Biological Bases of Behaviour Part 1
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Brain function and Endocrine System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Endocrine system
secrete chemical messengers (hormones) into blood
travel to target organs to bind to specific receptors
Endocrine glands
H – Hypothalamus
P – Pituitary
T – Thyroid
P – Parathyroid
A – Adrenal
P – Pancreas
G – Gonads (testes/ovaries)
Pineal Gland
produce melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythm
associated w/ seasonal affective disorder
Hypothalamus
Controls the endocrine system by signaling the pituitary gland to release hormones.
Thyroid gland
produces thyroxine which maintains and stimulates metabolic activities
Adrenal glands
atop kidneys
Pancreas
secrets the hormones insulin and glucagon, regulating. blood sugar
Ovaries/Testes
produce hormones necessary for reproduction
Pituitary gland
Known as the “master gland”
Releases hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction, under the direction of the hypothalamus.
Glial Cells
Guide growth of neurons
provide nutrition and get rid of waste
form insulation
Cell Body/Soma/Cyton
contains cytoplasm and nucleus
Processes information
Dendrites
receives info
neurogenesis
growth of new neurons
Glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter
information processing, especially memory formation in hippocampus
Endorphins
brains painkillers
GABA inhibits the firing of these neurons
Norepinephinre
attentiveness, sleeping, dreaming, and learnin
Agonists
bind to receptor site to produce the effect of neurotransmitter
antagonists
block receptor site inhibiting the effect of neurotransmitter
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain,
responsible for higher-order thinking, reasoning, perception, and voluntary movements.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the cerebrum
divided into lobes
controls thinking, planning, sensory processing, and voluntary movement.
Frontal Lobe
Controls decision-making, problem-solving, planning, personality, and voluntary movement (contains motor cortex)
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain (contains somatosensory cortex).
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for visual processing.
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information and is involved in memory and language.
Cerebellum
controls posture, equilibrium, and movement
Thalamus
directs incoming sensory signals to the correct brain areas (except smell).
Hypothalamus
Regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature, and hormones; links nervous and endocrine systems.
Pituitary Gland
“Master gland” of the endocrine system
controls hormone release.
Amygdala
Controls emotions, especially fear and aggression.
Hippocampus
Enables formation of new long term memories
Corpus Callosum
Connects the two hemispheres of the brain, allowing communication between them.
Medulla
Part of brainstem controlling heartbeat, breathing, and reflexes
Pons
Definition: Part of brainstem that helps coordinate movement and sleep/wake cycles
EEG (Electroencepgalogram)
Measures waves of electrical activity (brain waves) produced by neurons firing on the scalp
Where and when brain activity occurs
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
Shows brain activity by detecting where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a task.
Colored
fMRI (Functional MRI)
Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels.
Shows both structure and function
Magnetic Source Image (MSI)
EEG and MRI data to pinpoint the exact location of brain activity
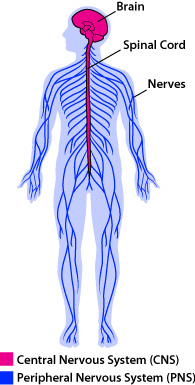
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous system
stimulate skeletal (voluntary muscle)
Autonomic Nervous system
Stimulate smooth (involuntary) and heart muscle
antagonistic sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic stimulation
response that help body deal w/ stressful events
eg dilated pupils, high heart rate, secretion of adrenaline
Parasympathetic stimulation
Calms body following sympathetic stimulation
Eg restore digestive function, returning pupil size
Spinal Cord
protected by membranes (meninges) and spinal column of bony vertebrae
start at base of back → base of skull → brain