Contrast Techniques: Eso, Gastro, Ugi, Lgi, And Ivp (Cram)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Fill in the blank: Contrast media may be ______ (appears dark) or ______ (appears bright).
negative, positive
A radiograph should always be taken of the patient prior to administering the contrast media. What is the term for this x–ray?
Scout (or survey) film
A patient is regurgitating food, has acute gagging, has dysphagia, or profuse salivation. What contrast study may be ordered?
Esophagram
What is a more common term for an esophagram?
Barium swallow
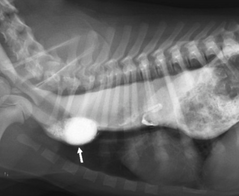
What is this condition called? It causes the regurgitation of food
Esophageal diverticulum
Note: Regurgitation can also be caused by scar tissue, a foreign body, or mediastinal lesion
True or false: If a patient cannot swallow at all, an emergency esophagram may be ordered
False. The inability to swallow is a contraindication of esophagrams (along with esophageal rupture), because barium can cause aspiration pneumonia
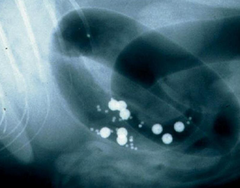
What are these?
BIPS, barium pellets available in capsules
How long is a patient fasted for an esophagram?
Fast for 12+ hours
True or false: Liquid barium given for an esophagram is very thick. You should give it via the buccal pouch 5 minutes prior to taking the first radiograph so it has time to travel the length of the esophagus
False. The patient should already be in lateral recumbency on the x–ray table at the time barium is given. The x–ray should be taken immediately
If no abnormalities are detected on the esophagram when using liquid barium and barium paste, how else can you give barium?
Mix barium with dog food
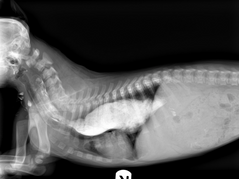
What is this condition called? It can cause stenosis (stricture) of the esophagus
Megaesophagus
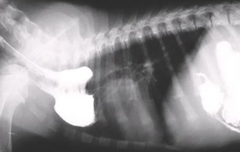
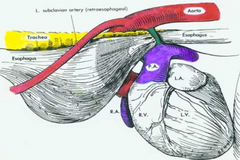
What is this condition called? It can cause stenosis (stricture) of the esophagus at the area of the heart
Vascular ring anomaly
Note: Condition is very rare
A patient is suspected of having a mass or foreign body in the stomach, has acute or chronic vomiting, blood in vomitus, or cranial abdominal pain. What contrast study may be ordered?
Gastrogram
Fill in the blank: Preparation for a gastrogram requires a ___ to ___ hour fast
12, 24
What are the three different types of gastrograms?
- Positive
- Negative
- Double (air/CO2 + barium)
If barium cannot be delivered via the buccal pouch, what device can be used?
Orogastric tube
Other than air or CO2 via stomach tube, what else can be used for a negative contrast gastrogram?
Carbonated beverage via the buccal pouch

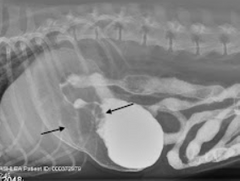
What is wrong with this patient's stomach? This is an abnormal finding on a gastrogram
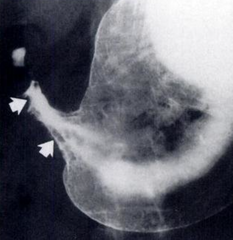
What is wrong with this patient's stomach? This is an abnormal finding on a gastrogram
Note: This image is human
Gastric ulcers
An UGI study includes which two structures?
- Stomach
- Small intestine
What does UGI stand for?
Upper Gastrointestinal Study
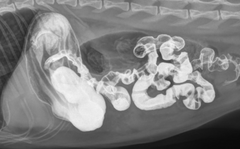
What is wrong with this patient's upper GI?
Linear foreign body (string, tinsel, etc.)
Name some indications for an upper gastrointestinal study
Non–responsive vomiting, persistent abdominal pain, blood in vomit, suspected foreign body, suspected neoplasms, palpable viscera in hernia, etc.
Why is large bowel obstruction a contraindication for UGI?
If barium cannot continue to be removed then will cause patient to be in pain/discomfort
Why is suspicion of ruptured stomach or intestine a contraindication for UGI?
Don’t want barium leaking into the peritoneal cavity, this can cause peritonitis
How long are patient's fasted for a UGI?
24 hours
What special step is taken to prepare for a UGI?
Enema
Which tranquilizer/sedative can be given to nervous patients undergoing a UGI?
Acepromazine, because it effects the GI motility less than other drugs
How often should you take radiographs during a UGI study? In what positions should you take them in?
Take right lateral and ventro–dorsal radiographs at 15 minute, 30 minute, 60 minute and 90 minute intervals
Fill in the blank: Normally barium should start to appear in the large intestine by ___ - ___ minutes
30 - 60
Fill in the blank: Normal small bowel transit time for micro–pulverized barium is ___ - ___ hours
2 - 3
How can you tell on radiograph that a patient has a UGI blockage?
If the patient has a total blockage barium will go no further regardless of time
Name some indications for a LGI study
Recurrent or continuous tenesmus (straining), recurrent or continuous diarrhea, excessive mucus in feces, bright red blood in feces, colonic obstruction, altered shape of the stool, suspected rectal mass, etc.
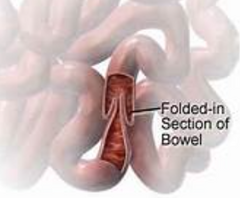
What is this condition called? It is also an indication for a LGI study
Intussusception
True or false: Like a UGI, contraindications for a LGI include rupture and total obstruction
True
What kind of contrast studies can be performed on the LGI?
- Positive
- Negative
- Double
How long do you fast a patient for LGI?
24 hours
12 hours before a LGI, what should you give to the patient?
Laxative
Immediately before a LGI, what should you give to the patient?
Enema
What type of pain control should be given to patients undergoing LGI?
General anesthesia, because it is considered a painful procedure
How is barium administered to a patient undergoing a LGI?
Via rectum
What type of catheter is required to administer barium during a LGI, and why?
Cuffed rectal catheter, you need to seal the anal sphincter

What special step should you do to prepare the contrast material for LGI?
Warm it
What complication can result from rough technique, or excessive volumes of contrast material applied during LGI?
Rupture of the colon
What complication can result from failing to elevate the pelvis, remove the contrast material, or inflate the cuff?
Flooding the table top with contrast material
If the contrast material administered for a LGI reaches a certain point, it is considered a complication, what is this point?
Ileum of the small intestine
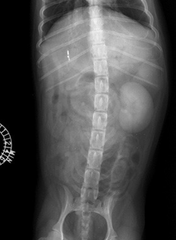
A contrast study of this organ is called what?
Nephrogram, study of kidneys
A contrast study of the collecting system and ureters is called what?
Pyelogram
Name some indications for excretory urography (including intravenous pyelography, and intravenous urogram)
Abnormal renal size or shape, suspected renal masses, persistent hematuria, proteinuria, crystalluria, polyuria, dysuria, etc.
What are the two contraindications for intravenous pyelography?
- Severe dehydration
- Severe shock
Do you fast a patient for intravenous pyelography?
Yes, for 24 hours. Bowel contents can obscure the kidneys, ureters, etc.
Do you use an enema for a patient undergoing intravenous pyelography?
Yes
What two clinical pathology tests are often ordered prior to a IVP?
- Creatinine
- BUN
What precaution has to be taken when administering contrast media IV for a IVP?
Iodinated compounds used for IVP can cause severe sloughing of tissues if injected perivascular! A indwelling catheter is necessary
How do you enhance the concentration of contrast media in the upper part of the urinary tract during an IVP?
Compression device for the adomen (can be just Vetrap)
Fill in the blank: ___ in ___ cats or dogs have an anaphylactic reaction to iodine based drugs used during IVP
Note: Keep emergency resuscitation kit on hand, reaction could be fatal
1, 80
How do the times for taking radiographs differ between a nephrogram and a pyelogram?
Nephrogram: Take a VD projection immediately after injection
Pyelogram: Take lateral and VD projections at 5, 10, and 20 minutes after injection
What is a common side effect of the iodine based drugs used for IVP?
Vomitting