pharmacology of blood vessels
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
where do arteries carry blood
carry blood away from the heart, towards organs and tissues
arterial blood is normally oxygenated but there is one exemption. what is the artery that carries deoxygenated blood
pulmonary arteries - deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
how do arteries branch in capillaries
elastic arteries → muscular arteries → arterioles → capillaries
role of capillary
vessels which bridge the arterial and venous systems
what type of muscle do walls of arteries, arterioles, venules and veins contain
smooth muscles
how is the contractions of blood vessels controlled
by mediators released:
locally from sympathetic nerve terminals
circulating hormones
endothelial cells
true or false: parasympathetic nerves are important in controlling vascular smooth muscle tone
false - parasympathetic not important
blood vessels have 3 layers, name each layer (hint: tunica ____)
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
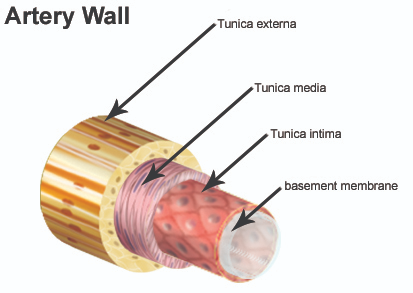
describe the tunica intima
inner lining of endothelial cells
thin layer of fine connective tissue dominated by elastic fibres
describe the tunica media
large elastic arteries
smaller vascular arteries
middle layer
large elastic arteries
e.g. aorta
high proportion of elastic tissue
smaller vascular arteries
large amount of smooth muscle
where do veins carry blood
carry deoxygenated blood from tissues to heart and lungs
veins normally carry deoxygenated blood, what vein is the exception
pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
veins have the same 3 layers as arteries (tunicae) but how does it differ
veins transport blood at a lower pressure - not as strong
difference between the venous walls and arterial walls
venous walls are:
thinner
contain less elastic, collagenous and smooth muscle tissue
easily distensible and compressible
why does the blood in veins give the vessels a blue colour
because it lacks oxygen and walls of veins are thin
what valves keep venous blood moving in the right direction
semilunar valves keep blood flowing towards heart
what assists venous blood flow
pumping action of skeletal muscle contraction
thoracoabdominal pump
what happens to pressure in thoraic activity during inspiration and what effect does this have on blood
pressure decreases → pulls blood into inferior vena cava
true or false: on exhalation, blood is forced into right atrium
true
why does the venous system act as a blood reservoir
total blood volume is unevenly distributed between arteries, veins and capillaries
arterioles determine peripheral resistance (PR), why is control of PR important in treatment of hypertension and angina
because PR determines arterial pressure and regulates blood flow through individual organs
cardiac output also affects blood pressure. what does cardiac output depend on
stroke volume and heart rate
sv x hr = co
overall, what is the equation to determine bp
bp = co x pr
blood pressure = cardiac output x peripheral resistance
what does stroke volume depend on
plasma volume and venous return
how does these factors affect heart rate
sympathetic
parasympathetic
sympathetic: increases heart rate
parasympathetic: decreases heart rate
what is vascular tone
he degree of contraction in the smooth muscles of blood vessel walls, which determines the vessel's diameter and affects blood pressure
vascular tone is regulated by many different systems. how do sympathetic nervous affect vascular tone
sympathetic nerves secrete noradrenaline which leads to vasoconstriction
vascular tone is regulated by many different systems. how do vascular endothelium affect vascular tone
secrete nitrous oxide (NO) which causes vasodilation
secretes endothelin mediator which controls vasoconstriction
what causes vasoconstriction of blood vessels
sympathetic nerves secrete noradrenaline
endothelium secretes endothelin mediator
what causes vasodilation of blood vessels
endothelium secretes NO mediator
vascular tone is regulated by many different systems. how do circulating hormones affect vascular tone
(hint: adrenaline and aldosterone)
adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline (causes vasodilation or vasoconstriction depending on receptor type)
beta-2 receptors = vasodilation
alpha 1 receptors = vasoconstriction
renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) secrete aldosterone
indirectly causes vasoconstriction by increasing sodium and water retention which raises bp
name the 3 systems that regulate vascular tone
sympathetic nerves
vascular endothelium
circulating hormones
what ion triggers vascular smooth muscle contraction
Ca2+
does vasoconstriction or vasodilation occur if:
[Ca2+] rises
[Ca2+] decreases
[Ca2+] rises: vasoconstriction
[Ca2+] decreases: vasodilation
entry and exit of Ca2+ ions across plasma membrane occurs through which channels and when are they opened
occurs through voltage gated Ca2+ channels
open when cell is depolarised
influenced by GPCRs
receptor-operated channels
how is Ca2+ ion exit controlled
mediated by Na+/Ca2+ ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange
what is the main storage site of Ca2+ in vascular smooth muscle
sarcoplasmic reticulum
many vasoconstrictors activate which compound
membrane-bound phospholipase C
how do vasoconstrictors activate phospholipase C
through GPCRs
what does activation of phospholipase C leads to
increased levels of IP3 which leads to receptor mediated release from sacroplasmic reticulum into cytoplasm
how is the released Ca2+ recaptured to the sarcoplasmic reticulum
by ATP-driven active transport system which is controlled by cAMP and cGMP
how do vasoconstrictors cause vascular smooth muscle contraction
1) IP3-mediated intracellular Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
2) membrane depolarisation (Ca2+ influx)
3) receptor-operated Ca2+ entry
why are endothelin concentrations higher in heart failure and hypertension
because endothelin is made in response to vasoactive mediators released following trauma, platelets, endotoxin and thrombinwhat
what inhibits endothelin synthesis
NO, natriuretic peptides (e.g. ABP, PGE2, PGI2
how do smooth muscle differ from striated and cardiac muscles
smooth muscles do not contain troponin
how does Ca2+ cause smooth muscle contraction
Ca2+ binds to calmodulin
activates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
this phosphorylates myosin light chains
enables myosin and actin to interact
causes contraction
what causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscles
decreased [Ca2+] → myosin phosphatase enzyme dephosphorylates myosin
[decreased/increased] myosin phosphatase activity or [decreased/increased] MLCK activity results in Ca2+ desensitisation
[decreased/increased] myosin phosphatase activity or [decreased/increased] MLCK activity results in Ca2+ sensitisation
[decreased/increased] myosin phosphatase activity or [decreased/increased] MLCK activity results in Ca2+ desensitisation[decreased
/increased] myosin phosphatase activity or[decreased/increased] MLCK activity results in Ca2+ sensitisation
how do vasodilators cause vascular smooth muscle relaxation
1) Inhibit Ca2+ entry though voltage gated Ca2+ channels by calcium channel blockers
2) increase intracellular cAMP or cGMP concentration
3) indirectly hyperpolarising membrane (K+ channel activators)
what enhances Ca2+ efflux
cAMP causes inactivation of MLCK which enhances Ca2+ efflux
what does cGMP do
cGMP activating cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG)
PKG phosphorylates L-type - Ca2+ channels in the cell membrane, which decreases their activity and reduces the influx of extracellular Ca2+ into the cell
how do vasodilators reduce cardiac workload
decreasing pre-load (reducing filling pressure) and after-load (reduced vascular resistance)
preload = how full the heart is before contractions
afterload = how hard the heart has to push to get blood out
how do vasodilators decrease pre-load and after load
reducing central venous pressure
reducing arterial pressure
increasing local tissue blood flow
which conditions are vasodilators clinically important for
hypertension
angina pectoris
cardiac failure