Theory - Intrinsic and Extrinsic Staining and Removal
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Classifications of Stains
Extrinsic and Intrinsic
Sources of stains
exogenous and endogenous
Can intrinsic stains be removed?
NO - they are within the tooth surface
How to recognize stains
-med history
-food records
-oral hygiene habits
Extrinsic stains
-On external tooth surface, can be removed
-Yellow
-Green
-Metallic
-Black Line
-Tobacco stains
-Brown Stains
(less common stains: orange, red, metallic)
Yellow stains
Dull, yellowish discoloration of dental biofilm
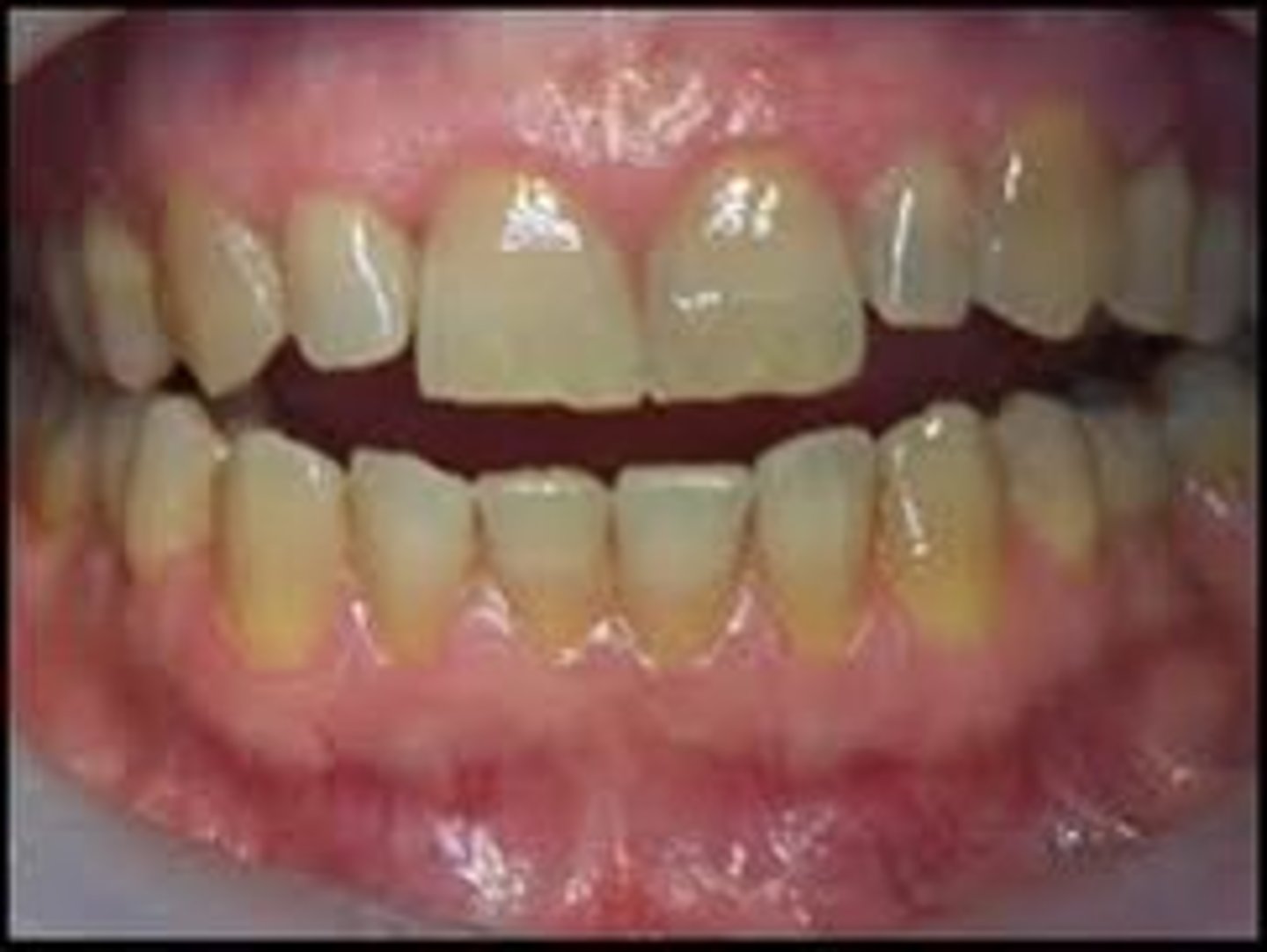
Green stains
Caused by chromogenic bacteria, fungi, chlorophyll
Metallic stains
Metallic dust industry, or drugs
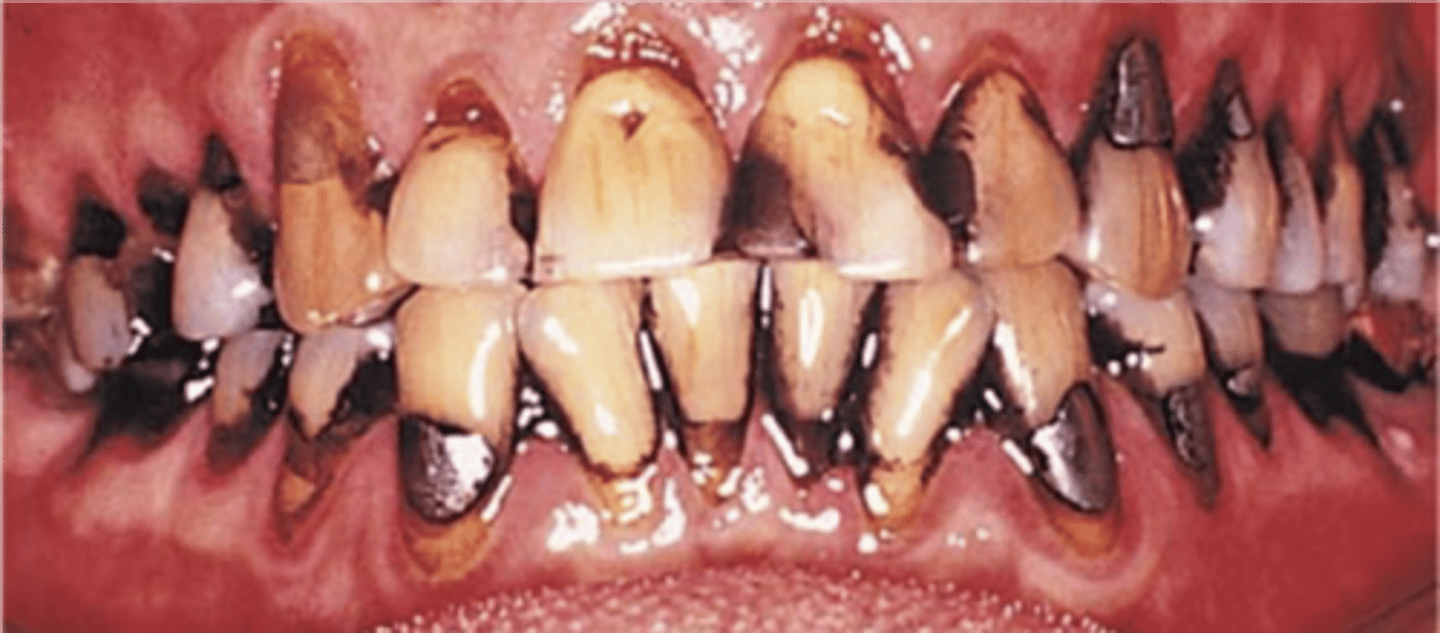
Black line stains
Calculus like stain forms along gingival margin
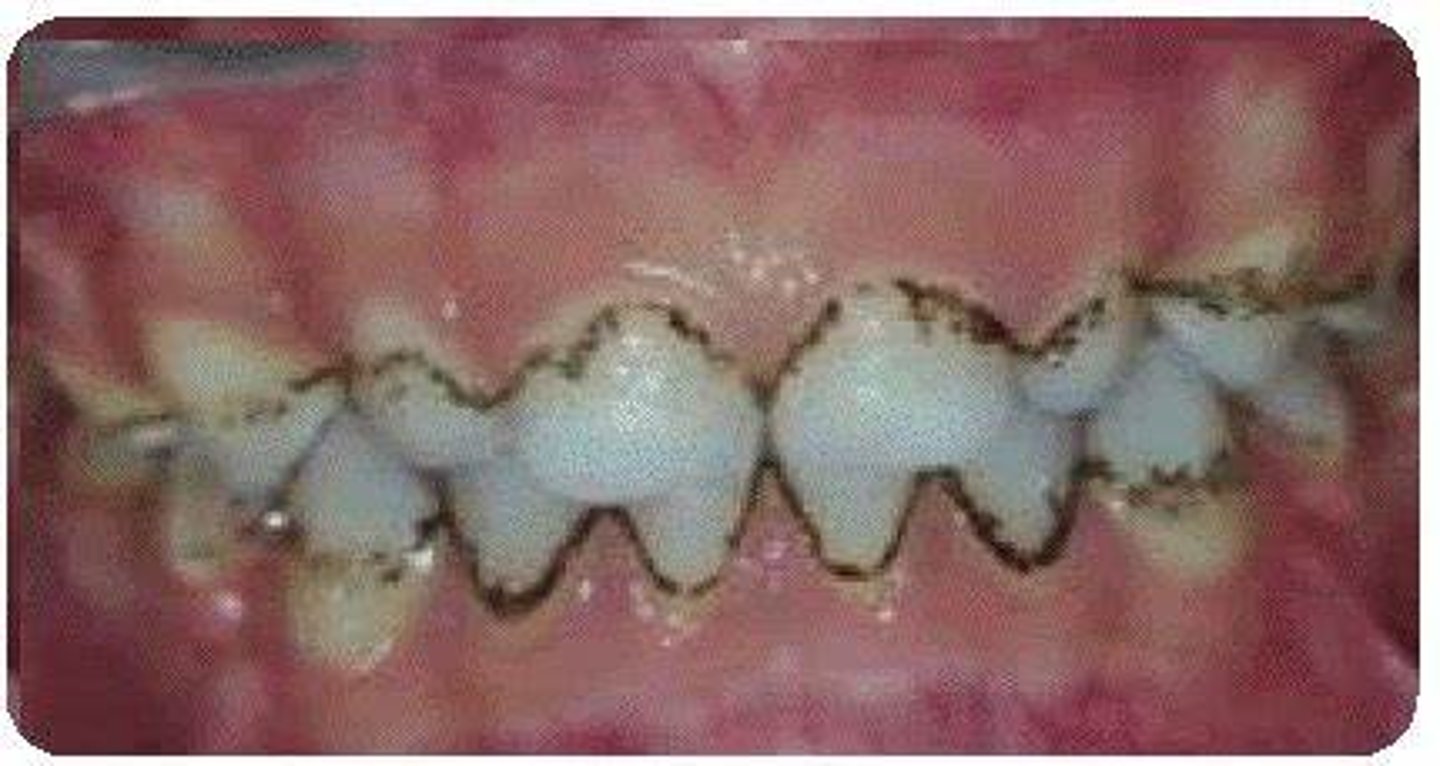
tobacco stains
light brown to dark leathery brown
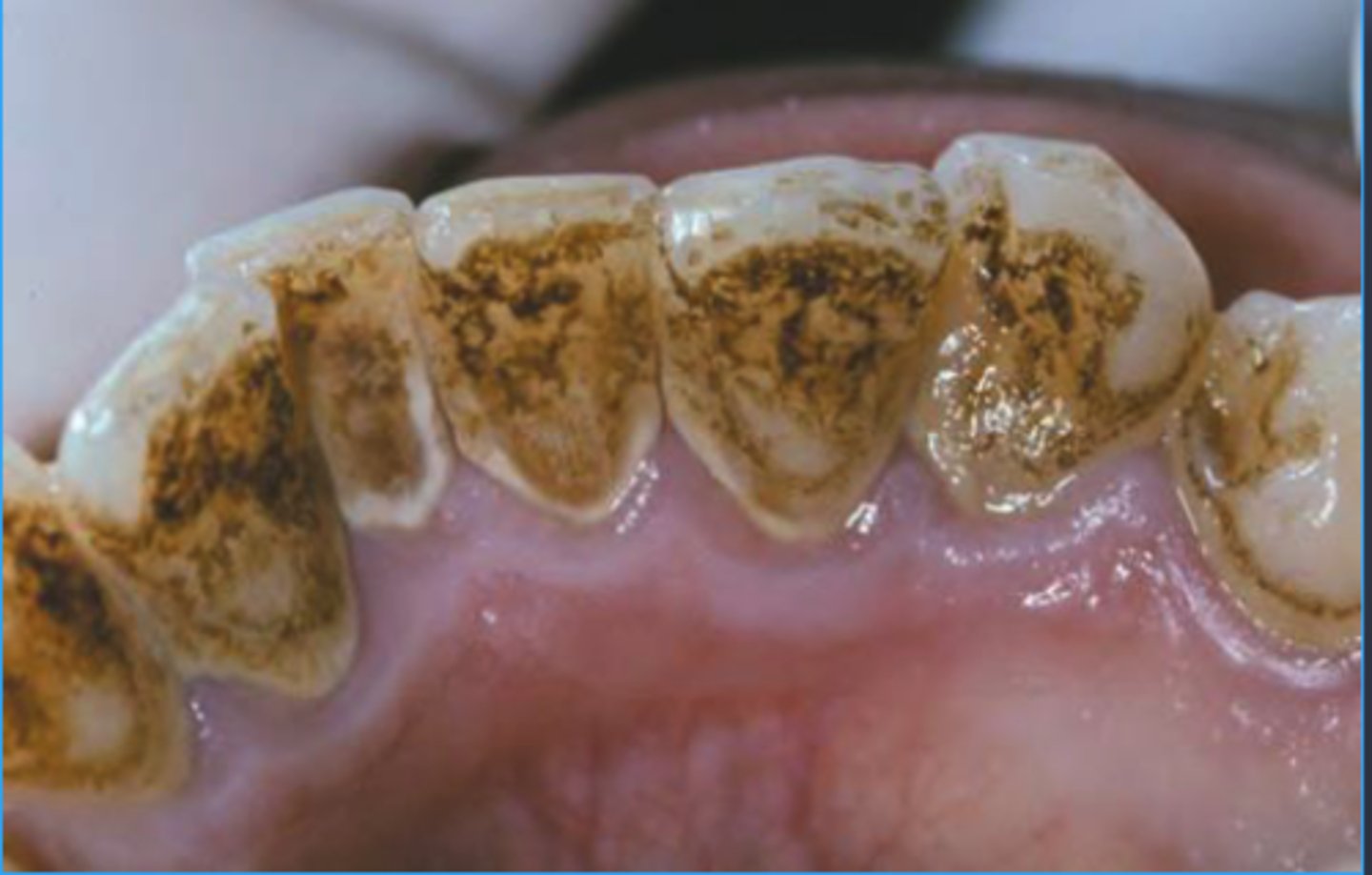
Brown stains
Due to brown pellicle
Stannous Fluoride
Betel Nut
Endogenous Intrinsic Stains
Stains within tooth structure; formed in the period of development
Pulpless teeth appearance
Appear slate gray, reddish-brown, dark brown
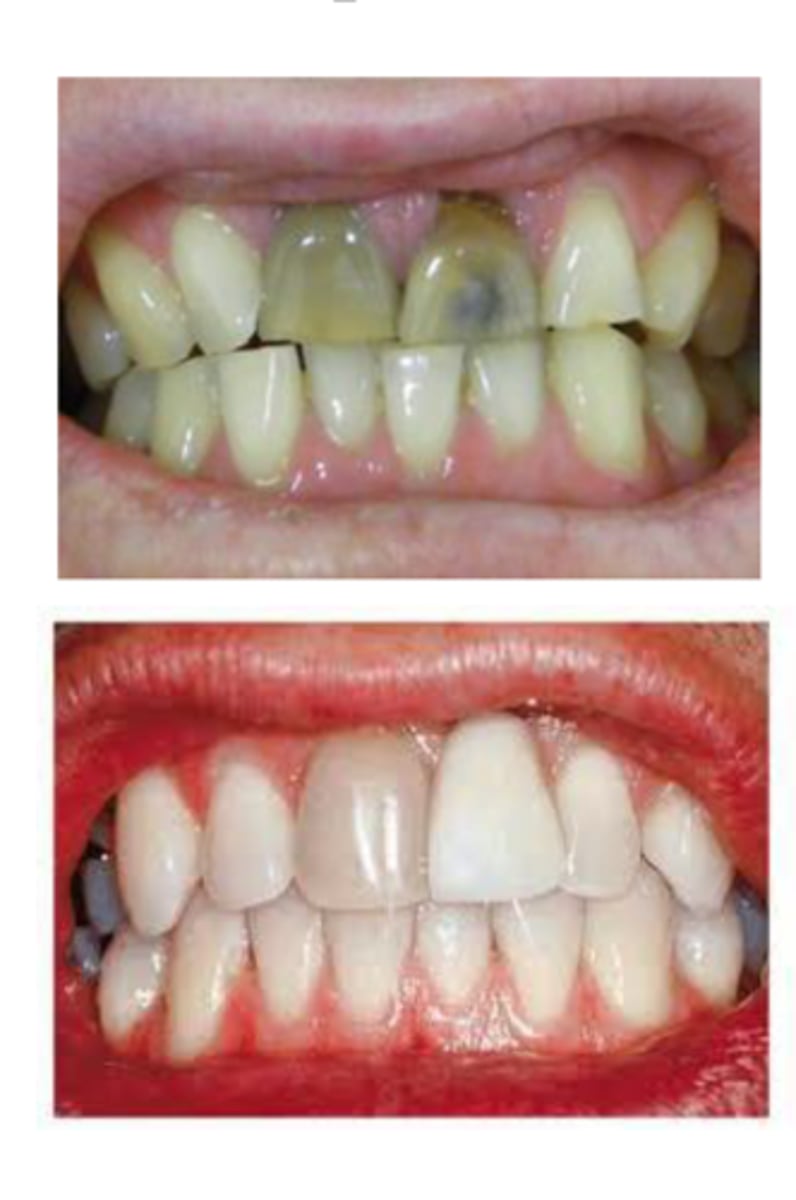
Tetracycline Staining
-Endogenous
-Intrinsic
-Light green to dark yellow
(Depends on dosage and length of time)
-Can be passed through placenta
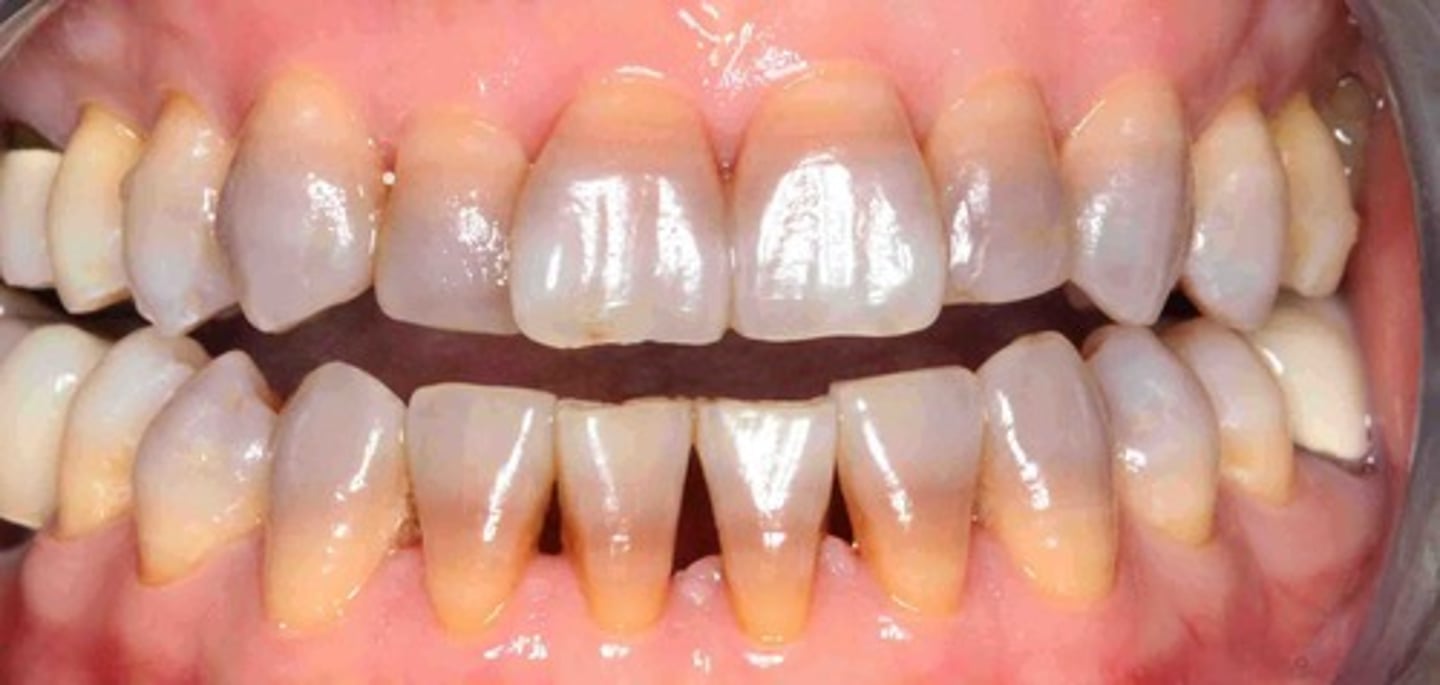
Amelogenesis Imperfecta
- Enamel missing due to disturbances of ameloblasts
- Yellowish-brown or gray-brown appearance
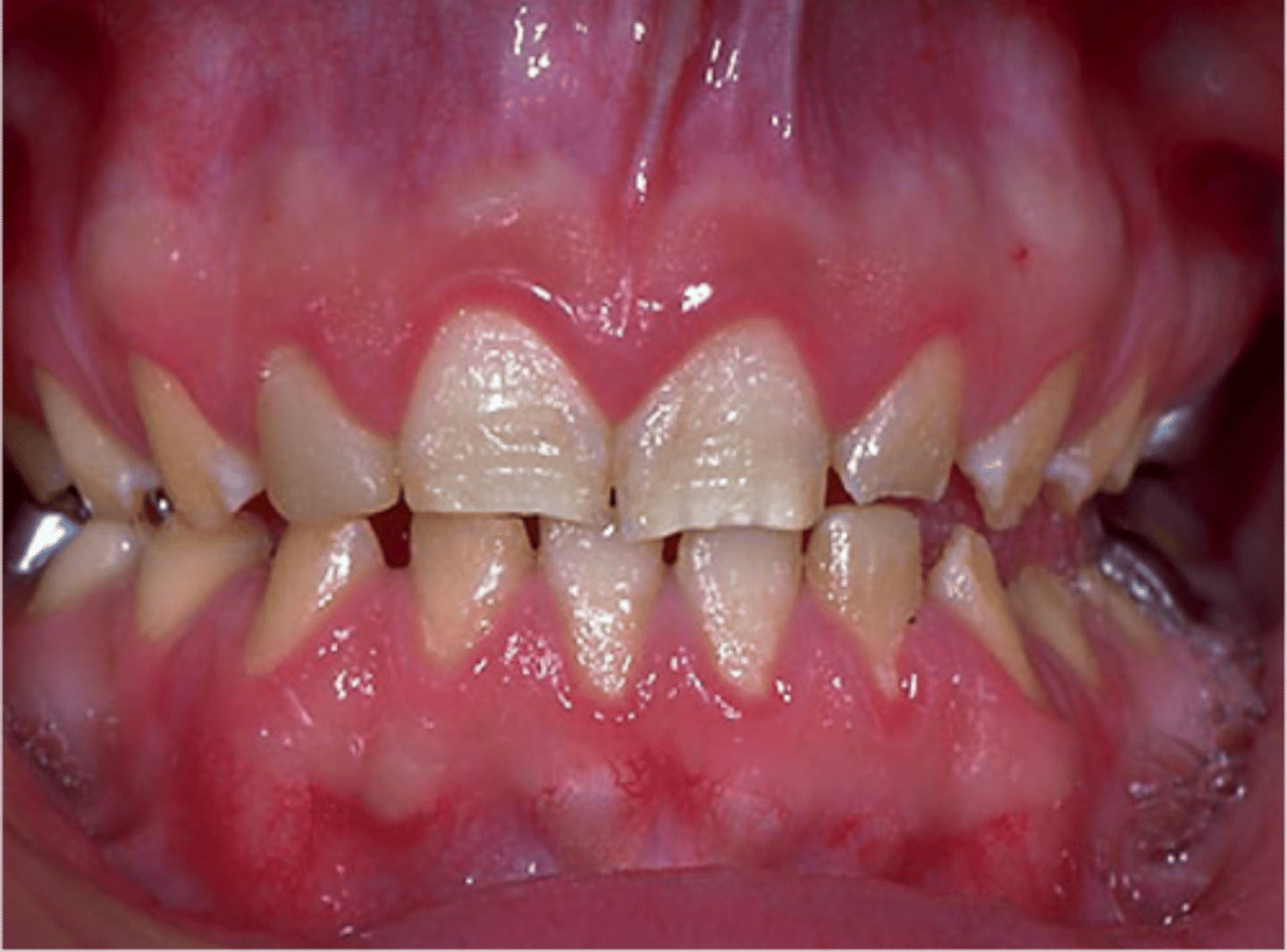
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
- Abnormal dentin due to disturbances in odontoblasts during development
- Appearance: Translucent or opalescent, gray to bluish-brown
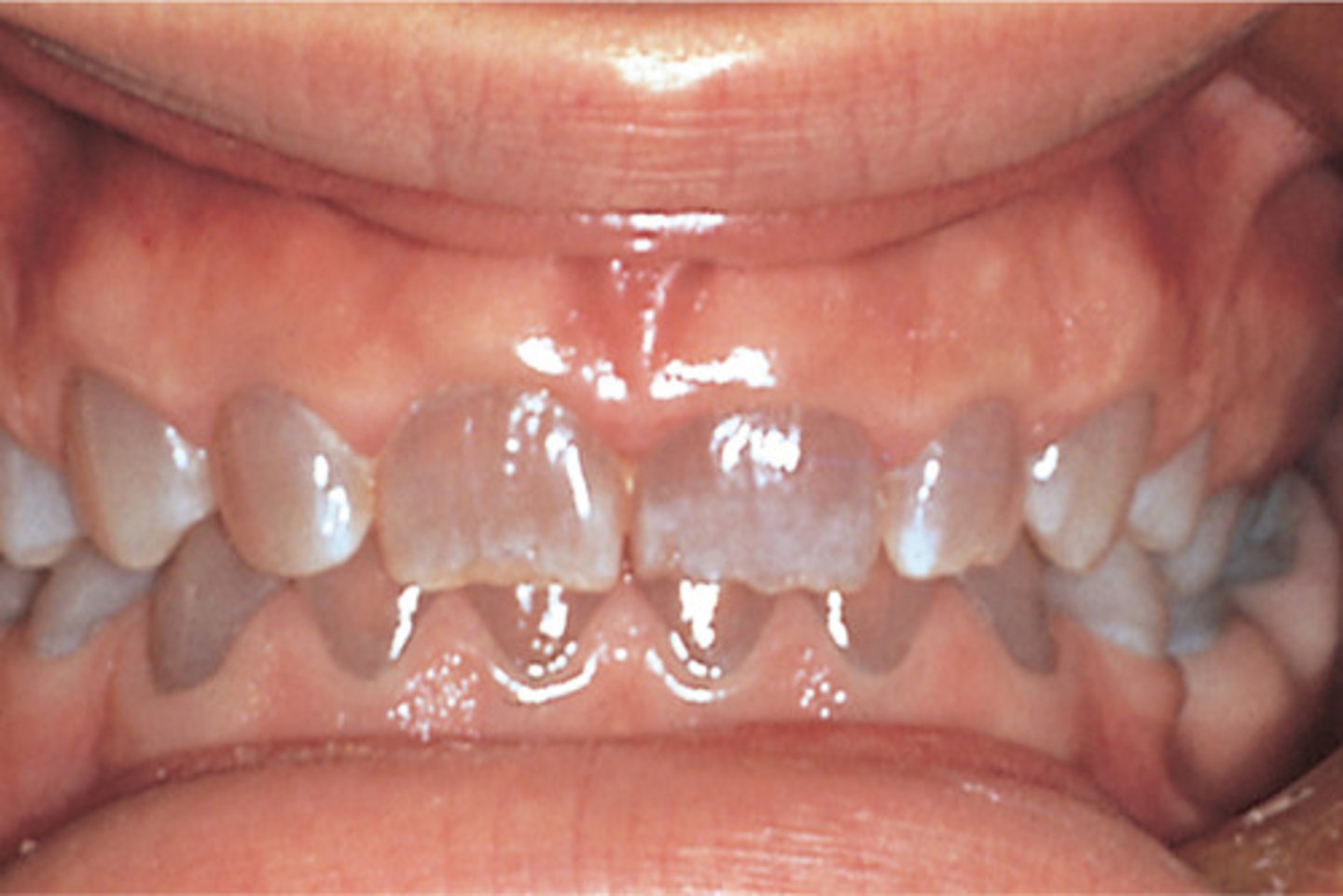
Enamel Hypoplasia
- systemic-chronologic; ameloblastic disturbance of short duration
- Local affects, usually a single tooth
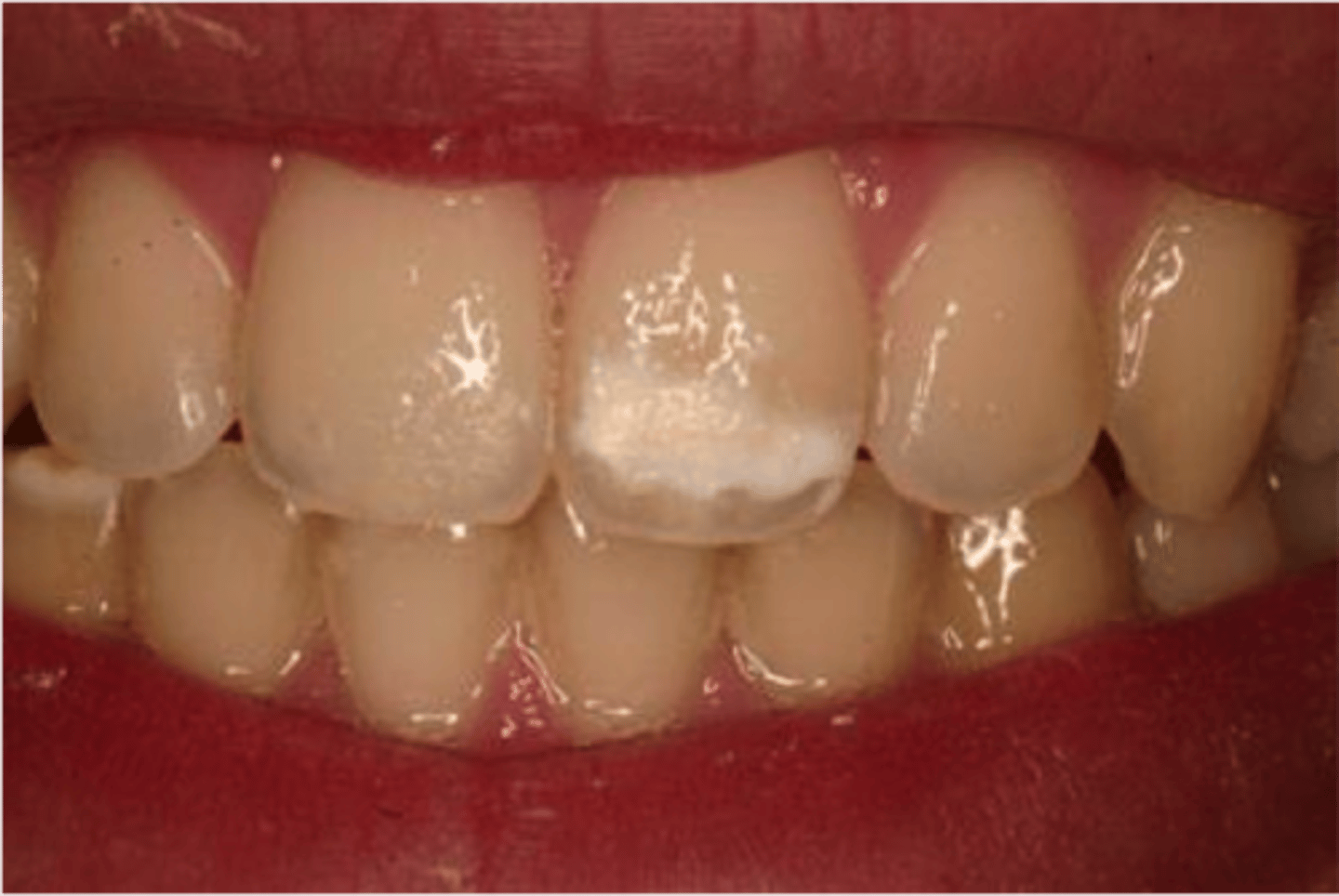
Dental Fluorosis (mottled enamel)
hypomineralization due to > 2ppm fluoride ingestion during mineralization
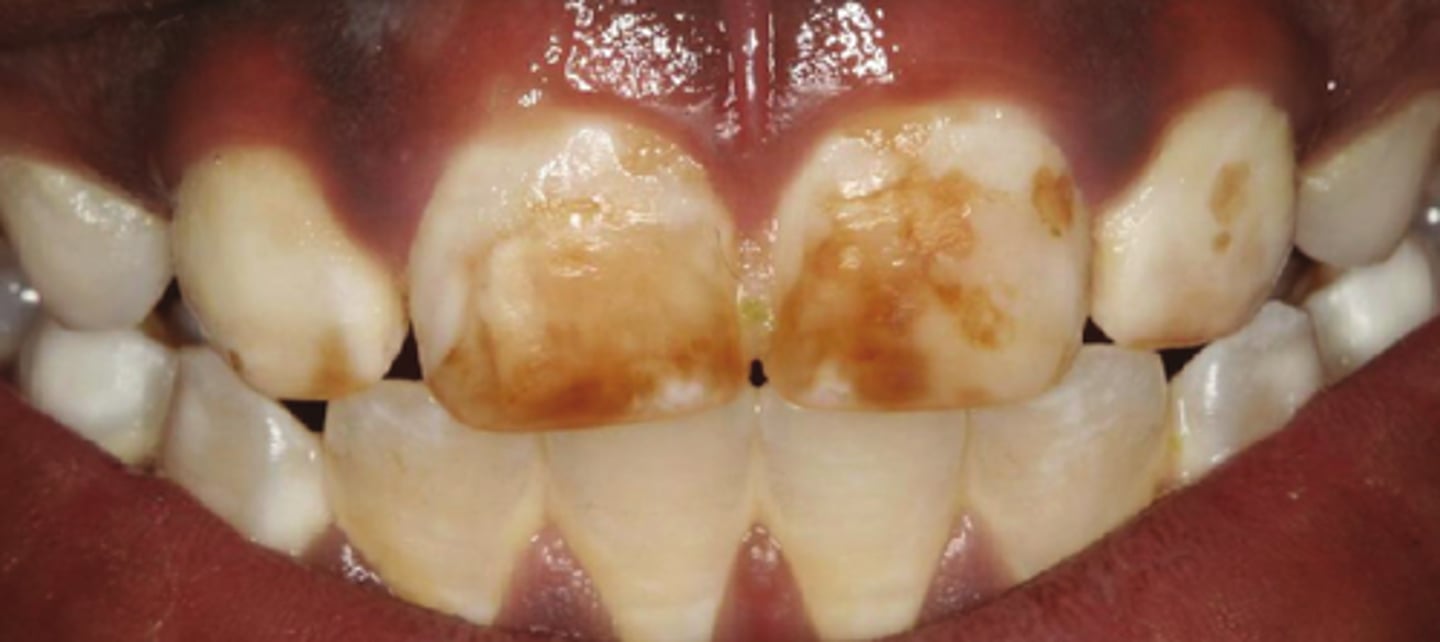
Exogenous stains
-Intrinsic or extrinsic stains due to an outside source, not from within the tooth
-Tobacco
-Green stains
Stains from silver amalgam
Metallic ions migrate from the restoration into the enamel and dentin
Copper amalgam stain
-Used in deciduous teeth
-Bluish green color
What to record when staining is observed?
color, type, extent, and location of stain
Example:
Yellow, light, tobacco stains on mandibular anterior lingual surfaces
Stain removal is associated directly with
biofilm or pellicle
Tenacious Stain
- Abrasion of tooth
- Removal of Fluoride-rich surface
- Overheating with power-driven polisher
purpose of polishing
to remove biofilm and stain
cautions with polishing
-Aerosols provide a means for disease transmission (use HVE or Isovac)
-Spatter (use PPE)
- can remove fluoride-rich enamel layer (remineralization interrupted)
Contraindications for polishing
- Newly erupted teeth
- when no extrinsic stain is present
- Gold, porcelain, composite resins
- Areas at risk for dental caries
- Caries
- Xerostomia
- Respiratory problems
- Head/neck radiation patients
- Patients with spongy, friable gingiva
- Not recommended on same day as SRP
Why to not polish newly erupted teeth
they have Fluoride rich enamel (fluorosis) that can be removed
Armamentarium (equipment) for polishing
-Prophy angle/brush
-Prophy paste (fine*, med, coarse)
-Slow speed handpiece
Supplemental Aids Stain removal
-Dental floss
-Abrasive polishing strips
-Saliva ejector
-Safety glasses (both patient and clinician)
-Disclosing agent
Polishing technique
1) Explain procedure to patient
2) Give pre-procedural rinse
3) Apply paste to tooth surfaces
4) Start low speed
5) Adapt rotating cup to tooth surface
(Flare cup on tooth surface)
6) Adapt cup to cervical area
(Cup flared under gingival margin, Apply light pressure to flare edges out and into sulcus)
7)Proceed across cervical
8)Polish incisal or occlusal portions
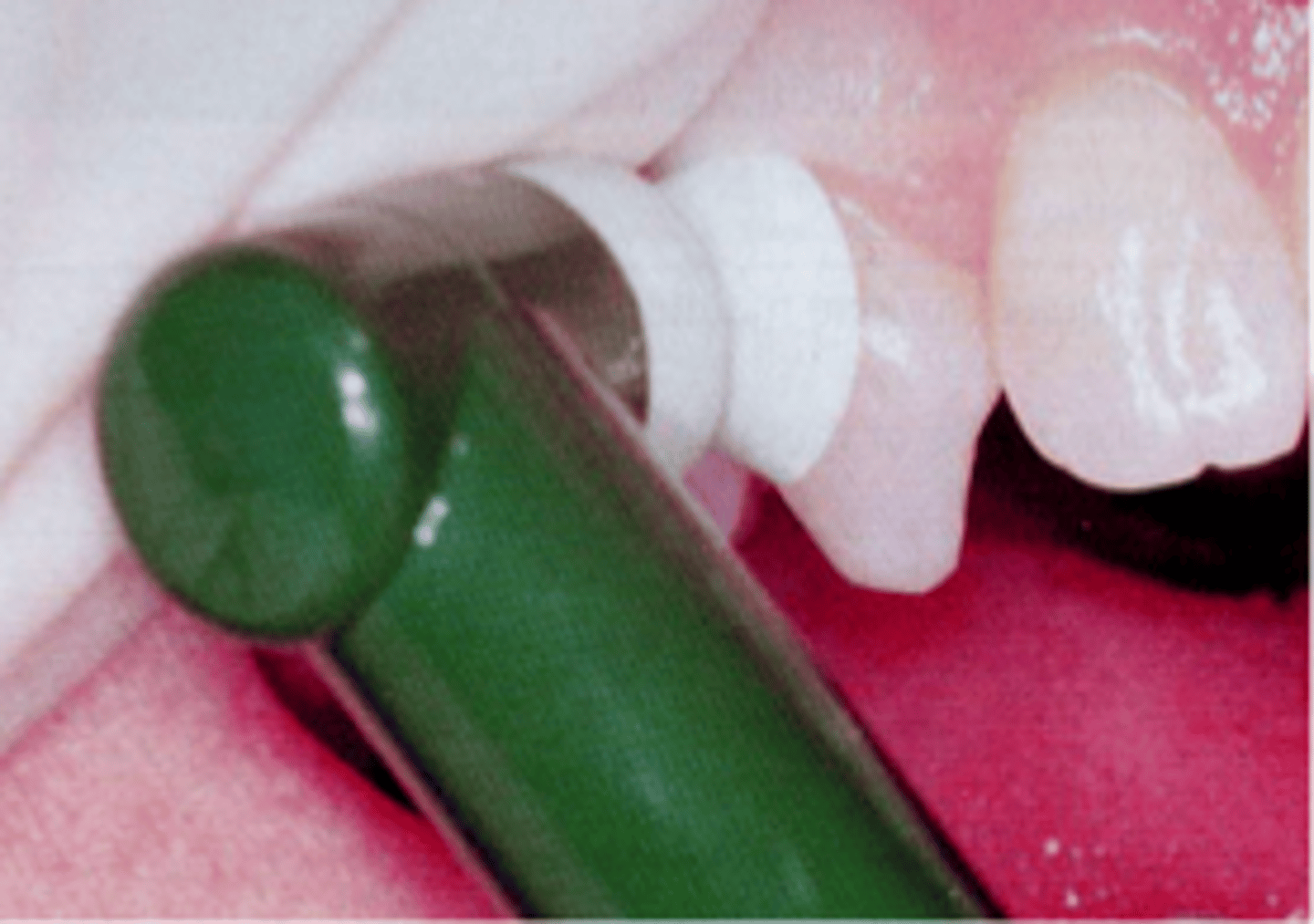
precautions while polishing
-Avoid holding up in area over 2 seconds
-Do not use abrasive on exposed root surfaces
-Use prophy brush on enamel surfaces only
-Apply abrasive with dental tape or finishing strips
-Floss all proximal spaces
when to use tin oxide/fine grit abrasive
-Gold
-Porcelain
-Composite resins
what does polishing produce?
- Produces smooth, glossy surface which reflects light
- Produces minute scratches on a surface
Types of Abrasives
finishing, polishing, cleansing
Finishing abrasives
-Fine agent
-Produces glossy surface
Mild abrasive
-Used for light to moderate stain
-More abrasive than finishing type
Cleansing Abrasives
-Coarse abrasive
-Most abrasive
-Removes moderate to heavy stain
Abrasive Action: Application Factors
-Speed
-Grit of paste & pumice
-Quantity of abrasive
-Pressure