purdue slhs 303 final exam
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
moving vocal tract to produce sounds
what is articulation?
w/in spaces of the vocal tract and gives distinct voice
what is resonance?
producing speech
-extremely complex and rapid task
-approximately 175 words per minute (20 speech sounds per second)
initiating eating
very complex
producing speech and initiating eating
-require coordination of hundreds of neural signals (action potentials) and muscle contractions
-careful examination of underlying structures (to diagnose and treat disorders
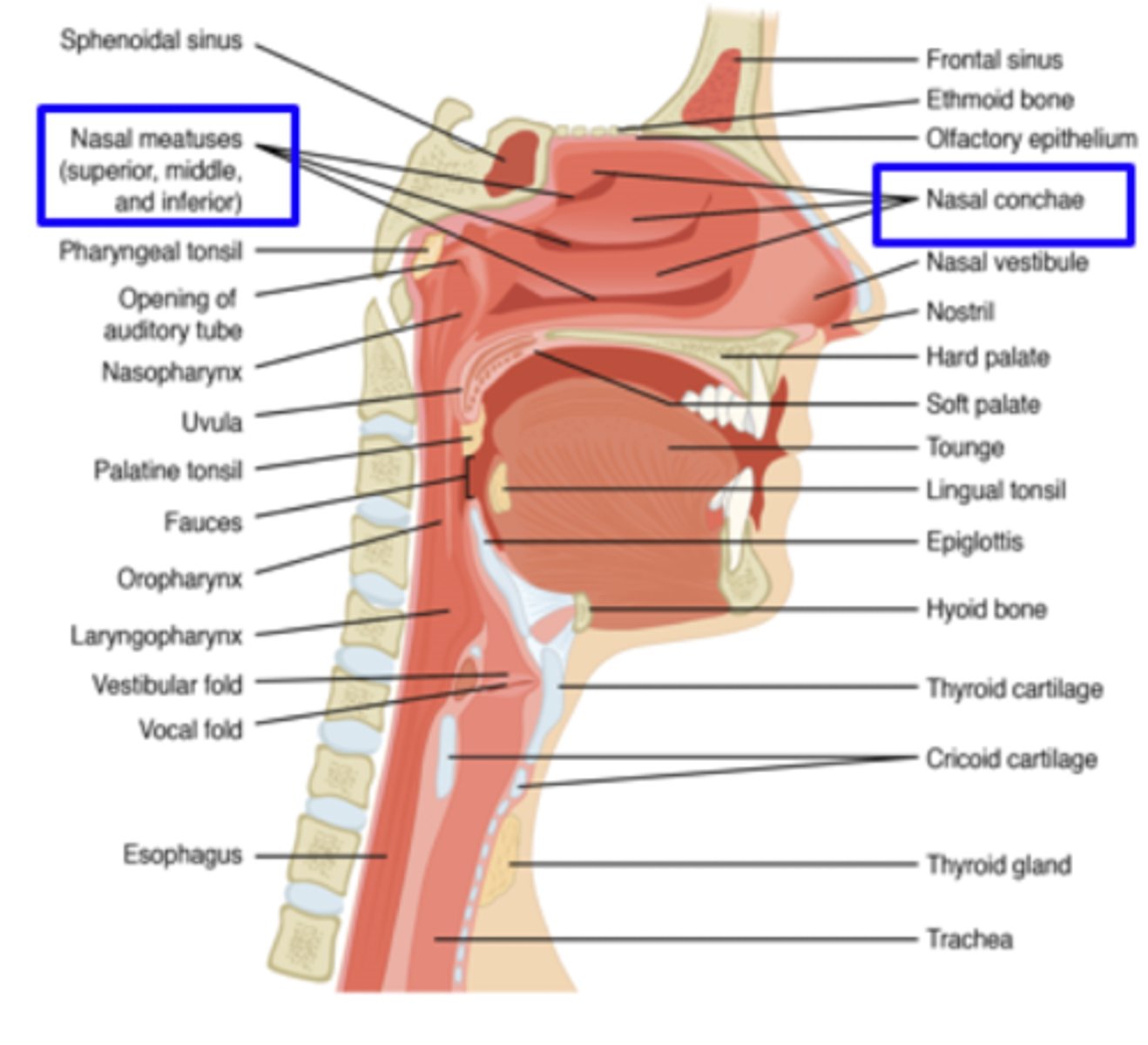
oral cavity and parts
lips, teeth, alveolar ridge, hard palate, soft palate, tongue, jaw, anger (palatogolssal muscle) facial pillars
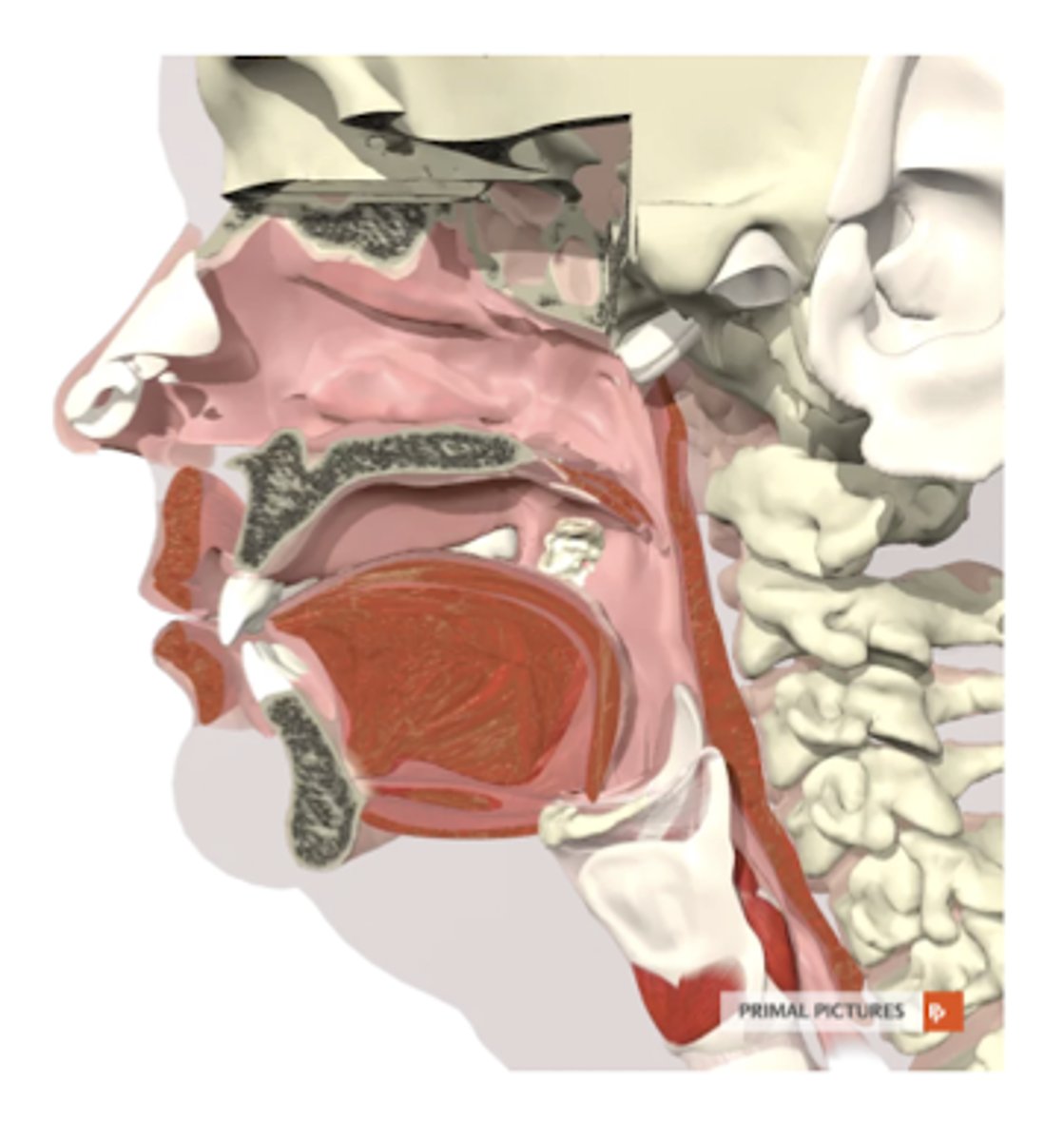
nasal cavity
borders: nares/nostrils to nasopharynx
anterior and posterior faucial pillars
arches formed by muscles
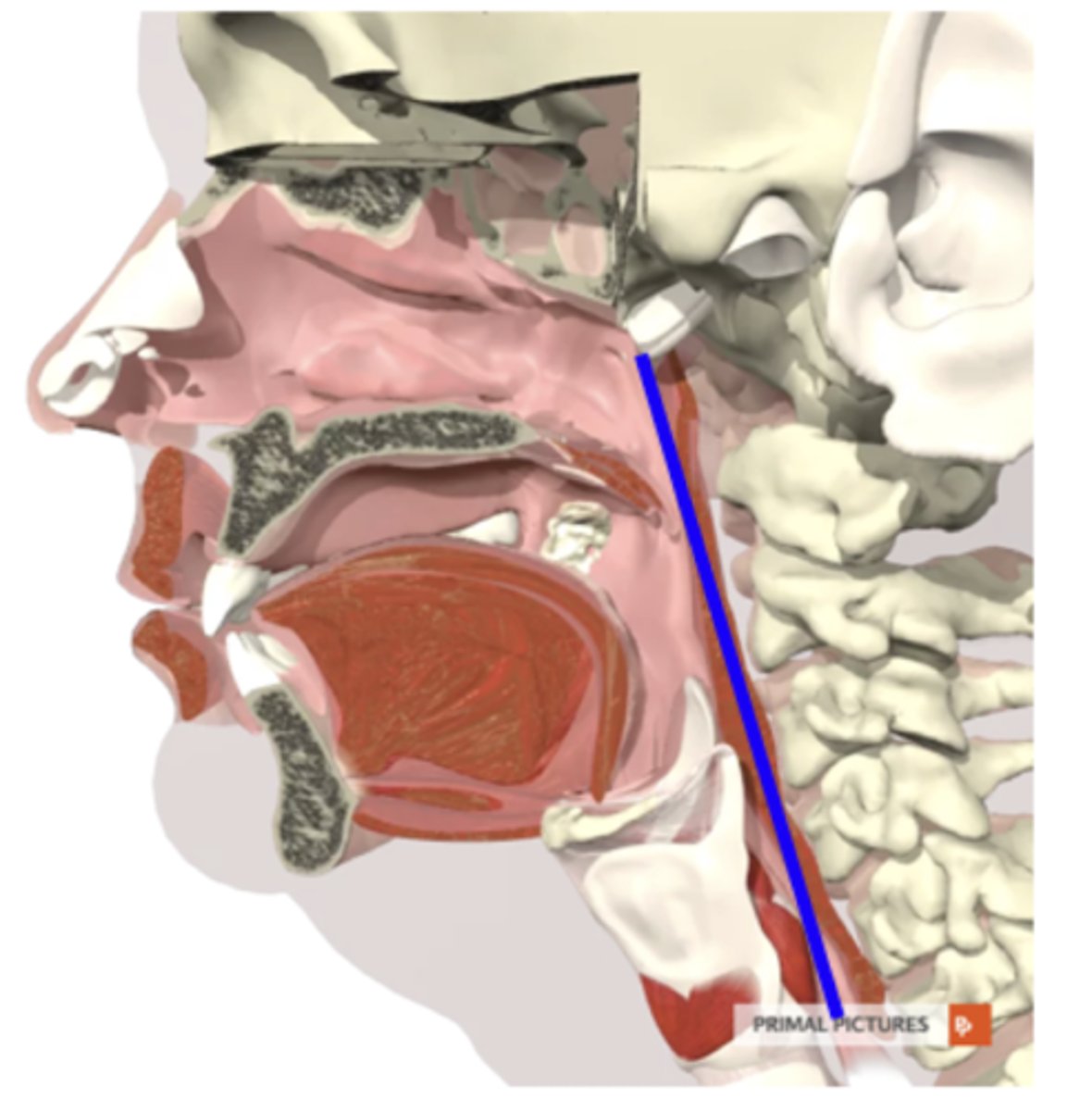
pharyngeal cavity
from base of skull to superior surface of cricoid cartilage
nasal cavity parts
nose and two chambers separated by septum
-each chamber: superior, middle, inferior conchae and meatuses (nasal passages)
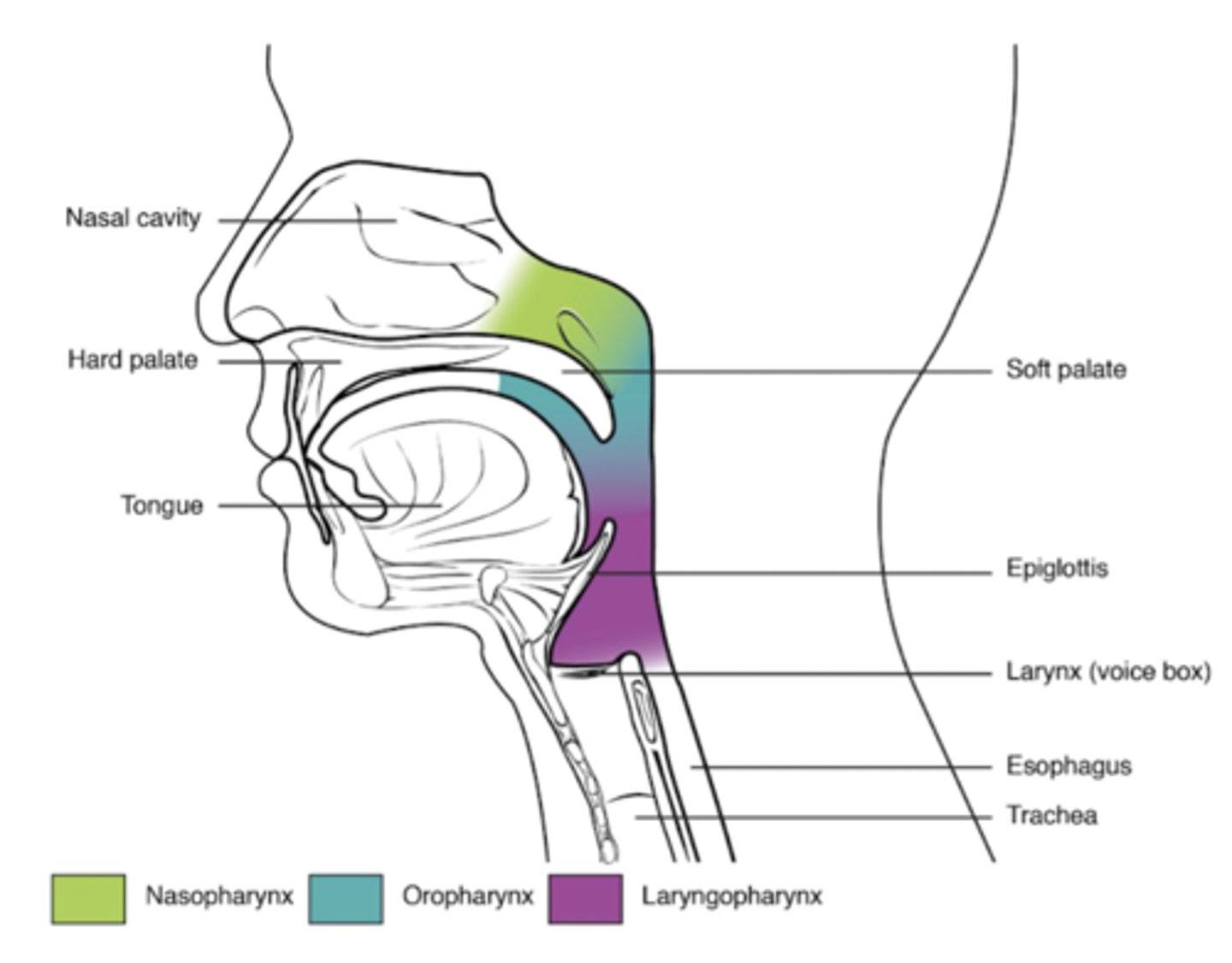
divisions of the pharynx
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
mobile articulators
moved by muscle contractions
-lips, velum, tongue, law/mandible, pharynx
immobile articulators
point of contact for other articulators
-teeth, alveolar ridge, hard palate
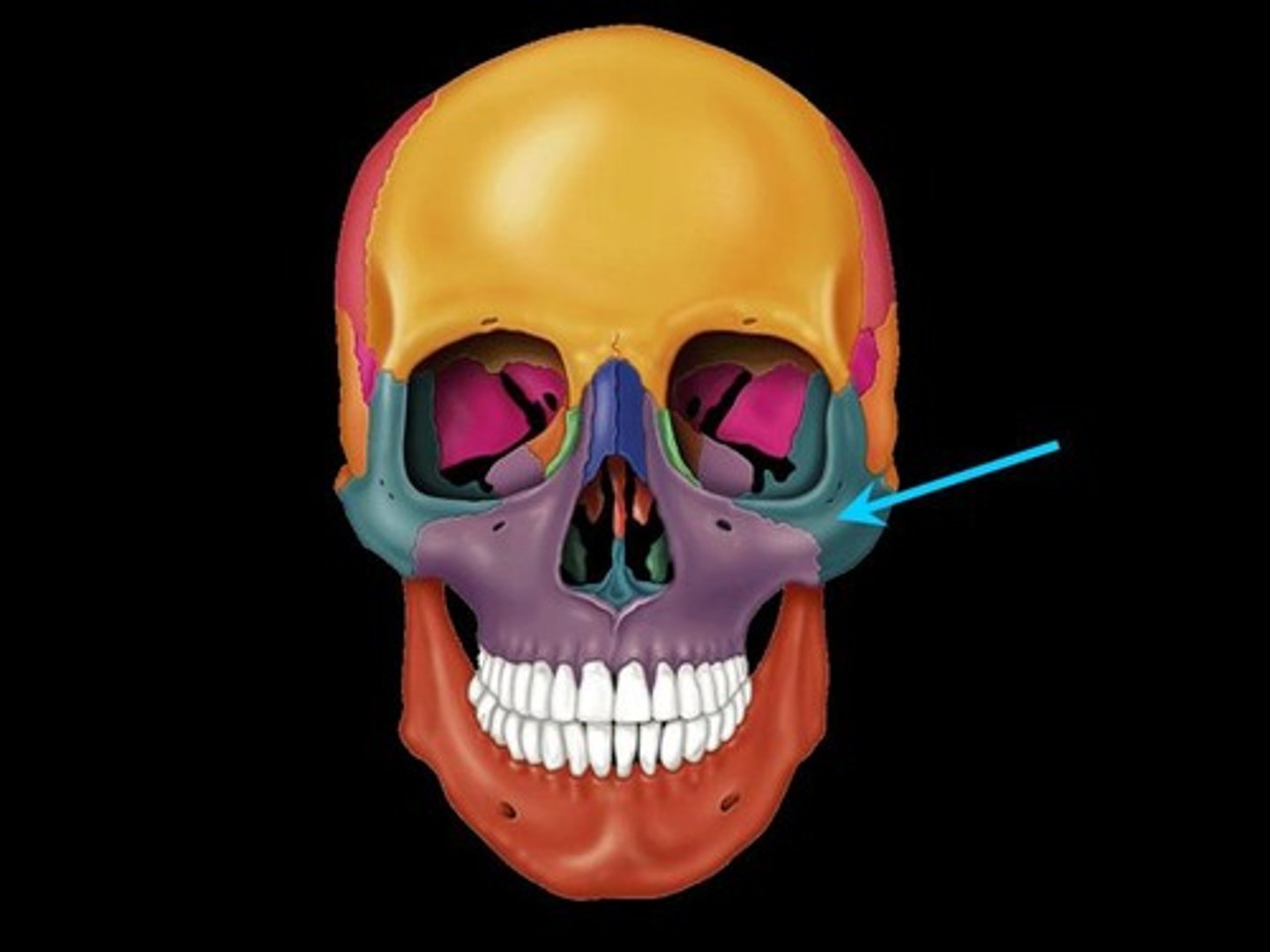
zygomatic bone
label this bone
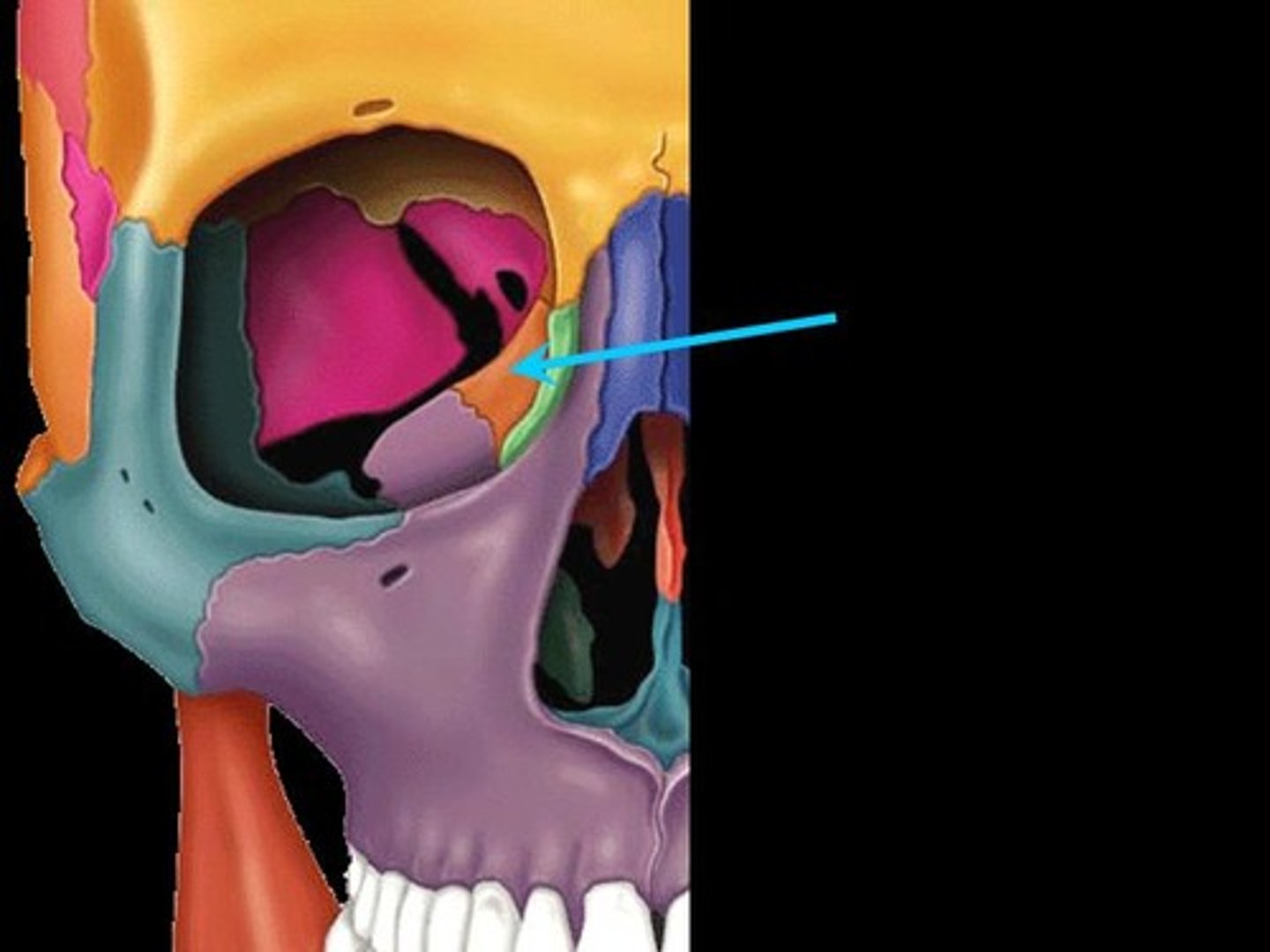
ethmoid bone
label this bone
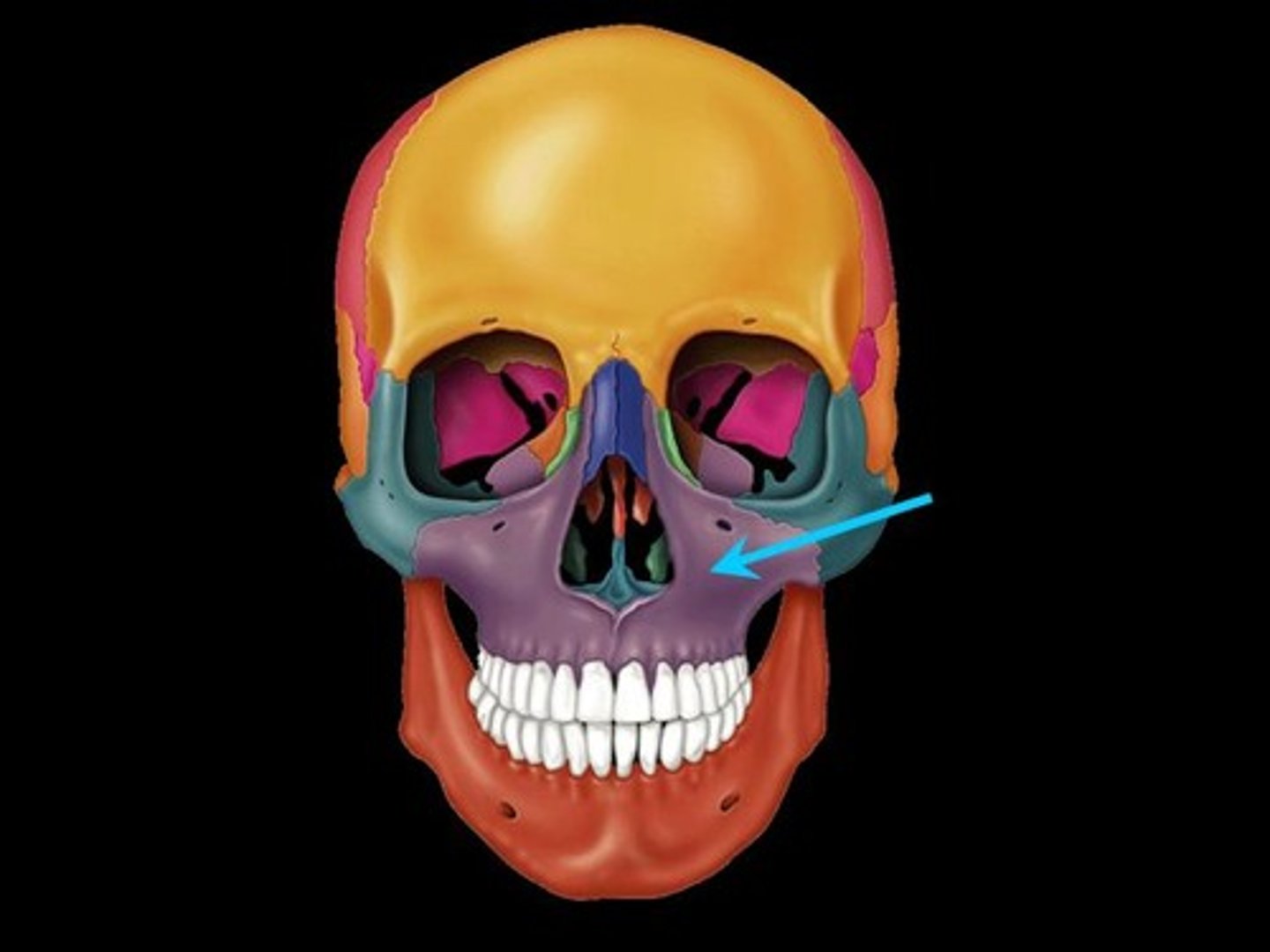
maxilla
label this bone
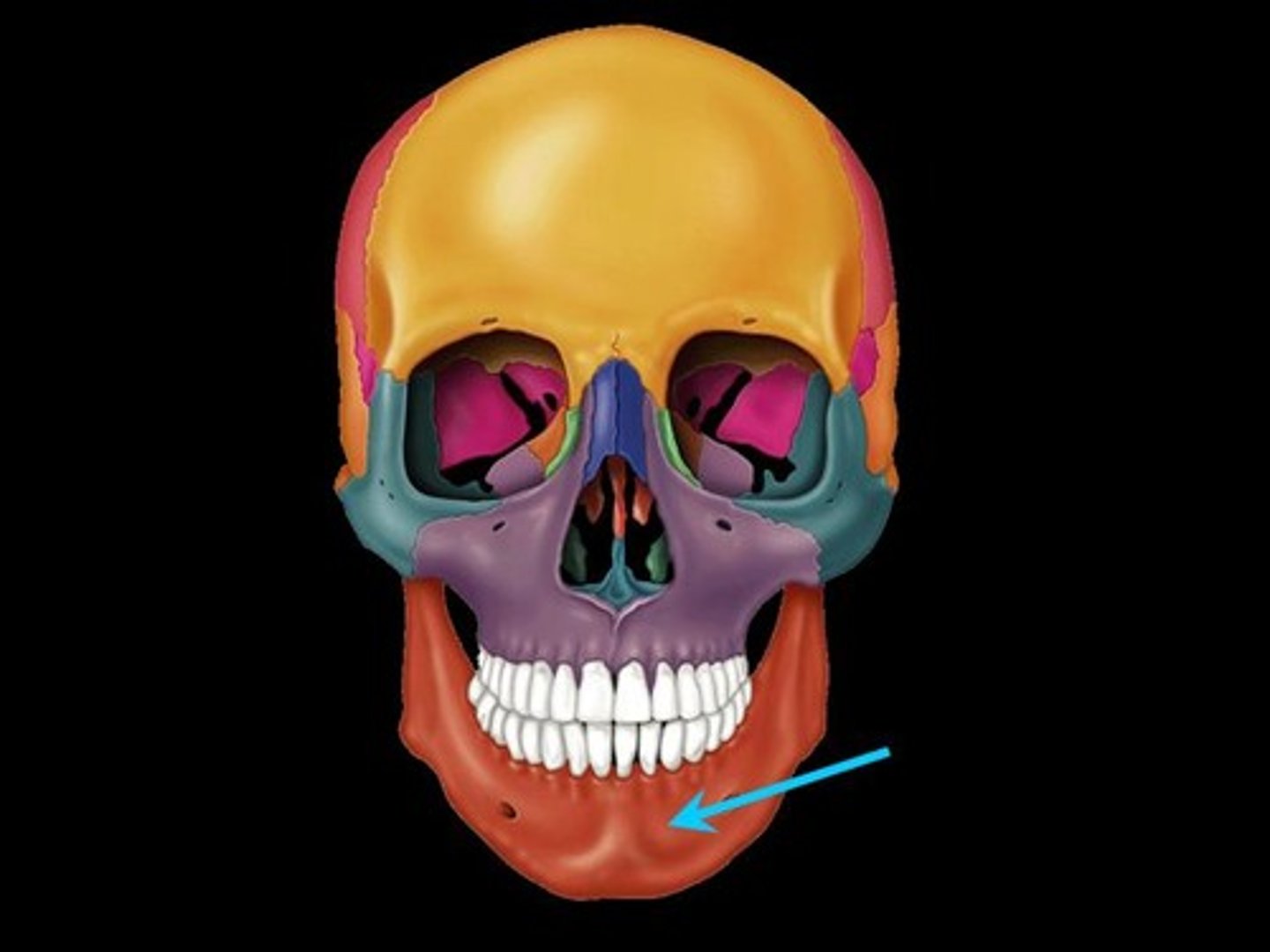
mandible
label this bone
teeth and their role
-housed within the mandible and maxilla
-biological function: chewing/mastication (break down foods)
-non-biological function- speech and facial structure (important for consonants and vowels)
-primary teeth = 20 (baby)
-permanent teeth = 32
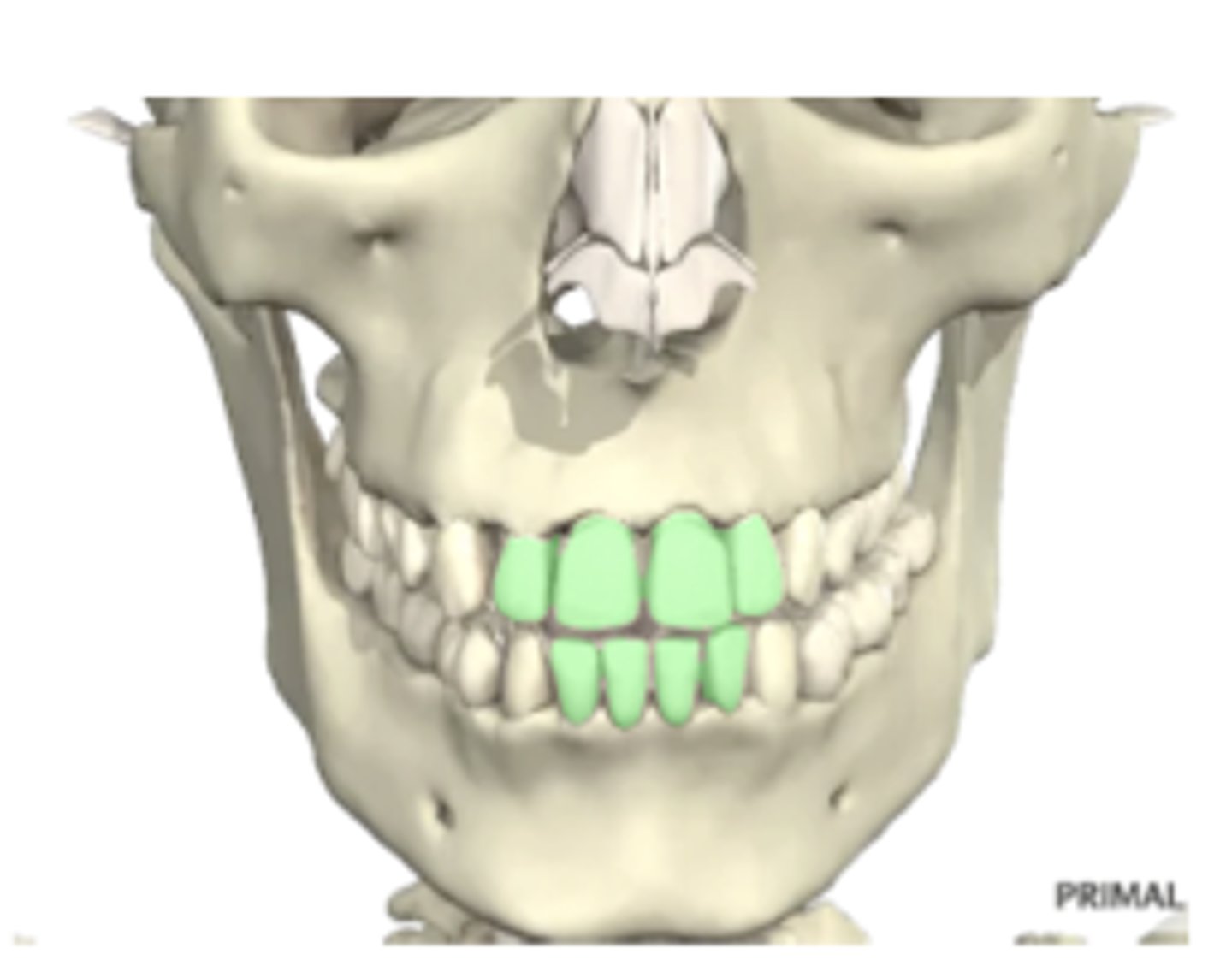
incisors
6 months to 6-8 years old
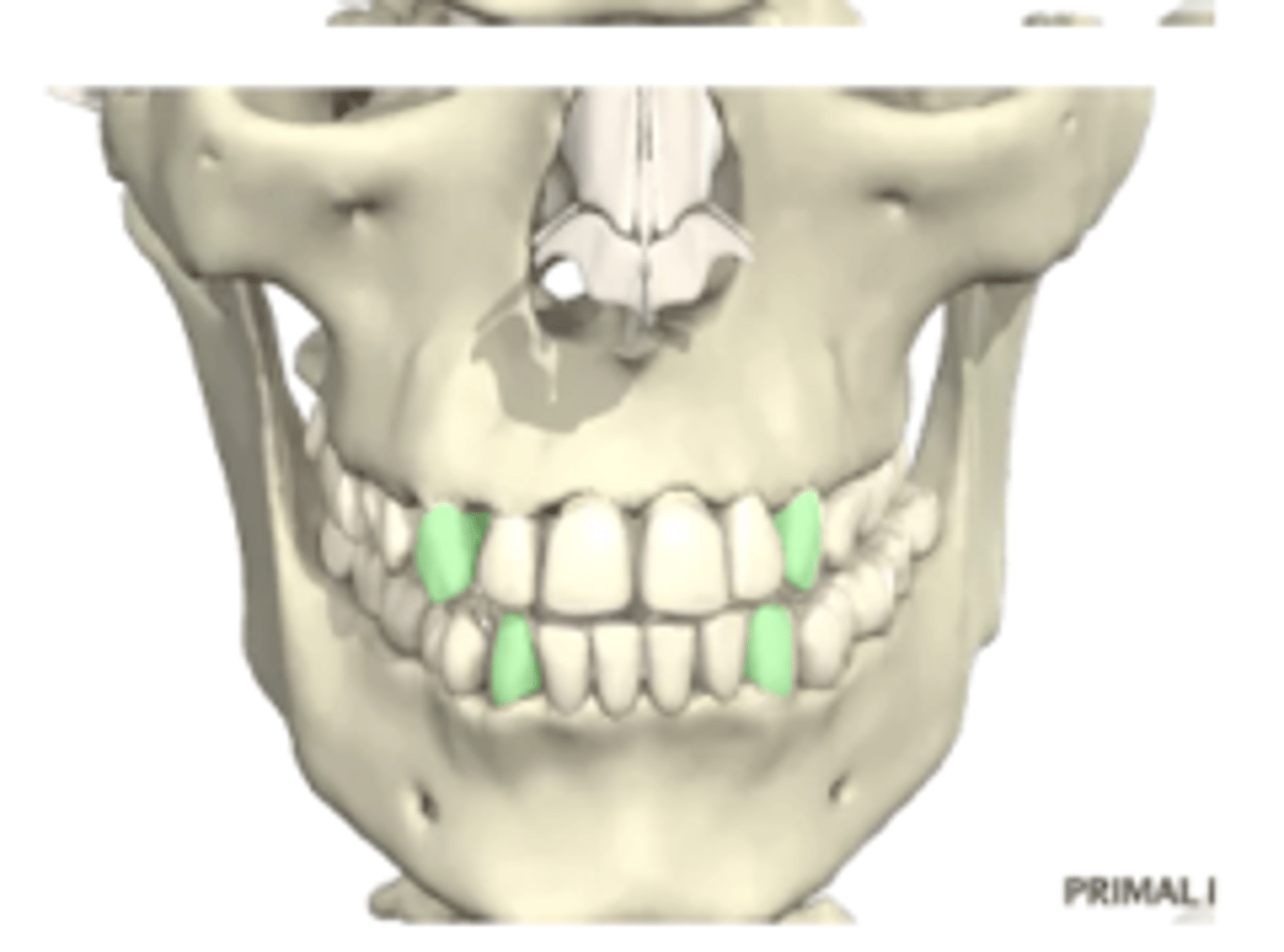
canines
1.5 years old to 9-12 years old
premolars
permanent 10-11 years old
molars
1st set- 1 year old to 6 years old
2nd set- 11-13 years old
3rd set- early adulthood (wisdom teeth)
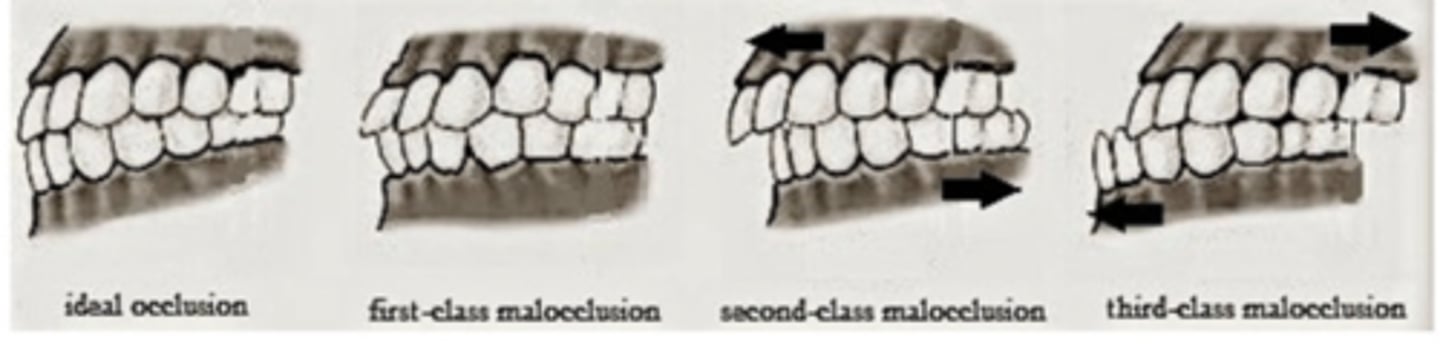
types of occlusion
Class I, Class II, Class III
levator labii superoris
label this muscle
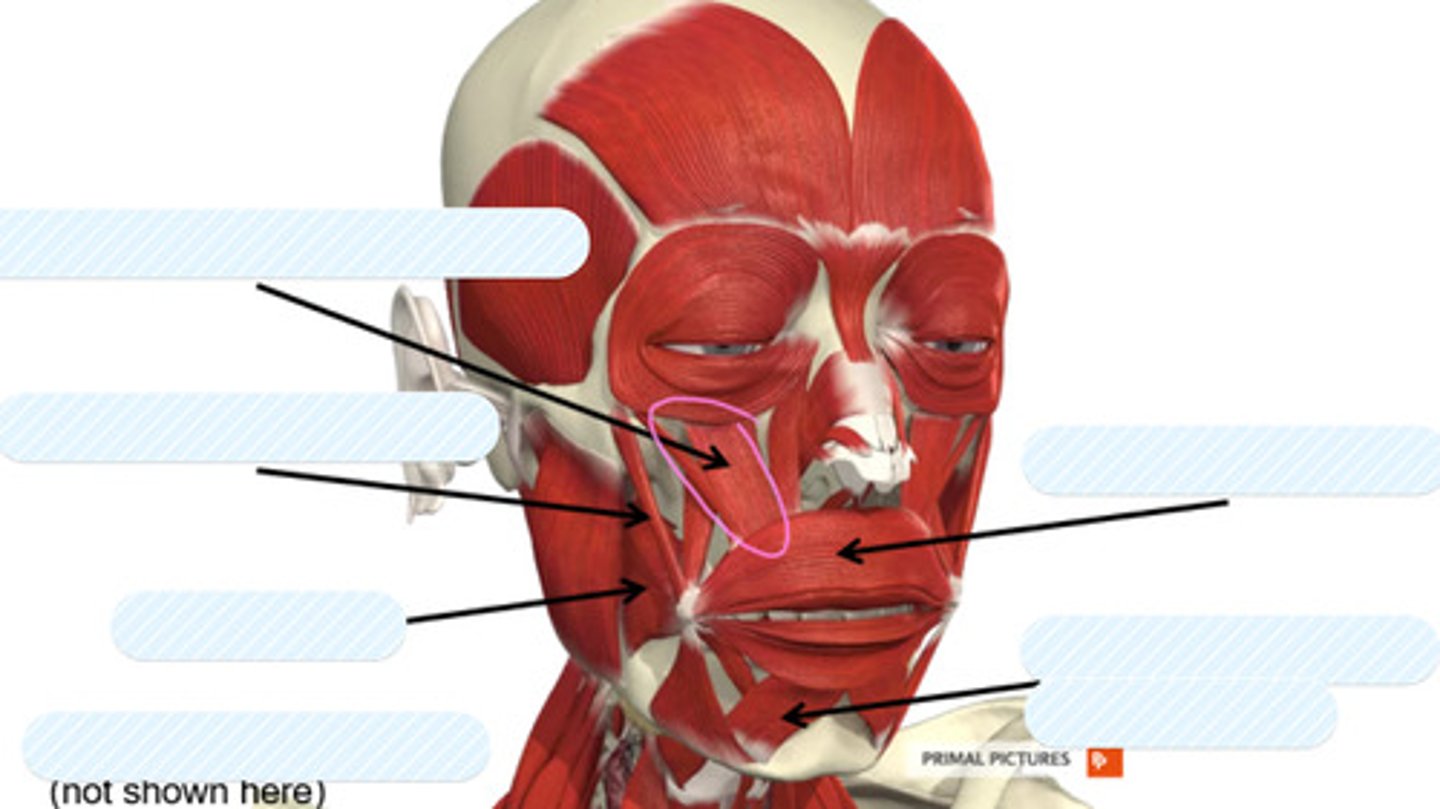
zygomaticus major
label this muscle
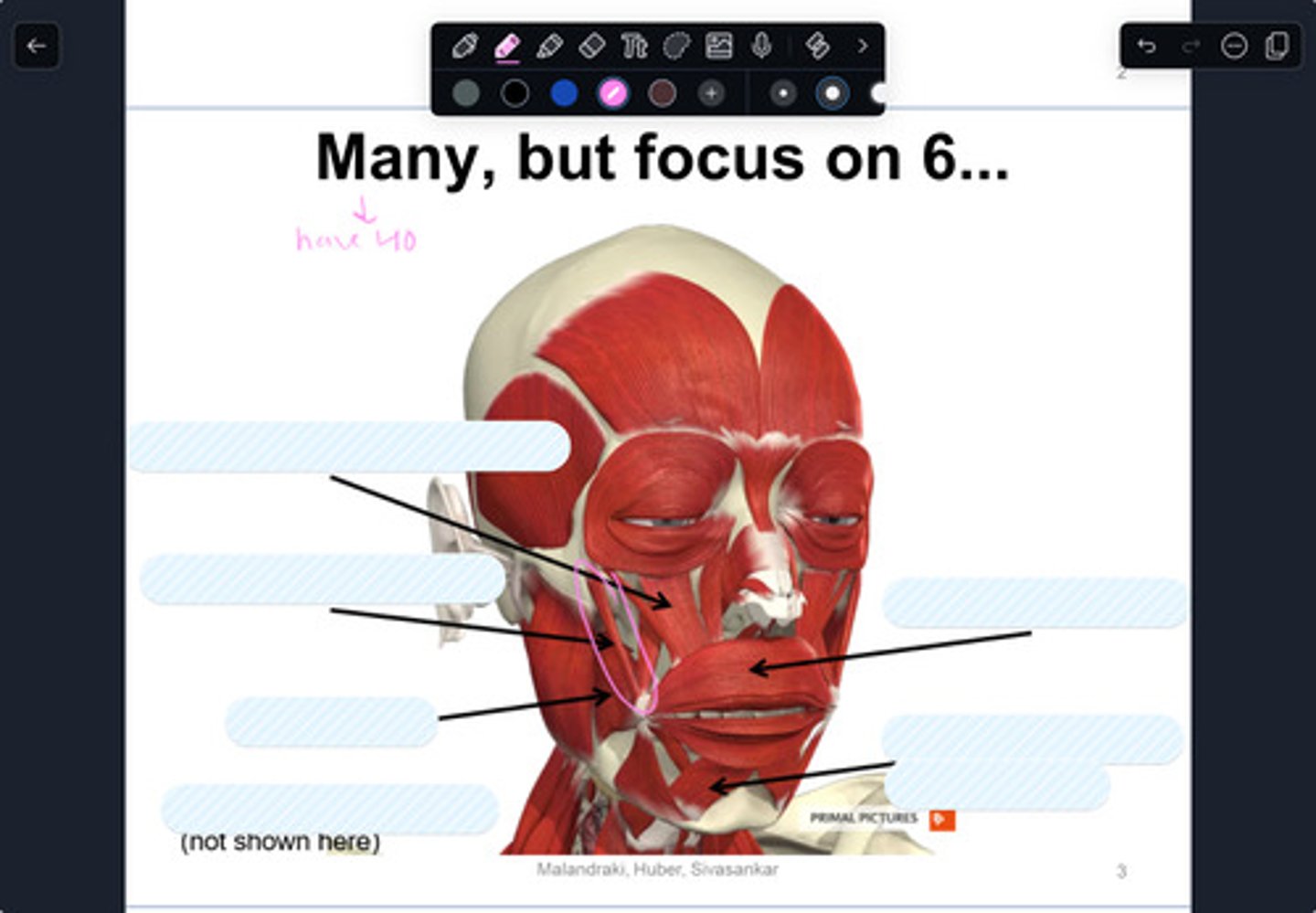
buccinator
label this muscle
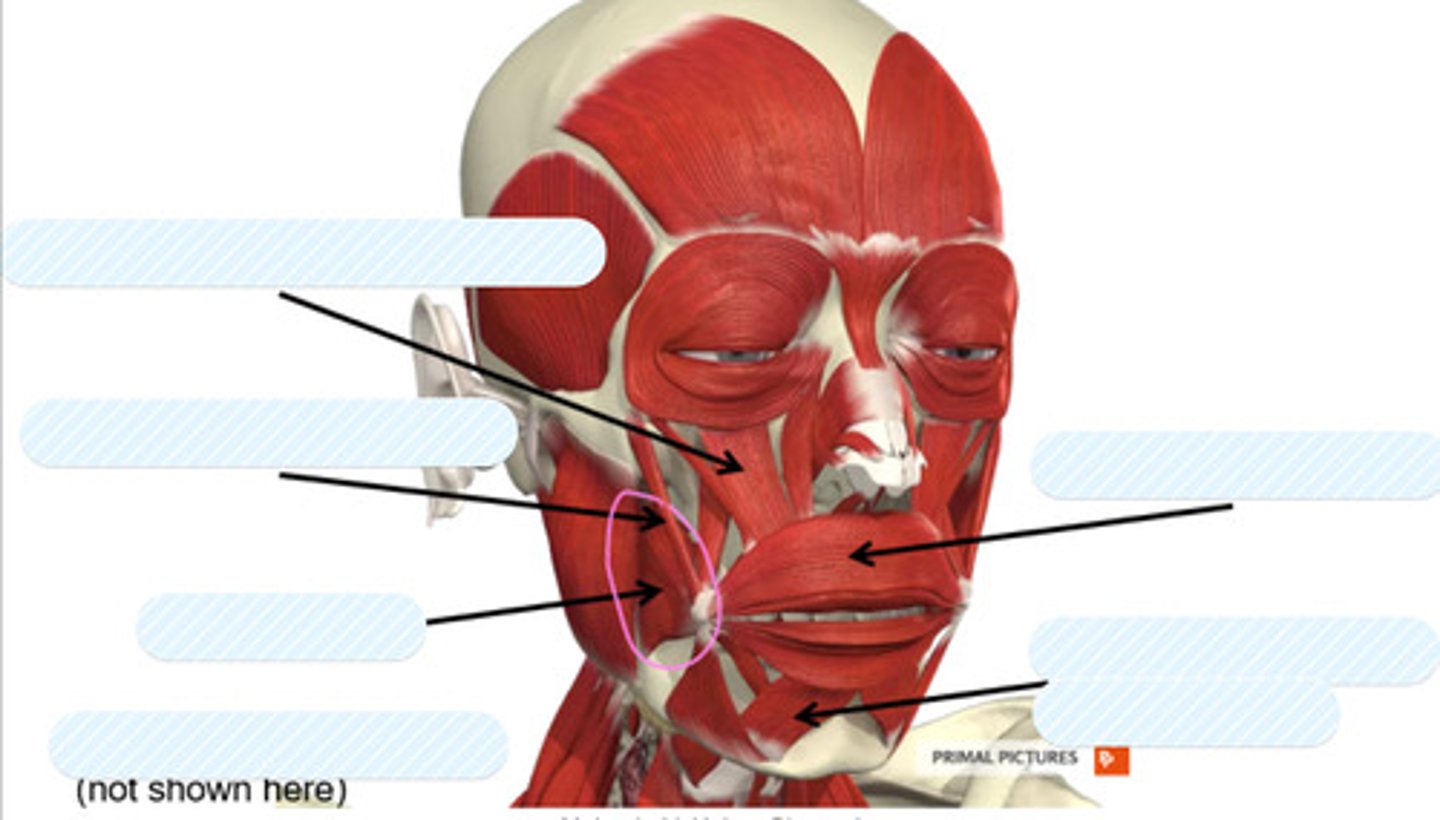
orbicularis oris
label this muscle
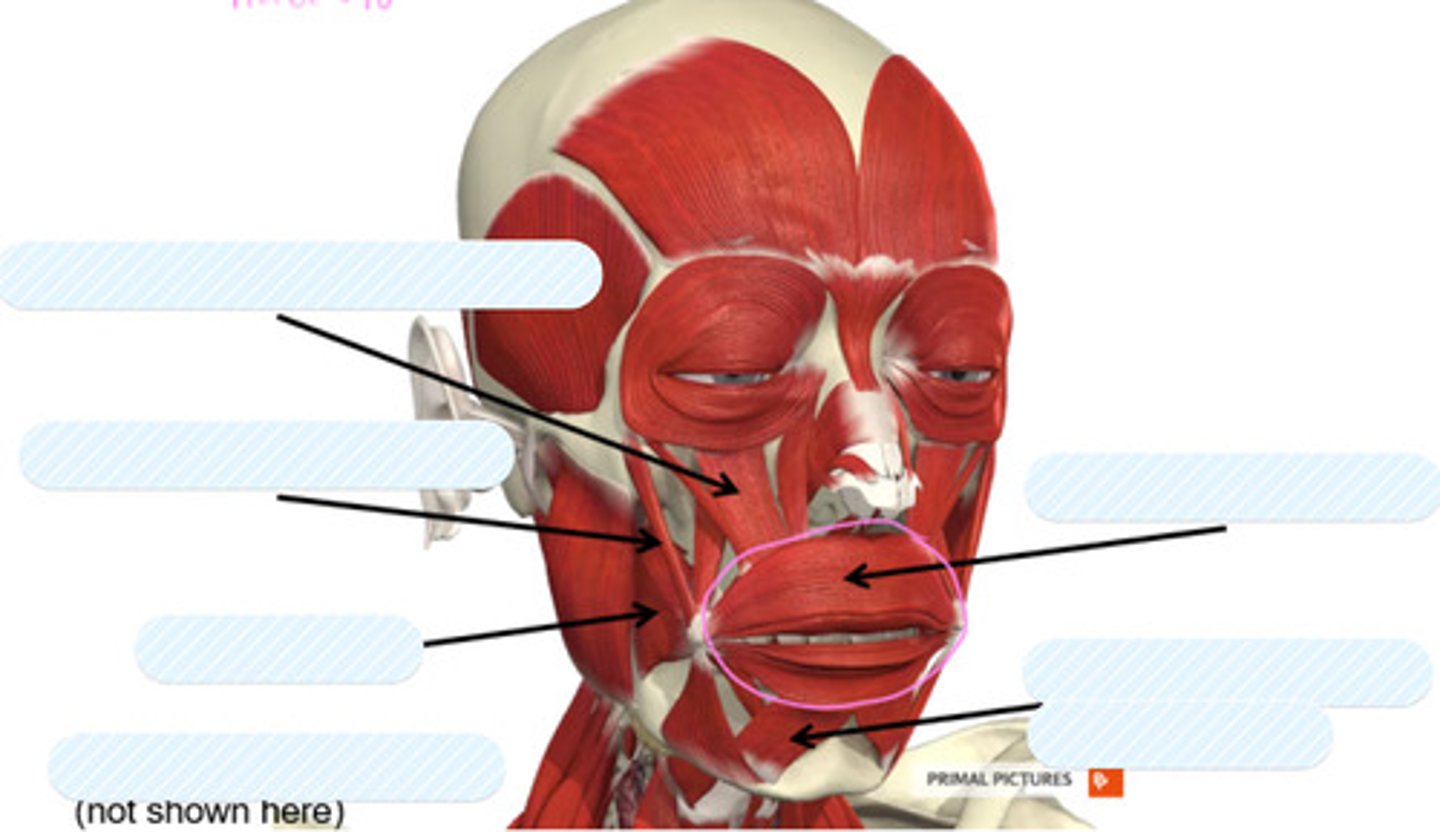
depressor labii inferiorus
label this muscle

mucosa of upper and lower lips
orbicularis oris insertion
maxilla, mandible, and deep layers of skin
orbicularis oris origin
-puckering of lips
-tight lip closure (oral plosives p/b)
orbicularis oris function
CN VII (facial nerve)
orbicular oris innervation
mandible and maxilla
buccinator origin
angle of the mouth
buccinator insertion
-lips: pull lips laterally (sucking from straw/nipple)
-cheek: tense cheek and presses cheek against teeth (when eating and chewing)
buccinator functions
CN VII (facial nerve)
buccinator innveration
frontal process of maxilla, infraorbital region and zygomatic bone
levator labii superioris origin
skin of upper lip and side cartilage of nose
levator labii superioris insertion
lips: elevates upper lip
mouth: raises angle of mouth
levator labii superioris functions
CN VII
levator labii superioris innervation
zygomatic bone
zygomaticus major origin
angle of the mouth
zygomaticus major insertion
draws angle of mouth upward and laterally (smiling)
zygomaticus major function
CN VII (facial nerve)
zygomaticus major innervation
mandible
depressor labii inferiorus origin
lower lip
depressor labii inferiorus insertion
pulls lip downward and laterally (frowning)
depressor labii inferiorus function
CN VII (facial nerve)
depressor labii inferiorus innervation
platysma
label this muscle
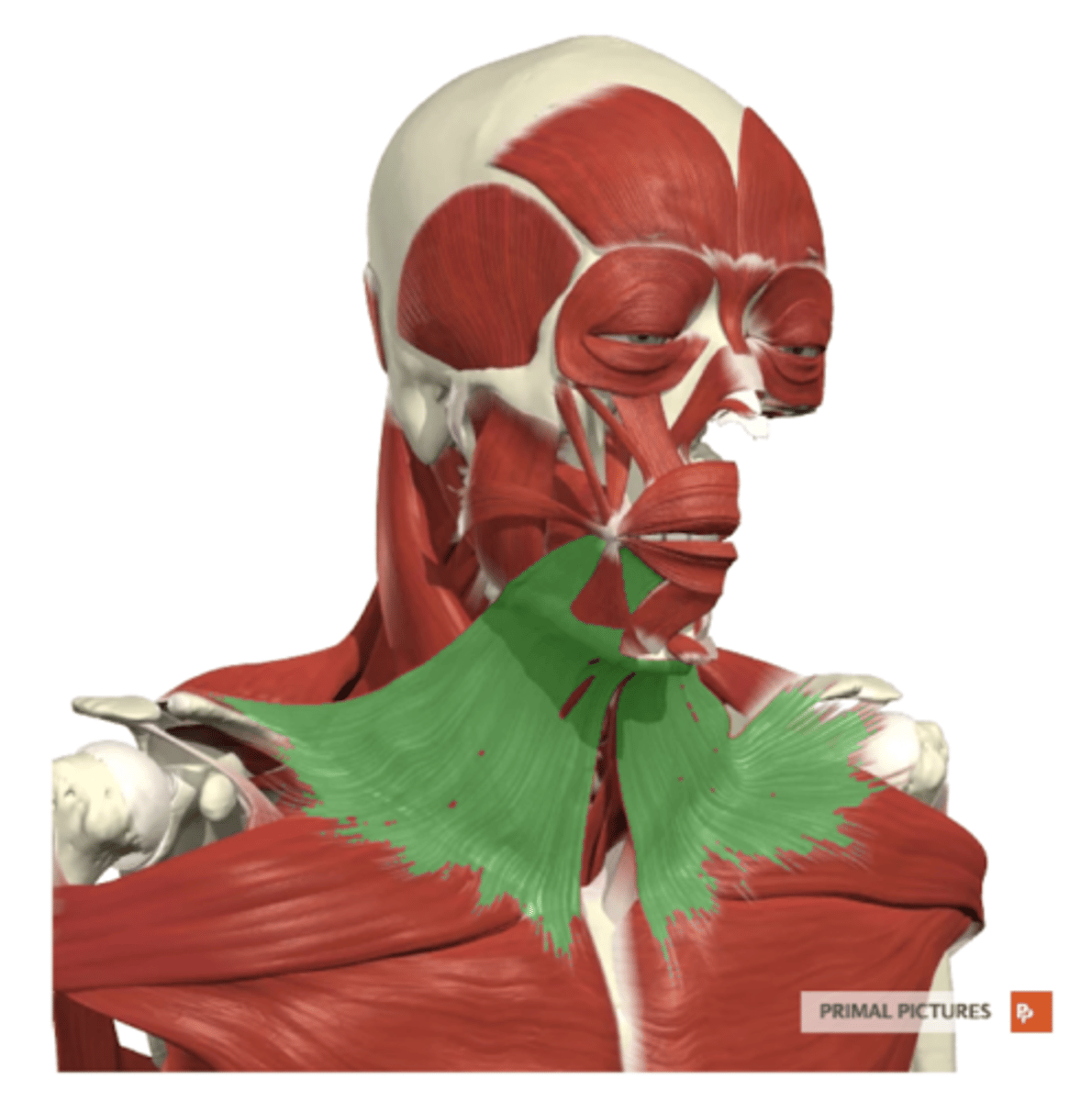
neck region on fascia of shoulder and chest
platysma origin
mandible, skin of cheek, angle of mouth, and orbicularis oris
platysma insertion
-tenses skin of lower face
-pulls corner of mouth inferiorly
-helps with mandible
platysma functions
CN VII (facial nerve)
platysma innervation
lips as an articulator
-mobile articulator
-primary contributor: orbicularis oris
-important lip movements for speech: lip rounding, and closure
lip round (and protrusion)
vowels (ex. /u/)
consonants (ex. /w/)
lip closure
bilabial consonants, and labiodental consonants (lower lip against upper teeth)
masseter
label this muscle
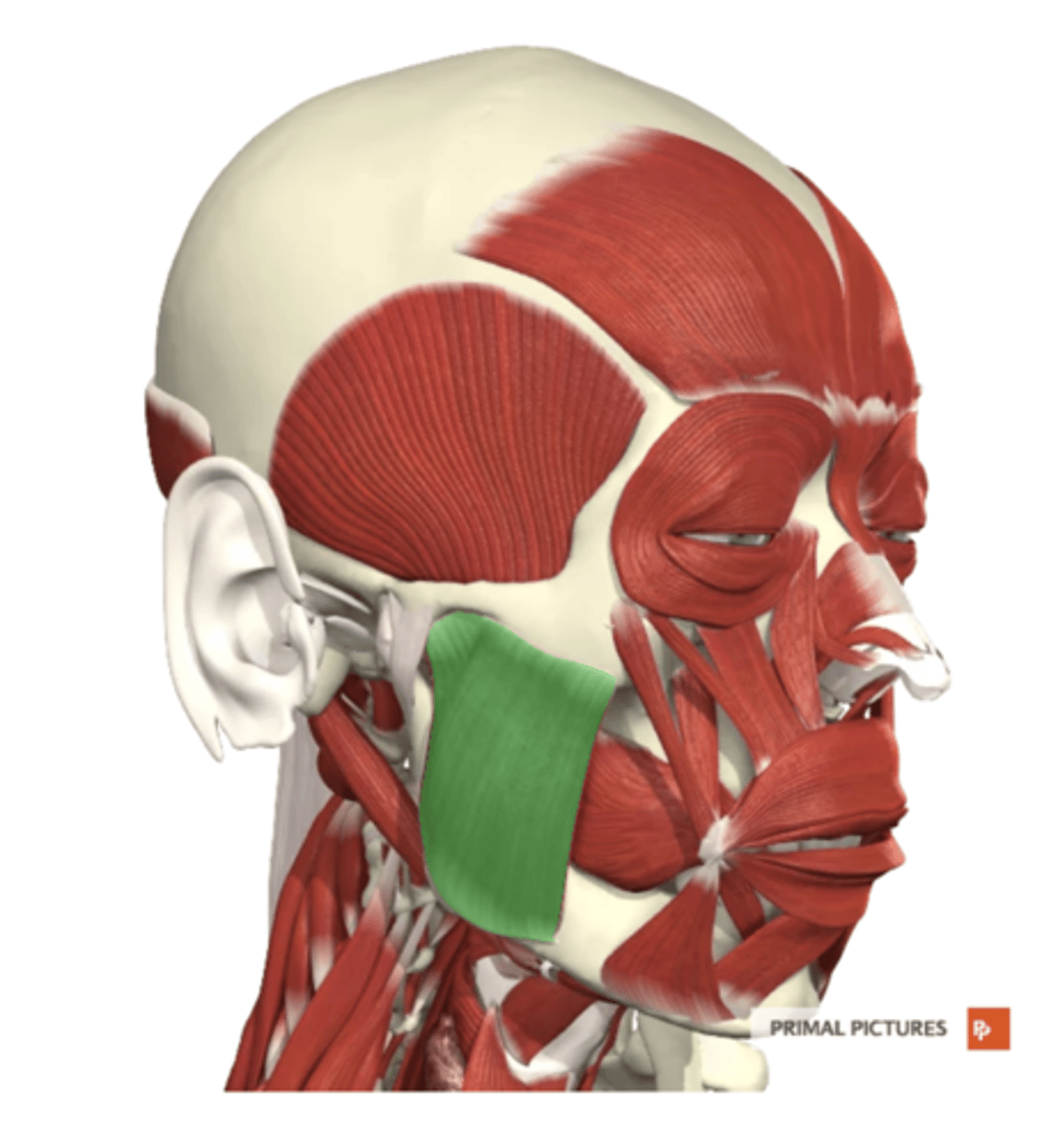
zygomatic arch
masseter origin
angle and lateral side of mandible
masseter insertion
-elevates mandible (closes jaw/mouth)
-protrudes law
masseter functions
CN V (trigeminal)
masseter innervation
temporalis
label this muscle
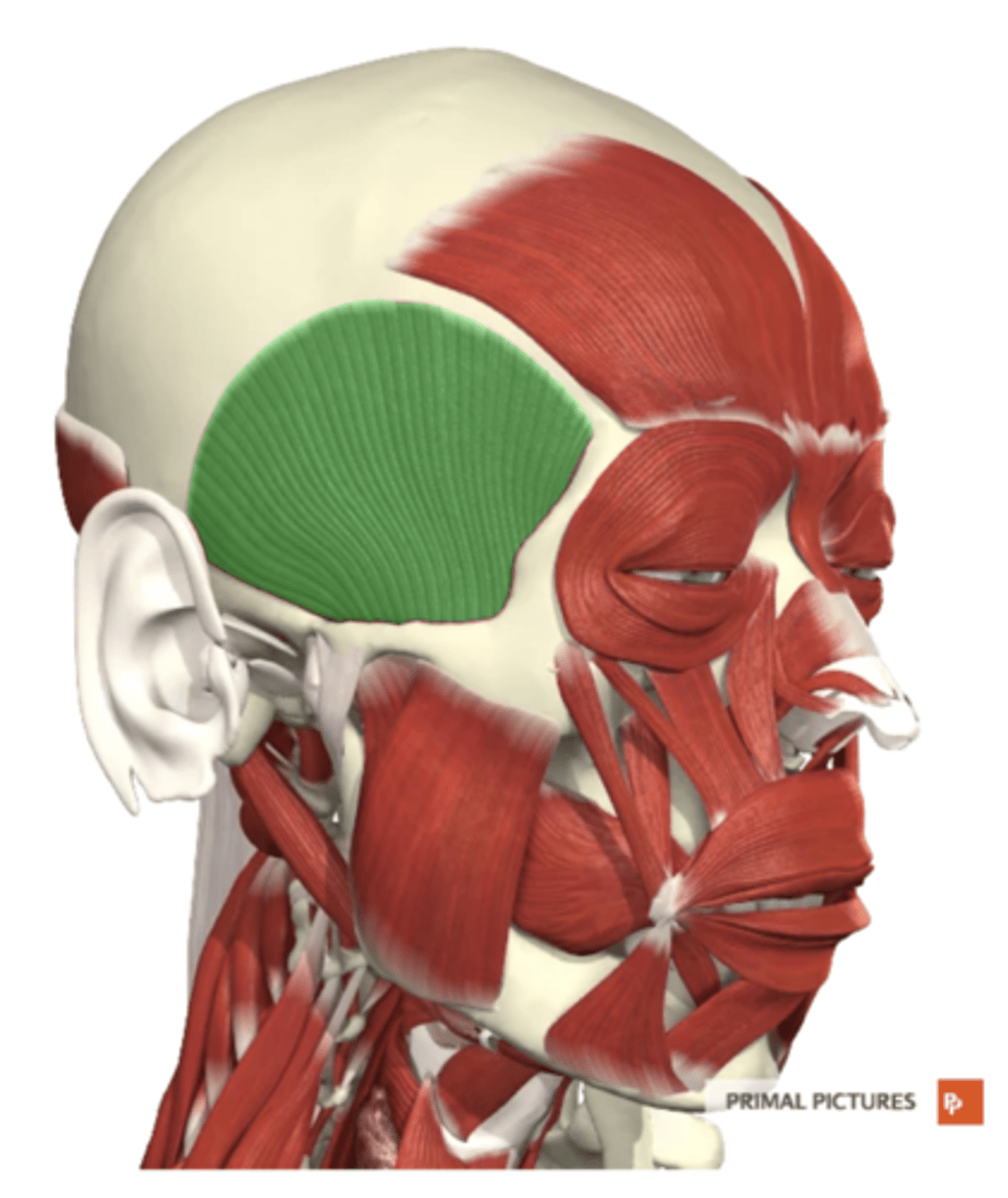
temporal bone
temporalis origin
top and part of ramus of mandible
temporalis insertion
-elevates mandible (closes law/mouth)
-retracts jaw
temporalis functions
CN V (trigeminal nerve)
temporalis innervation
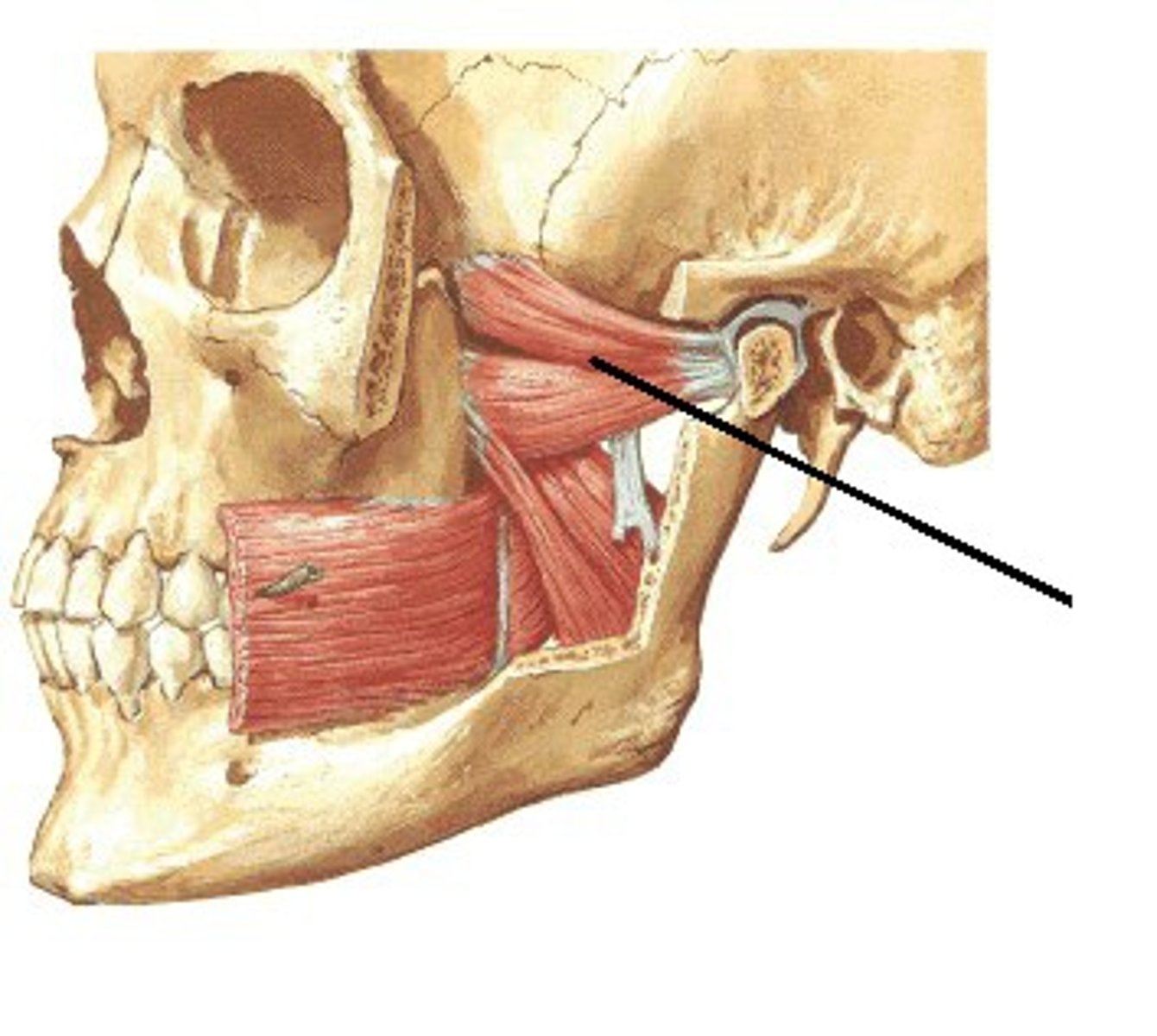
lateral pterygoid plate (sphenoid bone), and maxilla
medial pterygoid origin
ramus and angle (internal side) of mandible
medial pterygoid insertion
-elevates mandible (closes jaw/mouth)
-protrudes mandible
medial pterygoid functions
CN V (trigeminal nerve)
medial pterygoid innervation
medial pterygoid
label this muscle
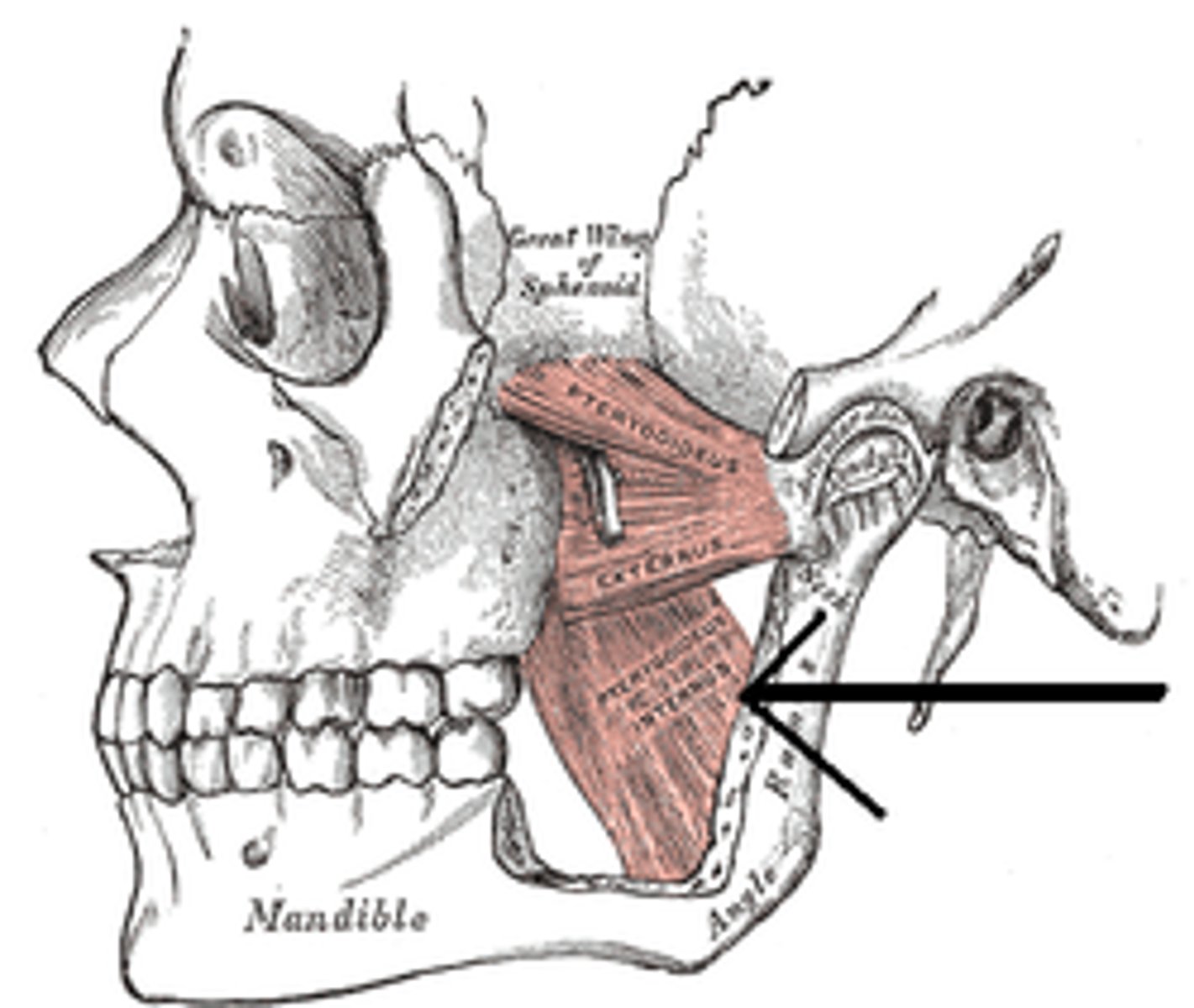
lateral pterygoid
label this muscle
greater wind of sphenoid, lateral pterygoid plate (lateral side of sphenoid)
lateral pterygoid origin
condyle of mandible, tempromandibular joint
lateral pterygroid insertion
-depresses mandible (opens jaw/mouth MAIN OPENER)
-protrudes mandible
-moves mandible laterally
lateral pterygoid functions
CN V (trigeminal nerve)
lateral pterygoid innervation
-depress jaw (opens jaw/mouth) [helpers for mouth opening]
-GH also shortens floor of the mouth
anterior belly of digastric, mylohyoid, and geniohyoid function
CN V
anterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid innervation
CN 1 and cervical plexus (CN I,II,III)
geniohyoid innervation
jaw/mandible as an articulator
-mobile
-produces changes in size of oral cavity
-assists in positioning of lips and tongue
-provides fine control of small movements of jaw associated with speech
-critical supportive role for lips and tongue
tensor veli palatini
label this muscle
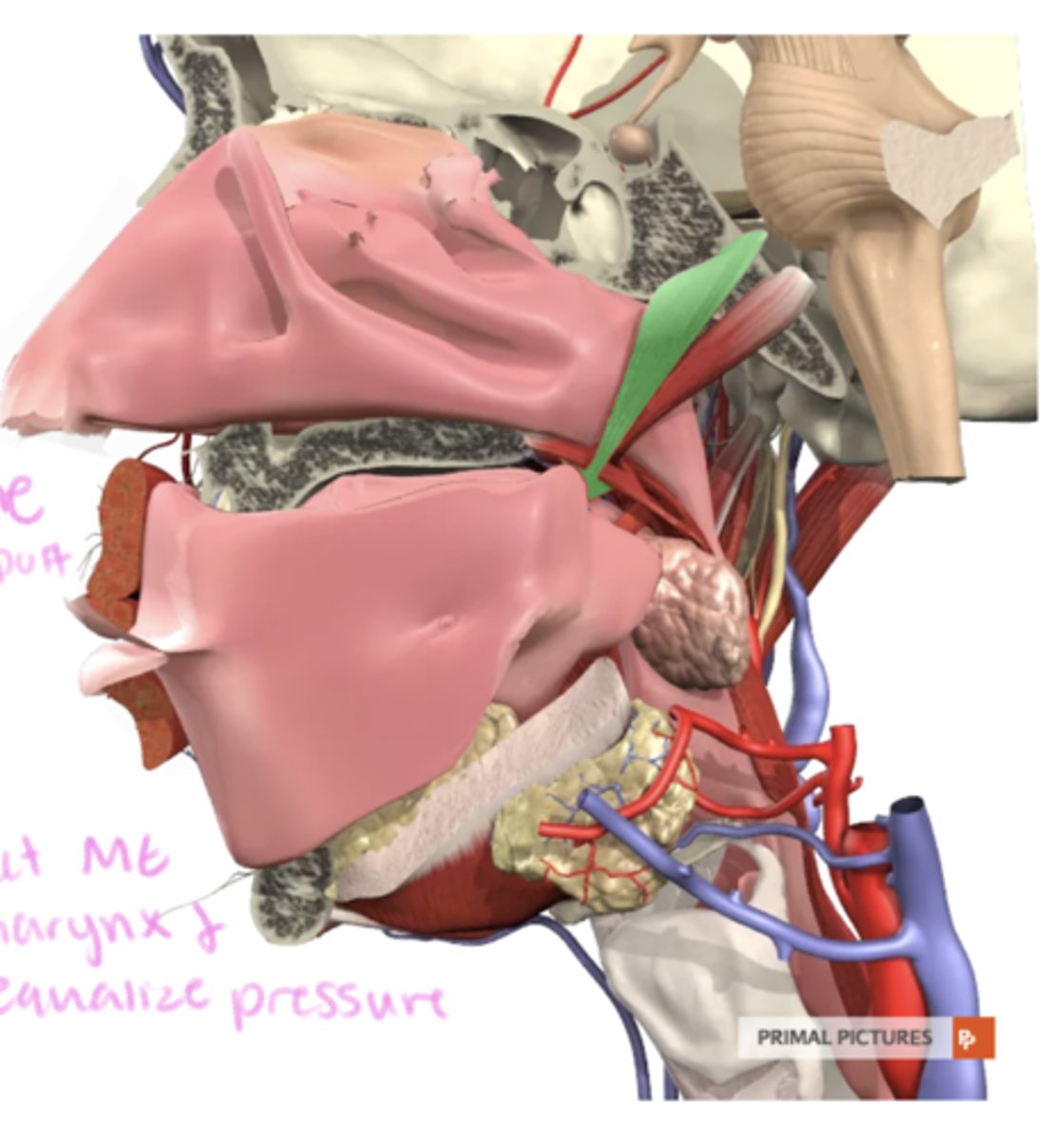
sphenoid bone, eustachian tube
tensor veli palatini origin
palatine aponerosis (membrane providing support to palate)
tensor veli palatini insertion
-tenses soft palate
-dilates (opens) eustachian tube
-connect ME to pharynx and equalize pressure
tensor veli palatini function
CN V
tensor veli palatini innervation
levator veli palatini
label this muscle
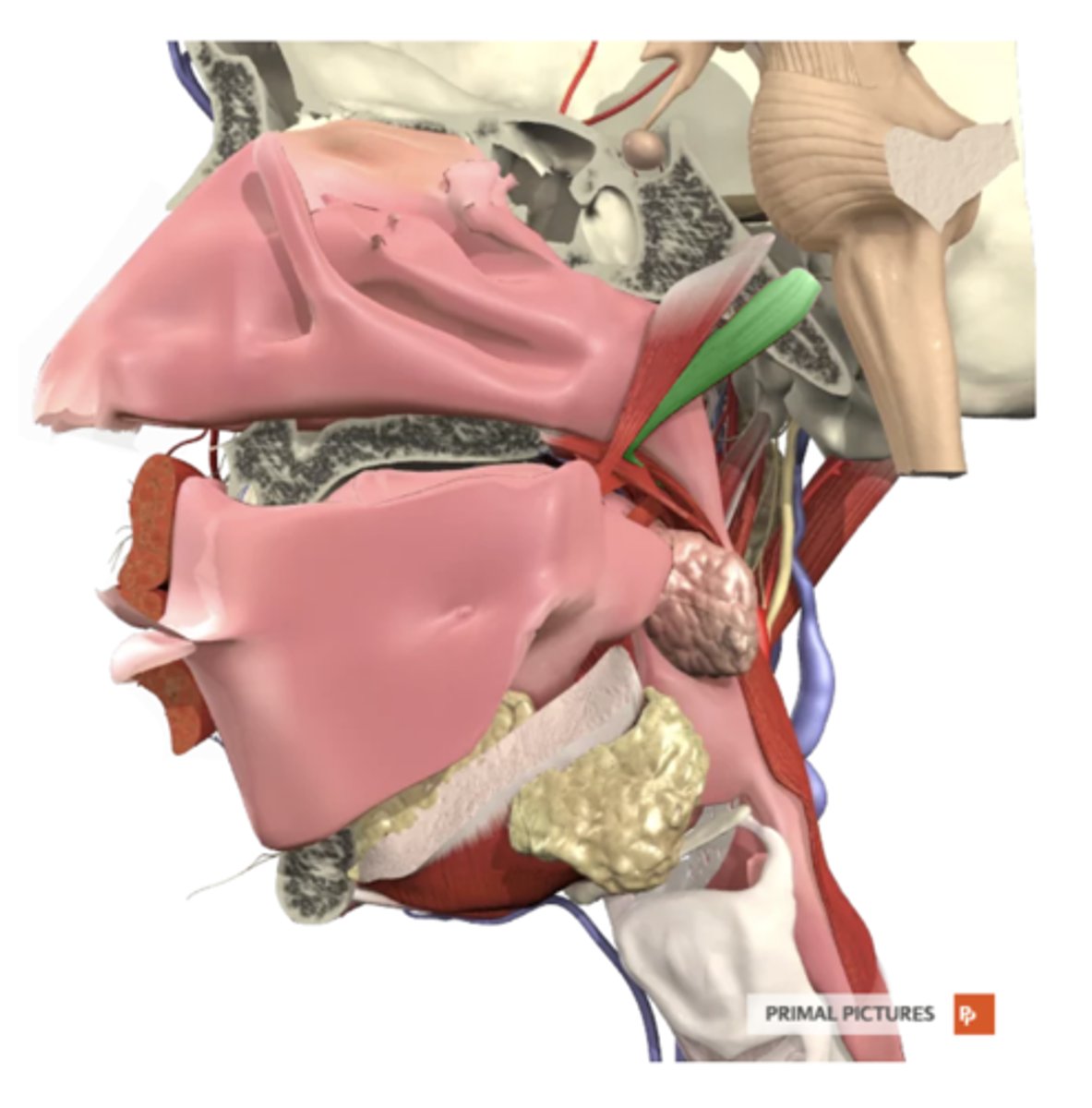
temporal bone and eustachian tube
levator veli palatini origin
palatine aponeuorisis
levator veli palatini insertion
elevates soft palate
levator veli palatini functions
CN X and CN XI (pharyngeal plexus)
levator veli palatini innvervation
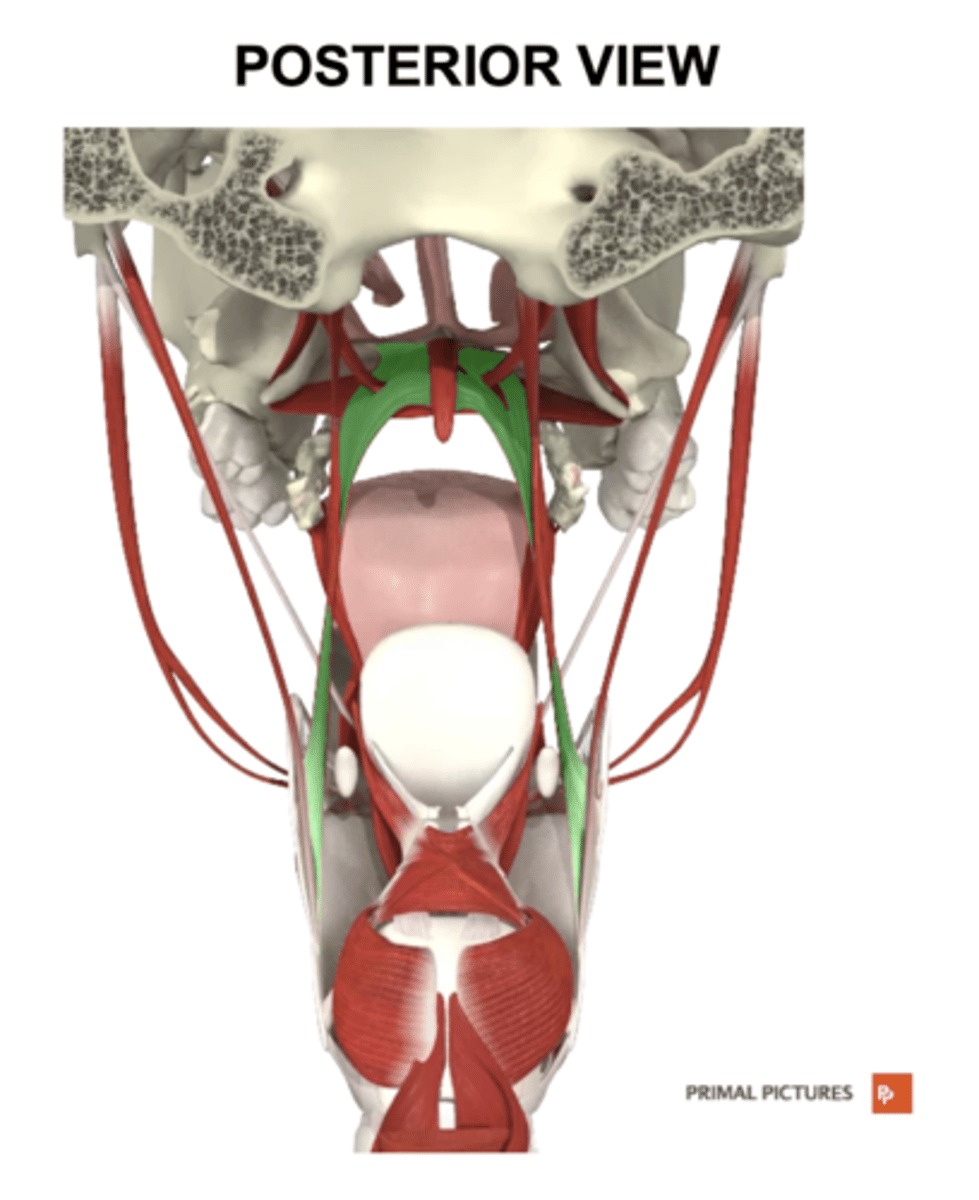
musculus uvulae
label this muscle
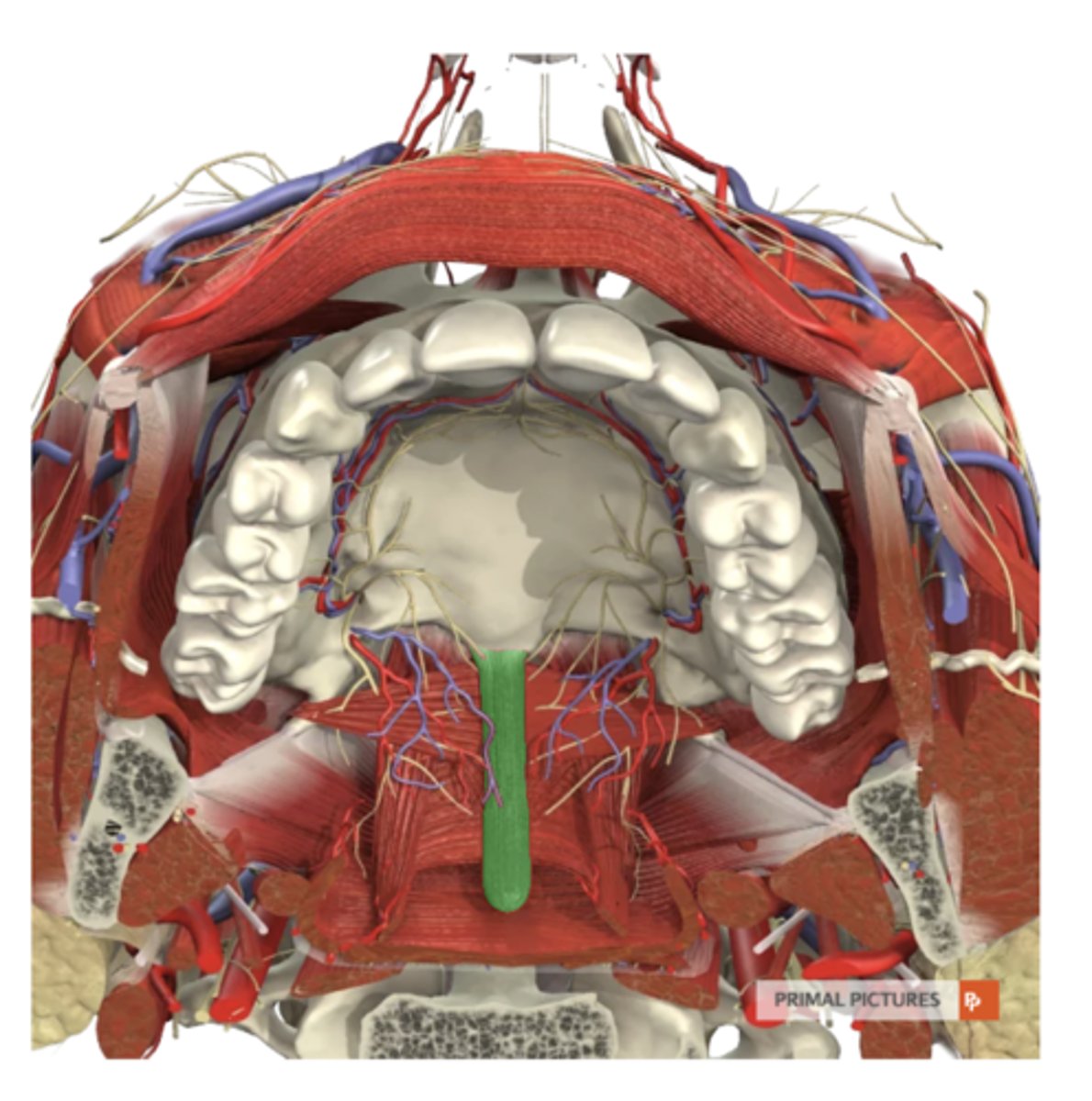
posterior nasal spine
musculus uvulae origin
-shortens uvula pulling it superiorly
-helps for complete VP closure
musculus uvulae functions
CN X and CN XI (pharyngeal plexus)
musculus uvulae innervation
palatoglossus
label this muscle
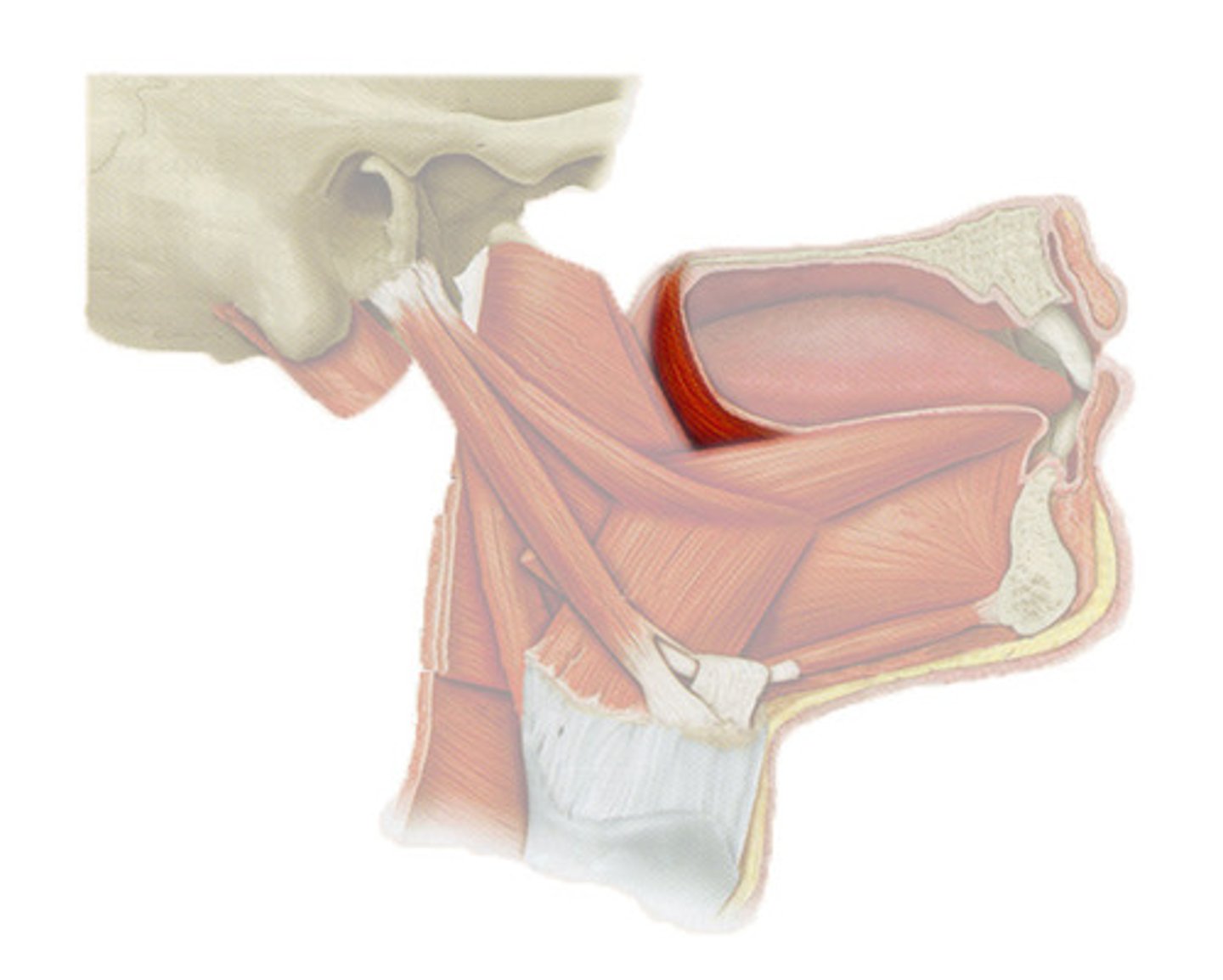
midline of soft palate/palatine aponeurosis
palatoglossus origin
sides of tongue
palatoglossus insertion
-depresses the sides of the soft palate
-elevates the posterior sides of the tongue
palatoglossus functions
CN X and CN XI (pharyngeal plexus)
palatoglossus innervation
palatopharyngeus
label this muscle