CHAPTER 2 Measurements and Calculations
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Chapter 2
Measurement
• Quantitative observation
• Properties that can be measured are called quantitative
properties
– Expressed using a number.
– Must always include the appropriate unit
• Uses numbers and units
– Number tells comparison
– Unit tells scale
Using Scientific Notation
• Placement and direction of a decimal point
– The number of places the decimal point is moved
determines the power of 10
– The direction of the move determines whether the power of
10 is positive or negative
Unit
The scale or standard being used to represent the results
of a measurement
– Scientists require common units to measure quantities such as
mass, length, time, and temperature
Most widely used standard systems of units
– English system (used in the United States (ft, Ga, lb....)
– Metric system (used in most of the world (m, L, Kg,....)
➡Preferred for scientific work
International System or SI
– Comprehensive system of units set up by an international
agreement
– Units based on and derived from the metric system
– General Conference on Weights & Measures (GCWM: 1960)
extensive property
depends on the amount of matter (sample size).
➡ Value of the same extensive properties are additive.
➡ Example: Mass, volume, length,....
intensive property
does not depends on the amount of matter (sample size).
➡ intensive properties are not additive.
➡ Example: temperature, density,....
Scientist use variety of devices (volume, T, mass, ....) to measure
the properties of matter
volumetric flask
graduated cylinder
pipette
burette
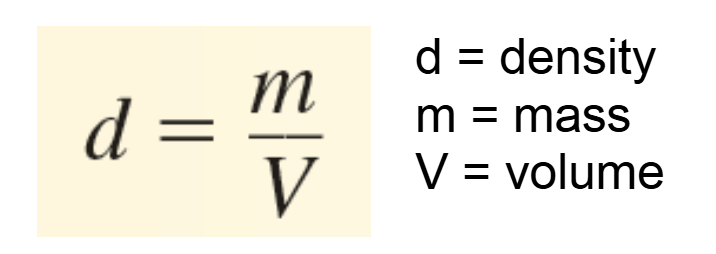
density
of a substance is the ratio of mass to volume.
kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
Other common units:
g/cm3 (solids)
g/mL (liquids)
g/L (gases)
Volume
• Measure of the amount of 3-D
space occupied by a
substance
• SI unit = Cubic meter (m3 )
• Commonly measured in cm3
• 1 mL = 1 cm 3
• 1 L = 1 dm 3
Mass
• Measure of the amount of
matter present in an object
• SI unit is Kilogram (kg)
• 1 kg = 2.2046 lbs
• 1 lb = 453.59 g
Uncertainty in Measurement
There are two types of numbers used in chemistry:
• Exact numbers which have defined values
- 1 kg = 1000 g,
- 1 dozen = 12 object,
- any number obtained by counting
• Inexact numbers
- Numbers obtained by any method other than counting
- Measured numbers are inexact because of the instruments and
operators or both
Certain and Uncertain Measurements
• A digit that must be estimated is called uncertain
• A measurement always has some degree of uncertainty
• Certain digits are recorded first followed by uncertain digits or the estimated number
The Reliability of a Measurement-Significant Figures
• An inexact number must be reported so as to indicate its uncertainty.
• This is done using significant figures.
• Significant figures are the meaningful
digits in a reported number.
• The last digit in a measured number is
referred to as the uncertain digit.
•The uncertainty is considered to be ±1 in the
place of the last digit.
Relative Uncertainty and % Uncertainty
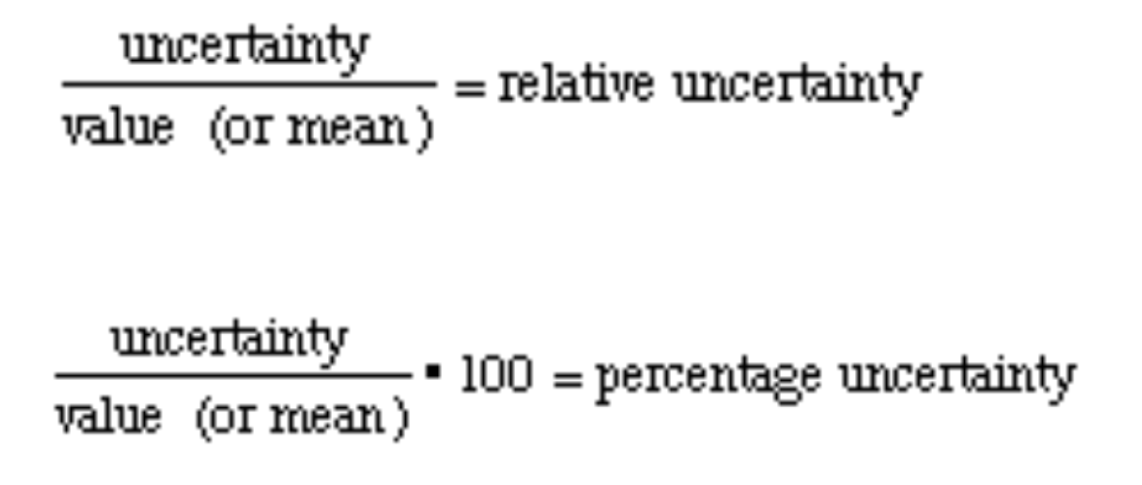
Dimension Analysis
• Most chemistry problems you will solve in this course are unit conversion problems.
• Using units as a guide to solving problems is called dimensional analysis.
Three Units for Measuring Temperature
• Fahrenheit
• Celsius
• Kelvin
The Celsius ( o C) degree - Kelvin (K) degree conversion.
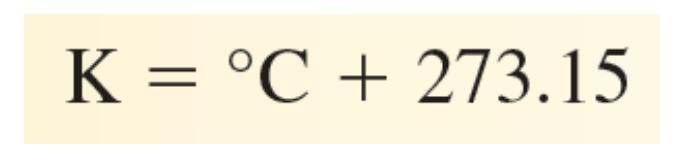
The Fahrenheit degree - Celsius degree conversion.

Precision and Accuracy
– precise if they are consistent with one another.
– accurate only if they are close to the actual value