Liver Anatomy, Vascular Supply, and Diagnostic Markers
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
What are the areas of the liver that are not covered by the peritoneum?
Gallbladder fossa, porta hepatitis, and the bare area around the IVC.
What is Glisson's capsule?
A connective tissue covering of the liver.
What is the size and weight of the liver?
The liver measures 21-22 cm transverse, 13-17.5 cm vertical, and 10-12.5 cm A/P depth, weighing 1400-1600 grams.
What separates the right and left lobes of the liver?
The main lobar fissure and the mid hepatic vein (functionally).
What is the function of the ligamentum teres?
It divides the inferior liver into right and left lobes and is a remnant of the left umbilical vein.
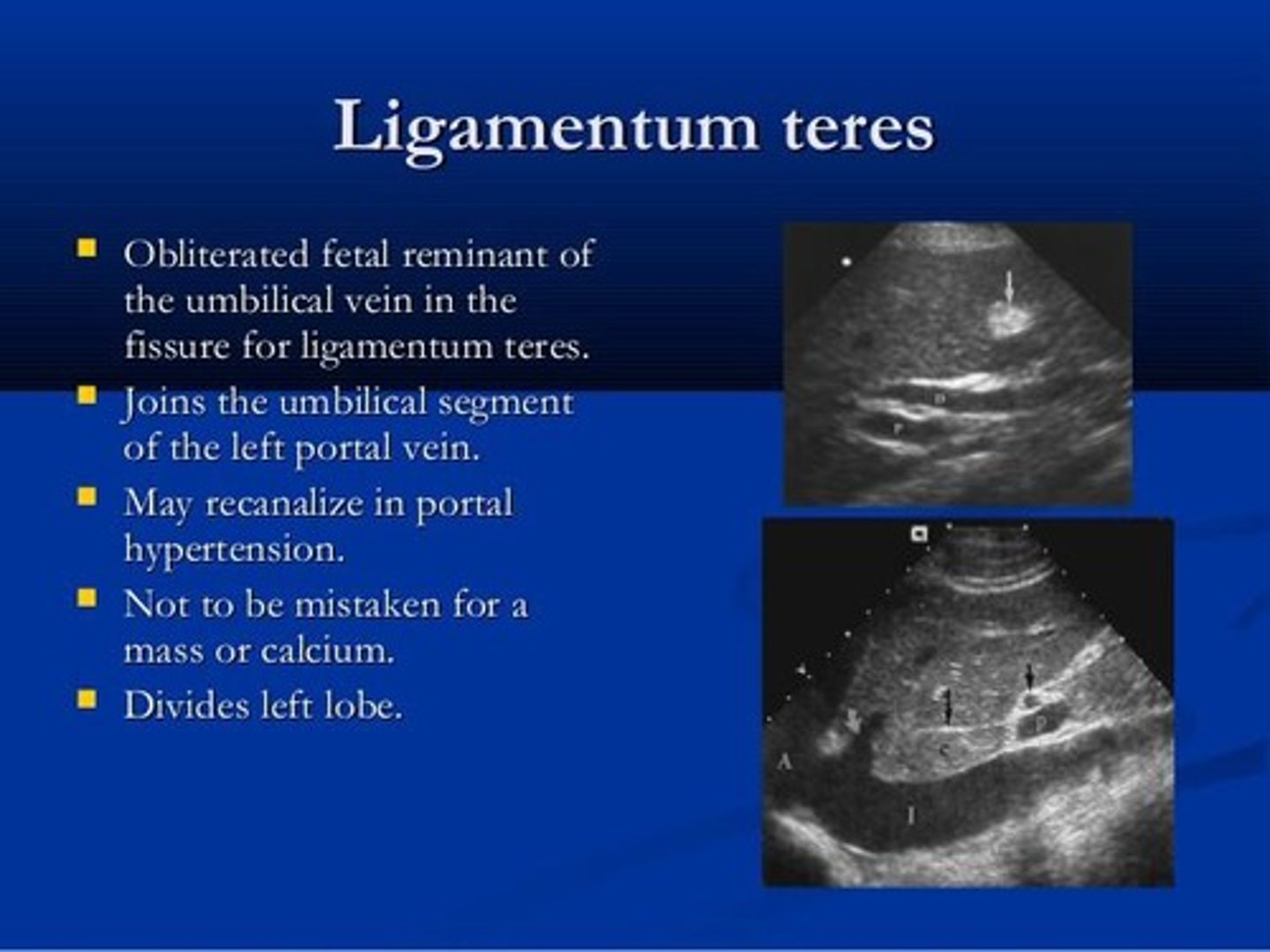
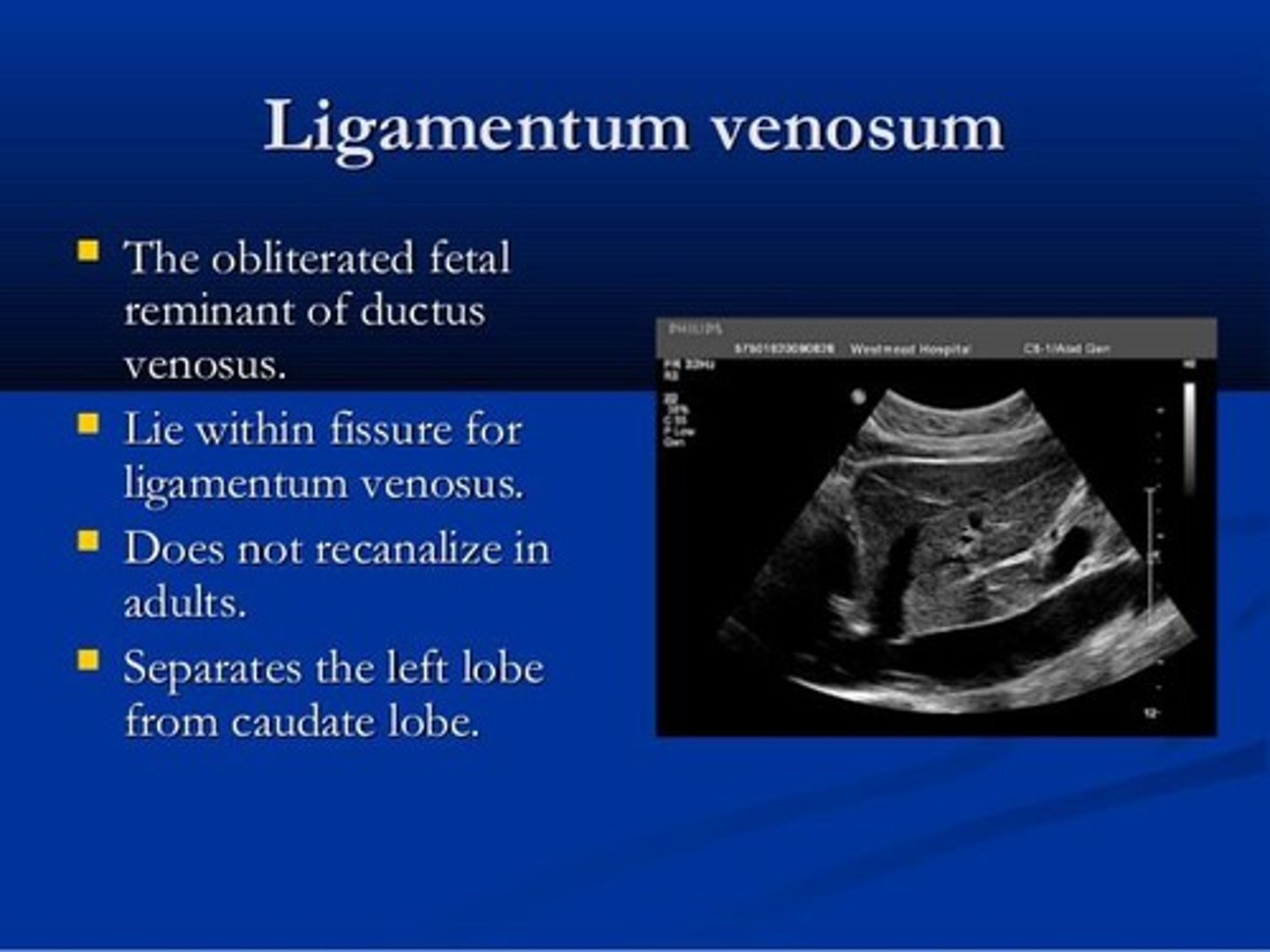
What is the function of the ligamentum venosum?
It separates the left lobe from the caudate lobe and is a remnant of the ductus venosus.
What is the main vascular supply to the liver?
The liver receives blood from the hepatic artery, which carries oxygen-rich blood, and the portal vein, which carries nutrient-rich blood from the intestines.
What is the role of bile produced by the liver?
Bile aids in the emulsification of fats and removal of waste products.
What is the significance of sludge in the bile?
Sludge results from bile stasis.
What does an increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) indicate?
tissue injury or death, commonly seen in acute hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatic necrosis.
What does alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation indicate?
Slight elevation in acute cirrhosis, hepatic metastasis, and pancreatitis; moderate to high increases in hepatocellular disease.
What does alkaline phosphatase indicate?
It is an indicator for intra or extra hepatic obstruction, carcinoma, abscess, or elevated in cirrhosis or hepatitis.
What is the significance of bilirubin levels in the blood?
Increased bilirubin indicates RBC destruction, liver malfunction, or ductal blockage, leading to jaundice.
What is the difference between indirect and direct bilirubin?
Indirect bilirubin (unconjugated) is elevated with increased RBC destruction; direct bilirubin (conjugated) is elevated due to obstruction.
What does a prolonged prothrombin time indicate?
It indicates liver disease with cellular damage, commonly seen in cirrhosis and metastatic disease.
What does low serum albumin suggest in liver disease?
It suggests decreased protein synthesis due to hepatocellular damage.
What is alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and its significance?
AFP is a protein made in the liver of a developing baby; high levels in adults can indicate liver cancer or other diseases.
What is the role of the right, mid, and left hepatic veins?
They drain blood from the liver to the IVC, with the right hepatic vein being the largest.
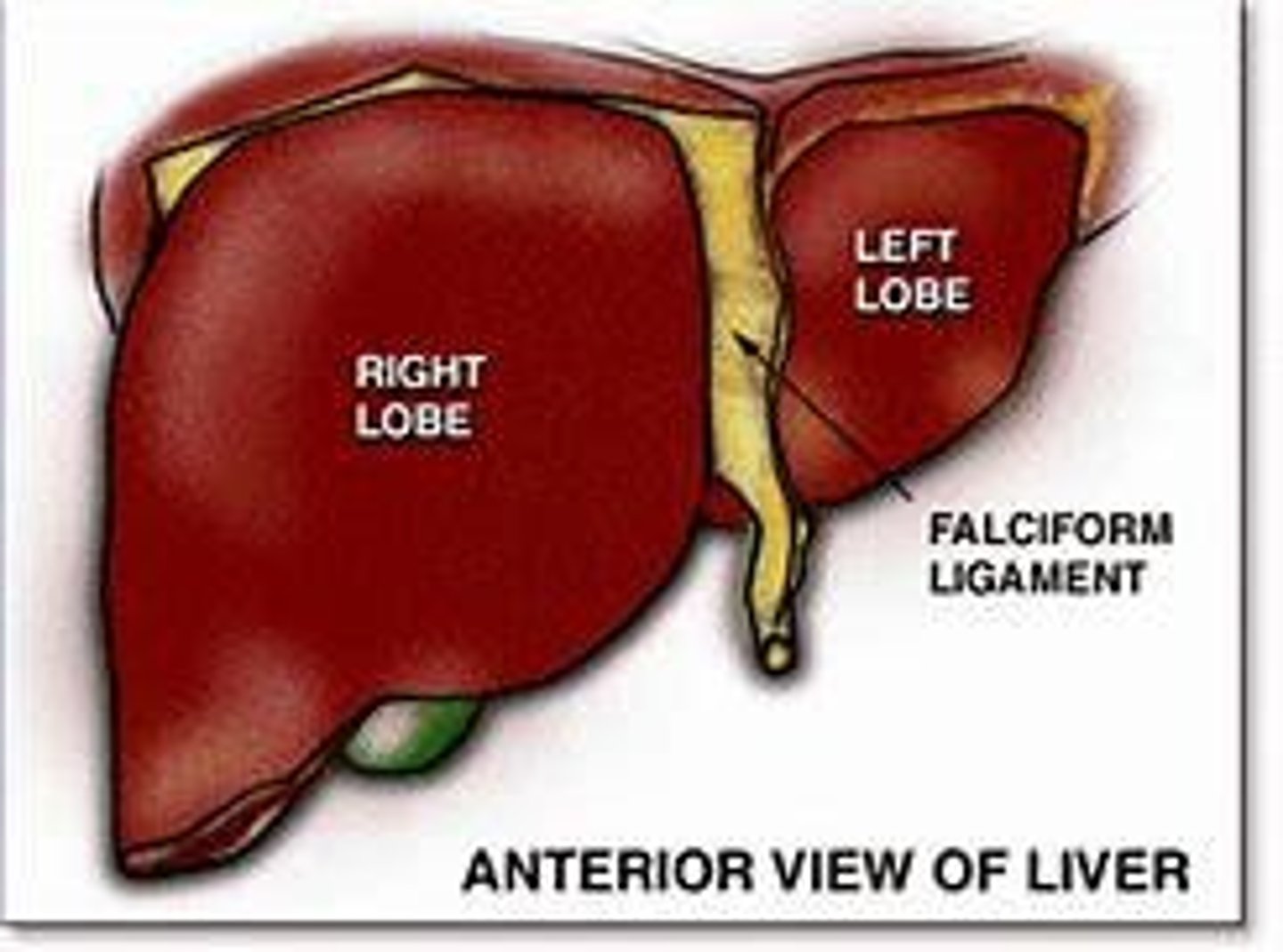
What is the function of the falciform ligament?
It attaches the liver to the front body wall and separates the anterior liver into left and right lobes.
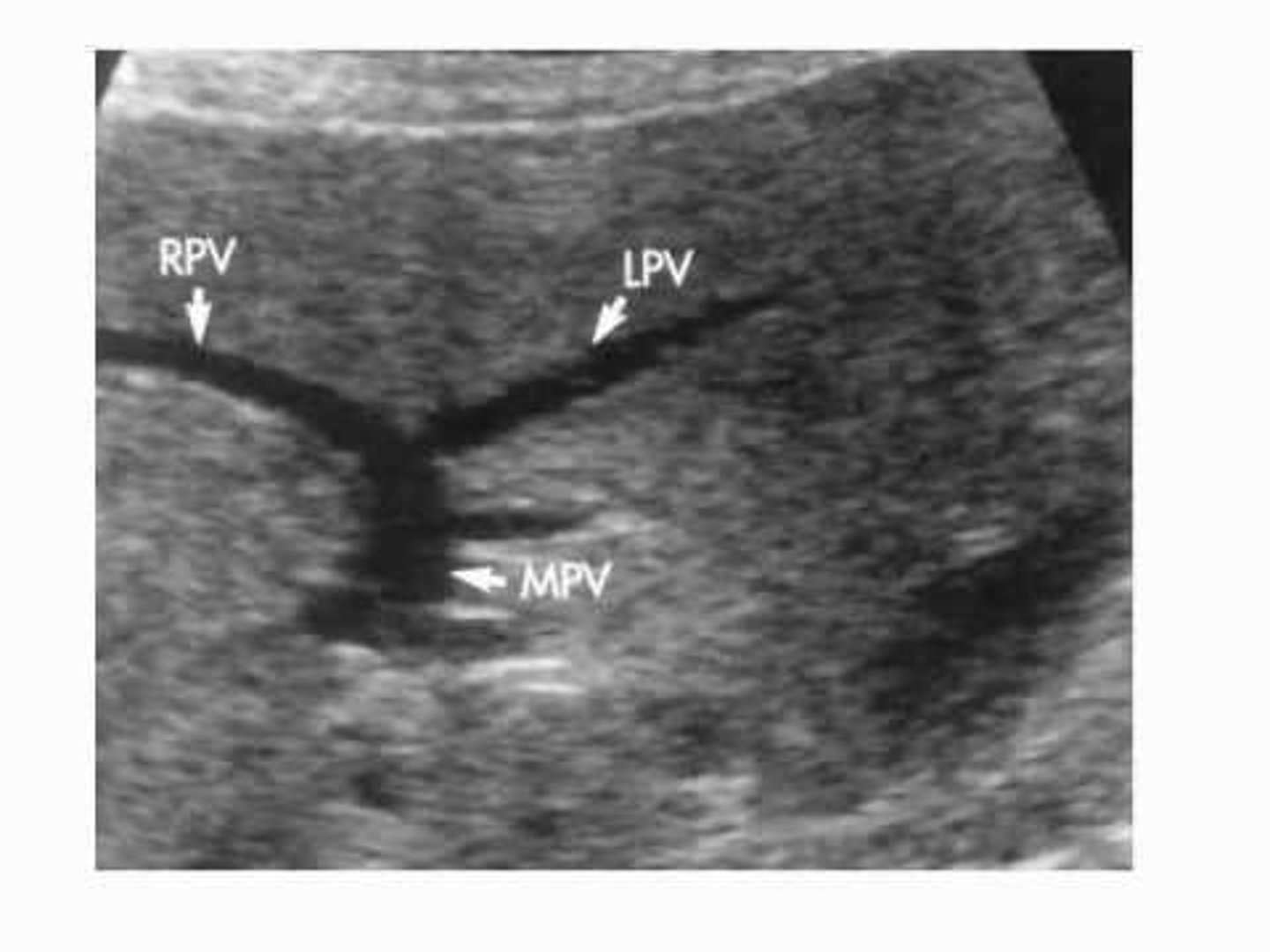
What is the main portal vein's significance?
It becomes larger at the portal hepatis and divides into the right and left portal veins.
What is the role of hepatic veins in liver function?
They drain blood from the liver to the IVC and become larger as they approach the diaphragm.
What is the clinical relevance of elevated lactic acid dehydrogenase?
It indicates tissue injury or death, with moderate increases seen in mono and mild increases in hepatitis.
What does the presence of gamma globulins indicate in chronic liver diseases?
elevated levels are commonly seen in chronic liver diseases.
What is the relationship between AFP levels and cancer diagnosis?
AFP levels can help diagnose liver cancer when used with other tests, but high levels do not always indicate cancer.
what is the largest organ in the abdominal cavity?
liver
what is the transverse measurement of the liver?
21-22 cm
what is the vertical measurement of the liver?
13-17.5cm
what is the depth of the liver?
10-12.5 cm
which lobe of the liver is the largest?
right lobe
why are ligaments and fissures more hyperechoic/echogenic?
collagen and fat surrounding structures
the right lobe is separated from the left lobe by the?
main lobar fissure
the left lobe is separated from the caudate lobe by the?
ligamentum vernosum
the caudate lobe drains into the
IVC
what is different about the caudate lobe
it has its own blood supply
what term means "reflects sound well"
echogenic
what connects the GB to the portal vein?
main lobar fissure
the mid hepatic vein sits within the?
main lobar fissure
what is the ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall, and separates the liver into left and right lobes?
falciform ligament
what ligament contains ligamentum teres?
falciform ligament
the ligamentum teres is also called the?
round ligament
the left umbilical vein turns into?
ligamentum teres
what ligament is a remanent of the ductus venosus?
ligamentum venosum
what ligament divides the left and caudate lobes?
ligamentum venosum
what artery and vein supplies the liver?
hepatic artery and portal vein
what drains from the intestines?
the portal vein
what carries blood from the aorta to the liver?
hepatic artery
the hepatic drains take blood from the ____ to the ____.
hepatic vein, IVC
which vessel looks like it has no wall?
hepatic veins
the right hepatic vein is the largest or smallest?
largest
the mid hepatic vein enters the IVC posteriorly or anteriorly?
anteriorly
True or False: the mid hepatic and left hepatic veins can join together?
true
the function of the liver is?
to form bile
bile is formed by?
hepatocytes
bile is held in the?
gallbladder
bile is made of?
water, bile pigments, and bile salts
what results from bile stasis?
sludge
what is alkaline phosphate produced by?
liver, bone, intestines, and placenta
prothrombin time is caused by?
the intake of vitamin k
a low serum albumin suggests?
decreased protein synthesis
what is the protein made in the liver of a developing baby?
AFP
healthy adults should have low or high levels of AFP?
low
a high AFP in an adult can be a sign of?
cancer in the liver, ovaries, or testicles
is it guaranteed that high AFP levels mean cancer as an adult?
no
A congenital variant that can sometimes be seen as an anterior projection of the liver and may extend inferiorly as far as the iliac crest?
Riedel's lobe
the liver is a major center of_______ which may be defined as the physical and chemical process whereby food stuffs are synthesized into complex elements.
metabolism
The accompanying loss of oncotic pressure in the vascular system allows fluid to migrate into the interstitial space, resulting in ____ in dependent areas
edema
Elevation of serum bilirubin results in __________ which is a yellow coloration of the skin, sclerae, and body secretions
jaundice
The landmarks of the liver include all except:
a. Right hypochondrium
b. Greater part of the epigastrium
c. Left hypochondrium
d. Right hypogastrium
right hypogastrium
hepatopetal means
towards the liver
heptaofugal means
away from the liver
hepatic venous flow is
hepatofugal (away from the liver)
generally, a wider pie sector or curved linear array transducer is the most appropriate to optimally image the ______ ______ of the abdomen.
near field
portal veins are _________ so they show up as the color ___ when CF is turned on
hepatopedal, red
portal vein walls are ________ compared to hepatic vein walls
hyperechoic
inspiration can move the liver _____
down
the liver is mostly found in the _____ ________
right hypochondrium
segment 1 is the
caudate lobe
how can you prove the patient has no gallbladder
including an image showing the main lobar fissure and the portal vein
why is it important to image the portal veins
they commonly clot
which are more superior hepatic or portal veins
hepatic
the liver converts sugars into _______ and then converts that into ______
glucose, glycogen
dietary fats are converted into ______ in the hepatocytes
lipoproteins
hepatocellular diseases are treated with
drugs
obstructive diseases are treated with
surgery
__________ bilirubin becomes __________ bilirubin
unconjugated, conjugated
why do we want the patient to be NPO for 6 hours
to see bile in the gallbladder
what is anterior to the caudate lobe?
ligamentum venosum
what is posterior to the caudate lobe
IVC
the liver is more _______ than the kidneys
hyperechoic
the liver is _________ compared to the spleen
hypoechoic
we use a ______ _____ array transducer to image the near field of the abdomen
curved linear
the liver is _________ compared to the spleen
hypoechoic
if a liver is small is the pathology more likely acute or chronic?
chronic
Sagittal protocol
Sagittal
1. Midline left lobe
2. Left lobe include caudate lobe and ligamentum venosum
3. Left Lobe /IVC/ Right Lobe
4. Right lobe include Main Lobar Fissure and Gallbladder
5. Right lobe to include diaphragm
6. Right lobe to include Right Kidney
transverse protocol
Transverse
7. Midline Left Lobe (possible caudate lobe and ligamentum venosum)
8. Right lobe include hepatic veins
9. Right lobe include hepatic veins with color
10. Right lobe include portal veins
11. Right lobe include portal veins with color
12. Right lobe to include portal vein and CBD (measure CBD)
13. Right lobe include right kidney and GB
14. Right lobe lateral edge with diaphragm
liver cells that play a role in the body’s defense
Kupffer cells
the vessel that serves as an intersegmental boundary between the medial and later left lobe
falsiform ligament
the boundaries of the bare area of the liver include
falsiform, coronary, and triangular ligament
Each of the following is a blood plasma protein or clotting factor except: Fibrinogen,
prothrombin, albumin, or arginine
arginine
The left portal vein serves as ________ between the medial and lateral left lobe
intersegmental boundary