Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5 The Integumentary System
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Functions of skin
Protection, Thermoregulation, Cutaneous Sensation, Vitamin D synthesis, Blood Reservoir, Excretion and Absorption.
Protective elements of skin
Keratin, Lipids, Glandular Secretions, Melanin
Thermoregulation
Controls internal temp
Vitamin D synthesis
You need Vitamin D to absorb calcium
Epidermis
Superficial layer of skin. Avascular. 4 different cell types (Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Langerhans cells, merkel cells)
Keratinocytes
90% of cells. Keratin
Melanocytes
8% of cells. Melanin (Pigments and absorb uv radiation.
Langerhans Cells
Immune function
Merkel cells
Touch
Layers of skin (Superficial to deep)
Epidermis, Dermis
Epidermal Layers (deep to superficial)
Stratum Basale, Stratum spinosum, Stratum granulosum, Stratum lucidum, Stratum corneum.
Stratum Basale
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Langerhans cells and Merkel cells are here. Deepest layer, and mitosis occurs.
Stratum Spinosum
Keratinocytes and Langerhans cells are here. Production of melanocytes here.
Stratum granulosum
Lamellar granules, apoptosis occurs here.
Stratum lucidum
Present only in thick skin
Stratum corneum
Keratin, and continuously shed (Outermost layer)
Dermis
Deep layer, Beneath epidermis, Vascular, LAyers: Papillary and reticular
Papillary Layer
Areolar connective tissue, Dermal papillae (finger like projections)
Reticular layer
Thickest layer, dense and irregular connective tissue
Hypodermis
Not apart of skin
Skin color
Hemoglobin, Cerotene, Melanin
Hemoglobin
Pigment in Red blood cells that carry oxygen. Oxygen in blood positively correlates with blood in area.
Carotene
Ingested- accumulates in stratum corneum. Color: Orangish yellow.
Melanin
Only pigment synthesized in skin. Freckles are bunches of melanocytes.
Albinism
Not capable of producing melanin
Vitiligo
Loss of melanocytes in patches of skin
Function of Hair
Protection, light touches
Anatomy of Hair
Shaft, root, hair bulb, hair papilla, matrix, arrector pilli muscle.
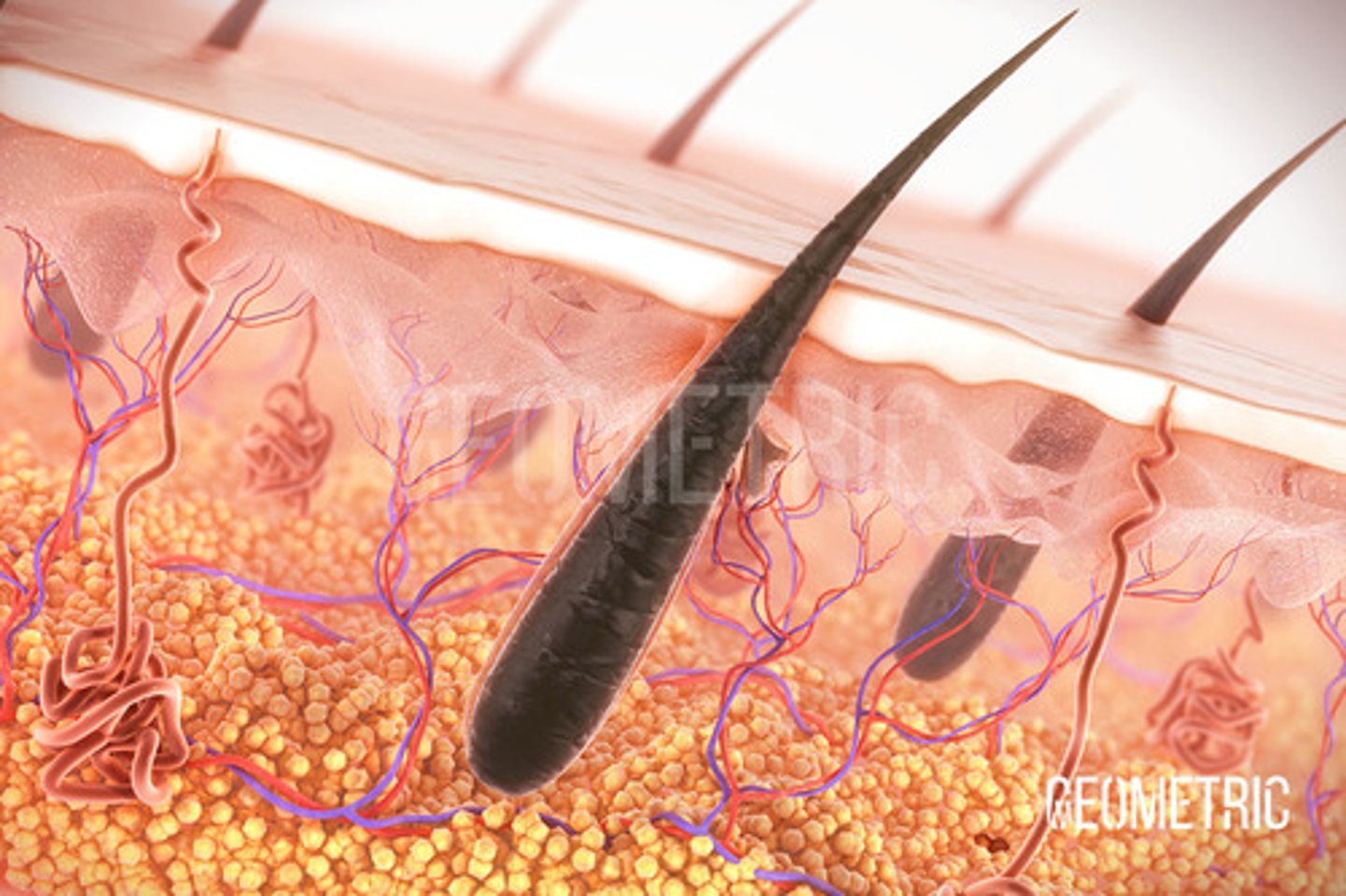
Shaft of hair
(Inside skin layer) Medulla, Cortex, Cuticle
Root of hair
Medulla, cortex, cuticle, (Outer hair part) Internal root sheath, external root sheath, dermal root sheath(Dermis)
Hair Follicle
Surrounds root
Alopecia
Condition characterized by the rapid onset of hair loss in a sharply defined area. Cause by genetics, endocrine disorder, chemo, or stress.
Skin exocrine glands
Sebaceous Glands, Sudoriferous gland, Apocrine gland, ceruminous gland
Seabaceous gland
Simple acinar, holocrine, duct opens into hair follicle. Secrete sebum.
Sebum
Prevents hair from drying out, keeps skin soft and pliable, prevents excessive evaporation of water.
Sudoriferous(Sweat) glands
Merocrine and ceruminous and apocrine glands
Merocrine (Eccrine) Gland
Simple tubular, found in palms, soles, and forehead, duct terminates on epidermis. Watery secretion, that regulates boy temp and does waste removal.
Apocrine(sweat) gland
Simple tubular, found in armpit and genital regions. Secretions are viscous (functions at puberty and stimulated during stress or sexual arousal).
Ceruminous (Wax) Gland
Simple tubular, merocrine, found in external auditory meatus (Ear). Excretes cerumen
Cerumen
Sticky barrier that stop the entrance of foreign bodies into ear.
Nails
Tightly packer keratinized cells
Nail body
Visible portion of nail. (from distal to proximal) Free Edge, Nail body, Luluna, Eponychium, Nail root (None visible).
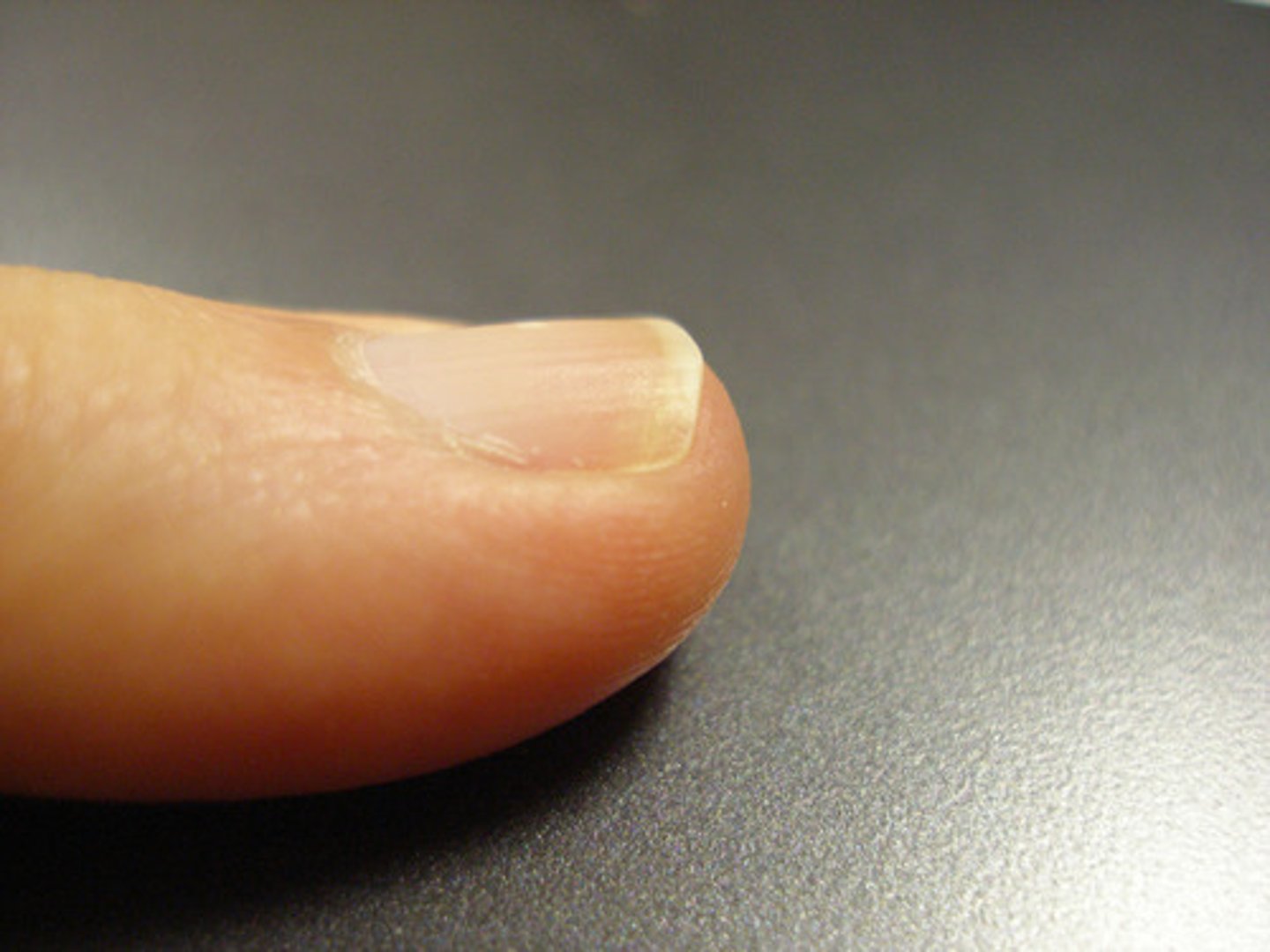
Lunula
is white (Thickened stratum basale)
Nail root
Under skin
Eponychium
Cuticle
Burns
1st, 2nd and 3rd degree burns. Tissue damage cause by extreme heat.
First degree burn
Hurts epidermis. Sunburn
Second Degree Burn
Damage dermis and hurt epidermis. blistering.
Third degree burn
Damage everything- need a skin graf. Charing
Rule of nines
ID the depth and severity of a burn