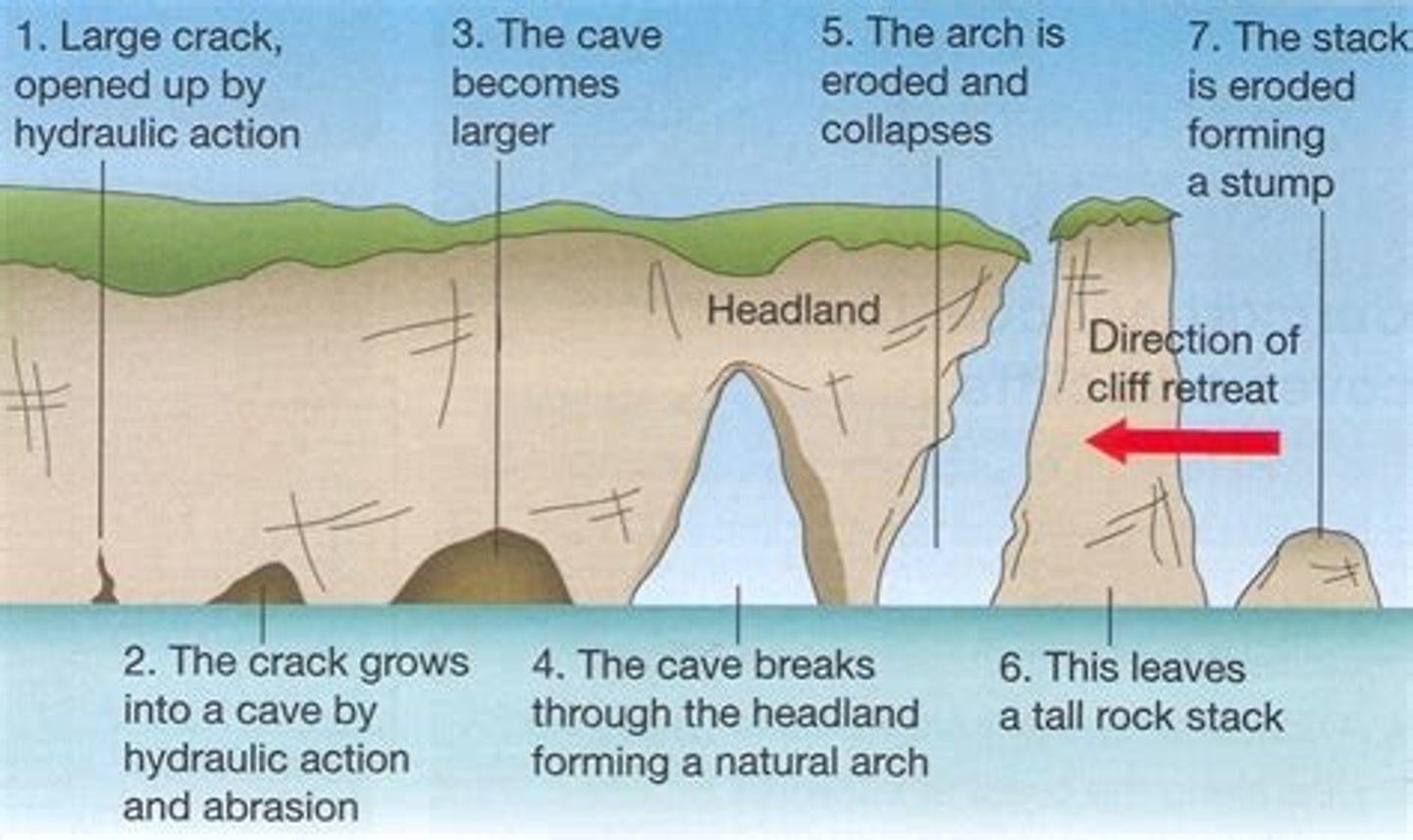
how caves, arches, blowholes and stacks are created
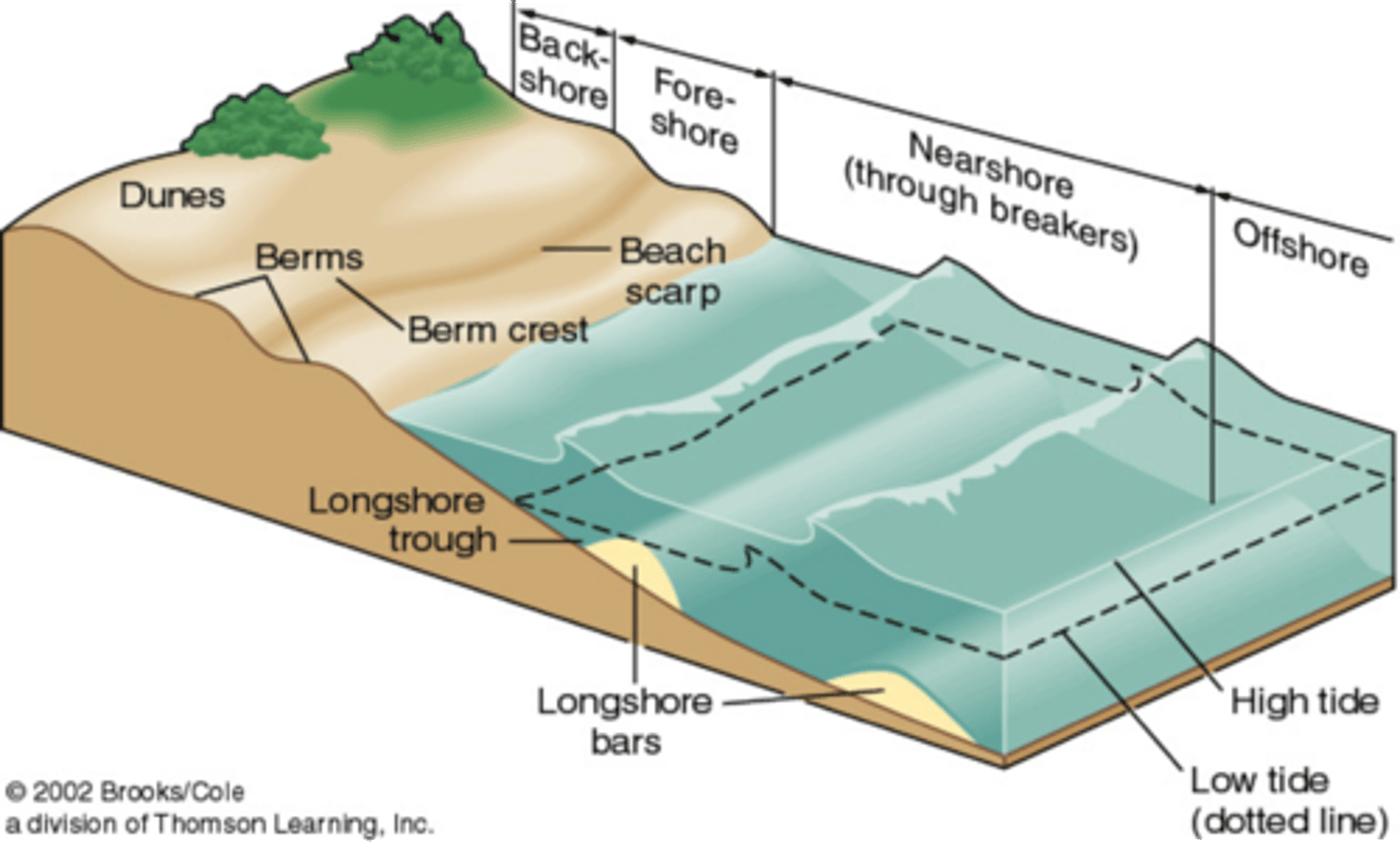
how beaches and sand dunes are formed
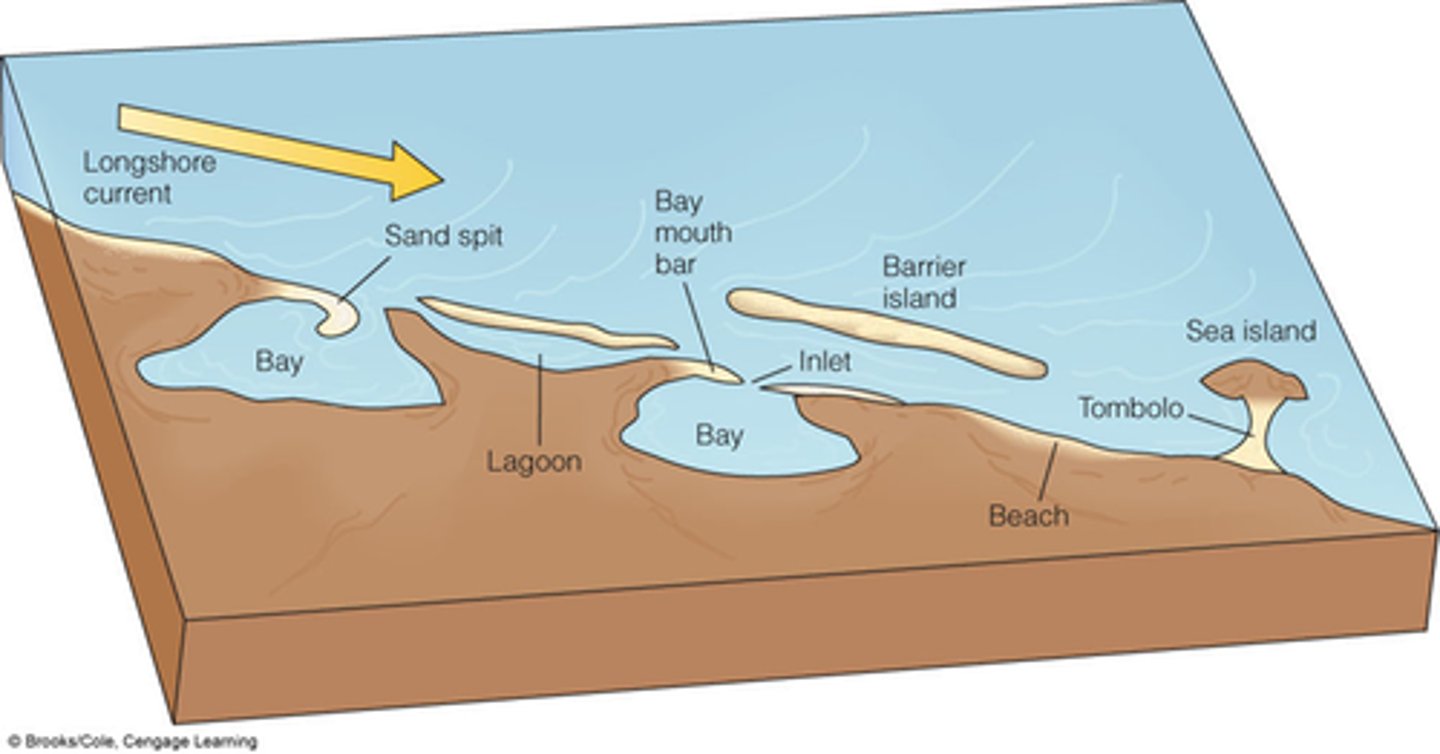
how deposition features such as tombolos, spits and sand bars are formed
Beach Nourishment
dumping new sand onto eroding beaches to restore them
Beach Nourishment: Disadvantages
1) Needs constant maintenance unless structures are built to retain beach, e.g. groynes.
Beach nourishment advantages
- relatively cheap and easy to maintain
- blends in with existing beach
- increases tourist potential by creating a bigger beach
Groynes
Wooden or concrete barriers at right angles to the beach
Groynes advantages
.Cheaper than sea walls - not too expensive *
.Build beach up locally = attract more tourists*
.Provides structures useful for fishing *
.Absorbs wave energy- reducing erosion
Groynes disadvantages
.Not very long-term
.Still quite expensive
.Reduce recreational value of the beach
.Cause high erosion rates downdrift- coastline further along because doesn't have any sediment deposited on it through LSD
.Unnatural
Offshore Breakwater
a partly submerged parrallel to beach rock barrier, designed to break up the waves before they reach the coast
Offshore Breakwater - advantages
.Slight protection from erosion
.Doesn't affect recreational value of the beach
.Doesn't affect any other beaches
Offshore Breakwater - disadvantages
.Doesn't defend against storms
.Stops recreation in the sea (surfing, boats etc.)
Sea Wall
A concrete wall which aims to prevent erosion of the coast by providing a barrier which reflects wave energy.
Sea Walls - advantages
.Highest level of protection in the short term
.Long lifespan of up to 50 years
.Effectively prevents erosion in the local area *
.Often provides a walkway /promenade for people to walk along
Eg Swansea Bay, S Wales
Sea Walls - disadvantages
.Beach level drops and could underline the wall
.More erosion further down the coast (greater downdrift)
.More erosion in areas that aren't protected
.Very high maintenance - the most expensive *
.Can be obtrusive and unnatural to look at *
managed retreat
Allowing low lying areas of low land value along the coast to be flooded in a controlled way.
Managed retreat advantages
.Cheaper than hard engineering - low value land *
.Creates a new habitat for wildlife *
.Develops a salt marsh- natural defence against storms
Managed Retreat - disadvantages
.Not suitable for highly developed areas
.Can ruin coastal farm land - land lost *
.Farmers/landowners need to be compensated*
Qualitative Indicators
A country's development in terms of factors that influence people's quality of life, instead of measuring development, it tries to describe it
quantitative indicators
easily measured and can be stated numerically, such as annual income or how many doctors there are in a country
· Define Standard of living
Quality of life based on ownership of necessities and luxuries that make life easier.
· Define wellbeing
The degree of satisfaction that an individual or group experiences when needs are met
human centred worldview
based on the belief that humans are the most important species and have several traits that set them apart from other species.
Supporting Services
Benefits of biodiversity that allow ecosystems to exist, such as primary production, soil formation, and nutrient cycling
Cultural Services
benefits of biodiversity that provide aesthetic, spiritual, or recreational value
· Define ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
selection criteria 7 great barrier reef
Must contain exceptional natural beauty or superlative natural phenomena.
selection criteria 8 wet tropics of queens land
Must represent key stages of Earth's history, showcasing the record of life, significant geological processes, or notable geomorphic features.

selction criteria 9 macquire island
Outstanding examples of ongoing ecological and biological processes in the evolution of terrestrial, freshwater, coastal, and marine ecosystems.
selection criteria 10 lord howe island
Must contain significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including threatened species of outstanding universal value.