Lecture 6 - Prescriptions & Drug Charts
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prescriptions & Drug Charts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Precribing
Prescribers must:
Electronically generate and/or write legible, unambiguous and complete prescriptions which must meet legal requirements
Effectively use the systems necessary to prescribe medicines
Document accurate, legible and comtemporaneous clinical records
Who can prescribe?
Medical practitioners: Doctors & dentists
Vetirinary surgeons
Non-medical prescribers: nurses, optometrists, pharmacists, physiotherapists, etc
Non-medical prescribers

Primary Care
NHS Prescription Documentation
Standardised to:
Minimise risk of fraudulency
Reduce error
Identify elements of accountability
Facilitate remuneration for medicines
Allow for the collection of data on precribing patterns and costs
Legal requirements
Patient identification: name & address
Age or DOB - if under 12 it’s a legal requirement to have the age written on the prescription
Signed - can’t be erasable
Dated
Name and address of practioner
Be written in idelible ink
Additional requirements for controlled drugs
Requirements for a safe prescription
The right drug
At the right does
By the right route
At the right time
To the patient
The right to refuse
considering contraindications, interactions, adverse effects and allergies
NHS FP10 Precription - Green

NHS FP10 Precription - Blue
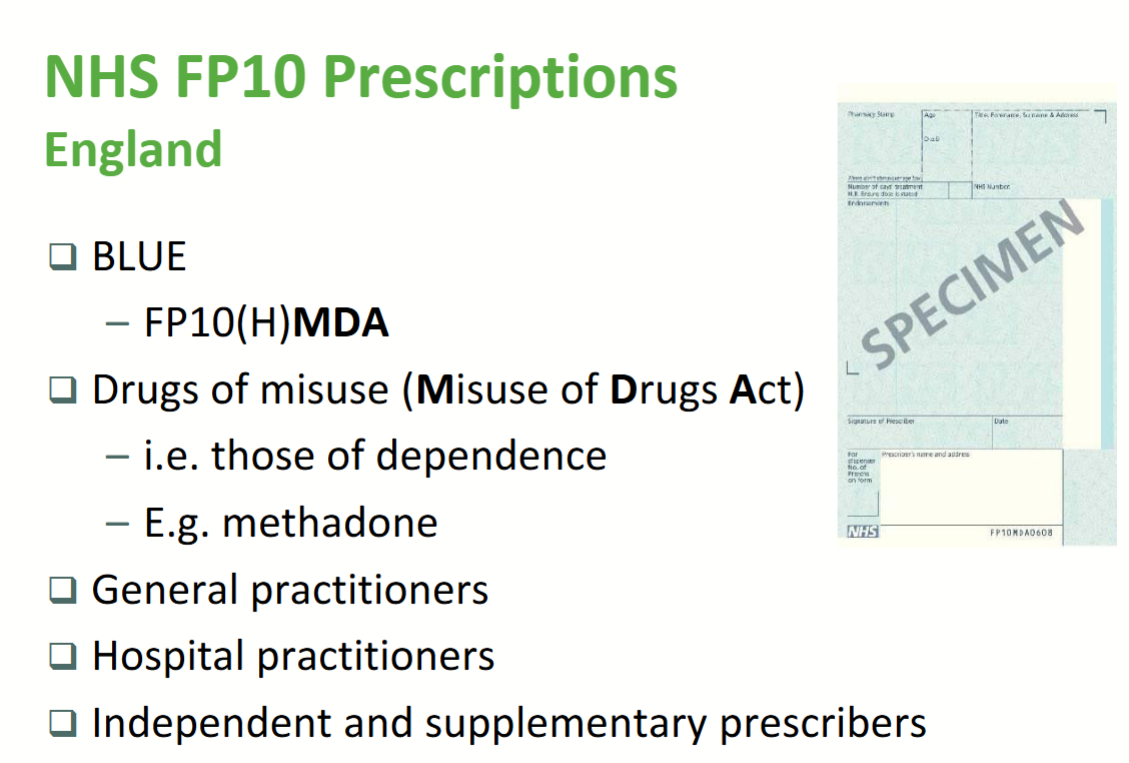
NHS FP10 Precription - Yellow

NHS FP10 Precription - Lilac

Requirements of the FP10
Patient name
Patient address
Age or DOB
Signature of the prescriber
Date
Name/qualifications of prescriber
Address of practitioner
Electronic Prescription Service
EPS allows the prescription to be sent electronically from the GP to a nominated community pharmacy
The pharmacist can prepare prescriptions in advance
The pharmacist can monitor medicine use as they are the consistent supplier for a patient
The legalities of the prescription remain the same

Secondary Care
Patient Specific Directions (PSD)
PSDs are issued in hospital
Written or electronic instructions from a doctor, dentist or non-medical prescriber for a medicine to be supplied or administered to a named patient after the prescriber has assessed the patient on an individual basis
Unlike primary care:
There’s no standard documentation for the PSD in English hospitals
Hospitals design, maintain, monitor and enforce their own documentation
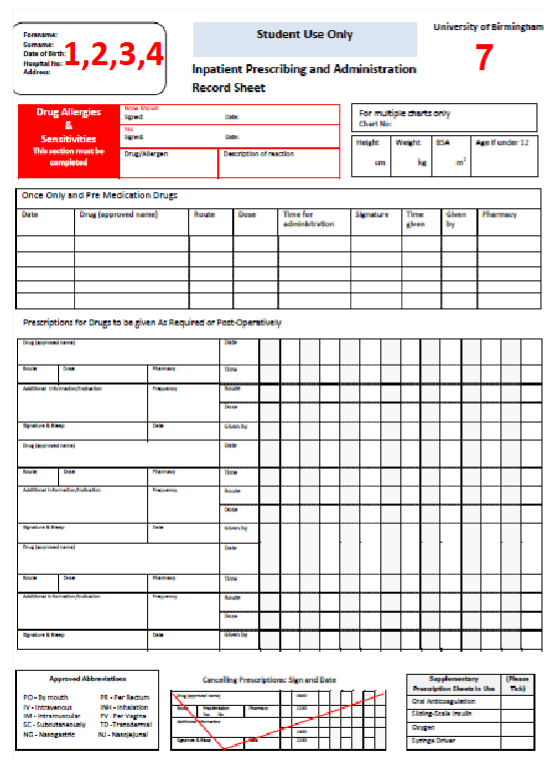
Inpatient Drug Charts
Patient demographics - they must allow for the documentation of:
Patient identifiable information
The allergy status of the patient
Patient information to inform the calculation of doses (height, weight, BSA)
Content - paper-based or electronic
Must allow for the instruction of:
Regular medicines
Variable regimens
Single, one-off doses
When required medicines
Infusions
And
What is to be given? drug name, form)
Why? (indication)
When? (date and time)
How? (route)
How often? (frequency)
Until when? (for a week, or to continue long-term?)
Requirements of the PSD
Patient name
Patient address
Age or DOB
Hospital number
Signature of prescriber
Date
Nam/qualifications of prescriber
Address of practitioner
PSD Documentation
Although not standardised, all are designed to:
Facilitate the documentation of a complete prescription
Reduce the risk of error
Minimise the risk of fraudulency
Identify elements of accountability
Documetn a patient’s pharmacological history for a single hospital admission
Outpatients
Hosptial specific outpatient prescription can only be given in the hosptial pharmacy
Medicines intended to treat the condition for which the patient was referred
Hosptial only medicines
Medicines requiring monitoring
Medicines required urgently
Or a hosptial FP10 may be issued
Prescribing for Discharge
TTO’s (to take out), TTH (to take home)
A direction for the pharmacy to supply
States all drug treatments that are to continue on discharge
States any changes in drug treatment during the hospitale stay
Why has a medicine been stopped?
Why has a dose been increased?
Why has adoes been reduced?
Why has a new drug been started?
Private practice
Private prescriptions
Who?
Can be issued by any prescribing practitioner
The patient pays for the cost of the medicines and for the pharmacists time
Why?
Private healthcare
Items that can’t be prescribed on the NHS
How?
There is no standard prescription documentation

Private CD Prescriptions
Controlled drugs
Pink
Ensures the supply of controlled drugs is auditable through the NHS Business Services Authority