CLAS242 - The Flavian Period
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

Identify and Analyze
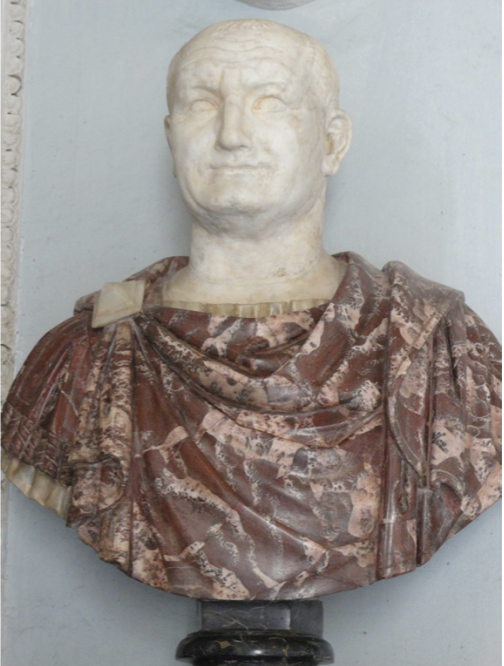
Portrait of Vespasian, Musei Capitolini, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Next Emperor
Nero was a weak emperor at the end
various uprisings before Nero commits suicide after the praetorian guards turned on him
Year of the Four Emperors
many people trying to claim the throne
Order of the 4
Galba, magistrate, proclaims himself against Nero, becomes Emperor
Otho kills Galba, becomes Emperor
Vitellius beats Galba in battle, Galba kills himself, Vitellius becomes Emperor
Vespasian kills Vitellius, now he is the new Emperor
Back to Italian Verism
consciously rejecting Augustan Classicism
differentiating himself from the Julio-Claudians
balding, wrinkles, nasolabial lines, etc.
actually looks his true age
“forget the chaos of the wars etc.”
age showing wisdom as a steady, calming, guiding hand
Message still more important thank showing what he truly looked like

Identify and Analyze
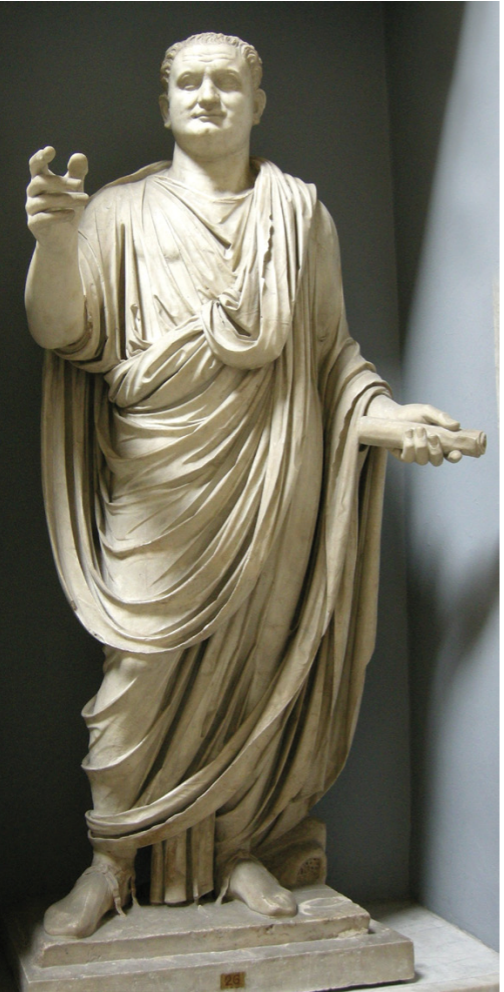
Portrait of Titus, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 68 CE
Next Emperor
Son of Vespasian
Verism
carried on from his father
jowls, big jaw, thinning hair, etc
so much consistency in Titus’ portraits that it can only be assumed that there was really only one model that was sent to artists
Change in Proportions
Augustus as Pontifex
tall and thin
Titus
squared off and more squat
mimicking of Italic relief sculpture, also seen on the Tomb of the Breadmaker
Magistrate
outfit with scroll in hand
Identify and Analyze (two images)
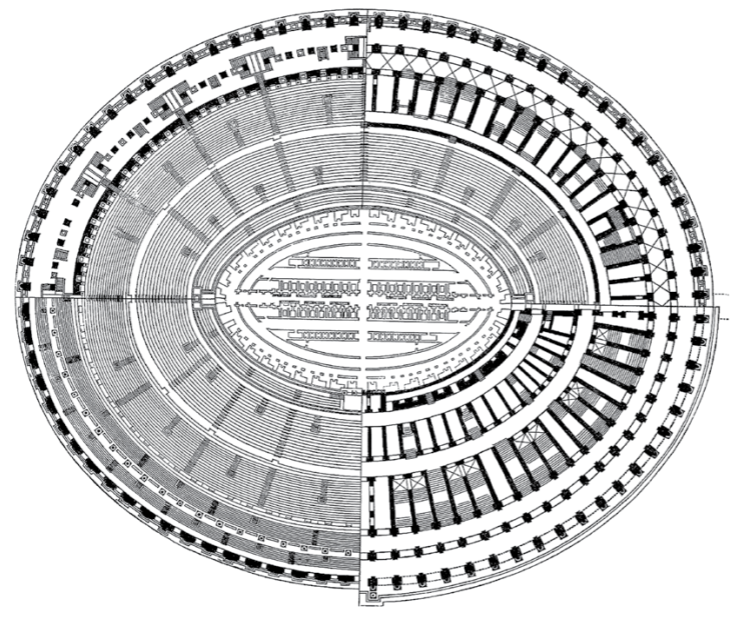
Colosseum, Rome, plan and elevation drawing
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
aka, the Flavian Amphitheatre
known as Colosseum for its proximity to he Colossus Neronis
a 120 foot tall bronze statue of Nero meant to mimic the Colossus of Rhodes
Golden Palace destroyed by Flavians
wanted to give the land back to the people
dedicated the colosseum in 80CE
Not only amphitheatre at time, nor very innovative
just the biggest/most lavish in Rome
everything that could be put into a colosseum was put into this
Features
Brickwork + Marble Panelling on outside
Use of concrete as a structural support for large-scale buildings with great unsupported spaces
Sections related to ticket prices
each entrance with specific numbers for seating
Retractable (kind of) roof
a giant tarp covered the top 3rd
ropes and pulleys on wenches on ground
sailors were hired to man the rigging since they had the experience
Sand floor
trap doors for animals to suddenly appear from
dollies/people to be lowered/raised up from
Watertight cement base
could flood the central area to recreate naumachiae
sea/naval battles
Basement
gladiator changerooms
cages for animals
Entertainment
reenactments of myth/historical fights
all the ones where Rome won, of course
public executions
3 Tiers
Tuscan columns on bottom
Ionic on the second
Corinthian on the 3rd
Meant to show the power of the Flavian emperors/their control over the resources of the empire
also benefits that their rule brings to Rome
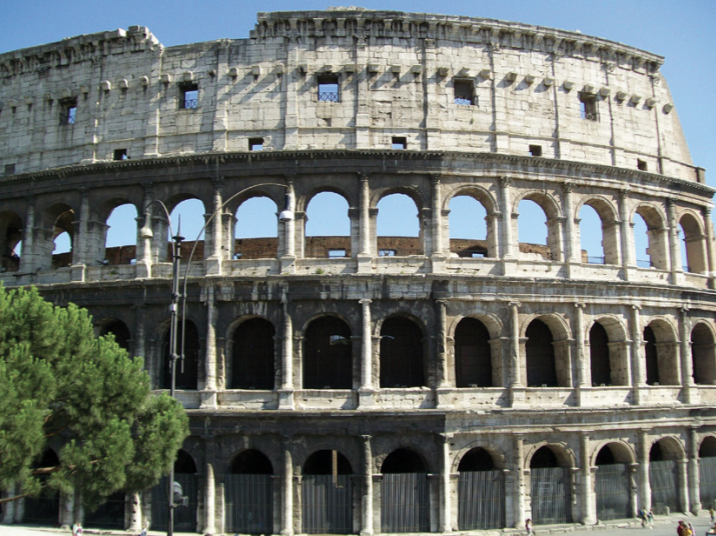
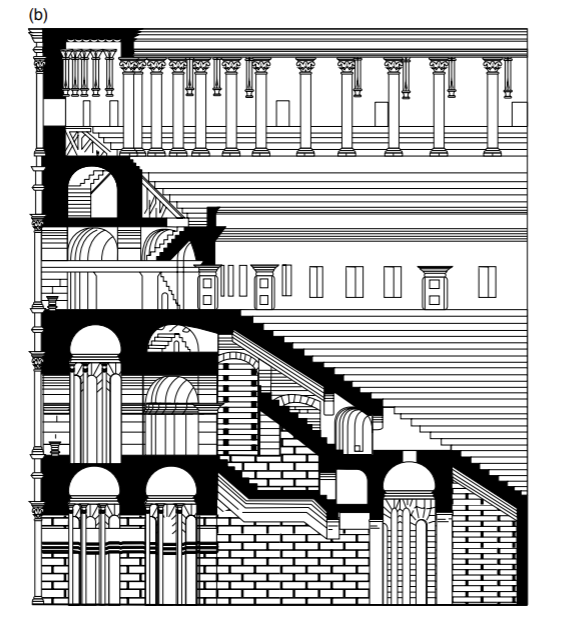

Identify and Analyze (two images)
Colosseum, Rome, facade and detail of entrance arcade
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
aka, the Flavian Amphitheatre
known as Colosseum for its proximity to he Colossus Neronis
a 120 foot tall bronze statue of Nero meant to mimic the Colossus of Rhodes
Golden Palace destroyed by Flavians
wanted to give the land back to the people
dedicated the colosseum in 80CE
Not only amphitheatre at time, nor very innovative
just the biggest/most lavish in Rome
everything that could be put into a colosseum was put into this
Features
Brickwork + Marble Panelling on outside
Use of concrete as a structural support for large-scale buildings with great unsupported spaces
Sections related to ticket prices
each entrance with specific numbers for seating
Retractable (kind of) roof
a giant tarp covered the top 3rd
ropes and pulleys on wenches on ground
sailors were hired to man the rigging since they had the experience
Sand floor
trap doors for animals to suddenly appear from
dollies/people to be lowered/raised up from
Watertight cement base
could flood the central area to recreate naumachiae
sea/naval battles
Basement
gladiator changerooms
cages for animals
Entertainment
reenactments of myth/historical fights
all the ones where Rome won, of course
public executions
3 Tiers
Tuscan columns on bottom
Ionic on the second
Corinthian on the 3rd
Meant to show the power of the Flavian emperors/their control over the resources of the empire
also benefits that their rule brings to Rome
Vomitorium
“spit the people out of the building”
barrel vaults for entrances/exits
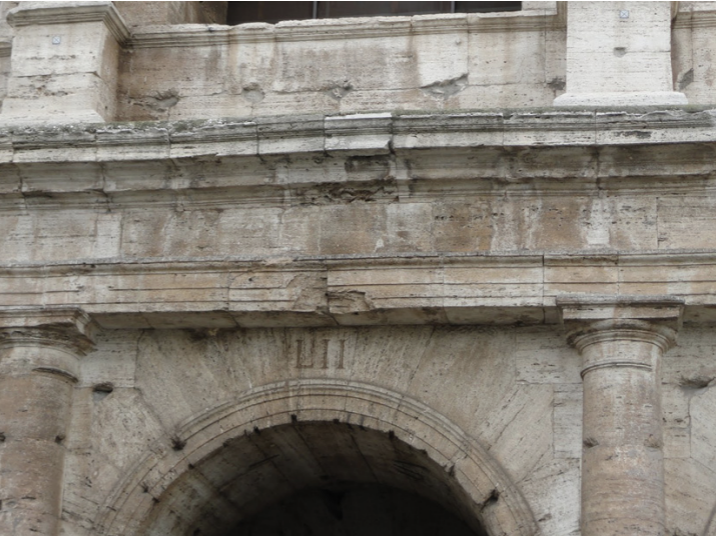


Identify and Analyze
Colosseum, Rome, sestertius of the amphitheater
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
aka, the Flavian Amphitheatre
known as Colosseum for its proximity to he Colossus Neronis
a 120 foot tall bronze statue of Nero meant to mimic the Colossus of Rhodes
Golden Palace destroyed by Flavians
wanted to give the land back to the people
dedicated the colosseum in 80CE
Not only amphitheatre at time, nor very innovative
just the biggest/most lavish in Rome
everything that could be put into a colosseum was put into this
Features
Brickwork + Marble Panelling on outside
Use of concrete as a structural support for large-scale buildings with great unsupported spaces
Sections related to ticket prices
each entrance with specific numbers for seating
Retractable (kind of) roof
a giant tarp covered the top 3rd
ropes and pulleys on wenches on ground
sailors were hired to man the rigging since they had the experience
Sand floor
trap doors for animals to suddenly appear from
dollies/people to be lowered/raised up from
Watertight cement base
could flood the central area to recreate naumachiae
sea/naval battles
Basement
gladiator changerooms
cages for animals
Entertainment
reenactments of myth/historical fights
all the ones where Rome won, of course
public executions
3 Tiers
Tuscan columns on bottom
Ionic on the second
Corinthian on the 3rd
Meant to show the power of the Flavian emperors/their control over the resources of the empire
also benefits that their rule brings to Rome
Vomitorium
“spit the people out of the building”
barrel vaults for entrances/exits
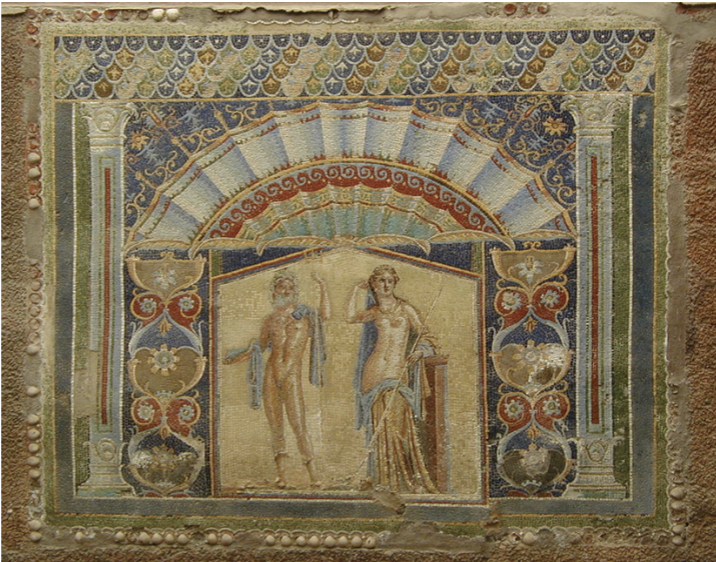

Identify and Analyze
Wall mosaic of Neptune and Amphitrite, Herculaneum
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Herculaneum
maybe a Greek colony as there are many Greek things there
slowly taken over by Italians in this sense
Wall Mosaic
not floor, wall
concrete, little cartoon plan, and then add on the tessarae
little squares that make up a mosaic
Tesselated - made up of tessarae
Polychromy
lots and lots of colours
most mosaics in Rome were black and white
easier in shades
far more expensive/elaborate
similarity to 3rd style
just that everyone is always playing off of everyone else
similarities coming from trends/inspirations
Marriage of Neptune and Amphitrite
more represented in Roman art than Greek
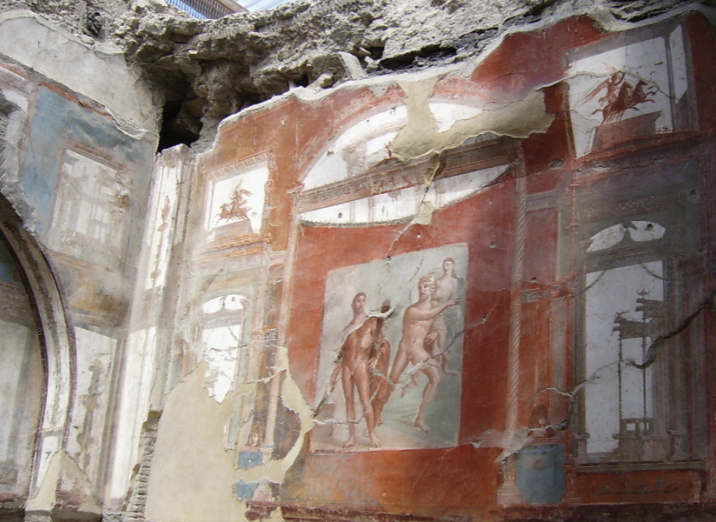

Identify and Analyze
Hercules painting, Sacellum of the Augustales, Herculaneum
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Meaning of Name:
little room for Priest of Augustus
anyone was able to come in and worship a deified emperor
Mythological scenes
Hercules, mythical founder of the city
also a favourite of the emperors
Greek Style
similar to sculpture
contrapossto, heroic nudism, curly hair and beard
all speaks the the history of Herculaneum
Egyptian blue
first synthetic paint ever created
meant to mimic the colour of lapis lazuli as a cheaper alternative
Romans call it cerulean
use of it demonstrates the wealth of Herculaneum
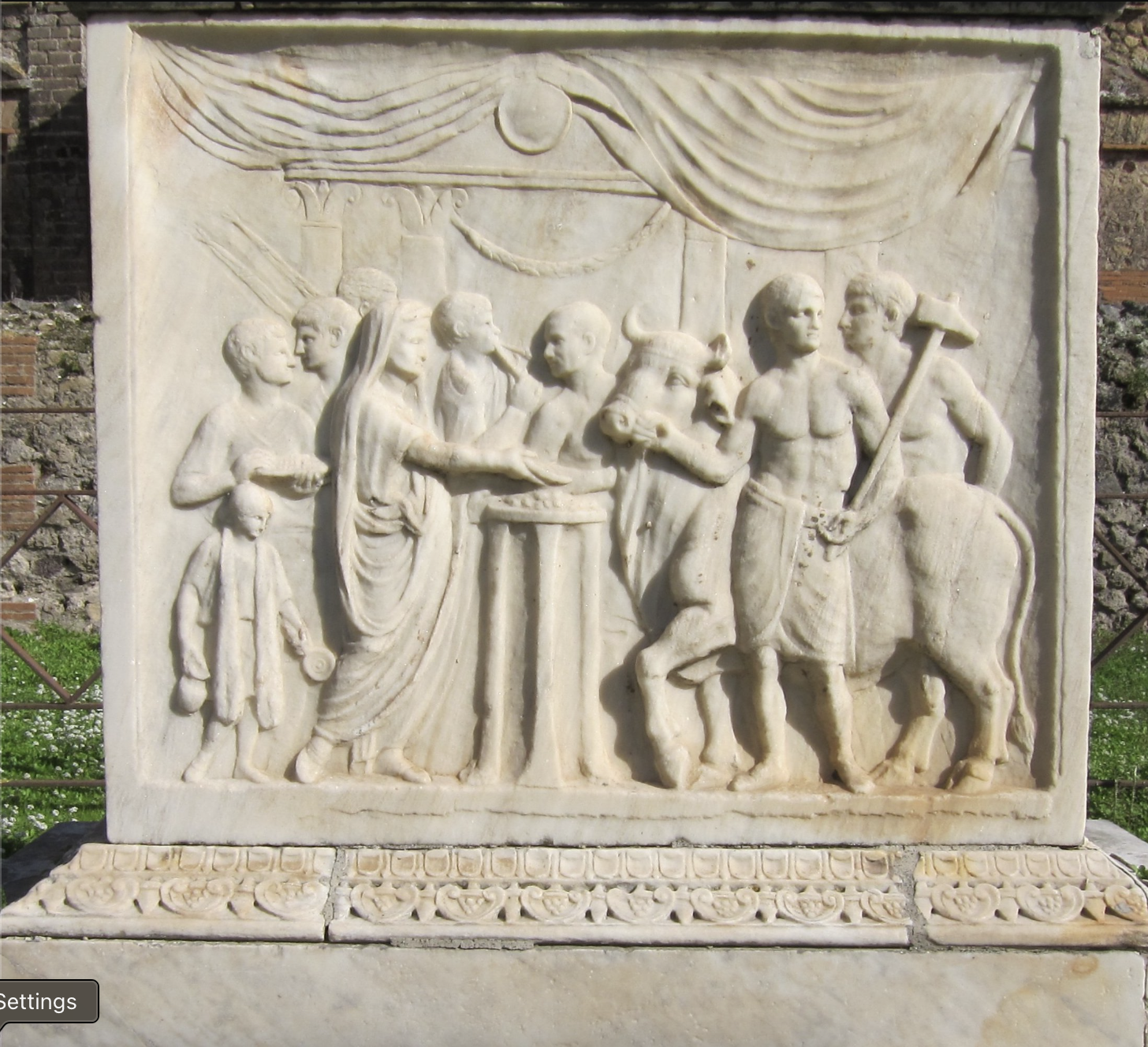

Identify and Analyze
Altar relief, Temple of the Deified Vespasian, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Sacrifice to Domitian
Next Emperor after Titus
brother of Titus, son of Vespasian
head covered - religious context
backdrop - temple
guy with ox and hammer for sacrifice
Greek Style
Identify and Analyze
Plan of the House of the Vettii, Pompeii, renovations
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Owned by Two Brothers
Aulus Vettius Conviva
Aulus Vettius Restitutus
freed slaves
got money and then presented their house as Roman like
example of a house that wasn’t owned by the rich
sub-elite commercial identity
House reorganized after earthquake in 62 CE
Tablinum
room in front for man of house to accept visitors/clients
does not exist here (removed) because they were slaves so no client system for them
house now opened directly into a peristyle garden
garden best styled/decorated in house in stead of atrium
now the most important reception area as well
Houses painting of Priapus
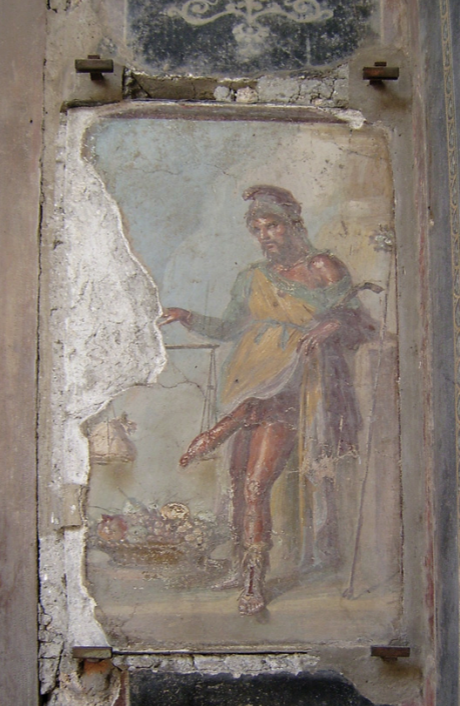

Identify and Analyze
Priapus painting, front foyer, House of the Vettii, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Priapus, god of Fertility
in charge of all kinds of fertility
yourself, peace, happiness, wealth, agriculture, children, etc.
representation of abundance
phallus on scale against a bag of money
“notice how they are balanced”
Priapus bringing fertility to money
cornucopia spilling out behind him
commercial rather that patrician identity
represented with large erect phallus
similar to Satyrs
always shown as erect because all they’re interested in is sex
comedic aspect of satyrs
Found in Entryway of House ofthe Vettii
Apotropaic
common attribute of entrance decoration
often incorporated phallic imagery

Identify and Analyze
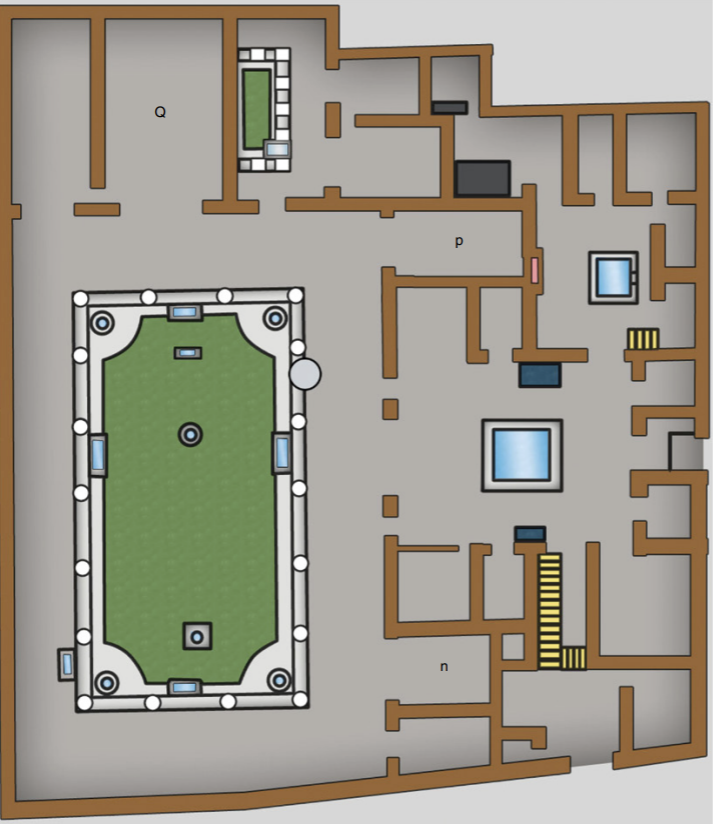
Pinacotheca n, House of the Vettii, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Pinacotheca
literally a picture gallery
a room deocrated with mural paintings that replicate Greek panel paintings
often copies or variations of famous pictures
All paintings linked to Greek myths that reinforce religious authority
all fourth style paintings
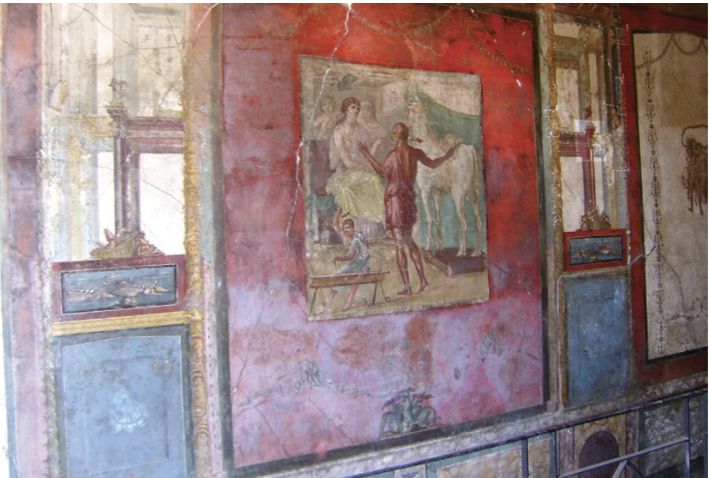
Pasiphae
King Mino’s wife
Minos angered Poseidon by withholding a beautiful white bull (sacred to Poseidon) from sacrifice to him
Poseidon cursed Pasiphae to fall in love passionately with that bull
Pasiphae ordered Daedalus to build her a cow that she could climb inside which would then allow the bull to fall in love with the wooden cow so that she could be fucked by the bull
she fell pregnant with the Minotaur

Identify and Analyze
Pinacotheca p, House of the Vettii, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Pinacotheca
literally a picture gallery
a room deocrated with mural paintings that replicate Greek panel paintings
often copies or variations of famous pictures
All paintings linked to Greek myths that reinforce religious authority
all fourth style paintings
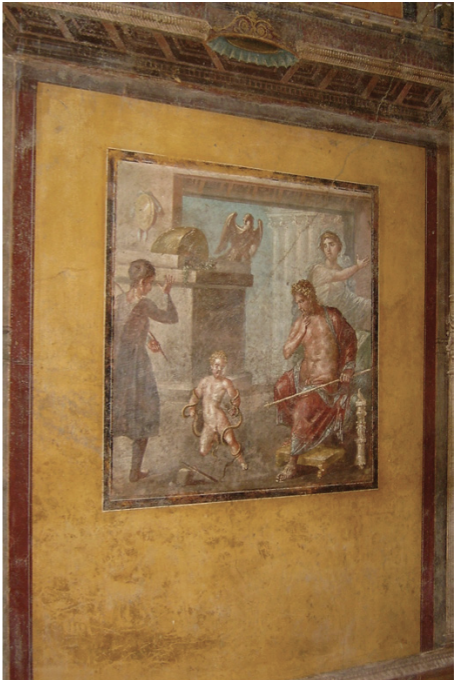
Baby Hercules
myth where two snakes crawled into his crib as a baby to kill him, sent by Hera (another bastard son of Zeus)
Hercules strangles them
based on Greek original from 5th century BCE

Identify and Analyze
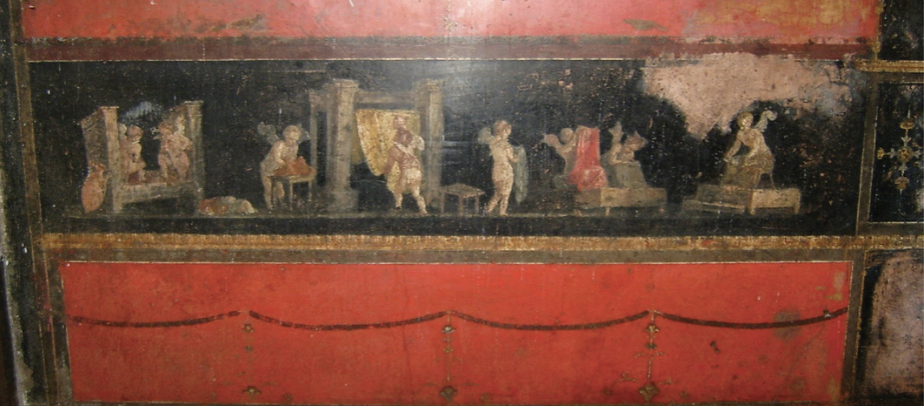
Cupids as fullers, painted frieze, reception room Q, House of the Vettii, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Multiple Cupids at once- becomes comedic in Roman art
laugh with them, not at them
baby doing manual labour - a baby can’t do that! how funny
later leads to renaissance baby angels
Tasks relating to Love
jewelry making
perfume making
garland stringing
cloth dying
Vettii
fullers
dye wool/cotton/leather
the process of dying STANK
included urine for well-working properties
happened in the heart of Pompeii, that city STANK

Identify and Analyze
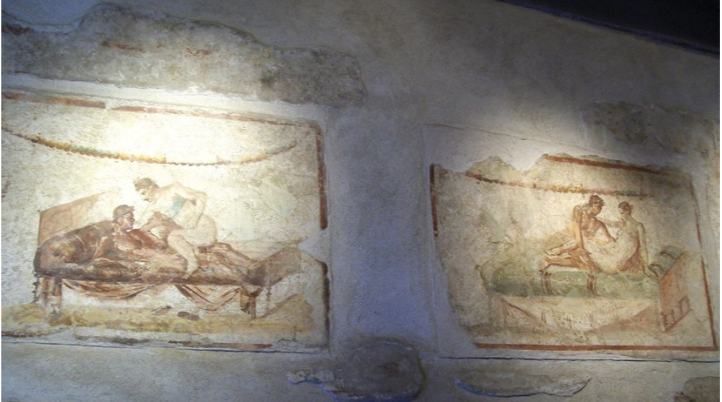
Paintings in the central hallway, lupanar, Pompeii
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Lupanar
a brothel
small cells, stone beds/pillows
contrats with evocative wall paintings in the hallway
Wall Paintings
erotic
meant to arose? menu items for the illiterate/couldn’t speak latin?
typically heterosexual
homosexual, more risqué, threesomes etc. were reserved more for private settings/domestic homes
Napals Museum
“Secret Room”
all of these “explicit” findings from Pompeii (which were everywhere) were hidden in there
“innapropriate” for the public to see
even though most of them were erect phalluses that had been put up throughout the city as apotropaic/fertility images
contained
nude statues/paintings
penis statues
dildos
opened up this room to the 18+ public 10-15 years ago
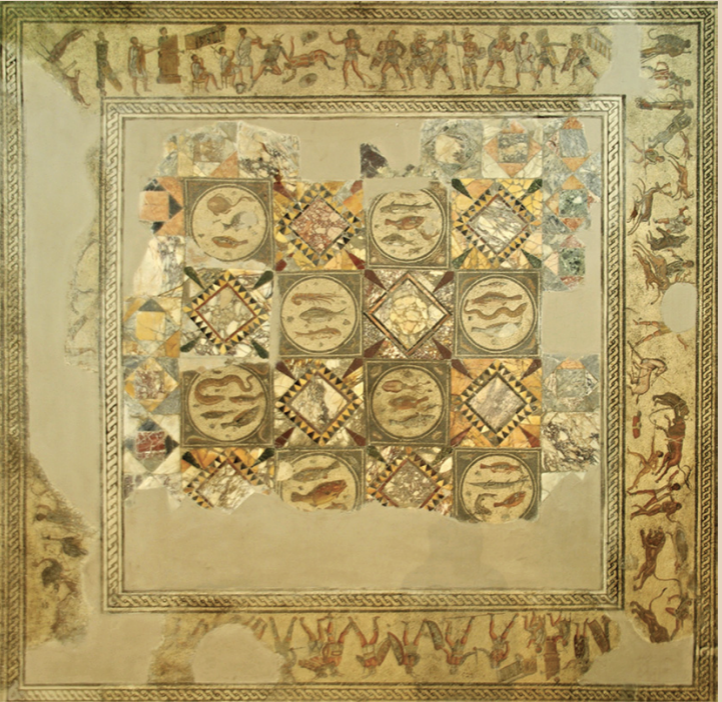

Identify and Analyze
Floor mosaic from a Roman villa, Zliten, Libya, Flavian
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Roman’s Material Production + Wealth
an example
North Africa
Romans moving there and their culture follows
Expensive
lots of colours and types of decoration
fish
real fish you can catch in the Mediterranean
Dining Room
to show guests and the public
you’re serving fish to your guests and you say “look down! that’s the fish we’re eating right now”
Mosaic Border
Athletic contests/Gladiator fights
Venationes
animal hunts
included deer and ostriches
Big Cat + man Tied Up
damnatio ad bestias
condemnation to the animals
feeding the Christians to the lions in the colosseum
Roman Laws of Fights
some kinds of gladiator fights were not allowed
these rules wrre loose in the provinces

Identify and Analyze
Detail of arena events, floor mosaic from a Roman villa, Zliten, Libya, Flavian
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Roman’s Material Production + Wealth
an example
North Africa
Romans moving there and their culture follows
Mosaic Border
Athletic contests/Gladiator fights
Venationes
animal hunts
included deer and ostriches
Big Cat + man Tied Up
damnatio ad bestias
condemnation to the animals
feeding the Christians to the lions in the colosseum
Roman Laws of Fights
some kinds of gladiator fights were not allowed
these rules wrre loose in the provinces
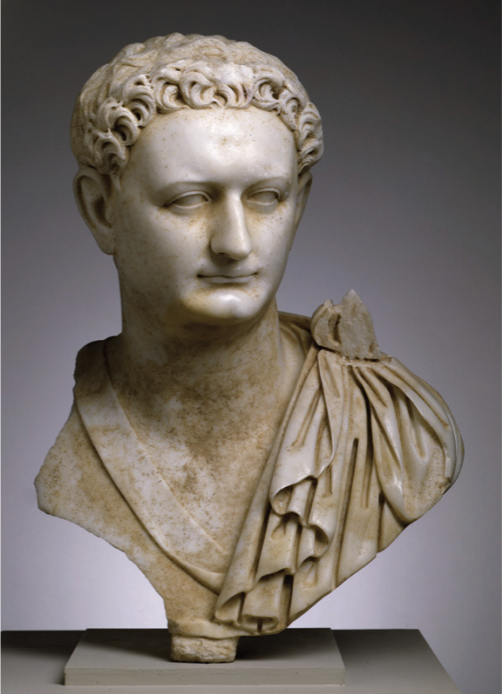

Identify and Analyze
Portrait bust of Domitian, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Next Emperor
son of Vespasian, brother of Titus
Titus died prematurely from a fever
last of Flavian rulers
Poor reputation
Damnatio Memoriae - “Damnation of Memory”
where everyone hates you so much they chip your face and name off of all your statues
an attempt to erase them from history
this one unaffected
Classical Elements
smoothness of the face
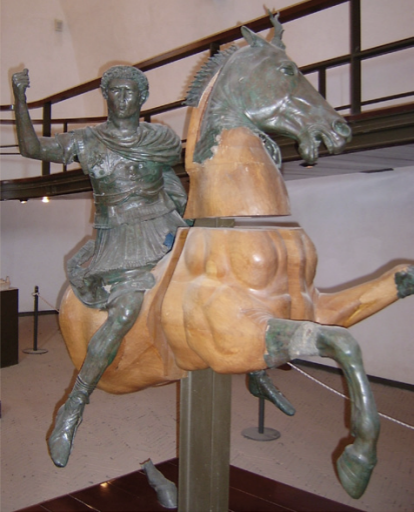

Identify and Analyze
Statue of Domitian, face replaced with Nerva, Sacellum of the Augustales
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Next Emperor
son of Vespasian, brother of Titus
Titus died prematurely from a fever
last of Flavian rulers
Poor reputation
Damnatio Memoriae - “Damnation of Memory”
where everyone hates you so much they chip your face and name off of all your statues
an attempt to erase them from history
this one later re-carved as Nerva, a later emperor
Emperor on Horse
role portraiture of military might
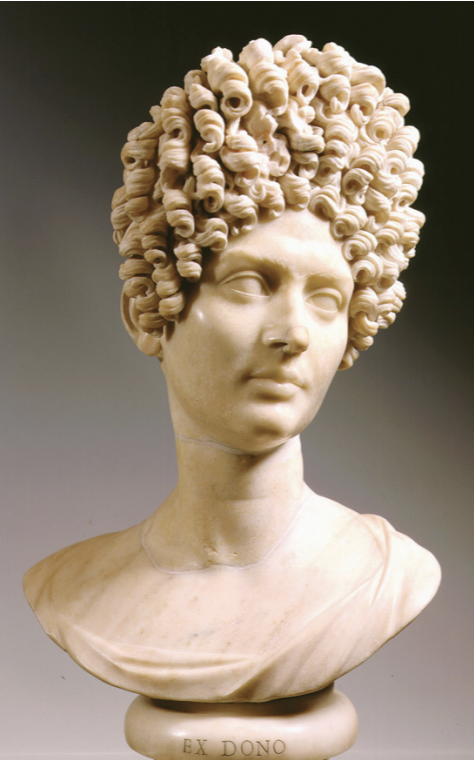

Identify and Analyze
Portrait bust of a Flavian lady, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Greek Classical Style
makes it impossible to track styles/chronologies
everyone mean to look like Greek Goddesses
How to tell differences?
hair and clothing changes with times
Elaborate Hair
as a way of women presenting their wealth/personal taste
Thought this style was only artistic/not real/impossible to do in reality
a hairdressed recreated it in real life with simple tools that would have been available at time period
Sculpture
chunks of hair vs. individual strands
much easier to carve clumps of hair to give the impression of individual hairs
bow drill
acts like a drill and a router
allows them to create huge pockets of shadow
interesting effect with light
highlights the 3D
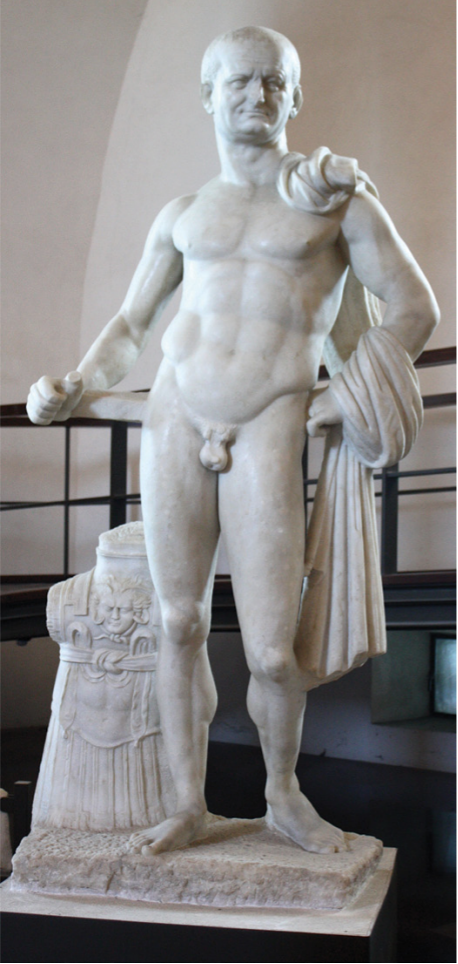

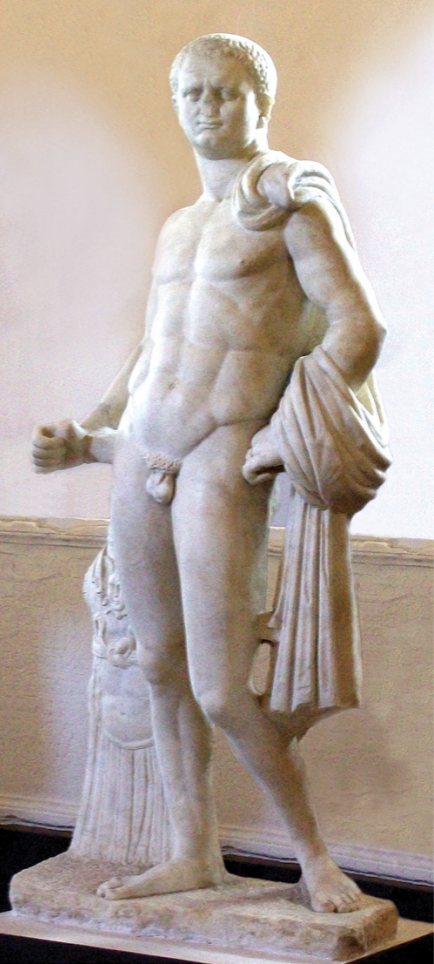
Identify and Analyze (two images)
Portraits of the Vespasian and Titus, Sacellum of the Augustales, Misenum
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Verism + Classical
older heads and Greek hero body combo
conveying message: Emperor is a hero
Common Roman viewer has no problem with the mixture
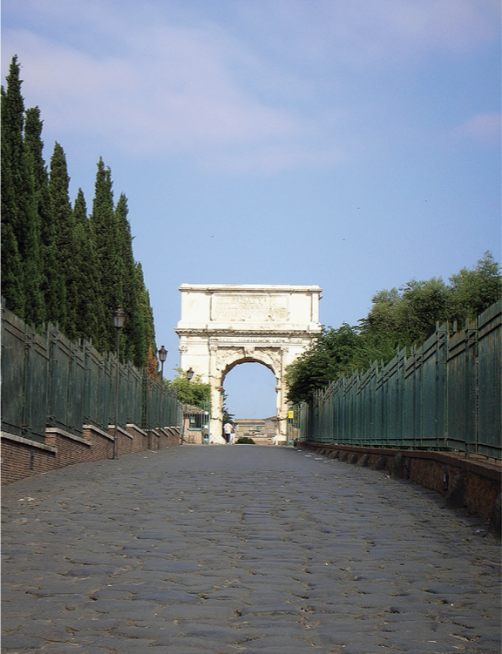


Identify and Analyze
Arch of Titus, Rome, overall view up the Via Sacra (Sacred Way)
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Roman Victory Arch
great example
once a general was successful, they host a triumph
then their relative would build an arch for them
Best surviving Arch
SPQR + “Divine Titus” and “Divine Vespasian”
if they are already deified - Domitian who built it
SPQR - Senatus Populusque Romanus - “Senate and the People of Rome
Spandrels
area above arch and below the very top of it
flying Victorias
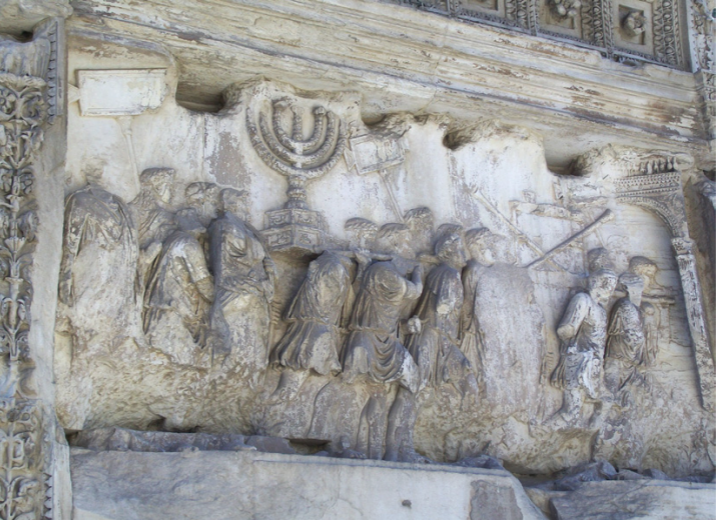

Identify and Analyze
Relief of Spoils from the Temple in Jerusalem, Arch of Titus, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Roman Victory Arch
great example
once a general was successful, they host a triumph
then their relative would build an arch for them
Best surviving Arch
SPQR + “Divine Titus” and “Divine Vespasian”
if they are already deified - Domitian who built it
SPQR - Senatus Populusque Romanus - “Senate and the People of Rome
Spandrels
area above arch and below the very top of it
flying Victorias
Inside Sculpture
surrounded by it when under the Arch
Military Campaign Scene
Menorah - put down of the revolt in Judea
bringing back the spoils. from sacking a Jewish temple
“we have power over your gods” - we have this religious object that is important to your worship
Victory Parade
Tabula ansata
would have been signs explaining to the surrounding crowd what they were seeing/what had happened
Arch on the Arch
¾ view
while crowd is in profile
as you move to the right, figures get smaller and in less relief until they are going under the arch
gives a sense of turning and three dimensional space

Identify and Analyze
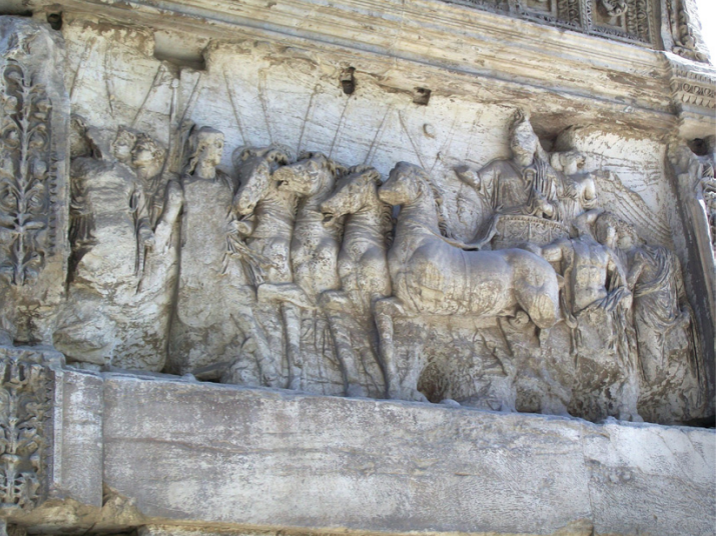
Relief of Titus in triumphal chariot, Arch of Titus, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Roman Victory Arch
great example
once a general was successful, they host a triumph
then their relative would build an arch for them
Best surviving Arch
SPQR + “Divine Titus” and “Divine Vespasian”
if they are already deified - Domitian who built it
SPQR - Senatus Populusque Romanus - “Senate and the People of Rome
Spandrels
area above arch and below the very top of it
flying Victorias
Inside Sculpture
surrounded by it when under the Arch
Triumph Procession Relief
Titus in Quadriga
four horse chariot
big deal, this was Santa in the Santa Parade level big
Mythical Figures
Victoria, crowning Titus
Virtus, personification of martial prowess
personifications of SPQR
Variation of heads for depth
lower detail in distance
Three Dimensional Attempt
Titus, ¾ view
Horse, profile
Gods, frontal
gives a sense of turning
Classical Style

Identify and Analyze
Cancelleria relief of adventus of Vespasian, Rome
Roman Victory Arch
great example
once a general was successful, they host a triumph
then their relative would build an arch for them
Best surviving Arch
SPQR + “Divine Titus” and “Divine Vespasian”
if they are already deified - Domitian who built it
SPQR - Senatus Populusque Romanus - “Senate and the People of Rome
Spandrels
area above arch and below the very top of it
flying Victorias
Inside Sculpture
surrounded by it when under the Arch
Top Panel Relief
crazy decoration
Coiffures
little rosettes/egg and darts
decorative and a way of breaking up the mundane
Titus on Eagle
Jupiter
symbolic of him being brought up to the heavens, being deified

Identify and Analyze
Cancelleria relief of profectio of Domitian, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Cancelleria Villa
Ideal + Classical
Adventus
Arriving
the emperor coming back from victory or touring
Profectio
Leaving
Emperor leaving for war or to go tour
Later both are standard representations of showing the emperor coming and going
Later re-carved as Nerva
Mythological Figures
Victoria
Mars
Minerva, his patron deity
Virtus, holding Domitian’s elbow while personifications of SPQR follow him

Identify and Analyze
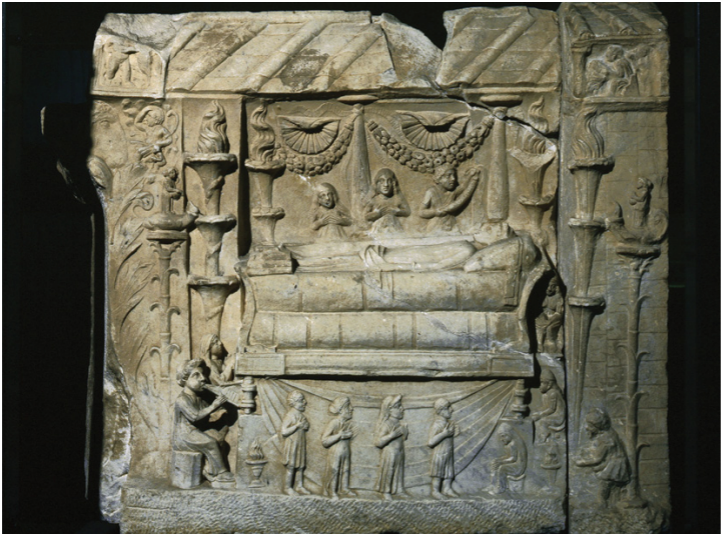
Collocatio relief, Tomb of the Haterii, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Private Relief Sculpture
continuity of Italic sculptural subjects and conventions
common wealthy did not equal those of emperor
don’t need to worry about political messages/gaining the favor of the people
Italic Style
scales + different heights
Collocatio
the lying in state of the deceased
subject in Greek, Lucanian, and Etruscan art
a wealth family would have it take place in the atrium of the family home
Identify and Analyze
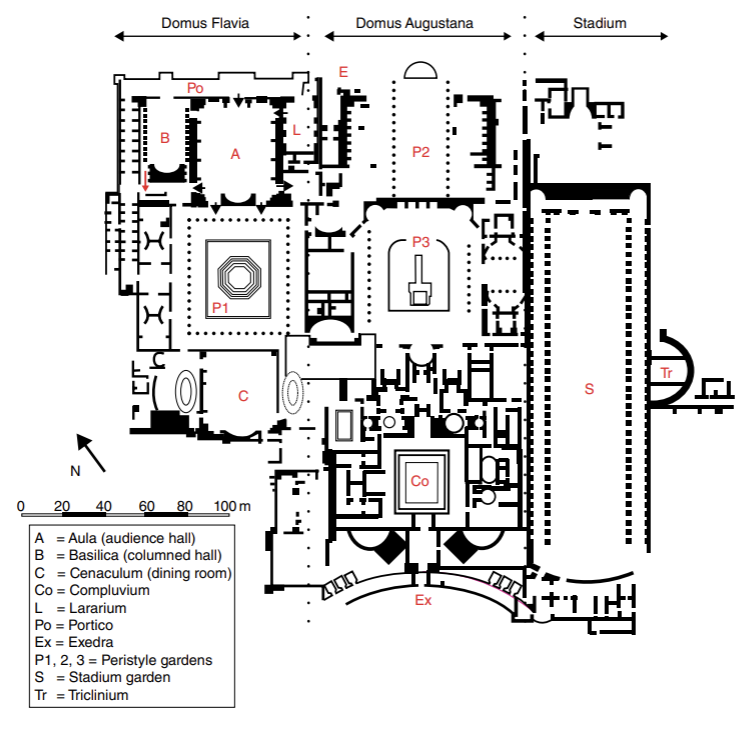
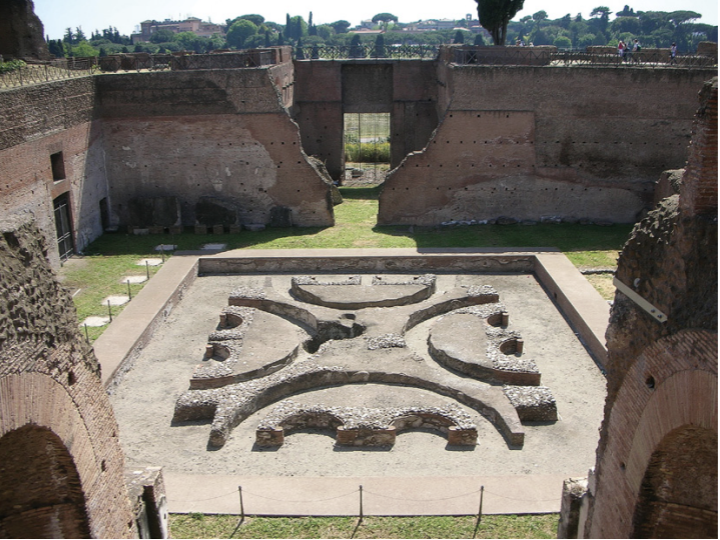
Plan of the Palace of Domitian, Palatine Hill, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
New Palace on Palatine Hill
taking over from Nero, leftover land from destruction of Domus Aurea
taking over of original house of Augustus
largest and best preserved palace
Baths, temples, stadiums
personal box for emperor off of his bedroom to watch events in stadium
Architects playing around with concrete
covers all earlier palaces of Tiberius, Caligula, and Nero

Identify and Analyze
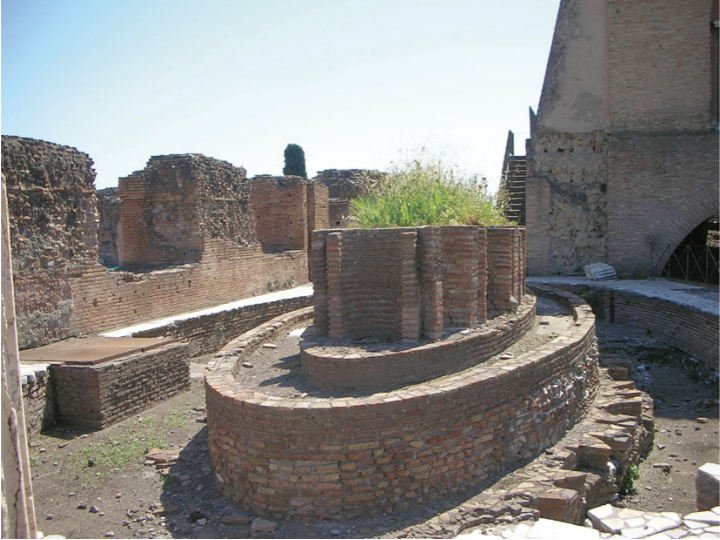
Garden with central fountain, Palace of Domitian, Palatine Hill, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
Peristyle
columns all around
Water fixtures
in middle
meant to be both entertaining while also having a cooling aspect
Modern though of Concrete
cheap alternative to other things
yet here you have it all throughout an Emperor’s palace
marble would break/crack easily
concrete outlasts many other things
Concrete
solved problem of how to light the rooms without daylight

Identify and Analyze
Fountain adjacent to the dining room, Palace of Domitian, Palatine Hill, Rome
The Flavian Period
69 CE - 96 CE
many water features
acts as a coolant in humidty/heat of Mediterranean climate
Emperors trying to offer all the comforts needed
known that architects would build windows with lots of wind behind and waterfalls in front to bring in a cooling spray
Hypocaust System
Roman
for when winter came
common in Roman baths
Warm Room
warm yourself up
stays warm through the bleed off of the hot room
built directly beside hot room
Hot Room
sweat off
floor supported by piers with a cavity below
slaves would keep fires beneath flooring
heat rises to heat the pools
heat also rises through channel pipes built into the walls of the hot room to heat those/the air too
Cold Room
Cool down