Joints
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Articulations information
points where bones come together, joints
arthr- = joint
arthritis= inflammation of the joints
classified by structure or function
Structural Classification of Joints
Fibrous- joint with no joint cavity
bones held together by fibrous connective tissue
sutures between bones of the skull are fibrous joints
Cartilagenous= lacks a joint cavity
bones held together by cartilage
pubic symphysis
Synovial- fluid filled cavity (synovial cavity)
bones held together by synovial capsule and often there are accessory ligaments
Functional classification of joints
synarthroses- joints that allow virtually no movement
sutures
amphiarthroses- joints that allow limited movement
pubic symphysis
Diarthroses- joints that allow free movement
knee
Articulations
Synarthroses- no movement
suture- fibrous connective tissue binds two bones tightly together
gomphosis- cone shaped peg in a socket (tooth in jaw)
synchondrosis- bones connected by hyaline cartilage (epiphyseal plate)
becomes synostosis when calcification is complete
Amphiarthroses
syndesmosis/ interosseous membranes- more fibers that a suture but not as tight.
allows slight movement
distal articulation of the tibia and fibula
Symphysis- fibrous cartilage (pubic symphysis)
Diarthroses
synovial joints- synovial cavity filled with synovial fluid
articular capsule and accessory ligaments (inside or outside capsule)
ends of bones covered with articular cartilage that has no perichondrium
capsule has dense fibrous outer layer
inner layer- synovial membrane that produces synovial fluid
lymph/hyaluronic acid and acts as lubricant
Menisci/articular discs- fibrous pads between synovial joints composed of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue
Bursae- sacs of fluid in body tissue that resemble a synovial joint without bone-to-bone articulation
fluid filled with inner synovial membrane and often connected to synovial cavity of a joint
prevent friction between the end of a bone and the surrounding soft tissue (tendons, ligaments, muscle
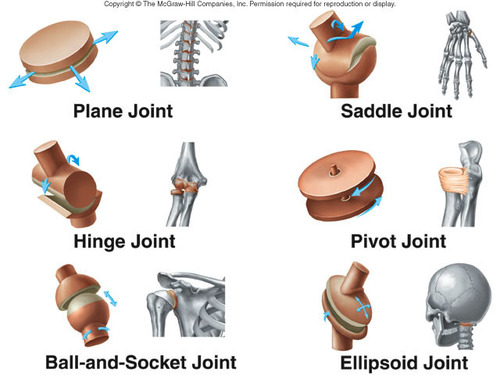
Synovial Joints
planar- flat curved surfaces allow back and forth or side to side movement
intercarpal and intertarsal joints
hinge- one bone with a convex surface fit into another bone with concave surface to allow an open-close movement
knee, elbow
pivot- rounded or pointed surface with one bone articulates with a ring formed partly by another bone and partly by a ligament
radioulnar- allows palm to turn
saddle- one bone is saddle shaped and the other bone fits like a rider in the saddle
between carpal bone and metacarpal of the thumb
ball-and-socket- The rounded projection, ball, of one bone fits into depression of another bone
shoulder and hip
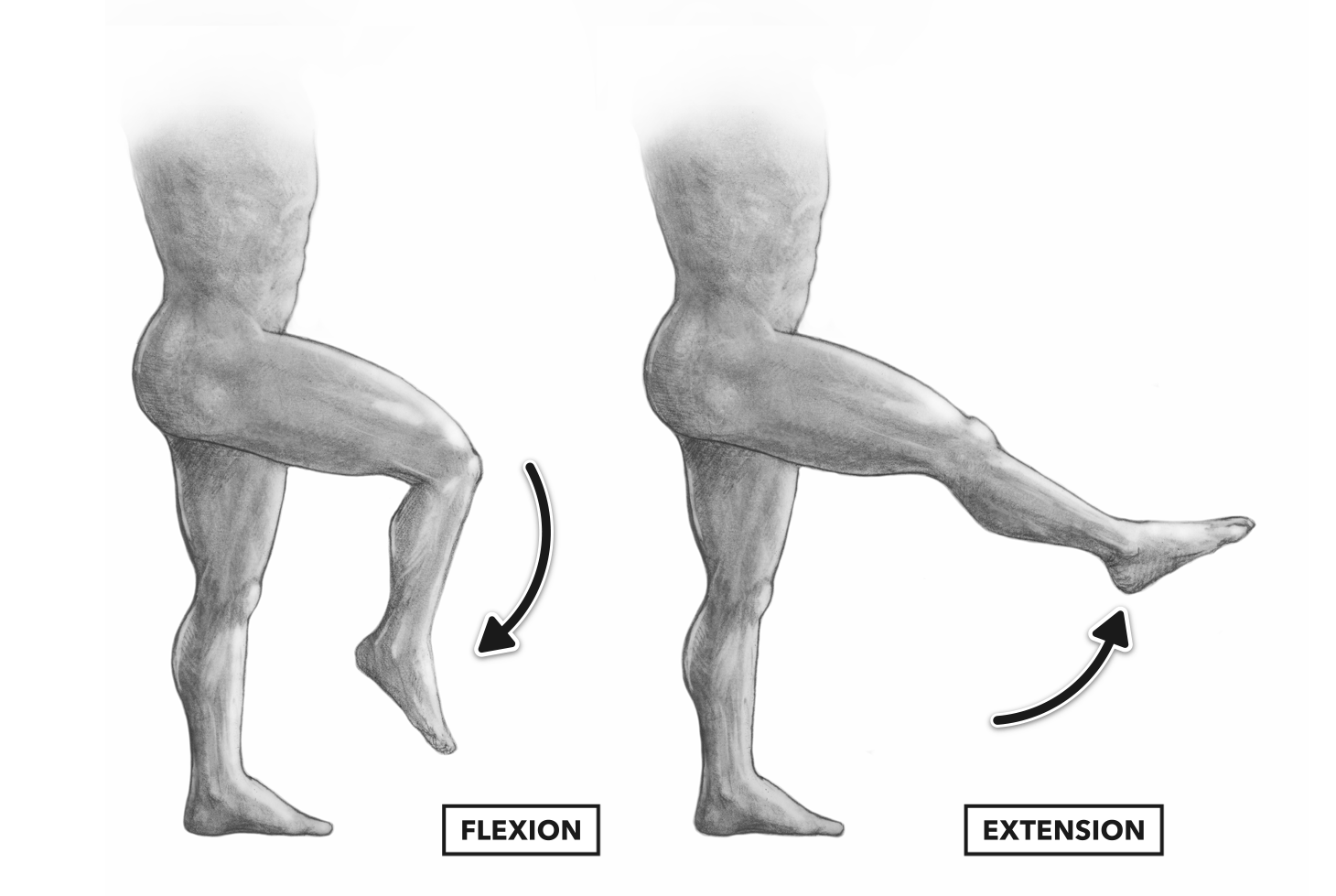
Movements
flexion-
1. decrease in the anterior angle between bones (except the knee and toes)
2. bend in the anterior or posterior direction
3. move out of anatomical position in the anterior or posterior direction
extension-
1. increase in the anterior angle between bones (except knee and toes)
2, straighten in the anterior or posterior direction
3. move to anatomical position in the anterior or posterior direction
hyperextension- extend beyond a straight line or beyond normal range
abduction- movement away from midline
adduction- movement toward midline
supination- turn palms forward (anatomical position) or up
pronation- turn palms back or down