Upper Limb Anatomy
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
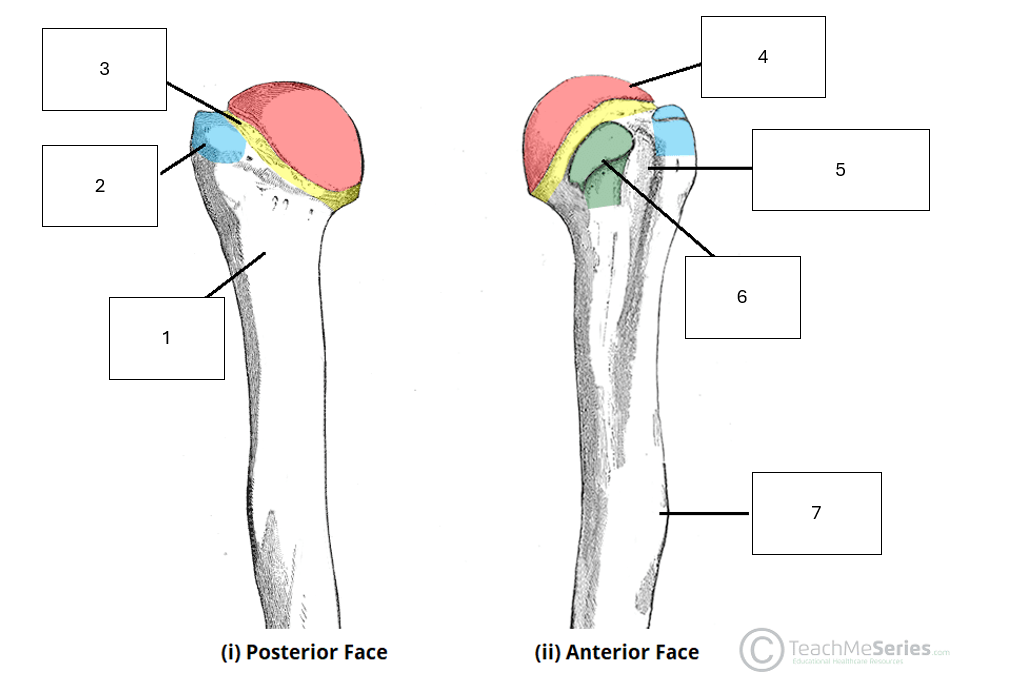
Name the missing anatomical features of the proximal humerus
1 - Surgical neck
2 - Greater tuberosity
3 - Anatomical neck
4 - Humeral head
5 - Intertubercular Groove
6 - Lesser tuberosity
7 - Deltoid tuberosity
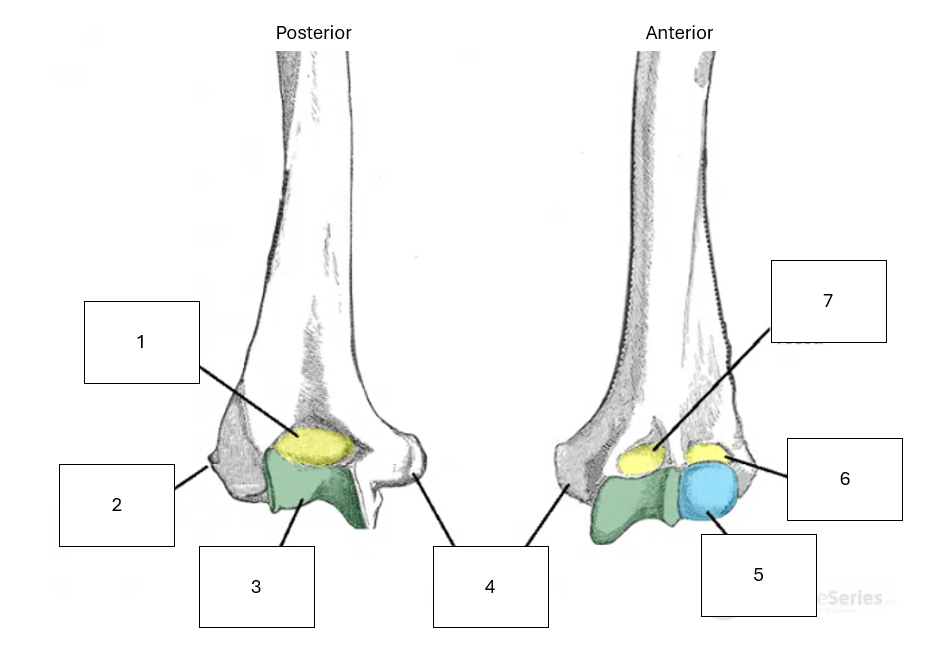
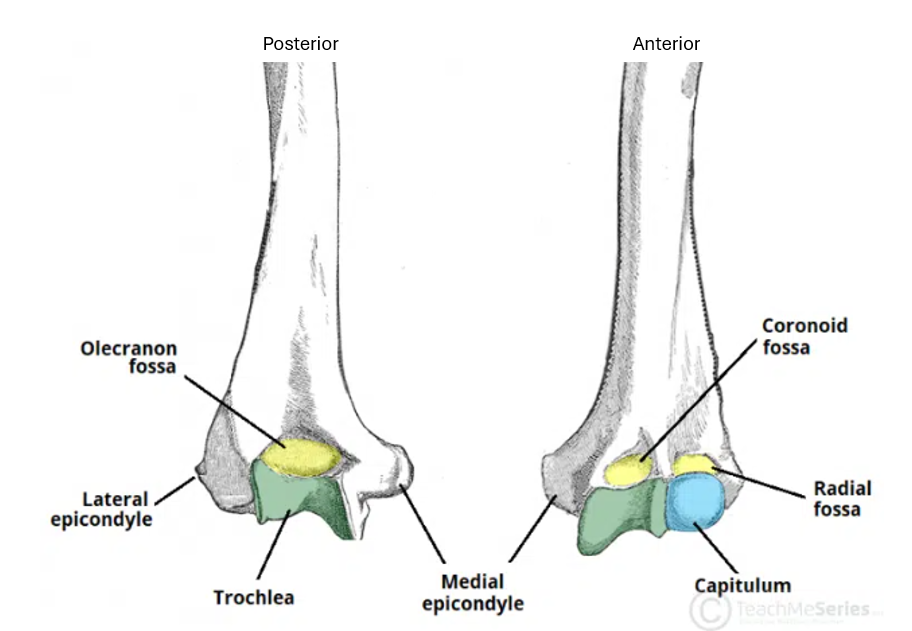
Name the missing anatomical features of the distal humerus
1 - Olecranon Fossa
2 - Lateral epicondyle
3 - Trochlea
4 - Medial epicondyle
5 - Capitulum
6 - Radial fossa
7 - Coronoid fossa
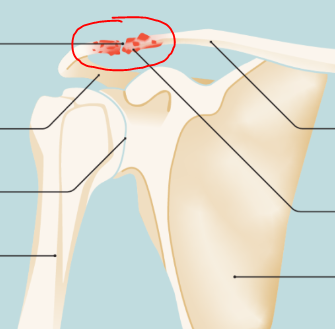
Name the joint shown
Acromioclavicular joint
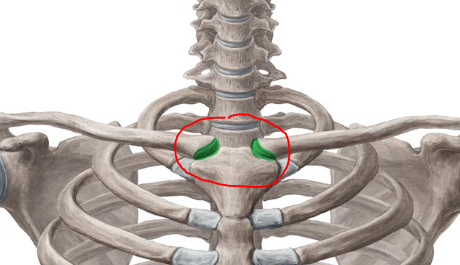
Name the joint shown
Sternoclavicular joint
What kind of joint is the sternoclavicular joint
Synovial, saddle joint
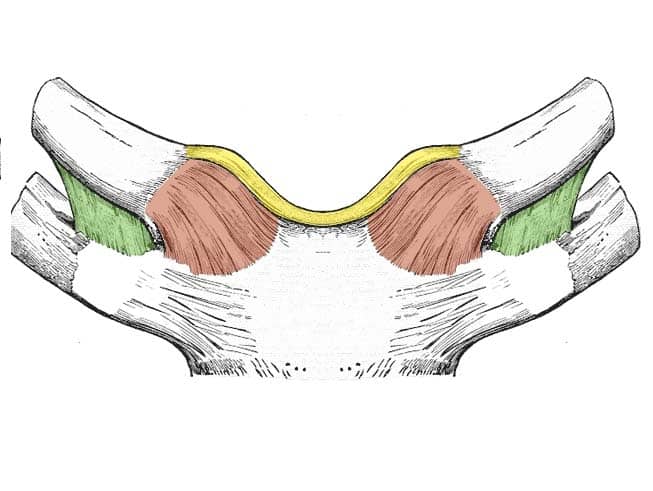
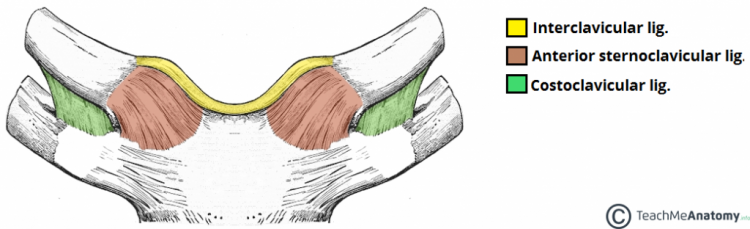
Name the sternoclavicular joint ligaments
Quite easy to remember
Interclavicular ligament - in between the right and left clavicles
Costoclavicular ligament - in between costal cartilage of first rib and clavicle
Sternoclavicular ligament - in between manubrium of the sternum and clavicle
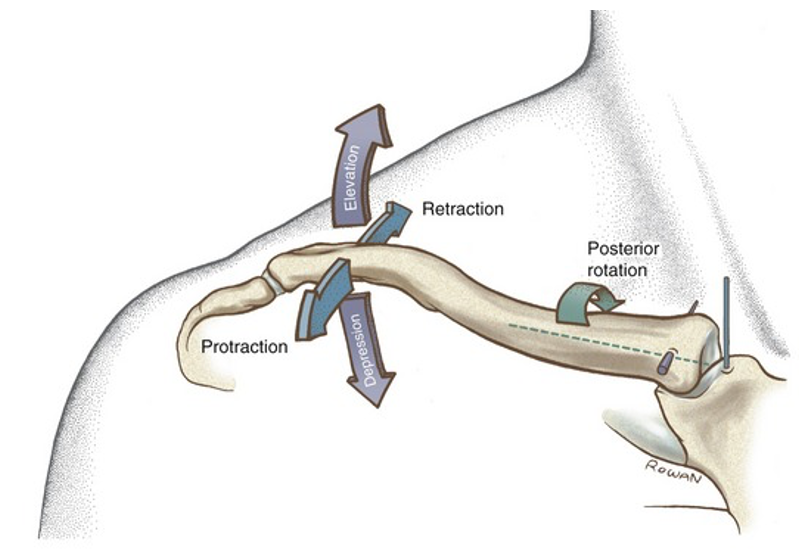
Briefly discuss the movements allowed in the sternoclavicular joint with reference to wider movements of the shoulder/upper limb
Elevation and depression - as per the same with the scapula and overall shoulder
Anterior and posterior movement - as the scapula protracts and retracts
Posterior rotation - as upper limb going into flexion and scapula upward rotates
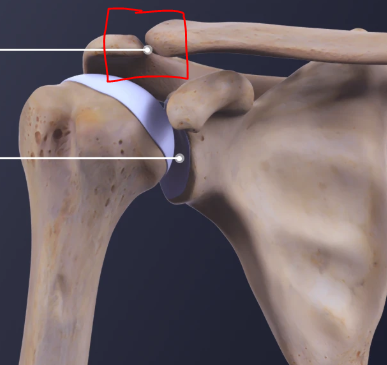
Name the joint highlighted
Acromioclavicular joint
What type of joint is the acromioclavicular joint
Synovial, plane joint
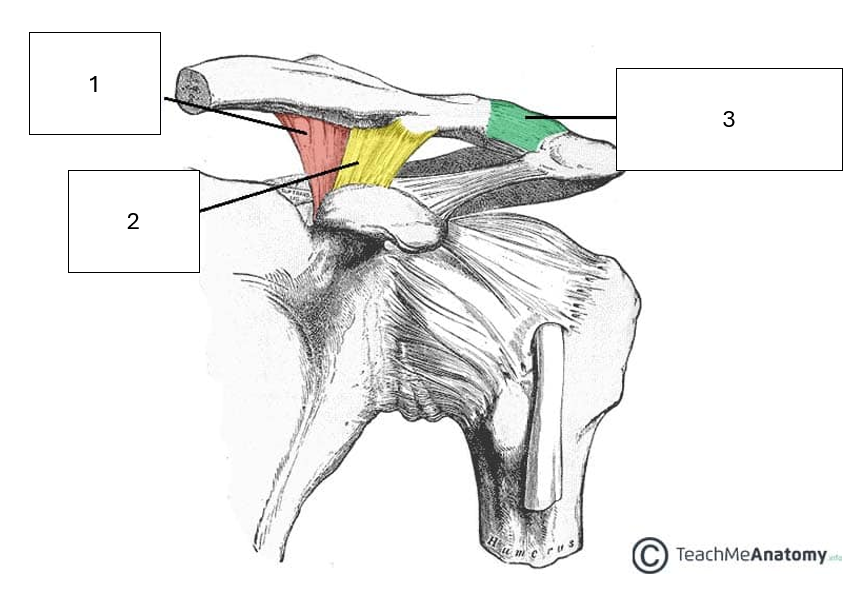
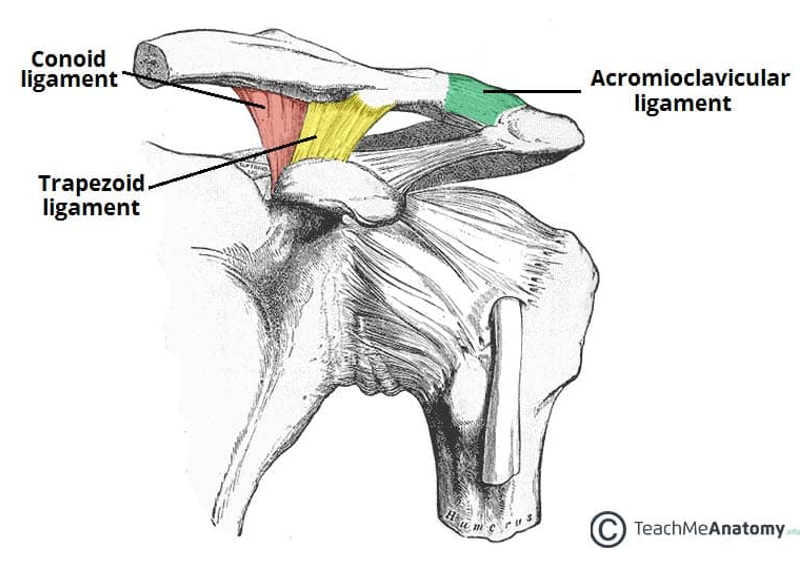
Name the ligaments of the acromioclavicular joint
1 & 2 combined are known as the coracoclavicular ligaments
3 - Acromioclavicular ligament. Easy one, goes between acromion of scapula and the clavicle
Briefly discuss the movements allowed in the acromioclavicular joint with reference to wider movements of the shoulder/upper limb
The AC joint moves passively and glides during movements of the scapula. Typically they are described as a scapular movement with respect to the clavicle.
Upward / downward rotation - the scapula moves into upwards rotation in relation to the clavicle
Internal / external rotation - the scapula internally rotates with protraction, and externally rotates with retraction, in relation to the clavicle
Anterior / posterior tilting - as the scapula tilts around the clavicle.
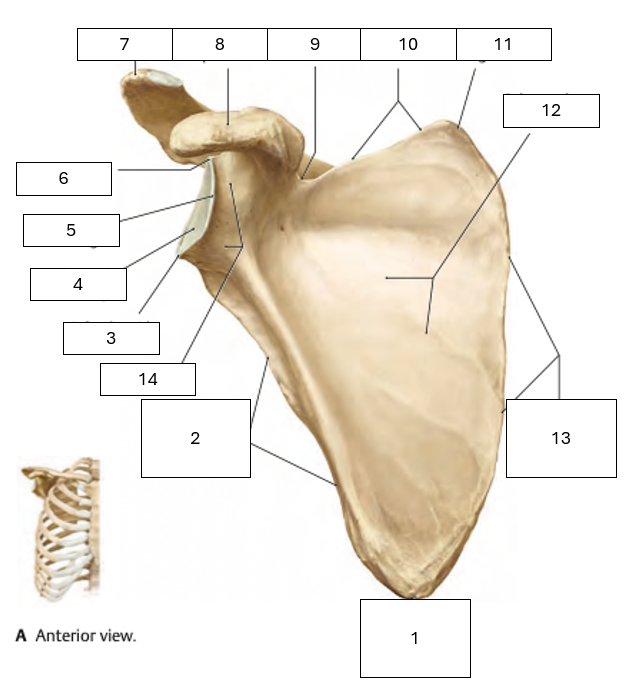
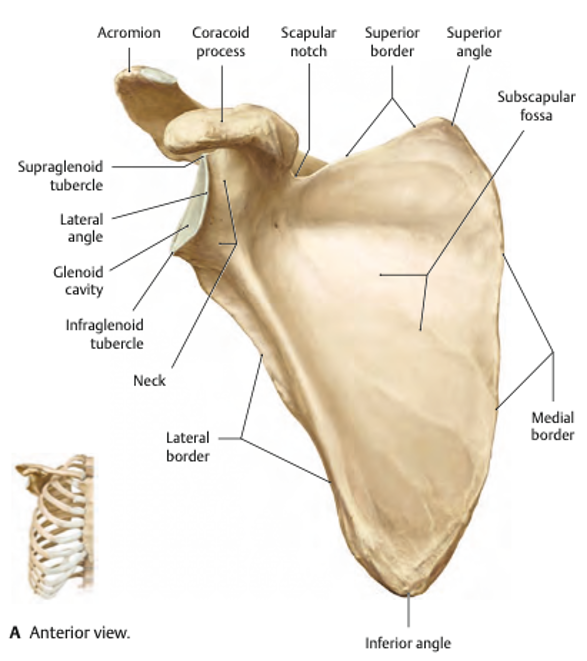
Name the missing scapula parts on this anterior view
1 - Inferior angle
2 - Lateral border
3 - Infraglenoid tubercle
4 - Glenoid cavity
5 - Lateral angle
6 - Supraglenoid tubercle
7 - Acromion
8 - Coracoid process
9 - Scapula notch
10 - Superior border
11 - Superior angle
12 - Subscapular fossa
13 - Medial Border
14 - Neck
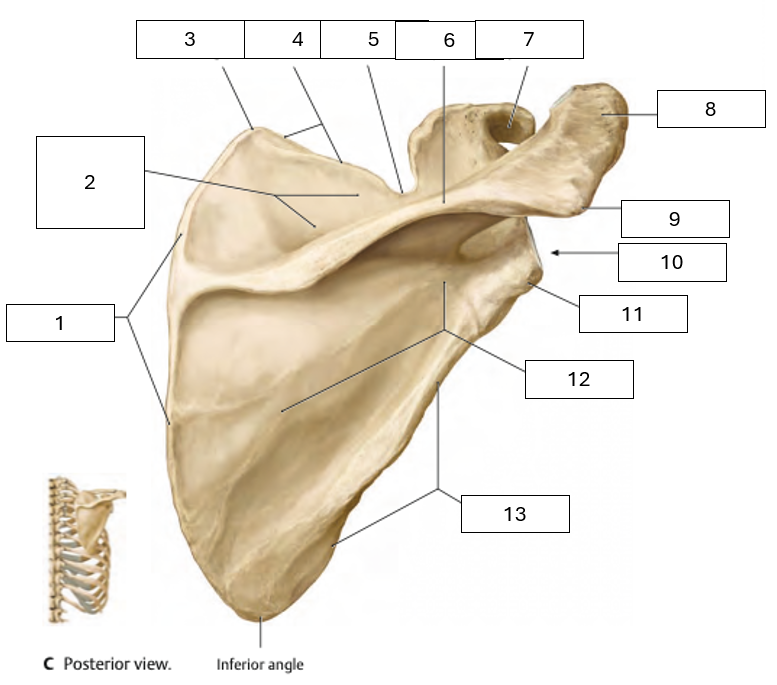
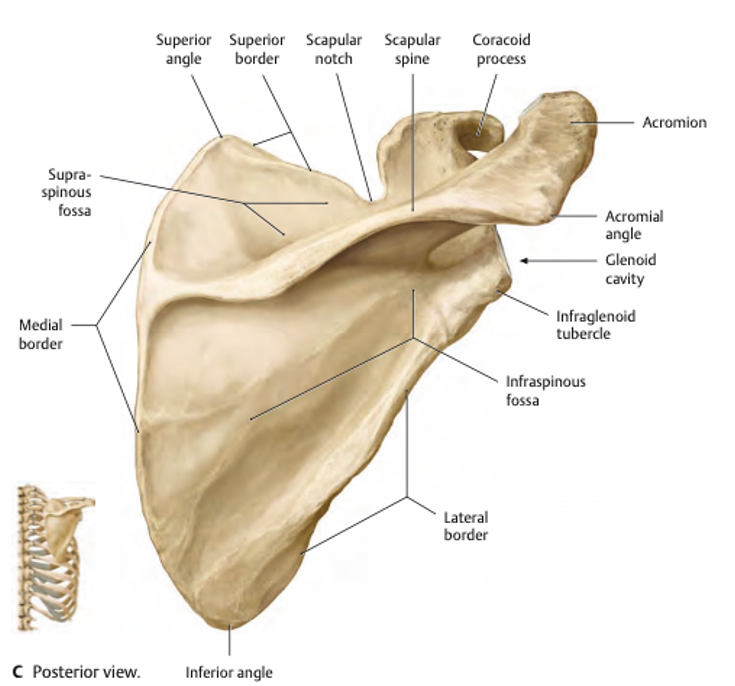
Name the missing scapula parts on this posterior view
1 - Medial Border
2 - Supraspinous fossa (where the supraspinatus originates)
3 - Superior angle
4 - Superior border
5 - Scapular notch
6 - Scapular spine
7 - Coracoid process
8 - Acromion process
9 - Acromion angle
10 - Glenoid cavity
11 - Infraglenoid tubercle (inferior of the glenoid cavity)
12 - Infraspinous fossa (where the infraspinatus originates)
13 - Lateral border
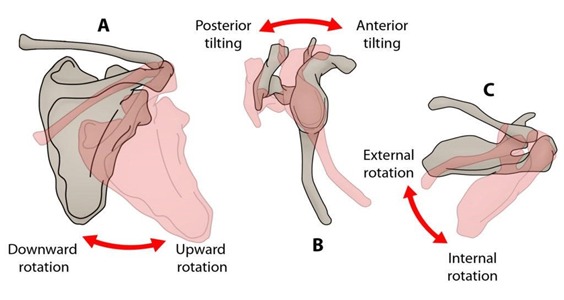
Demonstrate movements of the scapula and how they relate to movements of the shoulder as a whole
Upward and downward rotation - when arm goes into flexion and extension respectively.
Anterior and posterior tilt of - Elevation and depression of the scapula respectively, as the scapula moves around the curvature of the rib cage
External and internal rotation - As the scapula moves around the side of the rib cage in retraction and protraction respectively.
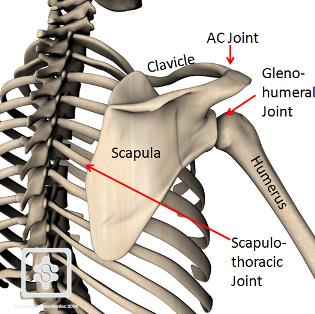
Discuss some key features of the scapulothoracic joint
Not a true anatomical joint, no union by synovial, cartilaginous or fibrous tissues
Refers to the relationship between the scapula and rib cage
The anterior face of the scapula is slightly concave, which sits on the slightly convex superolateral thoracic wall
The scapula is separated from the rib cage by the subscapularis muscle
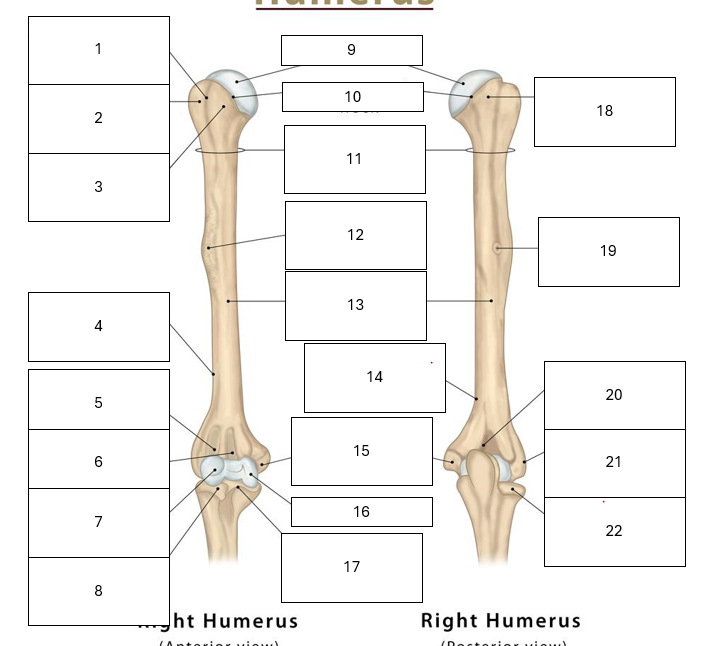
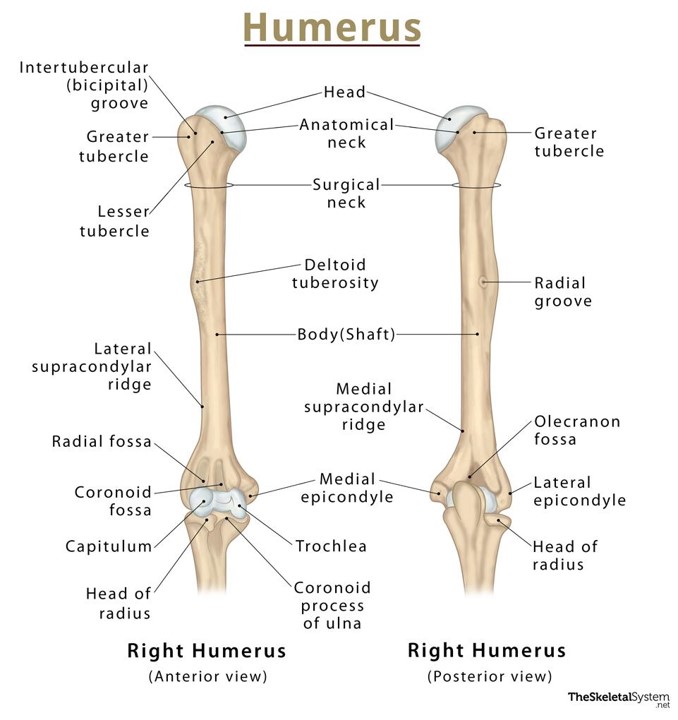
Identify the key parts of the humerus
1 - Intertubercular groove (in between tubercles)
2 - Greater tubercle
3 - Lesser tubercle
4 - Lateral supracondylar ridge (above later epicondyle)
5 - Radial Fossa
6 - Coronoid Fossa
7 - Capitulum
8 - Head of radius
9 - Head of humerus
10 - Anatomical neck
11 - Surgical neck
12 - Deltoid Tuberosity
13 - Shaft
14 - Medial supracondylar ridge
15 - Medial epicondyle
16 - Trochlea
17 - Coronoid process of ulna
18 - Greater tubercle
19 - Radial groove
20 - Olecranon fossa
21 - Lateral epicondyle
22 - Head of radius
Compare the terms tubercle and tuberosity
They are both bony prominences that are used as attachment sites for tendons and ligaments
A tubercle is smaller
A tuberosity is larger
Explain the function of the glenoid labrum
The labrum effectively depends the ‘socket’ of the glenohumeral joint, providing extra support and stability
Name the components of the rotator cuff
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
(SITS)
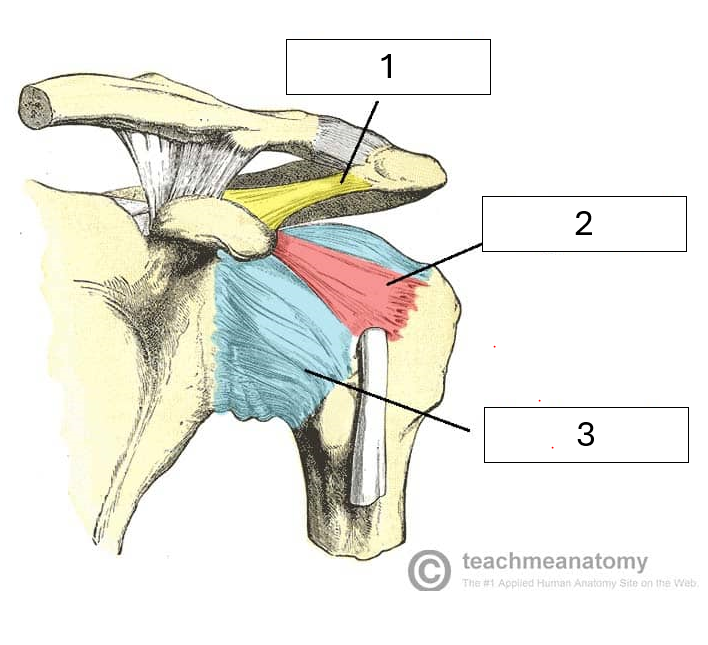
Name the missing ligaments
1 - Coracoacromial ligament - between coracoid process of the scapula and acromion
2 - Coracohumeral ligament - between coracoid process of the scapula and humerus
3 - Glenohumeral ligaments - between glenoid fossa of the scapula and humerus. Three components - superior, middle and inferior
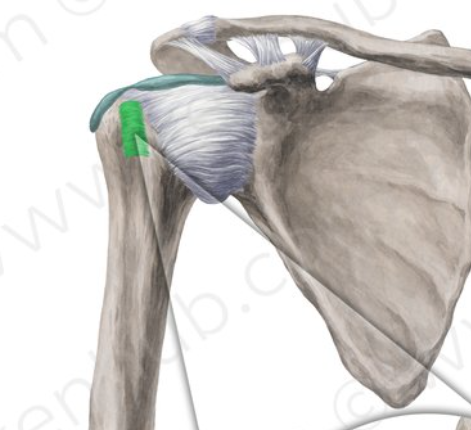
Name the highlighted ligament, and it’s function
Transverse humeral ligament, which attaches between the greater and lesser tuberosities of the humerus. It covers the intertubercular groove, preventing displacement of the biceps brachii tendon
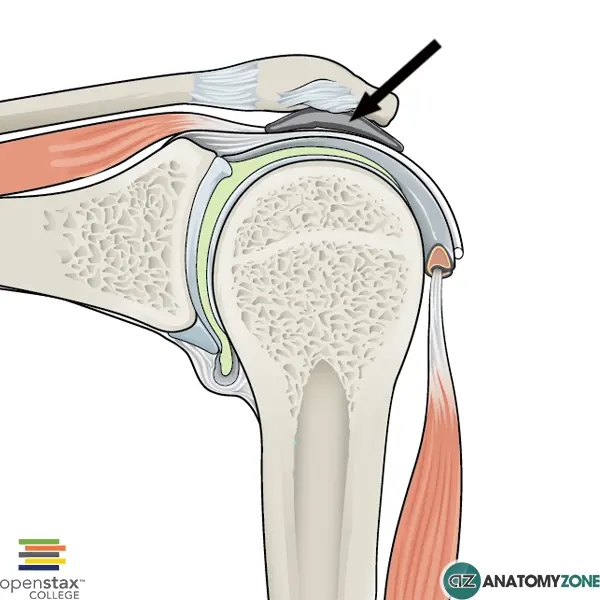
Name the highlighted bursa, and why it’s often troublesome
Subacromial bursa. This bursa sits in the narrow gap between the acromion and humeral head. It is a common cause of shoulder pain as it can get inflamed from repetitive overhead movements.
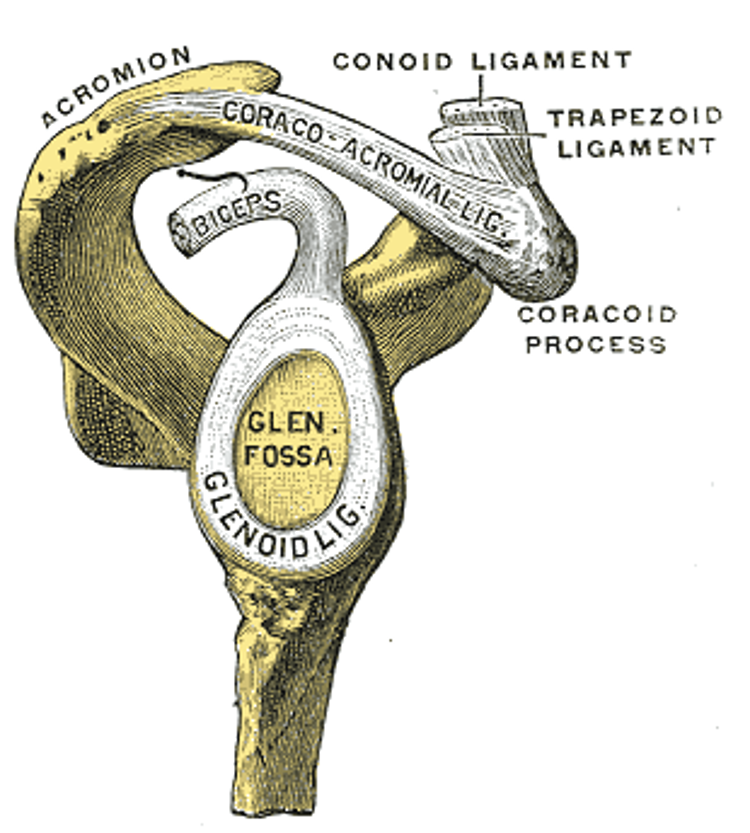
Briefly discuss how the coraco-acromial arch aids with shoulder stabiity
The combination of the coracoid process, acromion process and coracoacromial ligament aids in preventing upward dislocation of the glenohumeral joint.
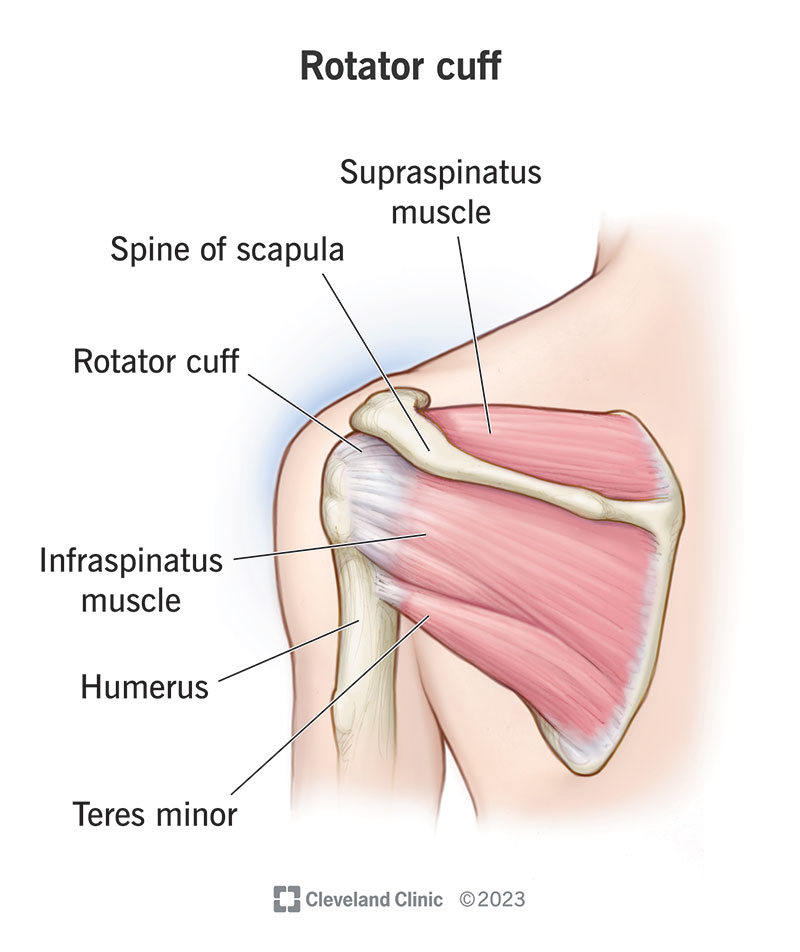
Briefly discuss how the rotator cuff aids with shoulder stability
The group of four muscles originate from the scapula and insert onto the head of the humerus, pulling it into the glenoid fossa.
State the prime movers of shoulder flexion
Anterior portion of deltoid
Clavicular origin component of pectoralis major
State the prime movers of shoulder extension
Latissimus dorsi
Posterior portion of deltoid
State the prime movers of adduction
Pectoralis Major
Latissimus dorsi
State the prime movers of abduction
0 - 15 degrees - Supraspinatus
15 - 90 degrees - Medial Deltoid
90 - 180 degrees - Serratus anterior, upper and lower trapezius
State the prime movers of protraction
Serratus anterior
Pectoralis major and minor
State the prime movers of internal rotation
Pectoralis major
Teres Major
Latissimus Dorsi
Subscapularis
State the prime movers of external rotation
Teres minor
Infraspinatus
State the prime movers of retraction
Rhomboid major and minor
Mid trapezius
Explain the cause of adhesive capulitis
A.K.A frozen shoulder, is caused by inflammation of the ligaments (forming the capsule) surrounding the glenohumeral joint, resulting in pain and reduced range of motion.
Briefly explain what is meant by shoulder impingement syndrome
A.K.A painful arc syndrome is caused when the subacromial space narrows, causing pain especially when lifting arm above head
Name the three joints that make up the elbow joint complex
Humeroulnar
Humeroradial
Proximal radioulnar
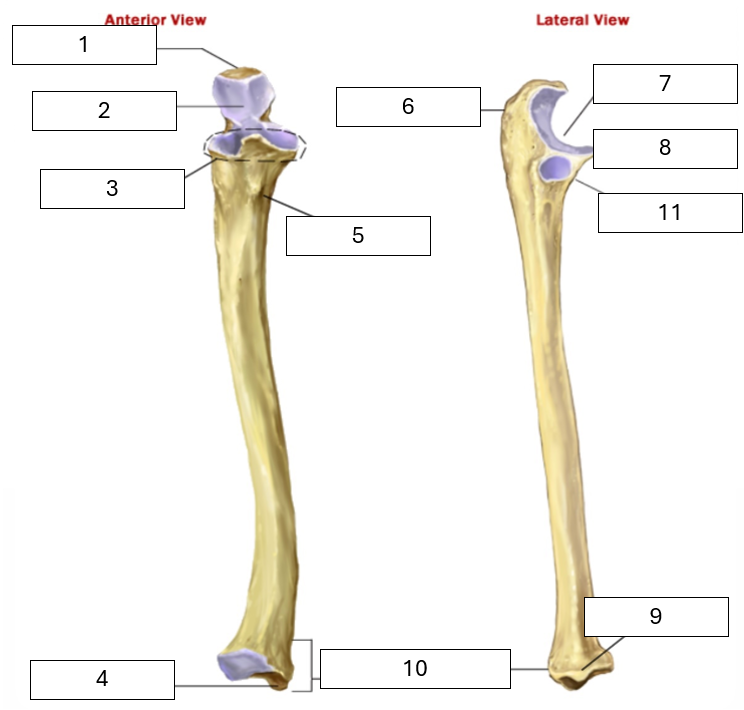
Name the missing parts of the ulna
1 - Olecranon process (main prominence of the elbow)
2 - Trochlea notch (articulates with the trochlea of the humerus)
3 - Coronoid process (proximal, anterior bony prominence)
4 - Styloid process (distal bony prominence, radius has one too)
5 - Ulnar Tuberosity
6 - Olecranon process (main prominence of the elbow)
7 - Trochlear notch
8 - Coronoid process
9 - Styloid process (again!)
10 - Head of ulna (the smaller end)
11 - Radial notch - articulates with the radius
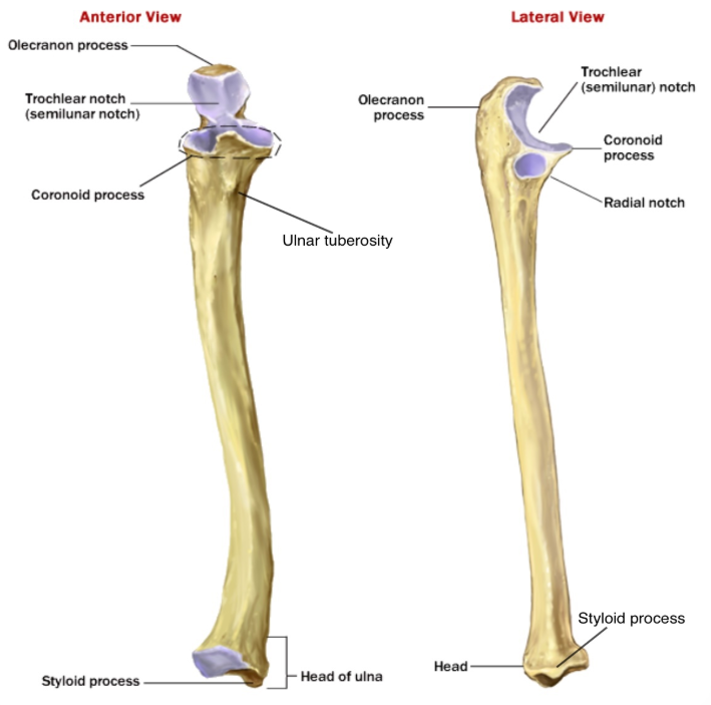
Name the two joints within the elbow joint and the parts of bone which make them
Humeroradial joint - made up of the capitulum of the humerus and head of radius
Humeroulnar joint - made up of the trochlea of the humerus and trochlear notch of the ulnar (lego hand)
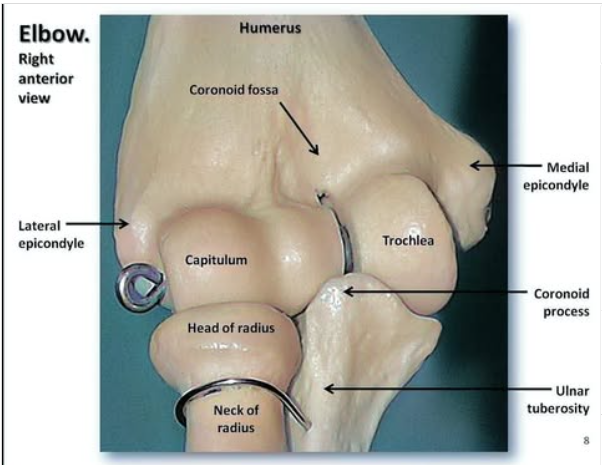
Which joint allows for pronation and supination of the forearm, and what’s actually happening in this movement?
Proximal radioulnar joint.
When pronating the head of the radius will rotate, and the radius itself will rotate around the ulna
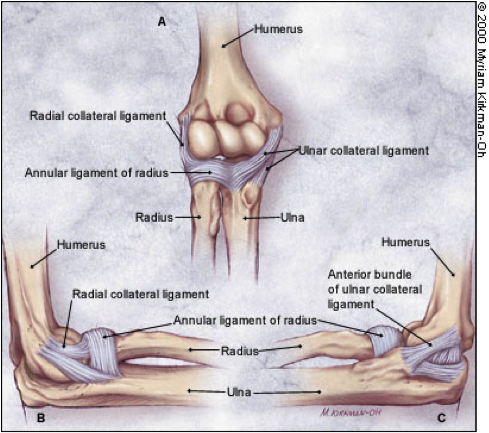
What are the three main ligaments in the elbow complex
Ulnar collateral ligament - between humerus and ulna
Radial collateral ligament - between humerus and radius
Annular ligament - around the radial head, from the radial notch
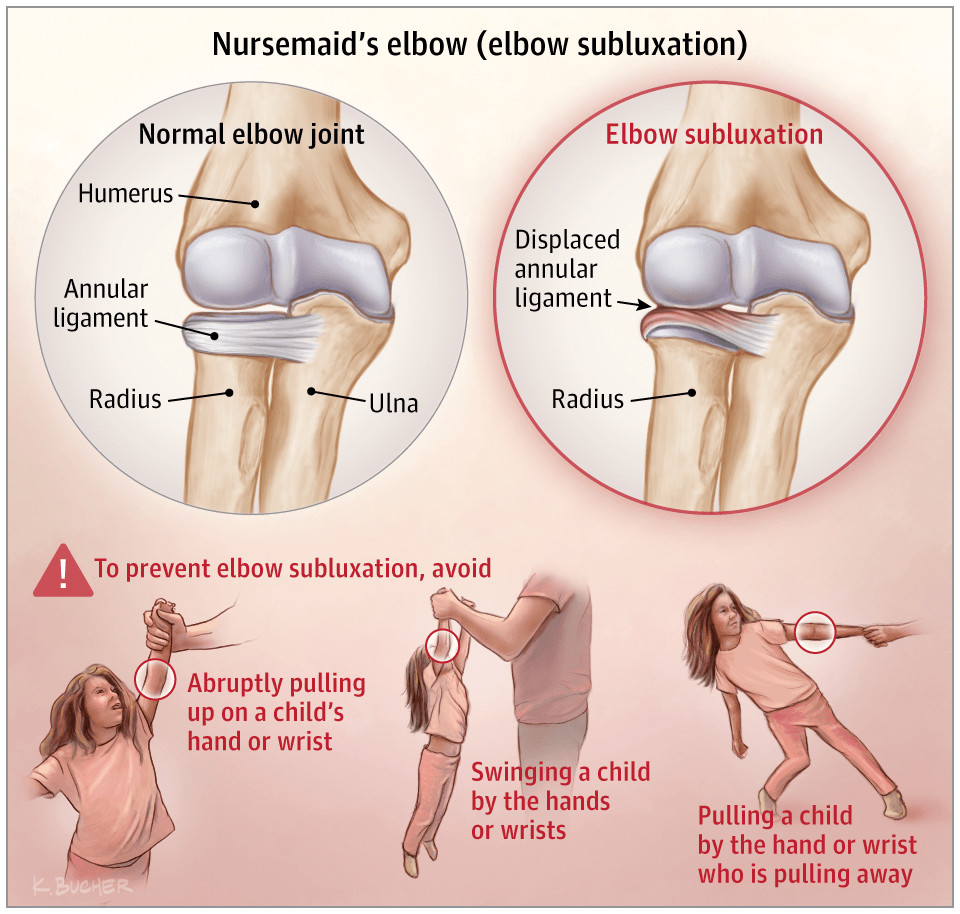
What is nursemaids elbow
This is when the annular ligament gets displaced as the radius is pulled distally, trapping it in between the radius and humerus. Most common in children.
What type of joint is the distal radioulnar joint?
Synovial, pivot joint
Name the muscles that produce flexion at the elbow
Biceps Brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
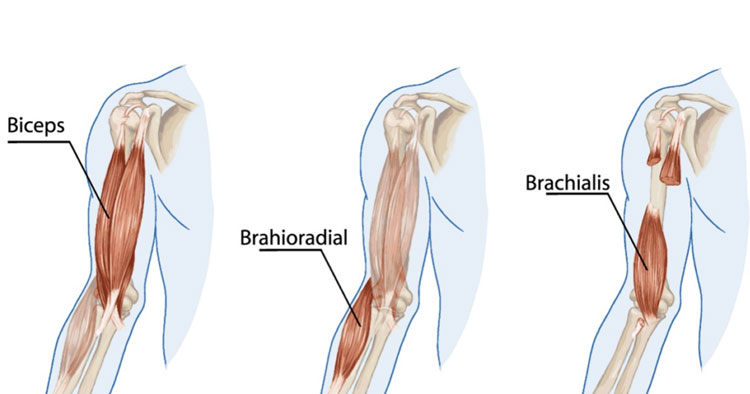
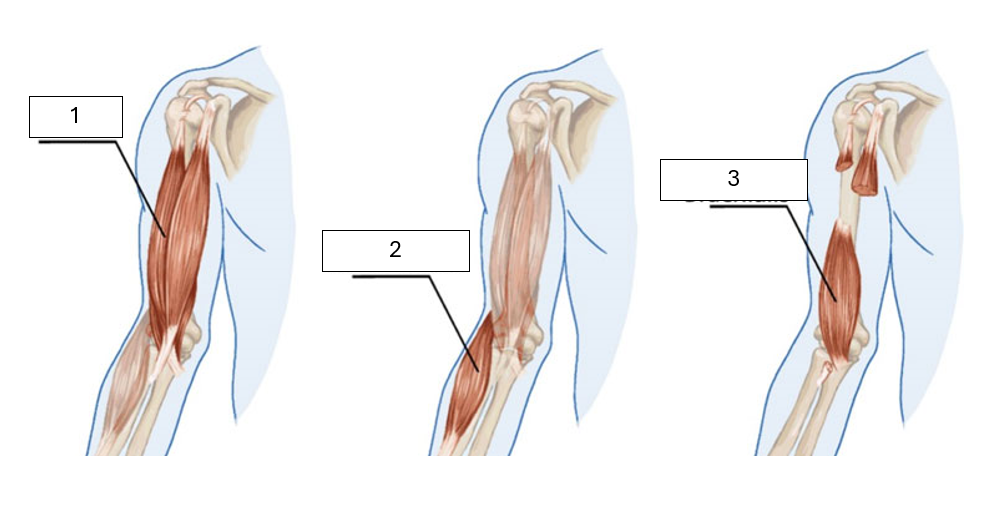
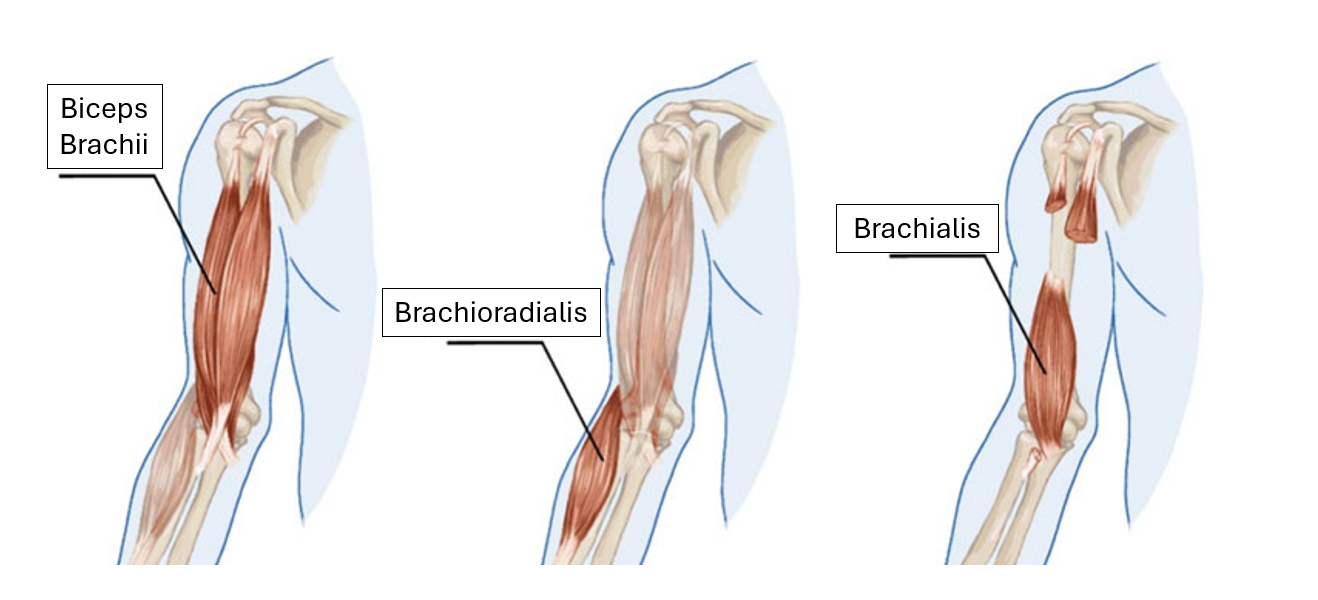
Identify the unknown muscles shown
1 - Biceps Brachii
2 - Brachioradialis
3 - Brachialis
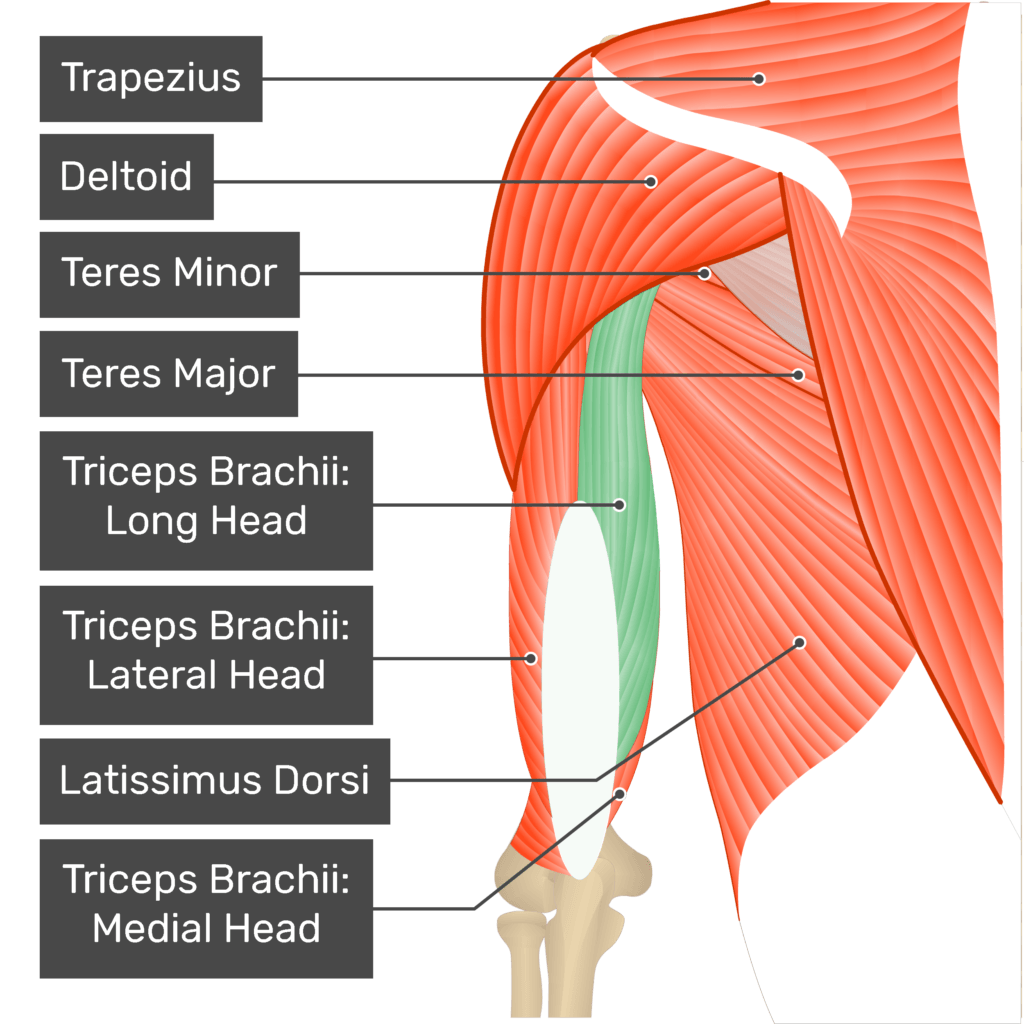
Identify the unknown parts of the tricep
Triceps Brachii:
1 - long head
2 - lateral head
3 - medial head
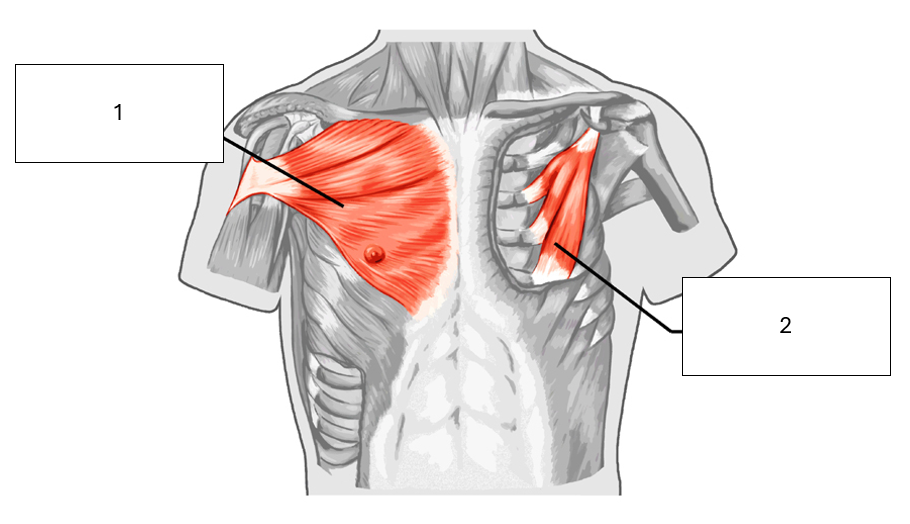
Name the unknown muscles shown
1 - Pectoralis major
2 - Pectoralis minor
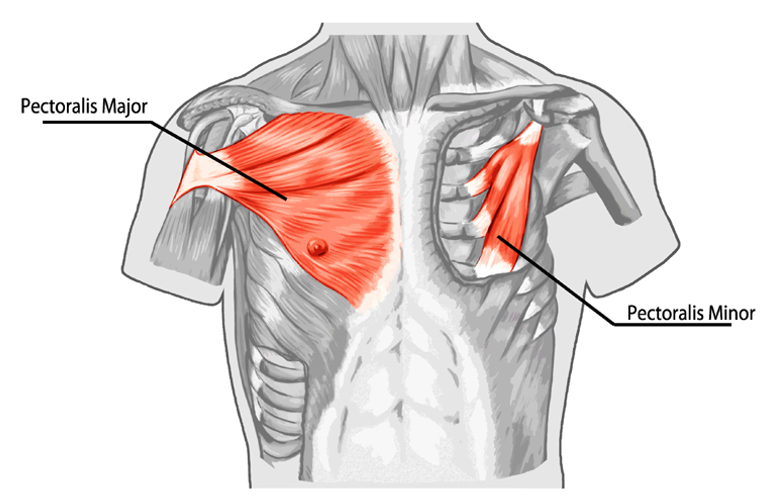
What is the origin and insertion of pectoralis major
Clavicular head, origin = clavicle, insertion = greater tubercle of humerus
Sternocostal head, origin = sternum and costal cartilage, insertion = greater tubercle of humerus
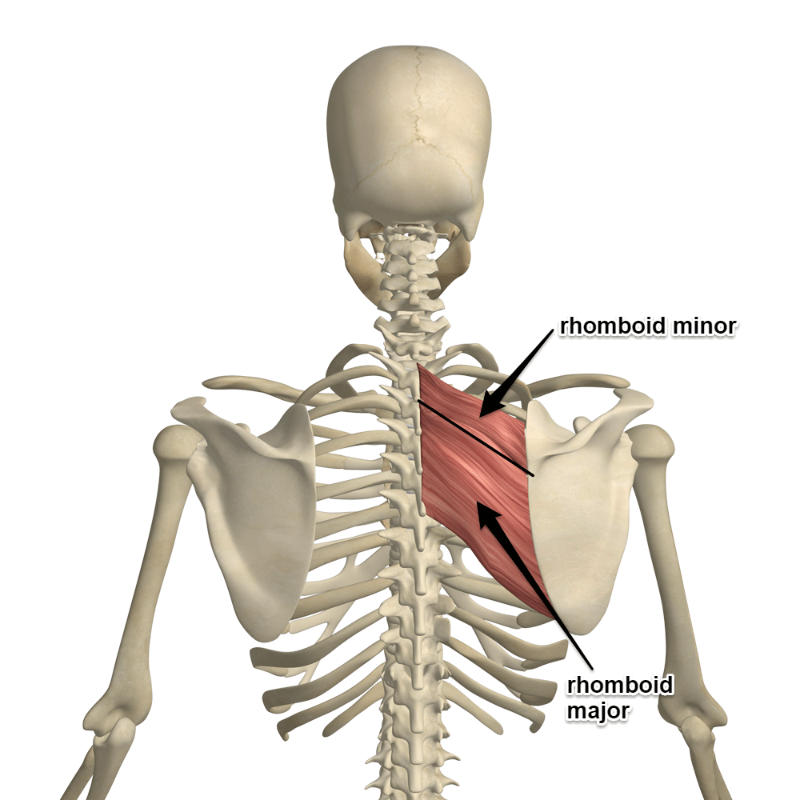
What is the origin and insertion of rhomboid major and minor
The rhomboid minor originates at C7 and T1
The rhomboid major originates at T2 to T5
Both muscles insert onto the medial border of the scapula
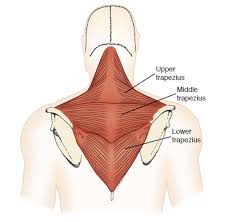
State the origin and insertions of the three parts the trapezius
Upper, Origin = Occipital, nuchal ligament, Insertion = clavicle
Middle, Origin = T1 - T4 spinous processes, Insertion = spine of scapula
Lower, Origin = T4 - T12 spinous processes, Insertion - medial end of spine of scapula
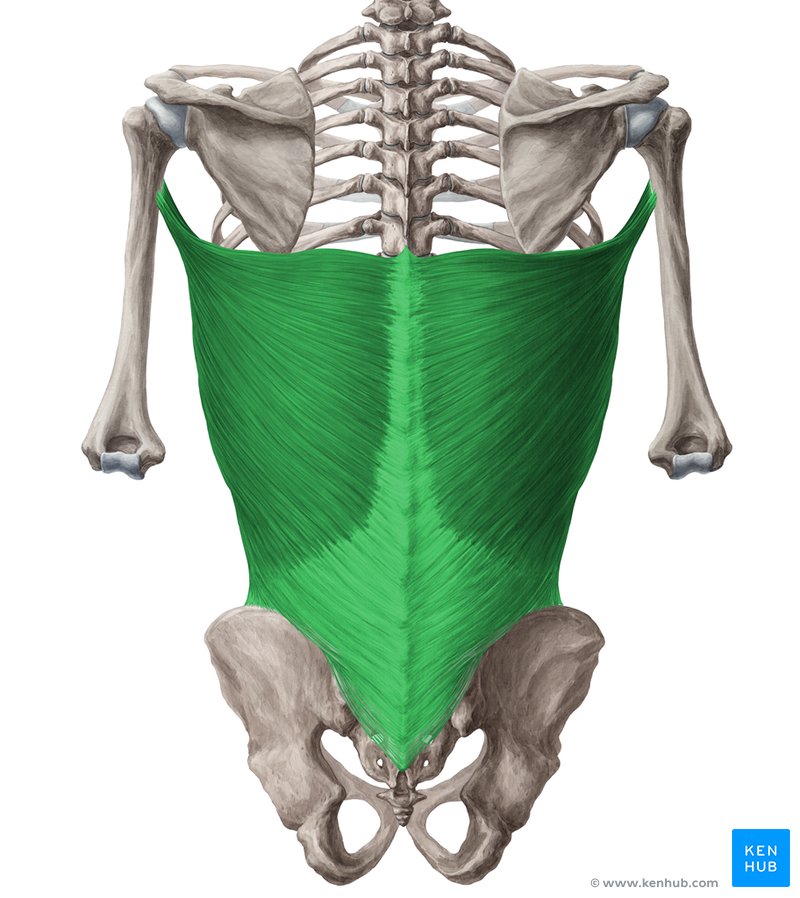
What is the origin and insertion of latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi originates at T7-T12, the illium (pelvis), ribs 9 - 12 and the thoracolumbar fascia
It inserts onto the intertubercular groove of the humerus
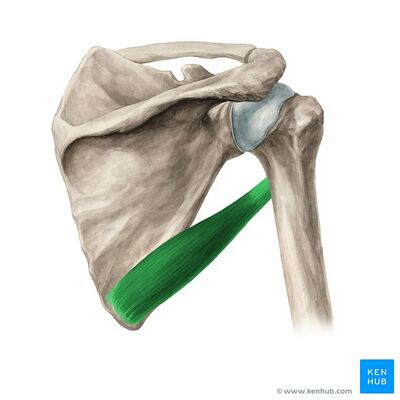
What is the origin and insertion of Teres Major
Origin - inferior angle of scapula
Insertion - intertubercular groove of the humerus
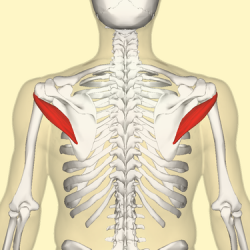
What is the origin and insertion of Teres Minor
Origin = lateral border of the scapula
Insertion = greater tubercle of humerus
What is the origin and insertion of infraspinatus
Origin - infraspinatus fossa
Insertion - posterior aspect of greater tuberosity of humerus
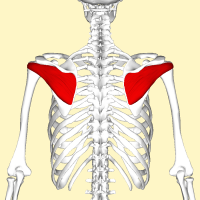
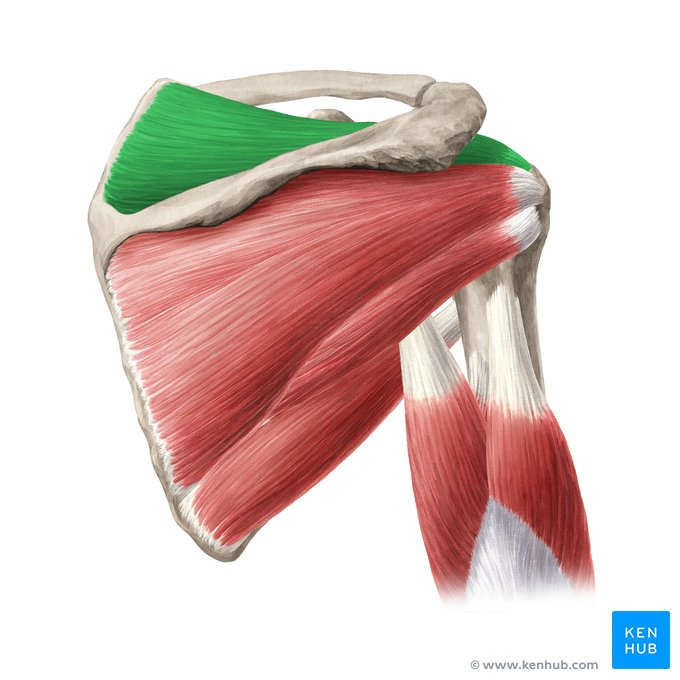
What is the origin and insertion of supraspinatus
Origin - supraspinatus fossa of the scapula
Insertion - greater tuberosity of humerus
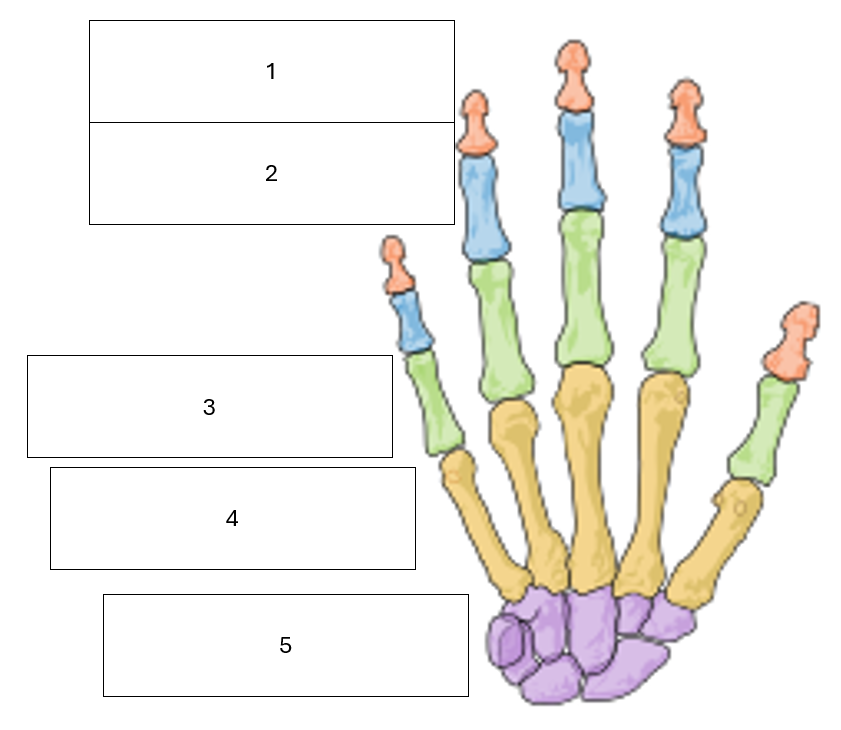
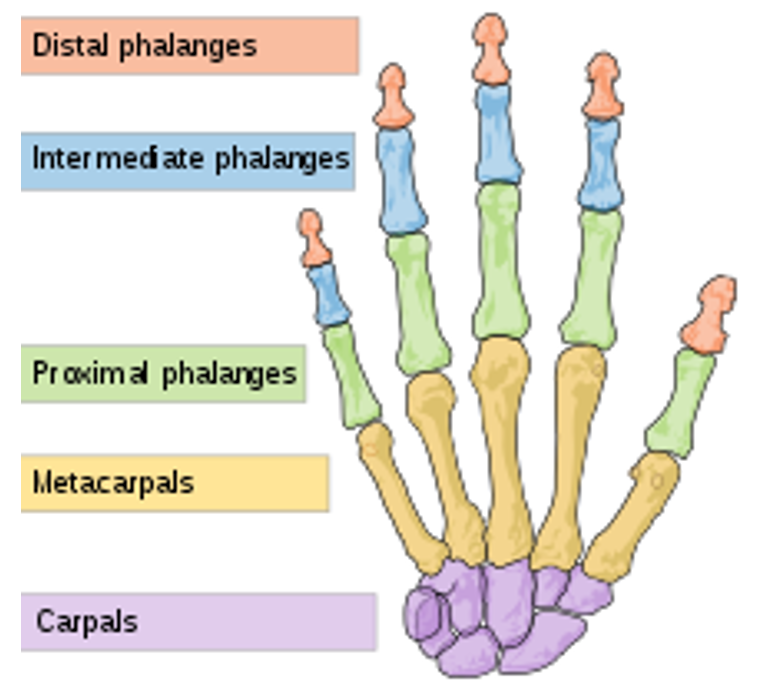
State the name of the hidden hand bone groups
1 - Distal Phalanges
2 - Intermediate Phalanges
3 - Proximal Phalanges
4 - Metacarpals
5 - Carpals
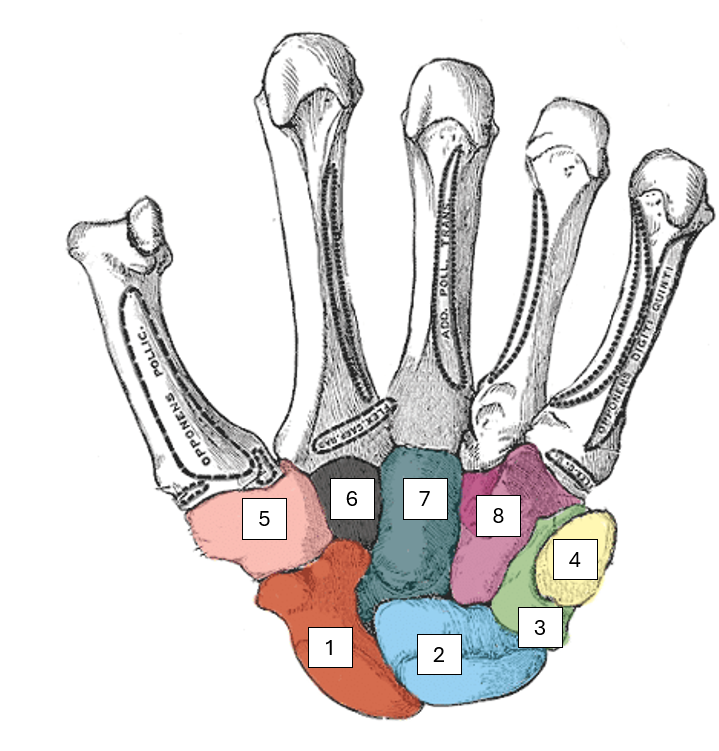
Name the carpal bones
Way to remember this, from lateral to medial, proximal to distal
Simply Learn The Parts That The Carpus Has
1 - Scaphoid
2 - Lunate
3 - Triquetrum (tri-kwet-trum)
4 - Pisiform
5 - Trapezium (um, thumb)
6 - Trapezoid
7 - Capitate
8 - Hamate
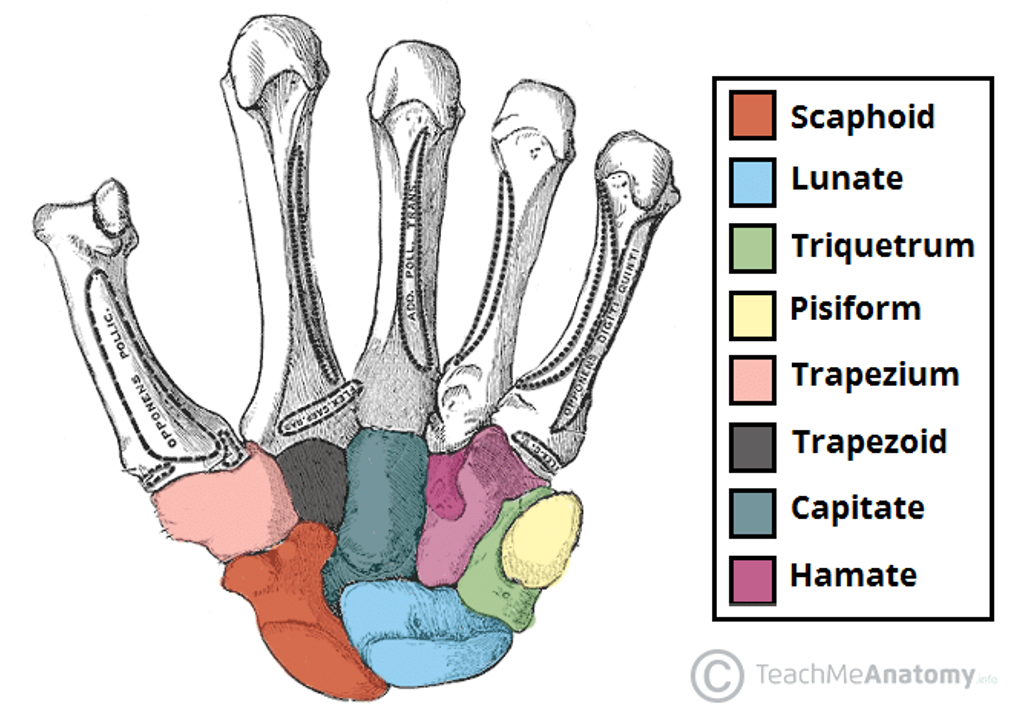
What is the formal name for the wrist joint
Radiocarpal joint
State the components of the radiocarpal joint
Radius bone
Articular disc
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
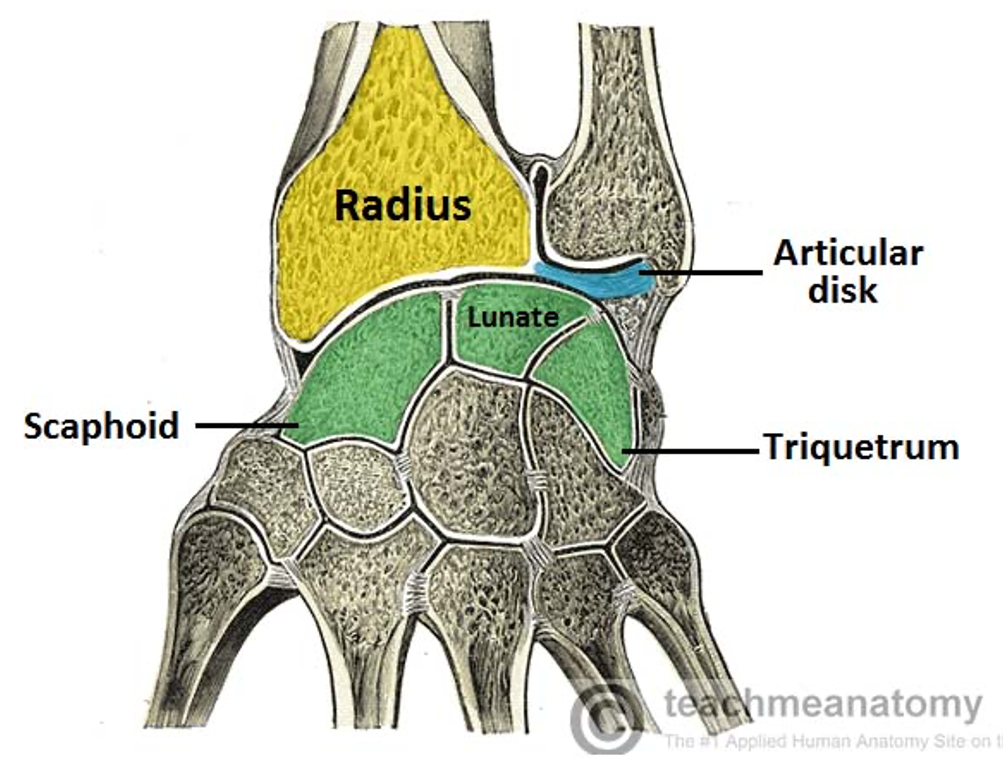
What movements are facilitated by the radiocarpal joint
Flexion
Extension
Radial deviation
Ulnar deviation
What type of joint is the wrist joint
Synovial, condyloid
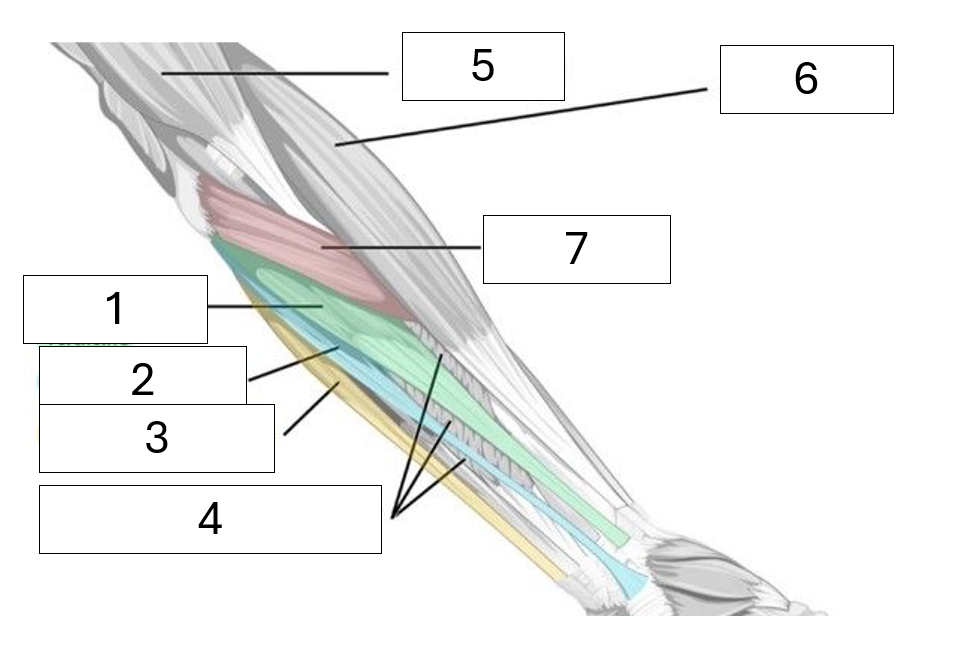
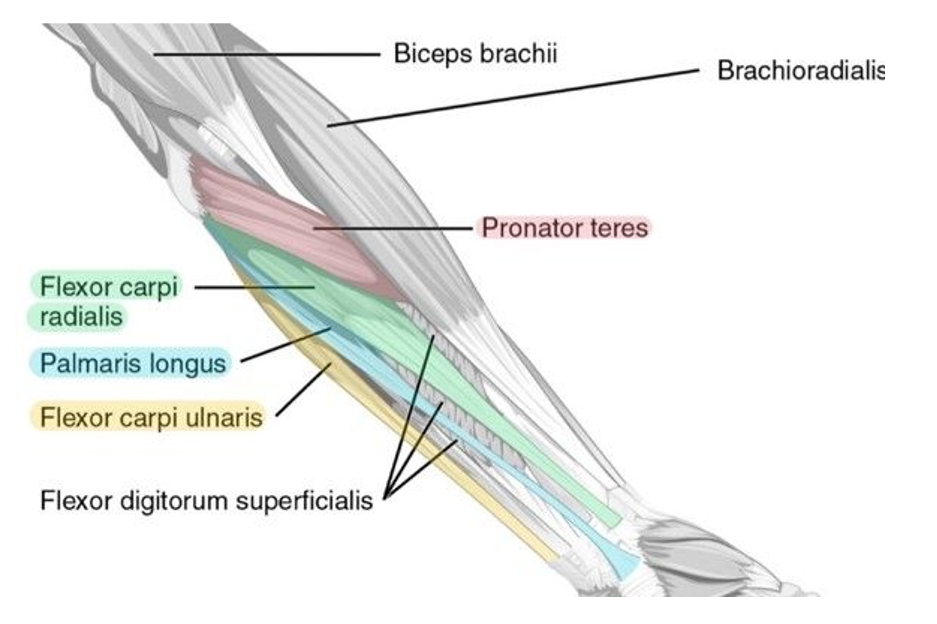
Name the muscles hidden in the image
1 - Flexor carpi radialis (inserts on radial side)
2 - Palmaris longus (is long and thin!)
3 - Flexor carpi ulnaris (inserts on the ulna side)
4 - Flexor digitorum superficialis
5 - biceps brachii
6 - Brachioradialis
7 - Pronator Teres
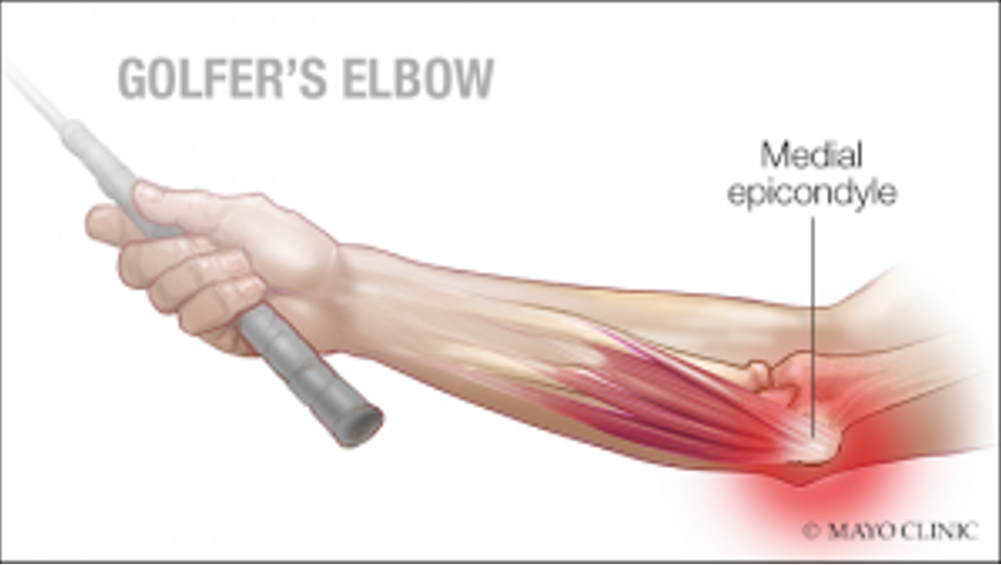
What is meant by golfers elbow
A chronic inflammation of the tendons attaching to the medial epicondyle and proximal wrist flexors, a.k.a medial epicondylitis
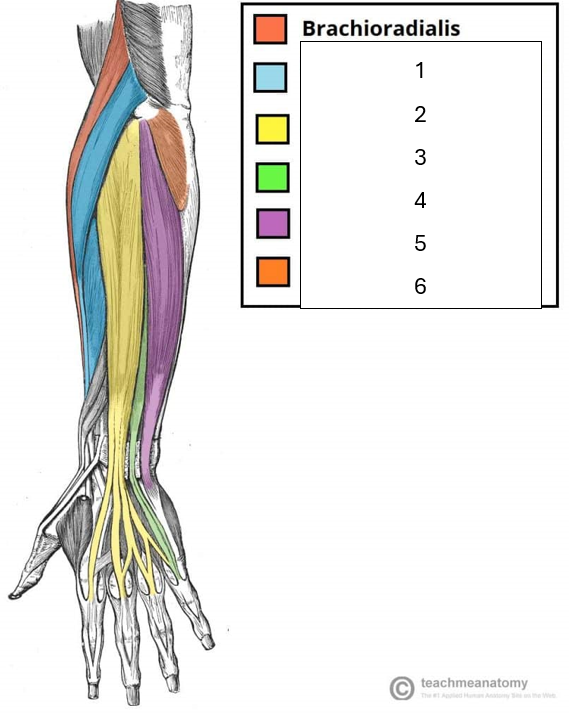
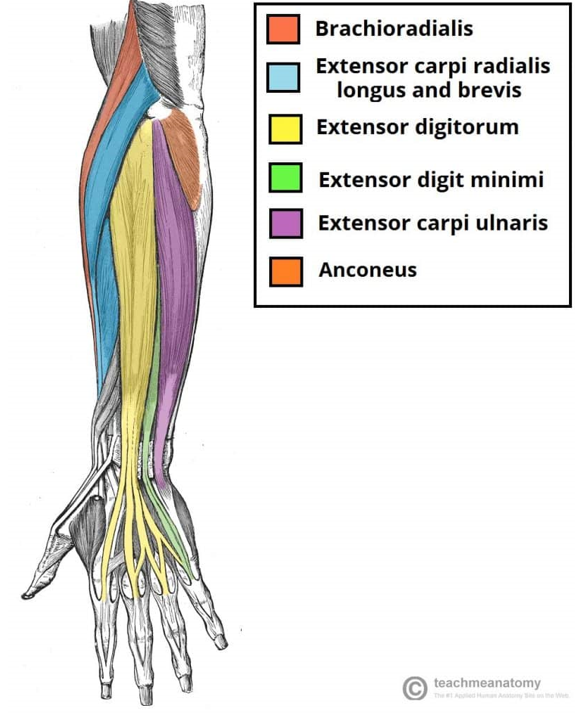
Name the muscles hidden in the image
1 - Extensor carpi radialis (on the radial side)
2 - Extensor digitorum
3 - Extensor digiti minimi (extends little finger)
4 - Extensor carpi ulnaris (on the ulnar side)
5 - Anconeus (small stabilizing muscle)
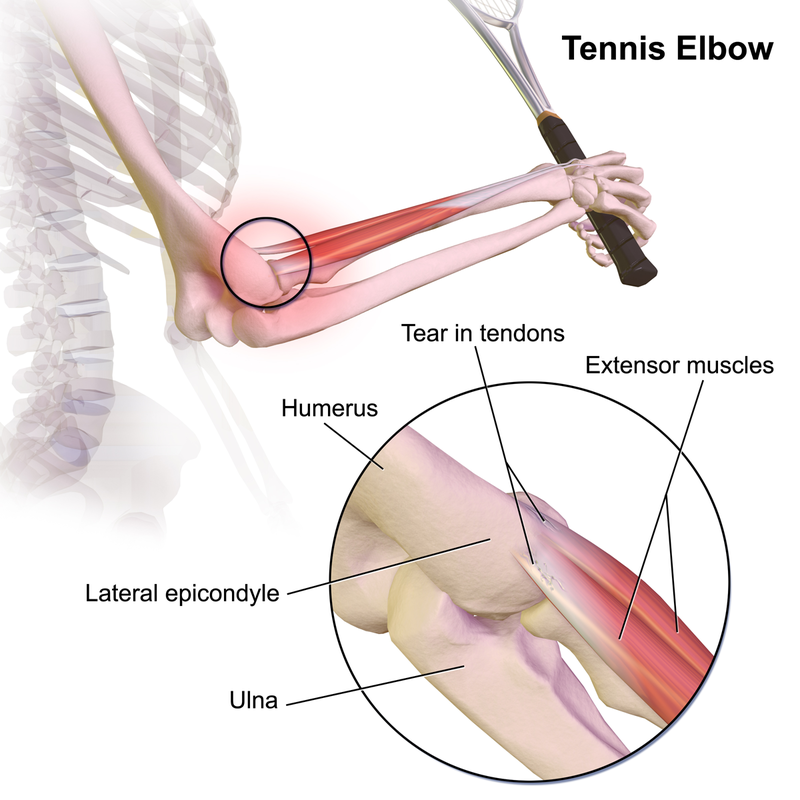
What is meant by tennis elbow
A chronic inflammation of the tendons attaching to the lateral epicondyle and proximal wrist extensors, a.k.a lateral epicondylitis
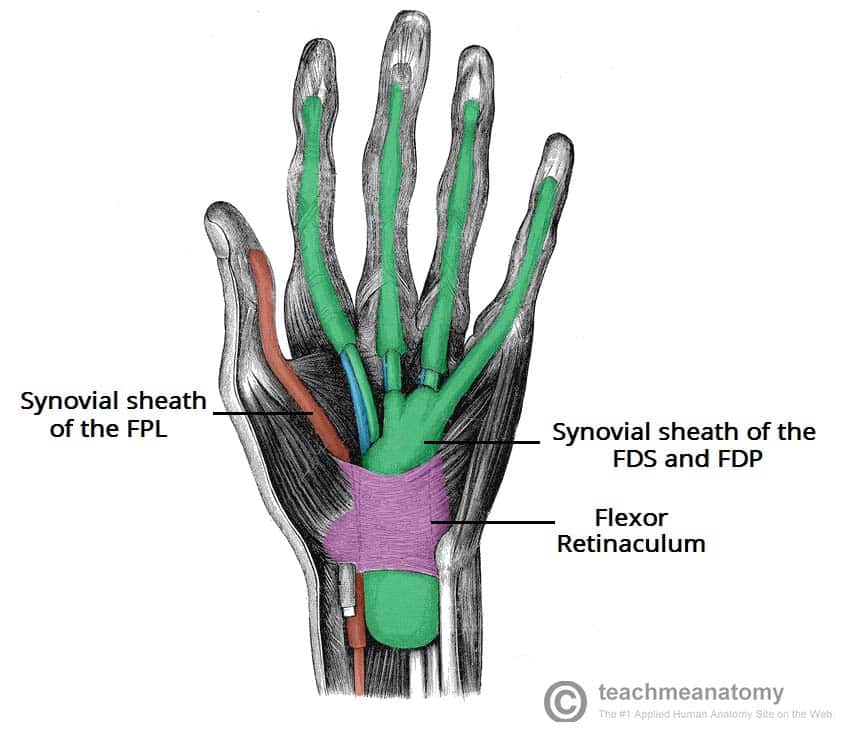
Where is, and what is the function of, flexor retinaculum
Ret-in-ack-ulum
Proximal, anterior hand. Ligament that forms the carpal tunnel and stabilises the carpal bones.
What is the function of the the flexor carpi radialis
flexion of the wrist
What is the function of the flexor carpi ulnaris
Wrist flexion and ulnar deviation
What is the function of the brachioradialis
elbow flexion
What is the function of pronator teres
pronation of the forearm
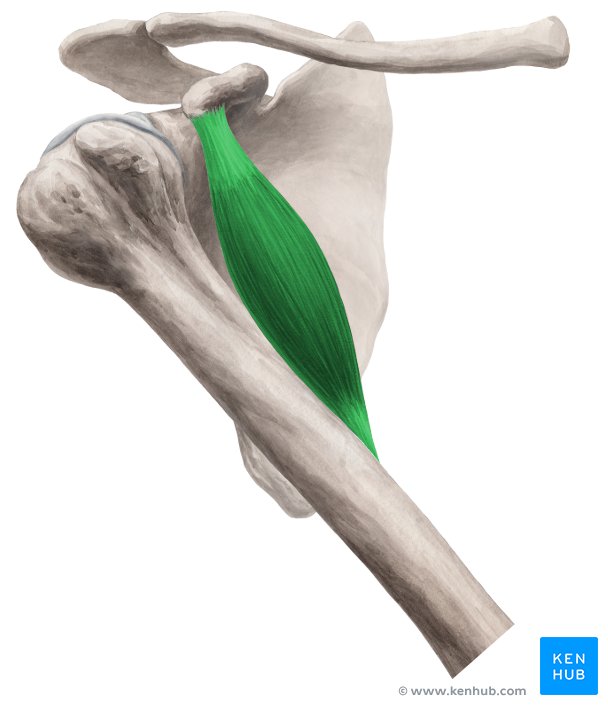
Identify the muscle highlighted
Coracobrachialis
Describe the function of the coracobrachialis muscle
Shoulder flexion and adduction
State the insertion and origin of the coracobrachialis
Origin: coracoid process
Insertion: shaft of humerus
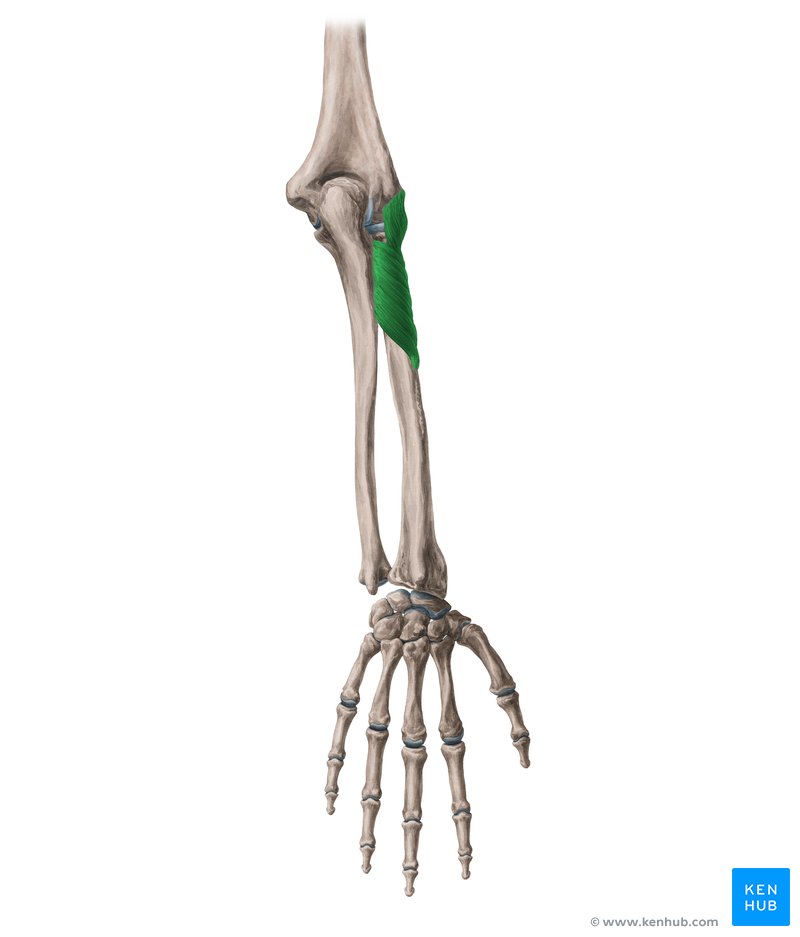
Name the highlighted muscle, and it’s insertion and origin
Supinator
Origin: ulna, lateral epicondyle of humerus, radial collateral ligament
Insertion: radius
What is the insertion and origin of the subscapularis
Origin: subscapular fossa
Insertion: lesser tuberosity of humerus
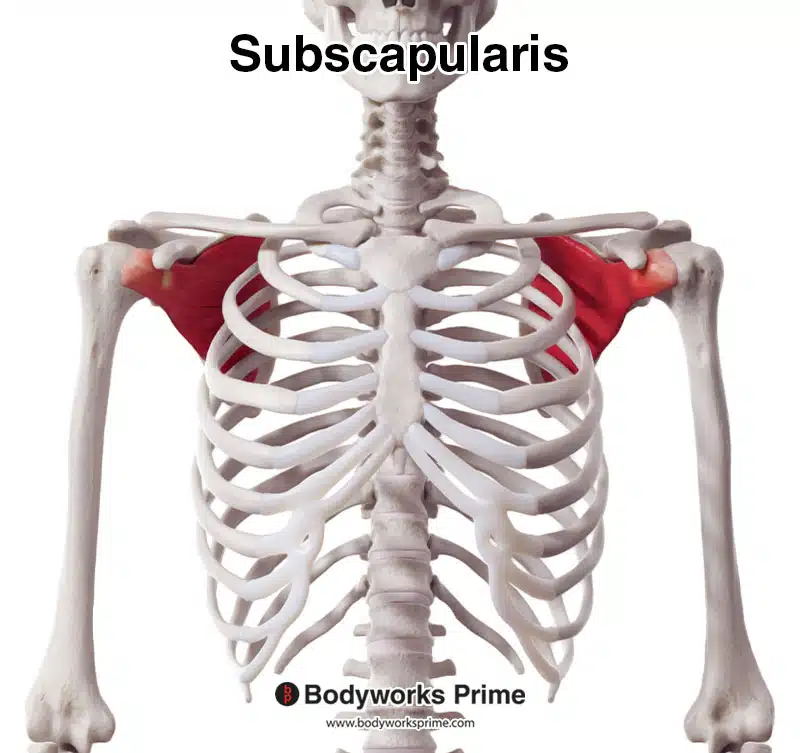
What movement does the subscapularis produce upon contraction
Internal rotation of the humerus
State where the nuchal ligament is found, and it’s function.
On the posterior face of the cervical spine. It attaches onto all cervical vertebrae C1-C7 and the occipital. It supports the cervical spine and prevents excessive movement