Apes Unit 2 introduction to climate
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
atmosphere
divided into several layers characterized directional change in temperature caused by differences their absorption of solar energy
where the layers split is where we have a directional change in temp
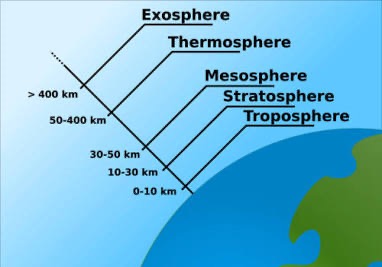
density and atmospheric pressure in the layers
both are influenced by gravitys pull on gas
density is the amount of molecules in a specific volume
atmospheric pressure is the force or the mass per unit area of a column of air
both are higher at sea level
troposphere
the layer closest to the earths surface and contains 75-80% of the air mass
made up of 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen
water vapor makes up to about 0.1% at the poles to 4% at the equator
trace amounts of soot, dust, and other gases such as ozone and greenhouse gases like methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide
movements of air in the troposphere play a key role in the earths weather and climate
primary greenhouse gases
water vapor H20
Carbon Dioxide Co2
Methane Ch4
nitrous oxide N2O
visible light in the lower atmosphere
visible light shines right through earths surface (green house gases allow it)
infrared radiation in the lower atmosphere
this gets blocked by greenhouse gases
the earth absorbs solar energy and transforms it to infared radiation, longer wavelength or heat which then rises in the lower atmosphere
the natural warming is the greenhouse effect which allows our planet to be habitable
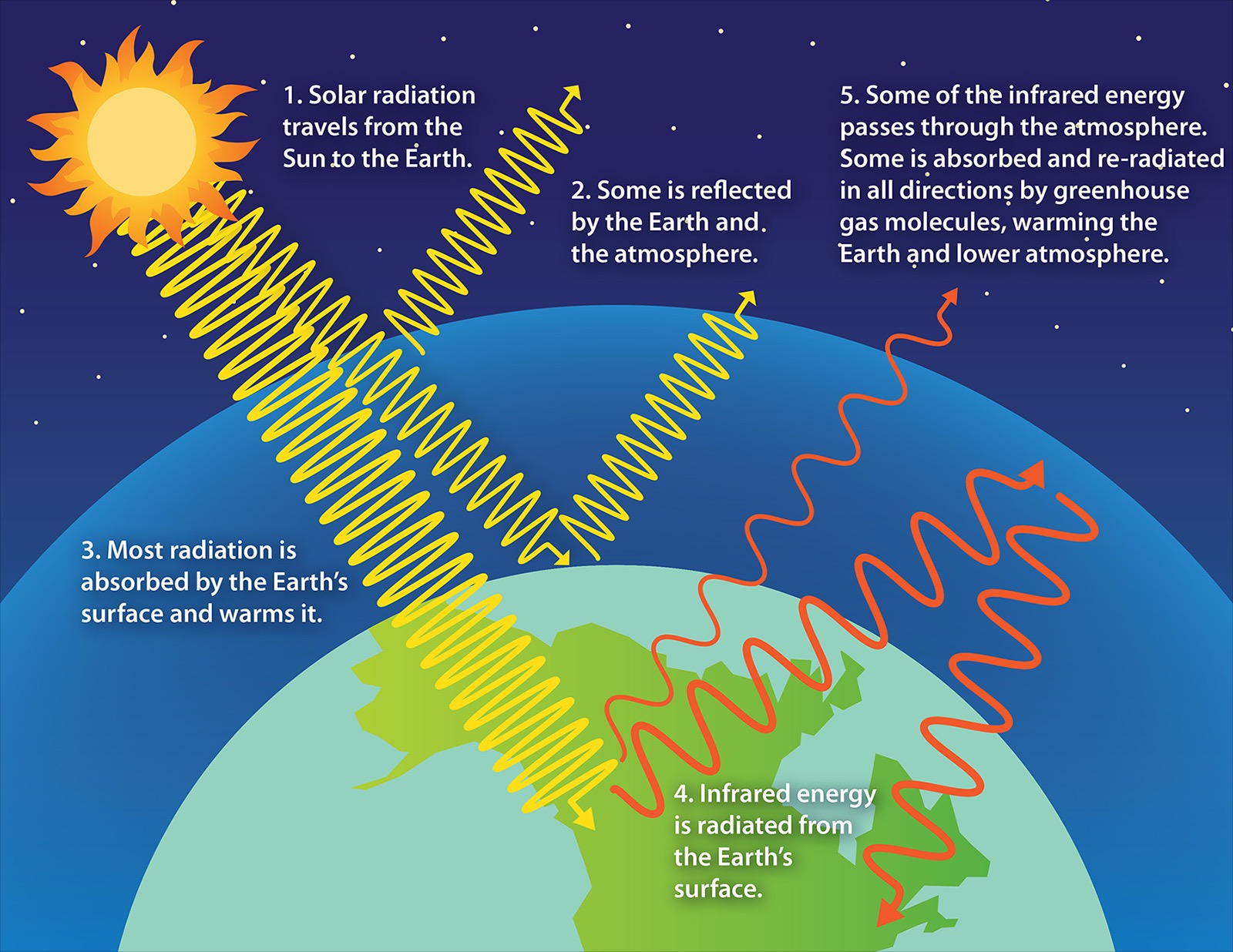
human enhanced global warming
is caused by humans releasing green house gases (burning fossil fuels and impairing earths ability to remove greenhouse gases (deforestation)
as we get coal and get oil which creates a thicker window of gases and I.R does not escape as easily
stratopshere
second closest layer to the earth, 11 miles (5 poles) to about 30 miles above the earth
it contains less density (molecules per volume) and the concentration is roughly the same except for water vapor (1000x less) and the ozone layer is much higher in concentration
ozone layer is known as the global sunscreen
ozone layer
1000x stronger in the stratosphere than the troposphere
is formed by a chemical reaction of 3o2 + UV=2O3
it absorbs UV causing it to split into o2 and o which creates o3 which keeps 95% of the UV radiation from reaching earth—> protects us from sunburn, cancer,etc
it also keeps o2 in the troposphere from converting to o3 which is considered a pollutant in earths surface (it is a good thing in the stratosphere though)
weather
condition of the atmosphere at a given time and place
humidity, wind speed, temperature, and rain fall
it fluctuates day to day
climate
the “average of the weather”w
seasonal effects over long periods of time
it is a major force in determining the distribution of living organisms and their abundance
what does uneven heating of the earth by the sun do
it causes air to circulate in the troposphere and lower stratopshere which distributes heat and moisture
light on earth
around the equator light hits earth directly so it has a higher energy/surface area
towards the poles earth decreases the intensity of light and heat
tropical climate zone
between 23.5 N (topic of cancer) and23.5 degrees S (tropic of Capricorn)
temperate climate zone
between 23.5 and 66.5 degrees north and south
weather is more variable
high and low fronts are less predictable
polar
between 66.5 degrees and 90 degrees
artic and antarctic circle
cold bc its farthest away from equator