Test for cations, flame tests and preciptate tests
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are cations?
positively charged ions
What are anions?
negatively charged ions
Test for cations
Metal cations in aqueous solution can be identified by the colour of the precipitate they form on addition of sodium hydroxide and ammonia
Ion: Ammonium (NH4+)
Result when Sodium hydroxide is added:
Ammonium gas produced turns damp red litmus blue
Why must the litmus paper be damp?
the water dissolves some of the chlorine so that it can react with the indicator on the litmus paper
Ion: Copper(II) Cu2+
Result when Sodium hydroxide is added:
Light blue precipitate formed
Ion: Iron(II) (Fe2+)
Result when Sodium hydroxide is added:
Green precipitate formed
What is a precipitate?
a solid that forms and settles out of a liquid mixture
Ion: Iron(III) (Fe3+)
Result when Sodium hydroxide is added:
Red-Brown precipitate formed
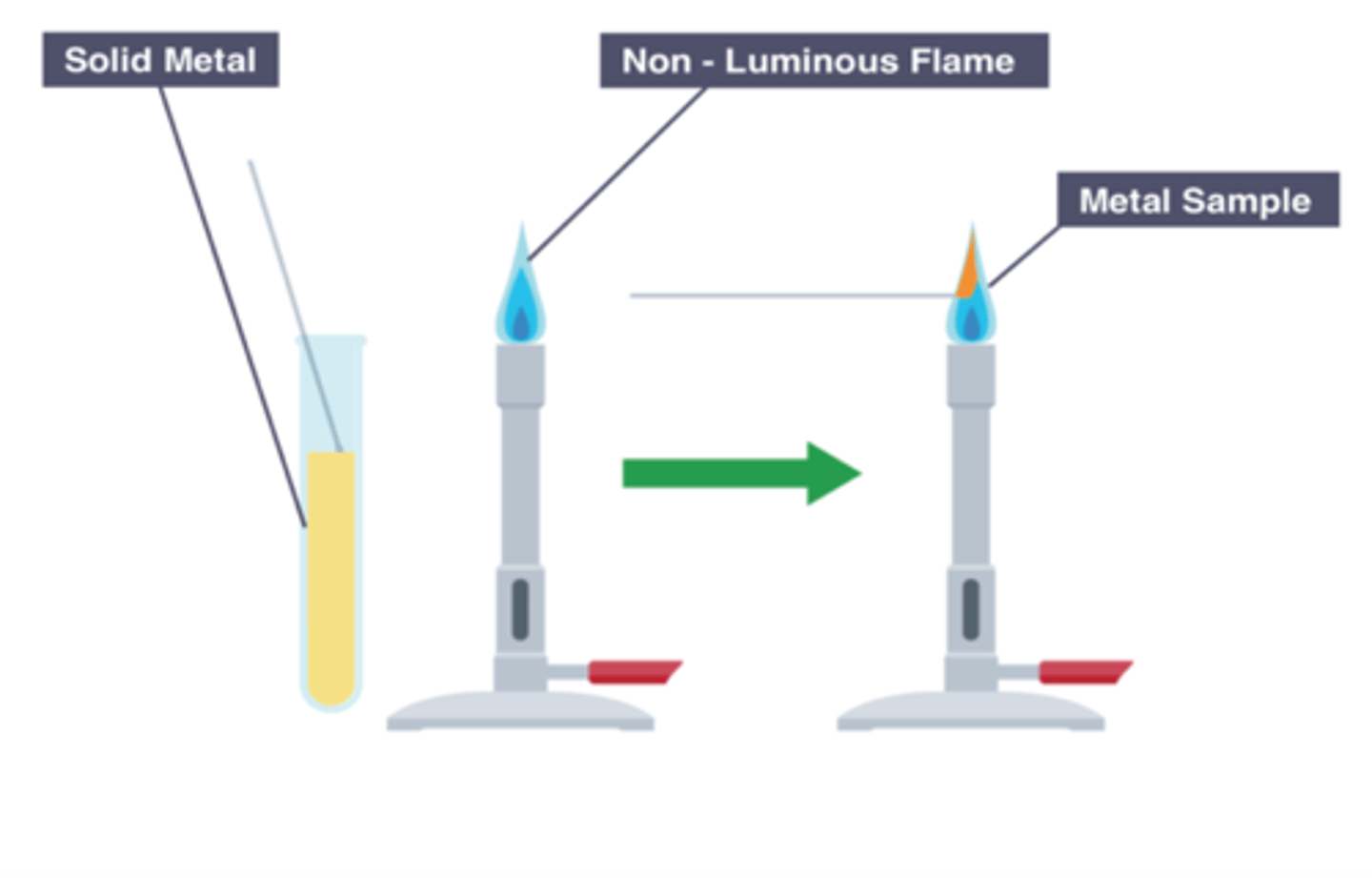
What is the flame test used for?
The flame test is used to identify metal ions by the colour of the flame they produce
Carrying out a flame test
-We use platinum/nichrome wire. This is because they do not give off a color or melt.
-We clean the wire by dipping it in HCl and holding it in the flame until no color can be seen.
-Then we dip the wire in the sample and hold it in a blue flame (hole open)
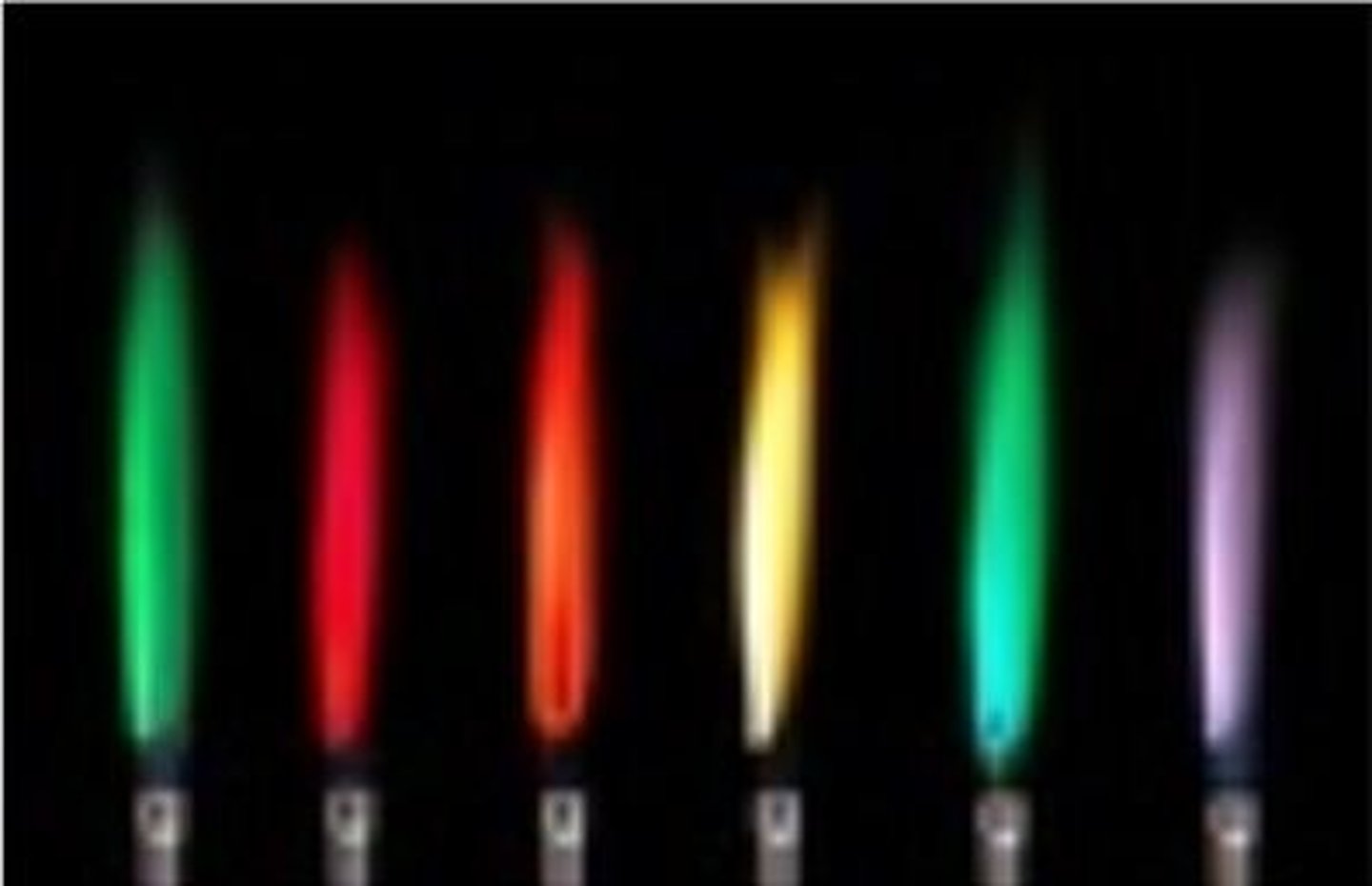

Flame test: If the flame is red what cation is present?
Lithium (Li+)

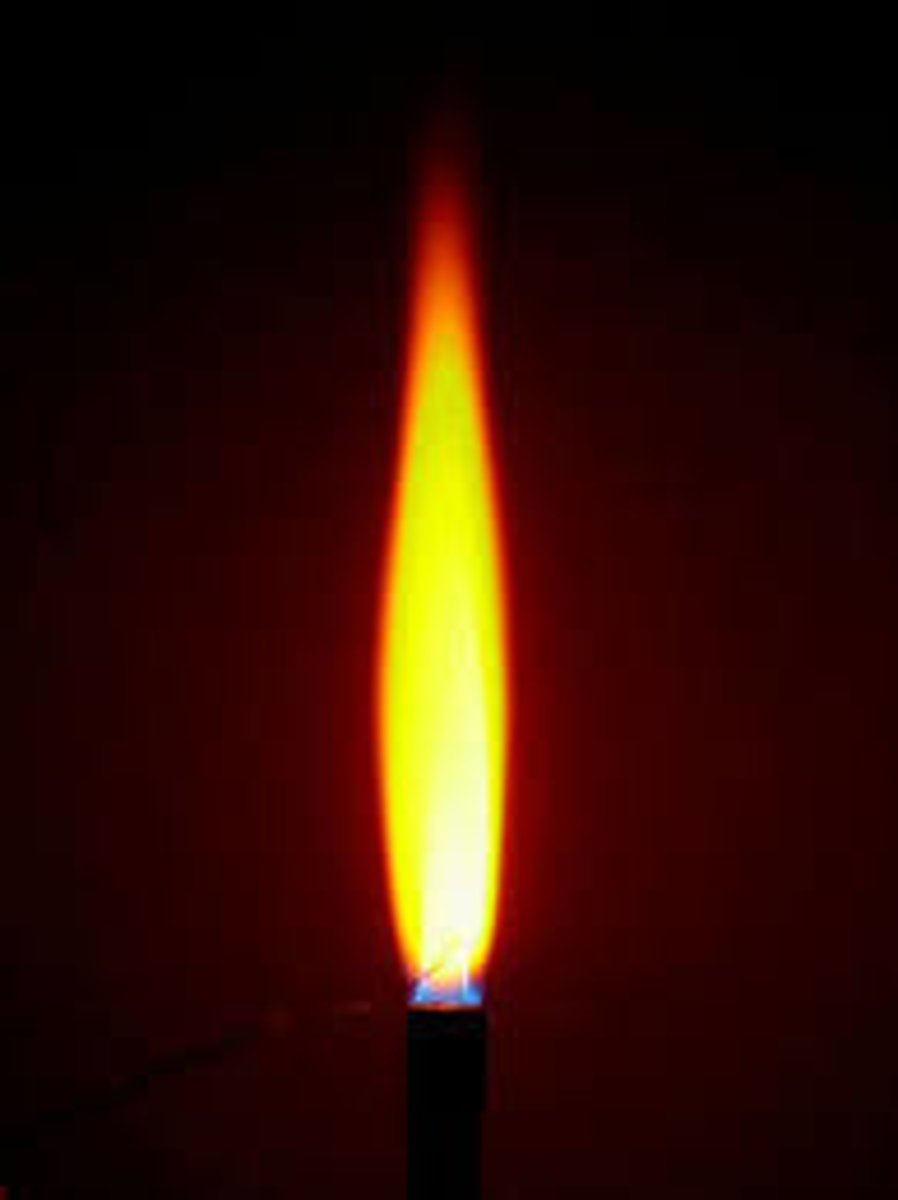
Flame test: If the flame is yellow what cation is present?
Sodium (Na+)

Flame test: If the flame is lilac what cation is present?
Potassium (K+)
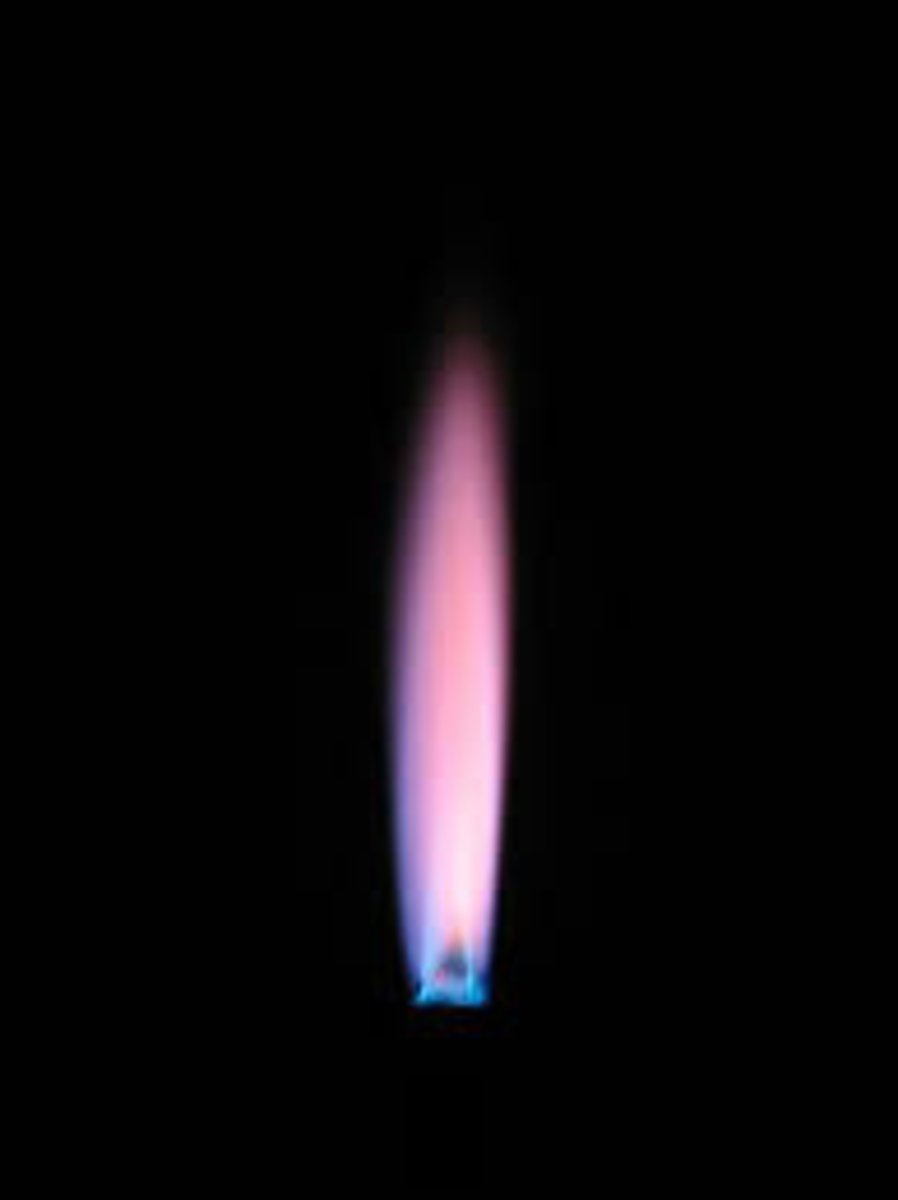

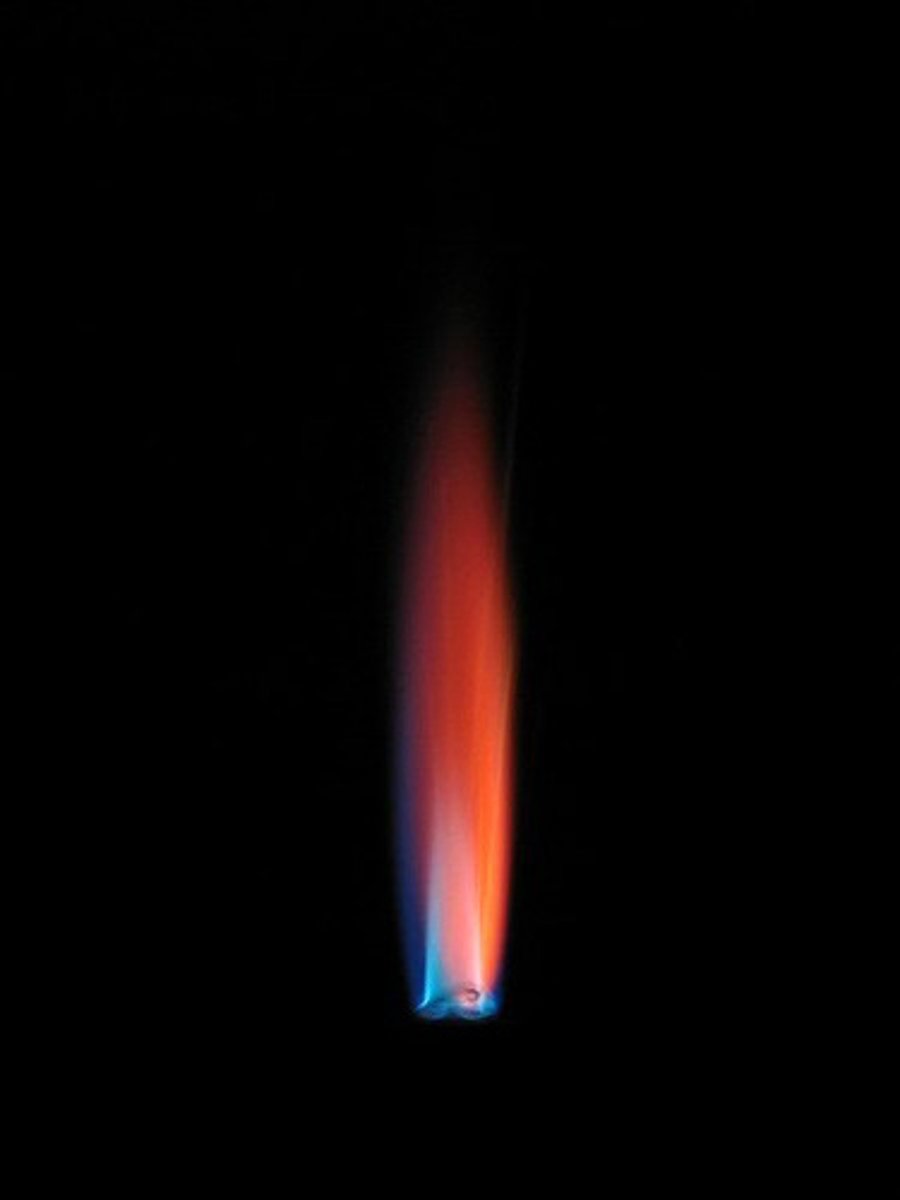
Flame test: If the flame is orange-red what cation is present?
Calcium (Ca2+)
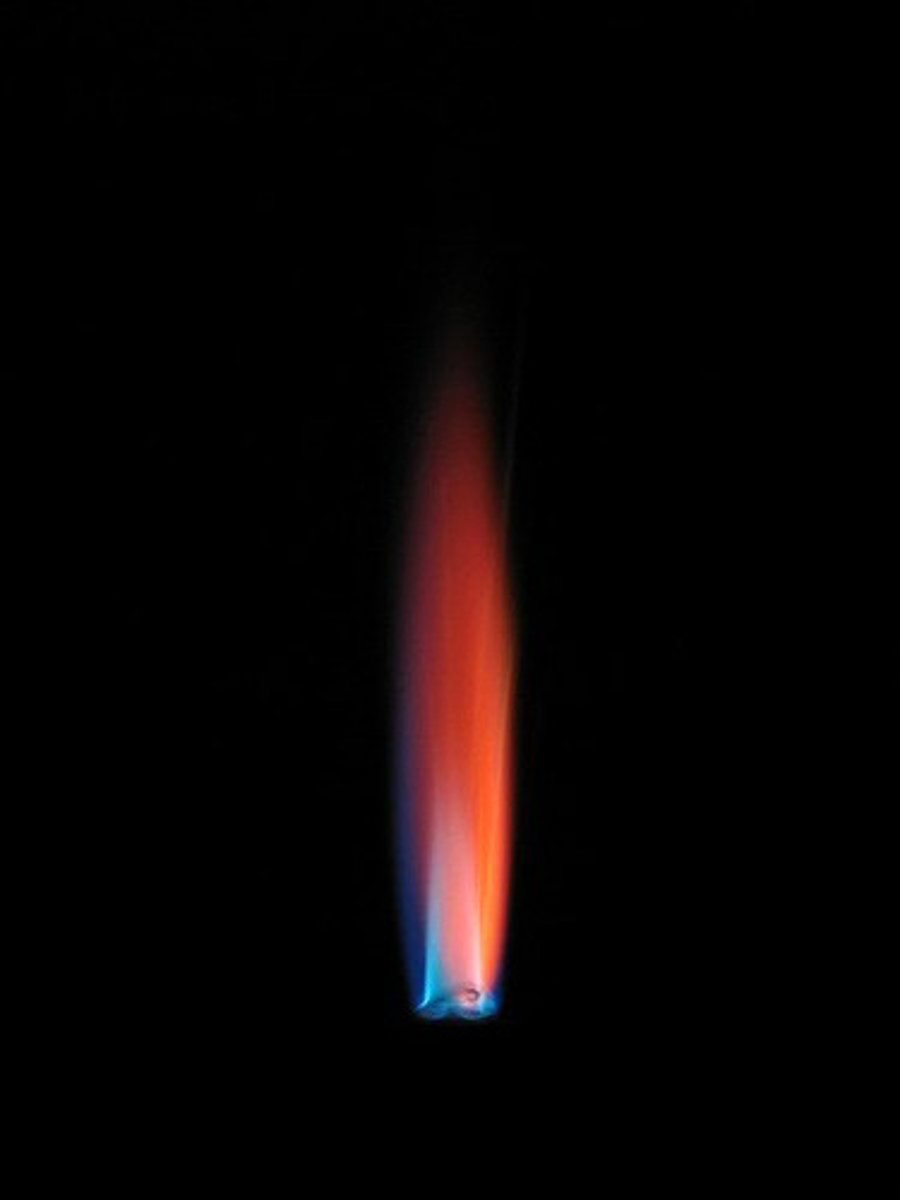

Flame test: If the flame is blue-green what cation is present?
Copper (Cu2+)
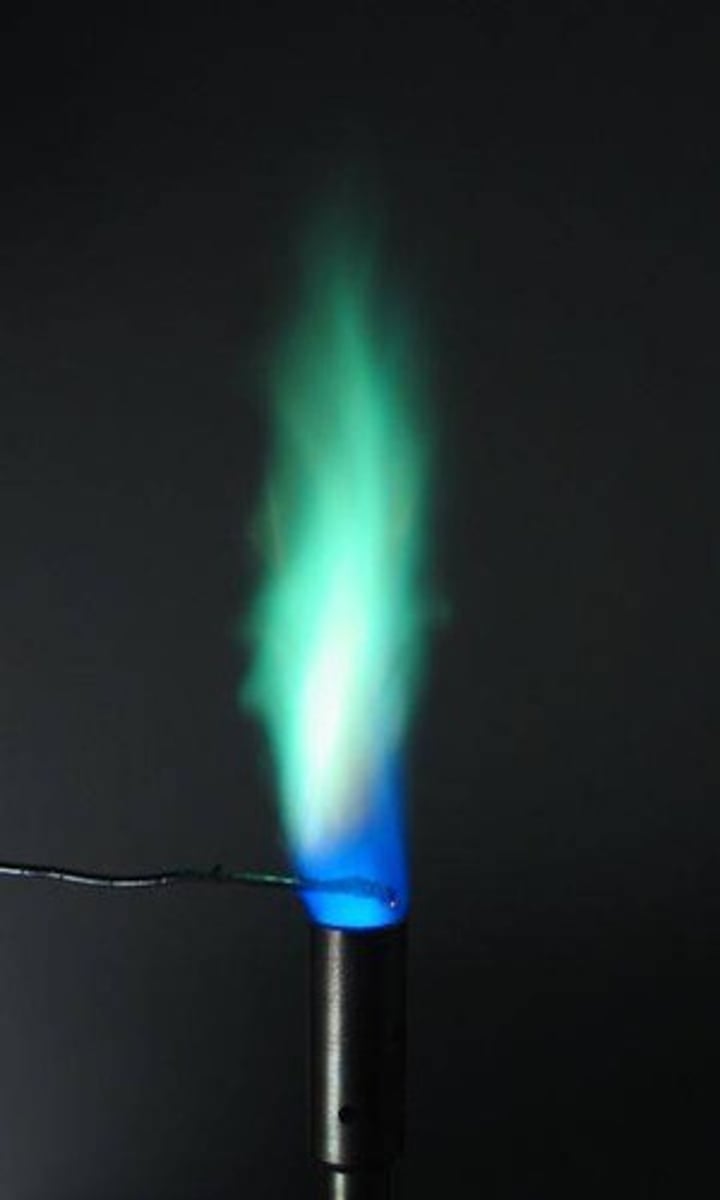

Flame test: Lithium (Li+)
red
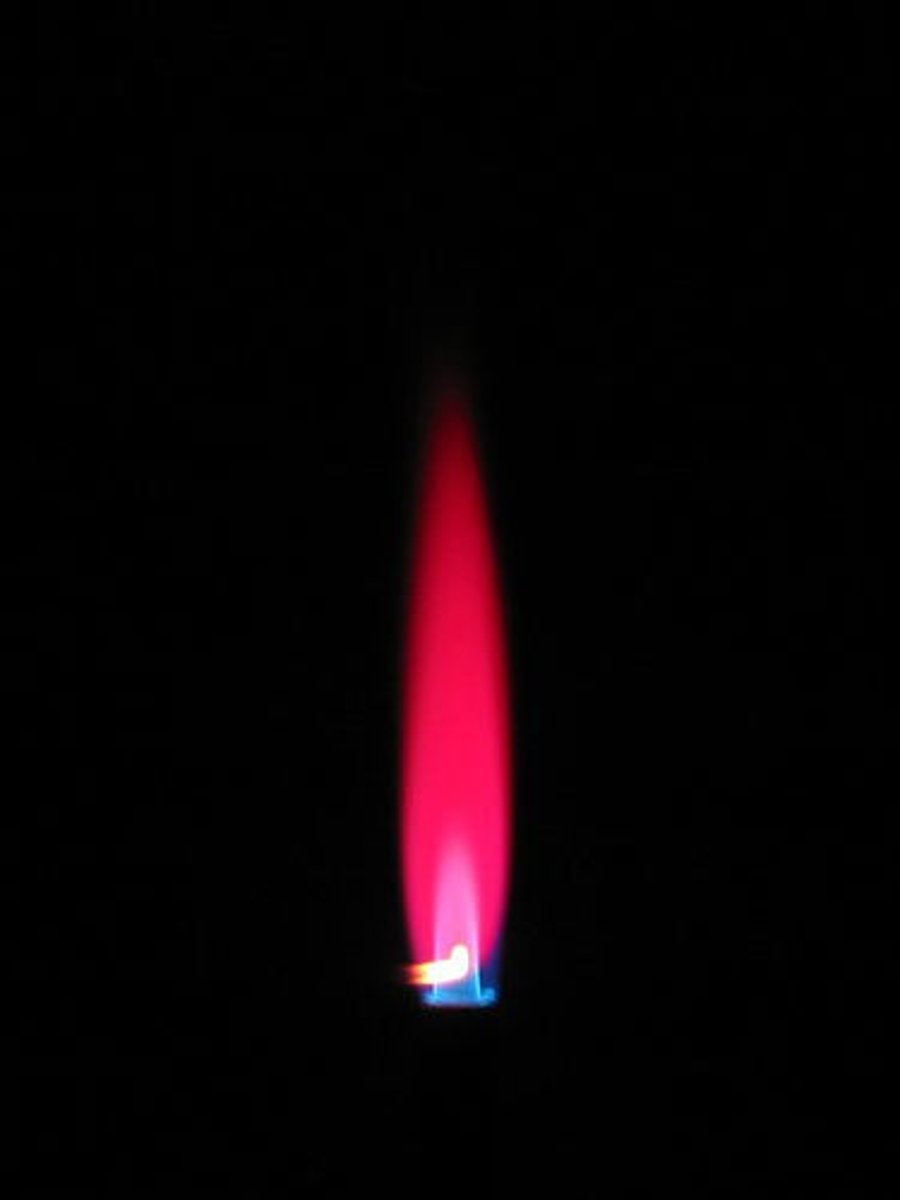

Flame test: Sodium (Na+)
yellow
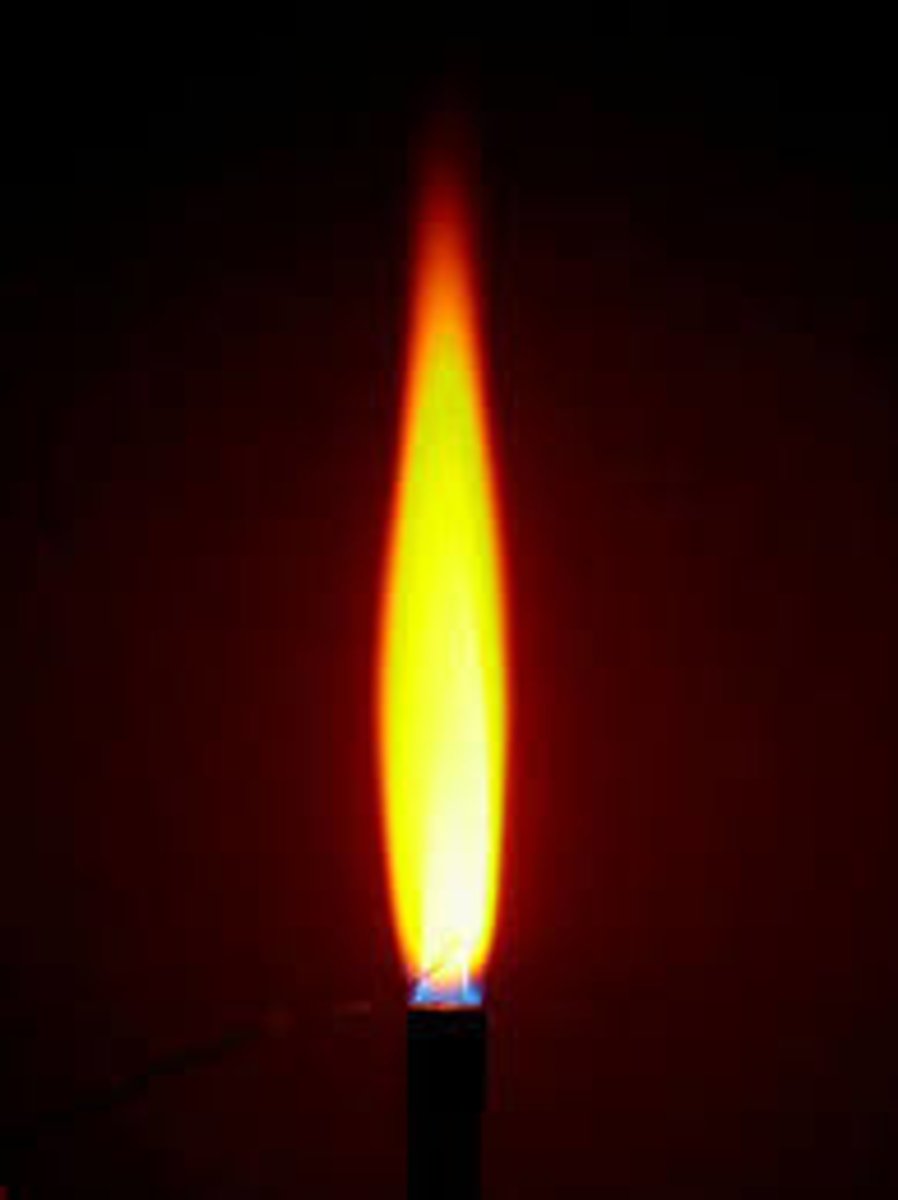

Flame test: Potassium (K+)
Lilac
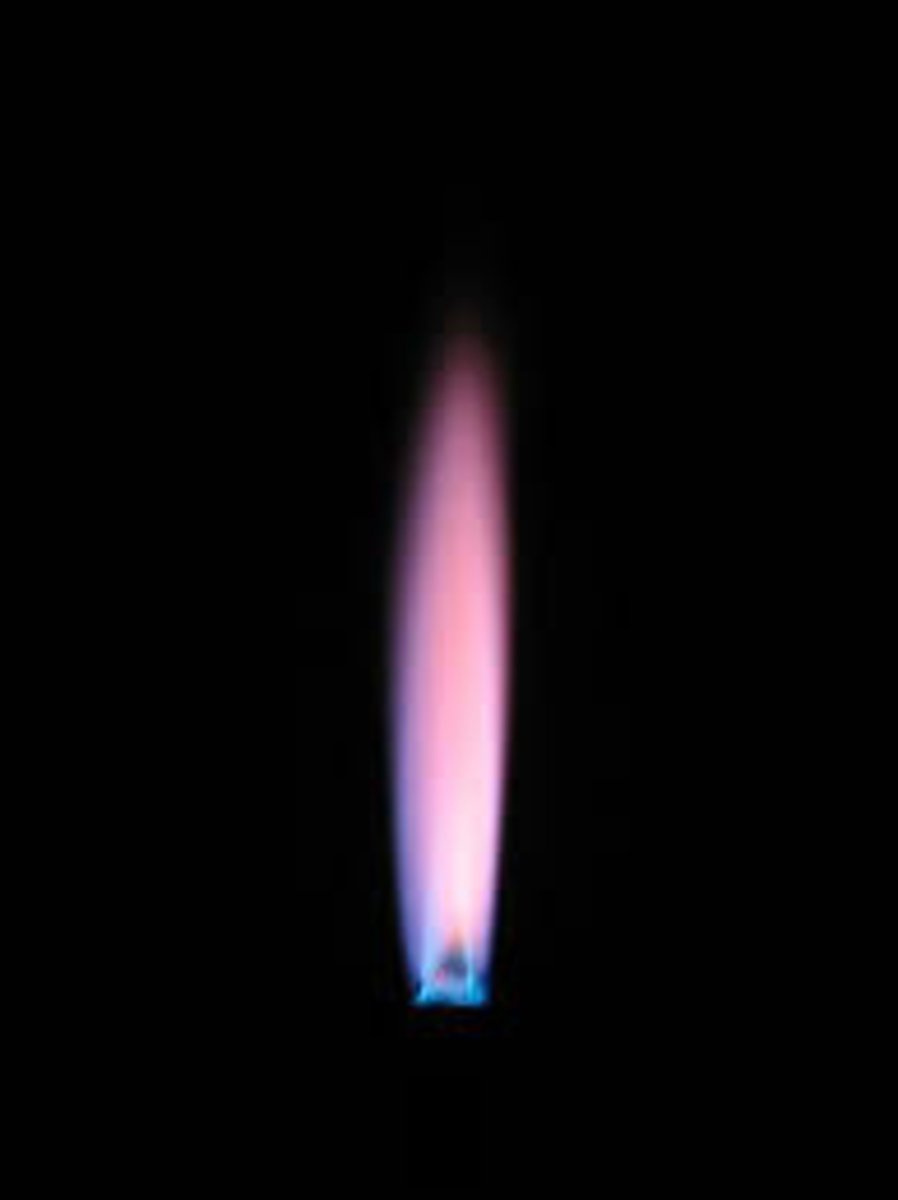

Flame test: Calcium (Ca2+)
orange-red
Flame test: Copper (Cu2+)
blue-green
Solubility rules intro
-Ionic compounds are generally soluble in water compared to covalent substances, but there are exceptions
-A knowledge of the solubility of ionic compounds helps us to determine the most appropriate method for the preparation of salts
Solubility Rules: soluble ionic compounds
-Compounds of sodium, potassium, and ammonium
-Sodium, potassium, and ammonium carbonates
-Sodium, potassium, and calcium hydroxides
-All nitrates
-All chlorides (+a few exeptions)
-All sulfates (+a few exeptions)
Solubility Rules: insoluble ionic compounds
-Silver and lead(II) chloride
-barium, calcium, and lead (II) sulfate
-All other carbonates
-All other hydroxides
Solubility rules: Why is calcium hydroxide different?
Calcium hydroxide is slightly soluble in water
Test for ammonium (NH4+)
-Add sodium hydroxide (a precipitate will not form)
-If ammonium ion is present it gives off ammonia gas. To make sure, place a damp piece of red litmus paper on the rim of the test tube. It will turn blue (alkaline)
