Mass spectrometry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is mass spectra used to do?
Identify the molecular mass of an organic compound and to gain further information about its structure
What is a molecular ion, and how is it formed?
When an organic compound is placed in the mass spectrometer, it loses an electron to form a positive ion - the molecular ion (M+)
Molecular ions are usually formed as a result of electron bombardment
How does a mass spectrometer work?
It detects the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the molecular ions which gives the molecular mass of the compound
Show the formation of the molecular ion from ethanol
C2H5OH + e- → CH2H5OH+ + 2e-
How do we find the molecular mass from a mass spectrum?
The molecular ion peak (M+ peak) is the clear peak at the highest m/z value on the right-hand side of the mass spectrum
On the mass spectrum you will usually see a very small peak one unit after the M+ peak. What is this and why does this exist?
This is the M+1 peak, which should be ignored
This peak exists because 1.11% of all carbon is present as the carbon-13 isotope
E.g. Propan-1-ol has a molecular mass of 60, but a small proportion of the alcohol molecules will contain an atom of 13C, and thus will have a molecular mass of 61, giving the M+1 peak
What is fragmentation and how does this occur?
The process where some molecular ions break down into smaller pieces known as fragments
Excess energy from the ionisation process causes bonds in molecular ions to vibrate, weaken and split into fragmentation ions
Apart from the M+ peak, there are also other peaks on the mass spectrum. Why is this?
The other peaks are caused by fragment ions, formed from the breakdown of the molecular ion
What are the products of fragmentation?
A positively charged fragment ion and a radical
Any positive ions formed will be detected by the mass spectrometer, but the uncharged radicals are not detected
Show the products of fragmentation of this molecular ion:
CH3CH2CH2OH+
CH3CH2CH2OH+ → CH2OH+ + CH3CH2⋅
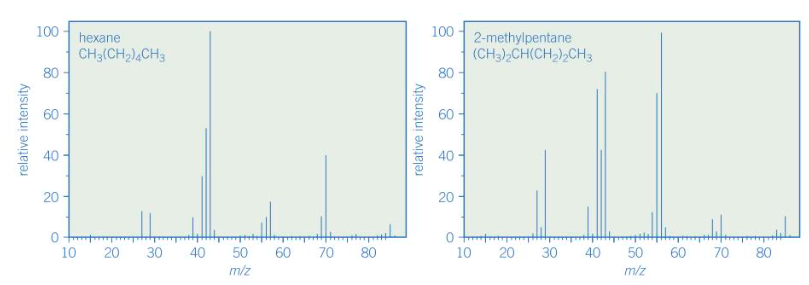
Give a similarity and a difference between these two mass spectra
Both have M+ peak at 86
Different fragmentation patterns
Give the m/z value for CH3+
15
Give the m/z value for C2H5+
29
Give the m/z value for C3H7+
43
Give the m/z value for C4H8+
56
Give the m/z value for C=O+
28
Give the m/z value for COCH3+
43
Give the m/z value for OH+
17
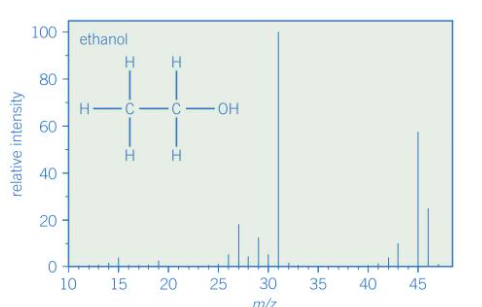
Give the main features of the spectrum
M+ peak at m/z = 46
Small M+1 peak at m/z = 47
A number of fragment ion peaks
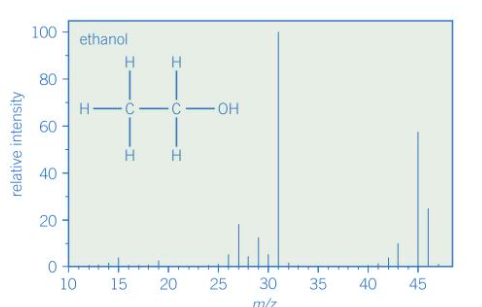
Give the fragment ions of the spectrum
Peak at m/z = 15 for CH3+
Peak at m/z = 29 for CH3CH2+
Peak at m/z =31 for CH2OH+
Peak at m/z = 45 for CH3CH2O+