Chem 30 - Unit 8 - Electrochemistry
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Operational Definition of Reduction + Example
When ores are reduced from oxides back to smaller, pure metals. Ex. Magnetite, Fe3O4(S), to Fe(3+)
Spontaneous Redox Reactions
Reactions which proceed with no addition of energy or any other stimulus. Redox reactions are spontaneous when the stronger reducing agent is losing electrons and stronger oxidizing agent is gaining electrons
1. Write unbalanced half-reactions that show the formulas of the given reactant and product. 2. Balance any atoms other than oxygen and hydrogen first. 3. Balance any oxygen atoms by adding water molecules. 4. Balance any hydrogen atoms by adding hydrogen ions. 5. Adjust for basic conditions by adding the same number of Hydroxide ions as the number of hydrogen present on both sides of the equation 6. Combine hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions into water 7. Cancel out water molecules Balance the charges by adding electrons
Oxidation Number
A number assigned to an atom in a compound if the electrons were completely held by the atom with the greatest electronegativity. Ex. H2O, oxygen oxidation number is -2, while hydrogen is +1. Will always add up to the charge of the compound or polyatomic ion
Charge (Q measured in C)
The total charge transferred by a cell or battery by the movement of charged particles, measured in coulombs. Q=It
Electric Current (I measured in A or C/s)
Rate of flow of charge past a point in a circuit, measured in amperes by an ammeter. The larger the electric cell, the greater the current that can be produced
○ Attach a Sacrificial anode
Nickel-Cadmium Battery
Rechargeable battery (secondary cells) which uses nickel oxide and basic cadmium as the redox reaction
Electrolysis
Supplying electrical energy to cause a non-spontaneous redox reaction to occur, to separate elements from their ores
Silver tarnish
Silver sulfide, formed from hydrogen sulfide in the air reacting with oxygen and the silver. 4Ag(s) + 2H2S(aq) + O2(g) -> 2Ag2S(s) + 2H2O
What can be used to remove silver tarnish? What’s the disadvantage of this?
Silver polish, but it also removes some of the silver along with it, which can lead to degrading over time.
What are the similarities between electrolytic and voltaic cells?
Cathode is reduced, anode is oxidizes, electrons move from the anode to the cathode, anions move to anode, cations move to cathode
Secondary Cell
A rechargeable cell. When it discharges, it is acting voltaic, and when it recharges, it is acting electrolytic. Ex. Nickel-Cadmium
The Chloride Anomaly
When chloride and water are the only reducing agents, chlorine gas will be produced instead of oxygen due to a variation in activation energies (not needed to understand this super well, just memorize the rule).
Chlor-Alkali process
The process of producing chlorine, sodium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas from the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride. Utilizes the chloride anomaly.
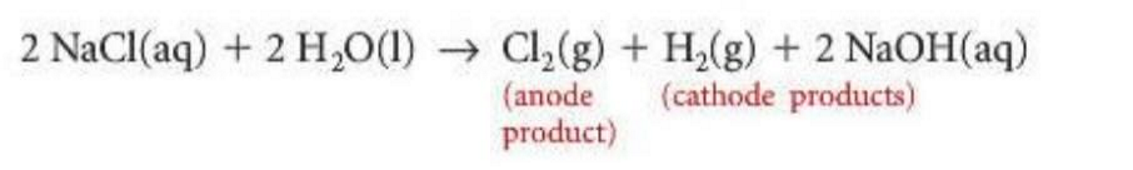
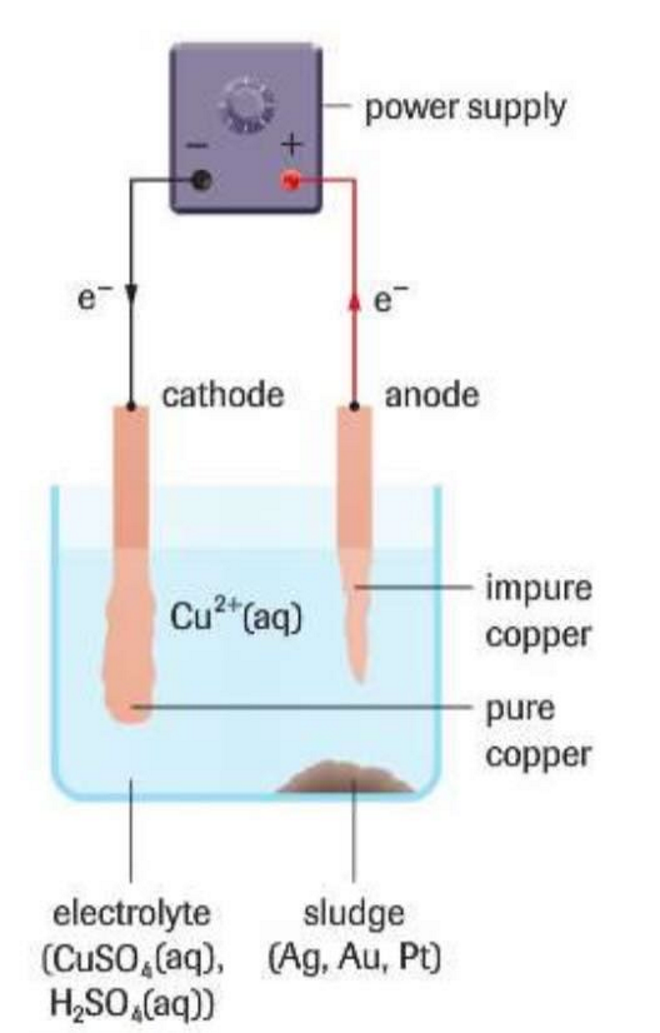
Electrorefining
Using an electrolytic cell to obtain high-grade metals at the cathode from impure metal at the anode. Example photo:
Electrowinning
Reducing metal cations from a molten or aqueous electrolyte at the cathode of an electrolytic cell. Some metals cannot be reduced in water-containing solutions as water is a stronger OA, and so must use molten metals as electrolytes
How is aluminum produced? What did the discovery of this method do?
Al2O3(s) must be dissolved in inert solvent cryolite to allow for the electrowinning of aluminum. This discovery changed aluminum's price from $45 000 per kg to only 90 cents.

Electroplating
Plating a metal at the cathode of an electrolytic cell, usually to keep costs cheap while preventing corrosion and improving appearance. Science still cannot successfully predict what may work for electroplating and so much of it is trial and error
What is hydrogen gas used for?
To produce hydrogen peroxide, ammonia, margarine, and petroleum
What is chlorine gas used for?
Sanitizing water, and producing bleach, plastics, pesticides and solvents
What is sodium hydroxide used for?
To make cellophane, pulp and paper, aluminum, and detergents
Coulomb
The charge transferred by a current of one ampere during one second
Faraday’s Law
Mass is directly proportional to the time a cell operates given a constant current
Faraday’s Constant
9.65×10^4 C/mole-, the coulombs of charge transferred for every mole of electrons flowing in a cell
Moles of electrons
ne- = Q/F or It/F
Shorthand for electrolytic cells
Anode | Ions , ions | Cathode
Plating of iron with zinc (cathode, anode, half reactions)
Uses iron at the cathode, zinc at the anode, and the half reactions of both the oxidation and reduction of zinc.